operating-systems
Analysis of entire programs as a single unit, or whole-program analysis, involves propagation of large amounts of information through the control flow of the program. This is especially true for pointer analysis, where, unless significant compromises are made in the precision of the analysis, there is a combinatorial blowup of information. One of the key problems we observed in our own efforts to this end is that a lot of duplicate data was being propagated, and many low-level data structure operations were repeated a large number of times.
We present what we consider to be a novel and generic data structure, LatticeHashForest (LHF), to store and operate on such data in a manner that eliminates a majority of redundant computations and duplicate data in scenarios similar to those encountered in compilers and program optimization. LHF differs from similar work in this vein, such as hash-consing, ZDDs, and BDDs, by not only providing a way to efficiently operate on large, aggregate structures, but also modifying the elements of such structures in a manner that they can be deduplicated immediately. LHF also provides a way to perform a nested construction of elements such that they can be deduplicated at multiple levels, cutting down the need for additional, nested computations.
We provide a detailed structural description, along with an abstract model of this data structure. An entire C++ implementation of LHF is provided as an artifact along with evaluations of LHF using examples and benchmark programs. We also supply API documentation and a user manual for users to make independent applications of LHF. Our main use case in the realm of pointer analysis shows memory usage reduction to an almost negligible fraction, and speedups beyond 4x for input sizes approaching 10 million when compared to other implementations.
Deploying Mamba models on microcontrollers (MCUs) remains challenging due to limited memory, the lack of native operator support, and the absence of embedded-friendly toolchains. We present, to our knowledge, the first deployment of a Mamba-based neural architecture on a resource-constrained MCU, a fully C-based runtime-free inference engine: MambaLite-Micro. Our pipeline maps a trained PyTorch Mamba model to on-device execution by (1) exporting model weights into a lightweight format, and (2) implementing a handcrafted Mamba layer and supporting operators in C with operator fusion and memory layout optimization. MambaLite-Micro eliminates large intermediate tensors, reducing 83.0% peak memory, while maintaining an average numerical error of only 1.7x10-5 relative to the PyTorch Mamba implementation. When evaluated on keyword spotting(KWS) and human activity recognition (HAR) tasks, MambaLite-Micro achieved 100% consistency with the PyTorch baselines, fully preserving classification accuracy. We further validated portability by deploying on both ESP32S3 and STM32H7 microcontrollers, demonstrating consistent operation across heterogeneous embedded platforms and paving the way for bringing advanced sequence models like Mamba to real-world resource-constrained applications.
30 Sep 2025
Operating system schedulers suffer from a fundamental semantic gap, where kernel policies fail to understand application-specific needs, leading to suboptimal performance. We introduce SchedCP, the first framework that enables fully autonomous Large Language Model (LLM) agents to safely and efficiently optimize Linux schedulers without human involvement. Our core insight is that the challenge is not merely to apply a better LLM, but to architect a decoupled control plane that separates the AI's role of semantic reasoning ("what to optimize") from the system's role of execution ("how to observe and act"), thereby separating the optimization problem into two stages: goal-inference and policy-synthesis. Implemented as Model Context Protocol(MCP) server, SchedCP provides a stable interface with three key services: a Workload Analysis Engine, an evolving Scheduler Policy Repository, and an Execution Verifier that validates all AI-generated code and configure before deployment with static and dynamic analysis.
We demonstrate this architecture's power with sched-agent, a multi-agent system that autonomously analyzes workloads, synthesizes custom eBPF scheduling policies, and deploys them via the sched\_ext infrastructure. Our evaluation shows that SchedCP achieves up to an 1.79x performance improvement, and a 13x cost reduction compared to naive agentic approaches, all while maintaining high success rate. By bridging the semantic gap, SchedCP democratizes expert-level system optimization and represents a step towards creating truly self-optimizing, application-aware operating systems. The code is open-sourced in this https URL
19 Jun 2025
Researchers from the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) and GenseeAI, Inc. conducted the first in-depth study of temporal performance in computer-use agents. The study found that large language model (LLM) calls are the dominant source of latency, accounting for up to 94% of task time, and agents take significantly more steps than humans; to address this, the authors introduced OSWorld-Human, a new human-centric efficiency benchmark, and the Weighted Efficiency Score (WES) to evaluate agent efficiency.
CrashFixer introduces an automated agent for resolving Linux kernel crashes by emulating developer workflows with LLMs and leveraging enhanced tooling. The system resolves approximately 76.67% of crashes on a small context benchmark and significantly reduces kernel build times, demonstrating the value of integrating execution traces and iterative reasoning for low-level software repair.
