KUNGFU.AI
We propose a novel class of language models, Latent Thought Models (LTMs),
which incorporate explicit latent thought vectors that follow an explicit prior
model in latent space. These latent thought vectors guide the autoregressive
generation of ground tokens through a Transformer decoder. Training employs a
dual-rate optimization process within the classical variational Bayes
framework: fast learning of local variational parameters for the posterior
distribution of latent vectors (inference-time computation), and slow learning
of global decoder parameters. Empirical studies reveal that LTMs possess
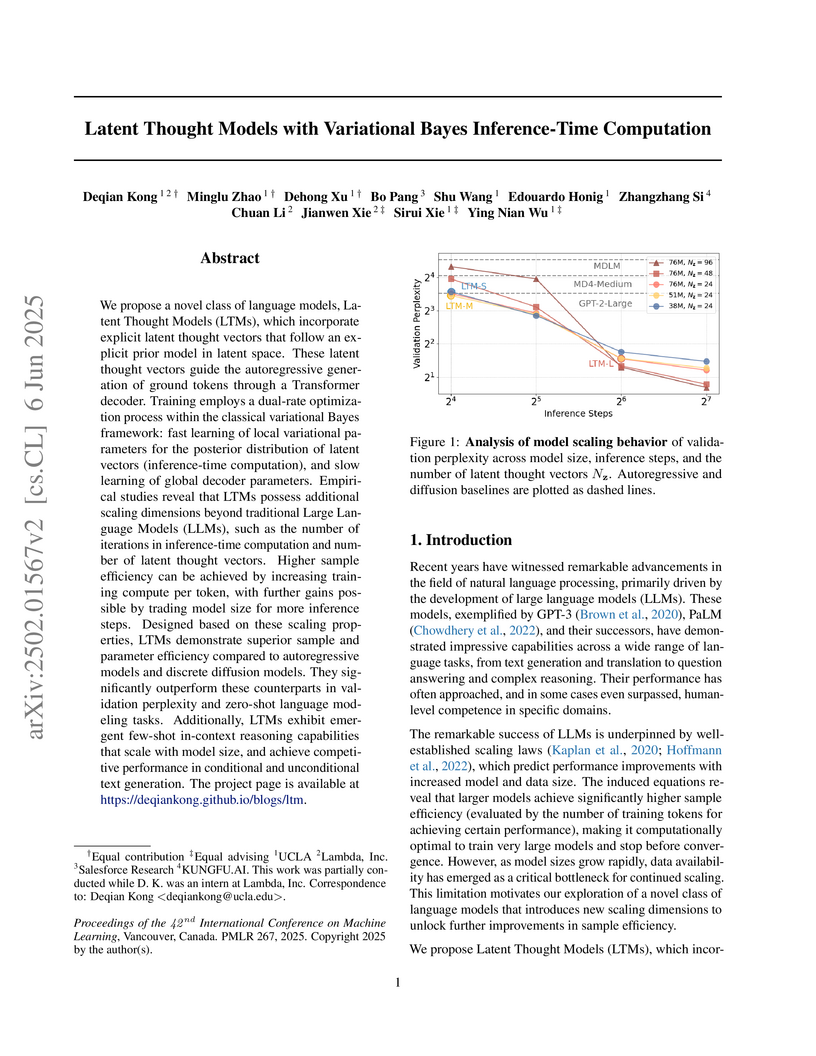
additional scaling dimensions beyond traditional Large Language Models (LLMs),
such as the number of iterations in inference-time computation and number of
latent thought vectors. Higher sample efficiency can be achieved by increasing
training compute per token, with further gains possible by trading model size
for more inference steps. Designed based on these scaling properties, LTMs
demonstrate superior sample and parameter efficiency compared to autoregressive
models and discrete diffusion models. They significantly outperform these
counterparts in validation perplexity and zero-shot language modeling tasks.