The second version of Intel Software Guard Extensions (Intel SGX), or SGX2,
adds dynamic management of enclave memory and threads. The first version
required the address space and thread counts to be fixed before execution. The
Enclave Dynamic Memory Management (EDMM) feature of SGX2 has the potential to
lower launch times and overall execution time. Despite reducing the enclave
loading time by 28--93%, straightforward EDMM adoption strategies actually slow
execution time down by as much as 58%. Using the Gramine library OS as a
representative enclave runtime environment, this paper shows how to recover
EDMM performance. The paper explains how implementing mutual distrust between
the OS and enclave increases the cost of modifying page mappings. The paper
then describes and evaluates a series of optimizations on application
benchmarks, showing that these optimizations effectively eliminate the
overheads of EDMM while retaining EDMM's performance and flexibility gains.
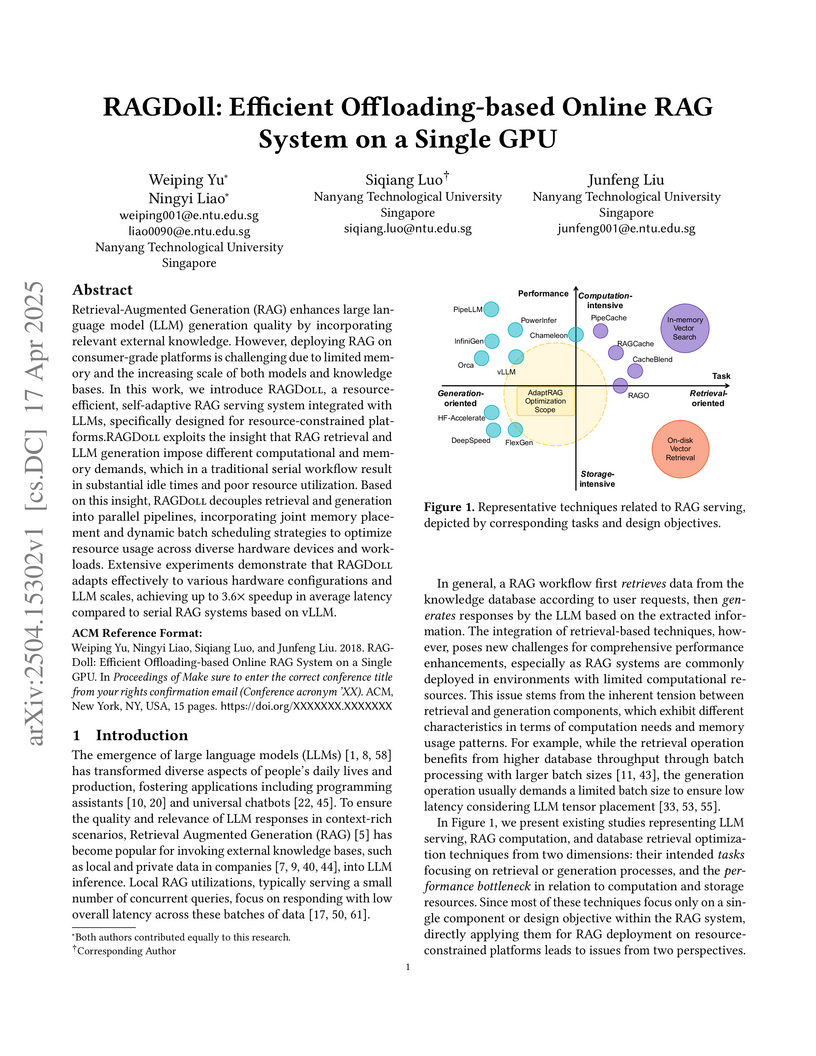
RAGDoll, developed by Nanyang Technological University, introduces an efficient offloading-based RAG system designed to operate on a single consumer-grade GPU. It optimizes the entire RAG pipeline through integrated memory management, parallel execution, and adaptive scheduling, reducing end-to-end latency and improving resource utilization.
The widespread adoption of LLMs has driven an exponential rise in their deployment, imposing substantial demands on inference clusters. These clusters must handle numerous concurrent queries for different LLM downstream tasks. To handle multi-task settings with vast LLM parameter counts, methods like Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) enable task-specific fine-tuning while sharing most of the base LLM model across tasks. Hence, they allow concurrent task serving with minimal memory requirements. However, existing LLM serving systems face inefficiencies: they overlook workload heterogeneity, impose high link bandwidth from frequent adapter loading, and suffer from head-of-line blocking in their schedulers. To address these challenges, we present Chameleon, a novel LLM serving system optimized for many adapter environments, that relies on two core ideas: adapter caching and adapter-aware scheduling. First, Chameleon caches popular adapters in GPU memory, minimizing the adapter loading times. Importantly, it uses the otherwise idle GPU memory, avoiding extra memory costs. Second, Chameleon uses a non-preemptive multi-queue scheduling to efficiently account for workload heterogeneity. In this way, Chameleon simultaneously prevents head of line blocking and starvation. We implement Chameleon on top of a state-of-the-art LLM serving platform and evaluate it with real-world production traces and open-source LLMs. Under high loads, Chameleon reduces P99 and P50 TTFT latency by 80.7% and 48.1%, respectively, while improving throughput by 1.5x compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
The performance of storage hardware has improved vastly recently, leaving the traditional I/O stack incapable of exploiting these gains due to increasingly large relative overheads. Newer asynchronous I/O APIs, such as io_uring, have significantly improved performance by reducing such overheads, but exhibit limited adoption in practice. In this paper, we discuss the complexities that the usage of these contemporary I/O APIs introduces to applications, which we believe are mostly responsible for their low adoption rate. Finally, we share implications and trade offs made by architectures that may be used to integrate asynchronous I/O into DB applications.
25 Sep 2024
Approximate nearest neighbor search (ANNS) has emerged as a crucial component of database and AI infrastructure. Ever-increasing vector datasets pose significant challenges in terms of performance, cost, and accuracy for ANNS services. None of modern ANNS systems can address these issues simultaneously. We present FusionANNS, a high-throughput, low-latency, cost-efficient, and high-accuracy ANNS system for billion-scale datasets using SSDs and only one entry-level GPU. The key idea of FusionANNS lies in CPU/GPU collaborative filtering and re-ranking mechanisms, which significantly reduce I/O operations across CPUs, GPU, and SSDs to break through the I/O performance bottleneck. Specifically, we propose three novel designs: (1) multi-tiered indexing to avoid data swapping between CPUs and GPU, (2) heuristic re-ranking to eliminate unnecessary I/Os and computations while guaranteeing high accuracy, and (3) redundant-aware I/O deduplication to further improve I/O efficiency. We implement FusionANNS and compare it with the state-of-the-art SSD-based ANNS system -- SPANN and GPU-accelerated in-memory ANNS system -- RUMMY. Experimental results show that FusionANNS achieves 1) 9.4-13.1X higher query per second (QPS) and 5.7-8.8X higher cost efficiency compared with SPANN; 2) and 2-4.9X higher QPS and 2.3-6.8X higher cost efficiency compared with RUMMY, while guaranteeing low latency and high accuracy.
vAttention introduces a dynamic memory management system for serving Large Language Models that eliminates KV cache fragmentation while maintaining virtual memory contiguity. This approach, leveraging CUDA virtual memory management (VMM) APIs, achieves up to 1.36x higher prefill throughput, up to 42% lower online inference latency, and enables out-of-the-box support for new, optimized attention kernels like FlashAttention-3.
The management of modern IT systems poses unique challenges, necessitating scalability, reliability, and efficiency in handling extensive data streams. Traditional methods, reliant on manual tasks and rule-based approaches, prove inefficient for the substantial data volumes and alerts generated by IT systems. Artificial Intelligence for Operating Systems (AIOps) has emerged as a solution, leveraging advanced analytics like machine learning and big data to enhance incident management. AIOps detects and predicts incidents, identifies root causes, and automates healing actions, improving quality and reducing operational costs. However, despite its potential, the AIOps domain is still in its early stages, decentralized across multiple sectors, and lacking standardized conventions. Research and industrial contributions are distributed without consistent frameworks for data management, target problems, implementation details, requirements, and capabilities. This study proposes an AIOps terminology and taxonomy, establishing a structured incident management procedure and providing guidelines for constructing an AIOps framework. The research also categorizes contributions based on criteria such as incident management tasks, application areas, data sources, and technical approaches. The goal is to provide a comprehensive review of technical and research aspects in AIOps for incident management, aiming to structure knowledge, identify gaps, and establish a foundation for future developments in the field.
AIOS, developed by Rutgers University, introduces an operating system-like architecture for managing LLM agents, enhancing resource allocation, concurrency, and security. The system achieves up to a 2.1x increase in throughput and exhibits linear scalability for concurrent agent tasks while maintaining or improving agent performance.