Additionally, LTMs exhibit emergent few-shot in-context reasoning capabilities
that scale with model size, and achieve competitive performance in conditional
and unconditional text generation.
04 Dec 2025
Active learning (AL) accelerates scientific discovery by prioritizing the most informative experiments, but traditional machine learning (ML) models used in AL suffer from cold-start limitations and domain-specific feature engineering, restricting their generalizability. Large language models (LLMs) offer a new paradigm by leveraging their pretrained knowledge and universal token-based representations to propose experiments directly from text-based descriptions. Here, we introduce an LLM-based active learning framework (LLM-AL) that operates in an iterative few-shot setting and benchmark it against conventional ML models across four diverse materials science datasets. We explored two prompting strategies: one using concise numerical inputs suited for datasets with more compositional and structured features, and another using expanded descriptive text suited for datasets with more experimental and procedural features to provide additional context. Across all datasets, LLM-AL could reduce the number of experiments needed to reach top-performing candidates by over 70% and consistently outperformed traditional ML models. We found that LLM-AL performs broader and more exploratory searches while still reaching the optima with fewer iterations. We further examined the stability boundaries of LLM-AL given the inherent non-determinism of LLMs and found its performance to be broadly consistent across runs, within the variability range typically observed for traditional ML approaches. These results demonstrate that LLM-AL can serve as a generalizable alternative to conventional AL pipelines for more efficient and interpretable experiment selection and potential LLM-driven autonomous discovery.
29 Nov 2023
The adaptive fitness of an organism in its ecological niche is highly reliant upon its ability to associate an environmental or internal stimulus with a behavior response through reinforcement. This simple but powerful observation has been successfully applied in a number of contexts within computational neuroscience and reinforcement learning to model both human and animal behaviors. However, a critical challenge faced by these models is the credit assignment problem which asks how past behavior comes to be associated with a delayed reinforcement signal. In this paper we reformulate the credit assignment problem to ask how past stimuli come to be linked to adaptive behavioral responses in the context of a simple neuronal circuit. We propose a biologically plausible variant of a spiking neural network which can model a wide variety of behavioral, learning, and evolutionary phenomena. Our model suggests one fundamental mechanism, potentially in use in the brains of both simple and complex organisms, that would allow it to associate a behavior with an adaptive response. We present results that showcase the model's versatility and biological plausibility in a number of tasks related to classical and operant conditioning including behavioral chaining. We then provide further simulations to demonstrate how adaptive behaviors such as reflexes and simple category detection may have evolved using our model. Our results indicate the potential for further modifications and extensions of our model to replicate more sophisticated and biologically plausible behavioral, learning, and intelligence phenomena found throughout the animal kingdom.
Federated learning is becoming increasingly relevant and popular as we
witness a surge in data collection and storage of personally identifiable
information. Alongside these developments there have been many proposals from
governments around the world to provide more protections for individuals' data
and a heightened interest in data privacy measures. As deep learning continues
to become more relevant in new and existing domains, it is vital to develop
strategies like federated learning that can effectively train data from
different sources, such as edge devices, without compromising security and
privacy. Recently, the Flower (\texttt{Flwr}) Python package was introduced to
provide a scalable, flexible, and easy-to-use framework for implementing
federated learning. However, to date, Flower is only able to run synchronous
federated learning which can be costly and time-consuming to run because the
process is bottlenecked by client-side training jobs that are slow or fragile.
Here, we introduce \texttt{flwr-serverless}, a wrapper around the Flower
package that extends its functionality to allow for both synchronous and
asynchronous federated learning with minimal modification to Flower's design
paradigm. Furthermore, our approach to federated learning allows the process to
run without a central server, which increases the domains of application and
accessibility of its use. This paper presents the design details and usage of
this approach through a series of experiments that were conducted using public
datasets. Overall, we believe that our approach decreases the time and cost to
run federated training and provides an easier way to implement and experiment
with federated learning systems.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.