The POSIX shell is a widely deployed, powerful tool for managing computer
systems. The shell is the expert's control panel, a necessary tool for
configuring, compiling, installing, maintaining, and deploying systems. Even
though it is powerful, critical infrastructure, the POSIX shell is maligned and
misunderstood. Its power and its subtlety are a dangerous combination.
We define a formal, mechanized, executable small-step semantics for the POSIX
shell, which we call Smoosh. We compared Smoosh against seven other shells that
aim for some measure of POSIX compliance (bash, dash, zsh, OSH, mksh, ksh93,
and yash). Using three test suites---the POSIX test suite, the Modernish test
suite and shell diagnosis, and a test suite of our own device---we found
Smoosh's semantics to be the most conformant to the POSIX standard. Modernish
judges Smoosh to have the fewest bugs (just one, from using dash's parser) and
no quirks. To show that our semantics is useful beyond yielding a conformant,
executable shell, we also implemented a symbolic stepper to illuminate the
subtle behavior of the shell.
Smoosh will serve as a foundation for formal study of the POSIX shell,
supporting research on and development of new shells, new tooling for shells,
and new shell designs.
It is common today to deploy complex software inside a virtual machine (VM).
Snapshots provide rapid deployment, migration between hosts, dependability
(fault tolerance), and security (insulating a guest VM from the host). Yet, for
each virtual machine, the code for snapshots is laboriously developed on a
per-VM basis. This work demonstrates a generic checkpoint-restart mechanism for
virtual machines. The mechanism is based on a plugin on top of an unmodified
user-space checkpoint-restart package, DMTCP. Checkpoint-restart is
demonstrated for three virtual machines: Lguest, user-space QEMU, and KVM/QEMU.
The plugins for Lguest and KVM/QEMU require just 200 lines of code. The Lguest
kernel driver API is augmented by 40 lines of code. DMTCP checkpoints
user-space QEMU without any new code. KVM/QEMU, user-space QEMU, and DMTCP need
no modification. The design benefits from other DMTCP features and plugins.
Experiments demonstrate checkpoint and restart in 0.2 seconds using forked
checkpointing, mmap-based fast-restart, and incremental Btrfs-based snapshots.
We present, MultiK, a Linux-based framework 1 that reduces the attack surface for operating system kernels by reducing code bloat. MultiK "orchestrates" multiple kernels that are specialized for individual applications in a transparent manner. This framework is flexible to accommodate different kernel code reduction techniques and, most importantly, run the specialized kernels with near-zero additional runtime overheads. MultiK avoids the overheads of virtualization and runs natively on the system. For instance, an Apache instance is shown to run on a kernel that has (a) 93.68% of its code reduced, (b) 19 of 23 known kernel vulnerabilities eliminated and (c) with negligible performance overheads (0.19%). MultiK is a framework that can integrate with existing code reduction and OS security techniques. We demonstrate this by using D-KUT and S-KUT -- two methods to profile and eliminate unwanted kernel code. The whole process is transparent to the user applications because MultiK does not require a recompilation of the application.
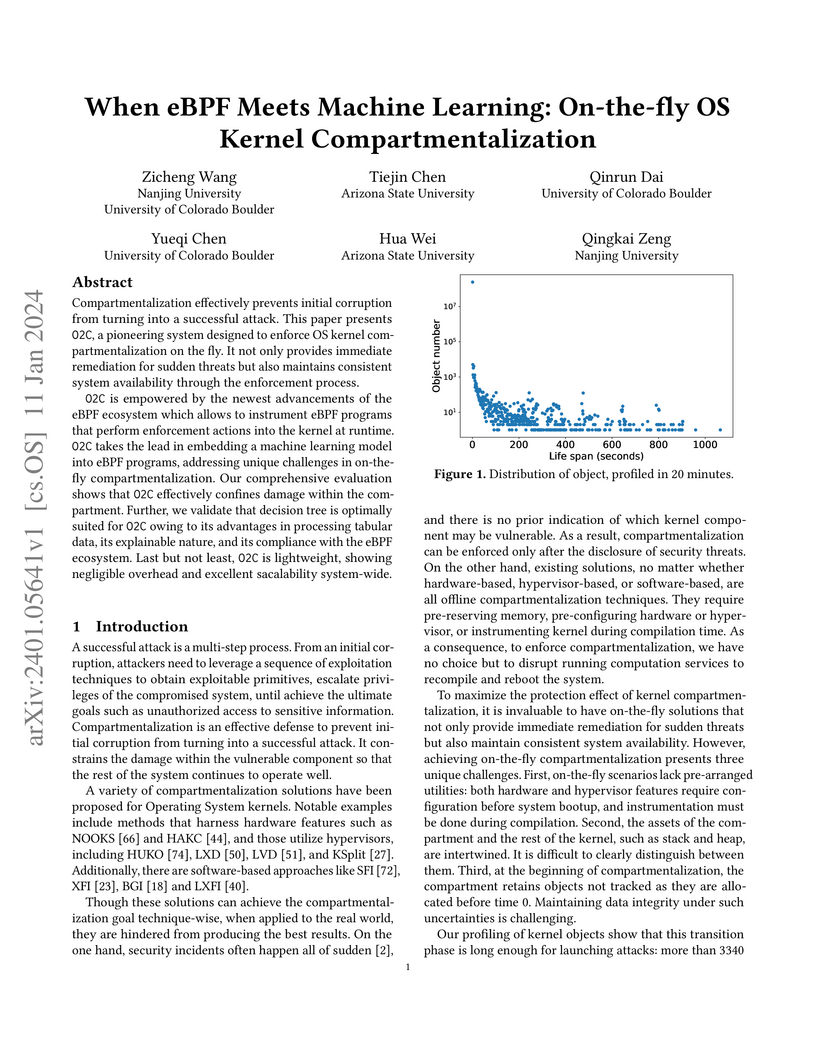
Compartmentalization effectively prevents initial corruption from turning
into a successful attack. This paper presents O2C, a pioneering system designed
to enforce OS kernel compartmentalization on the fly. It not only provides
immediate remediation for sudden threats but also maintains consistent system
availability through the enforcement process.
O2C is empowered by the newest advancements of the eBPF ecosystem which
allows to instrument eBPF programs that perform enforcement actions into the
kernel at runtime. O2C takes the lead in embedding a machine learning model
into eBPF programs, addressing unique challenges in on-the-fly
compartmentalization. Our comprehensive evaluation shows that O2C effectively
confines damage within the compartment. Further, we validate that decision tree
is optimally suited for O2C owing to its advantages in processing tabular data,
its explainable nature, and its compliance with the eBPF ecosystem. Last but
not least, O2C is lightweight, showing negligible overhead and excellent
sacalability system-wide.
Fuzzing network servers is a technical challenge, since the behavior of the
target server depends on its state over a sequence of multiple messages.
Existing solutions are costly and difficult to use, as they rely on
manually-customized artifacts such as protocol models, protocol parsers, and
learning frameworks. The aim of this work is to develop a greybox fuzzer
(StateaAFL) for network servers that only relies on lightweight analysis of the
target program, with no manual customization, in a similar way to what the AFL
fuzzer achieved for stateless programs. The proposed fuzzer instruments the
target server at compile-time, to insert probes on memory allocations and
network I/O operations. At run-time, it infers the current protocol state of
the target server by taking snapshots of long-lived memory areas, and by
applying a fuzzy hashing algorithm (Locality-Sensitive Hashing) to map memory
contents to a unique state identifier. The fuzzer incrementally builds a
protocol state machine for guiding fuzzing.
We implemented and released StateaAFL as open-source software. As a basis for
reproducible experimentation, we integrated StateaAFL with a large set of
network servers for popular protocols, with no manual customization to
accomodate for the protocol. The experimental results show that the fuzzer can
be applied with no manual customization on a large set of network servers for
popular protocols, and that it can achieve comparable, or even better code
coverage and bug detection than customized fuzzing. Moreover, our qualitative
analysis shows that states inferred from memory better reflect the server
behavior than only using response codes from messages.
This paper envisions a revolutionary computing paradigm where a Large Language Model functions as an Artificial Intelligent Operating System (AIOS), upon which diverse LLM-based AI Agent Applications are built. It formalizes this concept by systematically mapping traditional operating system components to LLM capabilities and outlines a future ecosystem where natural language serves as the primary programming interface.
Trusted execution environments (TEEs) are being used in all the devices from
embedded sensors to cloud servers and encompass a range of cost, power
constraints, and security threat model choices. On the other hand, each of the
current vendor-specific TEEs makes a fixed set of trade-offs with little room
for customization. We present Keystone -- the first open-source framework for
building customized TEEs. Keystone uses simple abstractions provided by the
hardware such as memory isolation and a programmable layer underneath untrusted
components (e.g., OS). We build reusable TEE core primitives from these
abstractions while allowing platform-specific modifications and application
features. We showcase how Keystone-based TEEs run on unmodified RISC-V hardware
and demonstrate the strengths of our design in terms of security, TCB size,
execution of a range of benchmarks, applications, kernels, and deployment
models.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.