Ask or search anything...
PromptHMR introduces a promptable transformer-based architecture for 3D Human Pose and Shape (HPS) estimation that integrates diverse spatial and semantic side information. It achieves state-of-the-art accuracy in recovering detailed 3D human models in challenging crowded and interacting scenes, and its video extension produces world-grounded human motion with reduced foot skating.
View blogResearchers at MPI-IS and Meshcapade developed CameraHMR, which establishes a new state-of-the-art in 3D human pose and shape estimation by integrating accurate camera intrinsic predictions and generating high-fidelity pseudo ground truth data. This approach yields more realistic 3D human reconstructions and superior 2D alignment across various challenging benchmarks.
View blogThis paper presents ChatPose, a framework that enables Large Language Models to understand, reason about, and directly generate 3D human poses represented by SMPL parameters from both visual and textual inputs. The model demonstrates superior performance in novel speculative pose generation and reasoning-based pose estimation tasks, leveraging the LLM's world knowledge to infer poses from implicit cues and identify specific individuals within complex scenes.
View blogA framework combines optimization-based fitting with dense contact modeling to reconstruct 3D human-object interactions from single images, introducing a dataset of 4,123 images with 3D contact annotations across 44 object categories and demonstrating improved generalization to unconstrained scenarios compared to existing approaches.
View blogA method from Meshcapade and Max Planck Institute generates detailed 3D hair geometry from single images using diffusion models and a novel synthetic dataset of 40,000 hairstyles, enabling accurate reconstruction of diverse styles including afros and balding patterns while maintaining real-time rendering capabilities in game engines.
View blogResearchers at Meshcapade and the Max Planck Institute developed PRIMAL, a generative motor system that enables 3D avatars to produce perpetual, realistic, and responsive motions in real-time. This model outperforms existing baselines in motion realism and responsiveness, adapting efficiently to new tasks with limited data and demonstrating effective real-time control in interactive environments.
View blogTokenHMR introduces a novel framework for 3D human pose and shape estimation that resolves the inverse relationship between 2D keypoint accuracy and 3D pose fidelity. It achieves this by combining a threshold-adaptive loss scaling mechanism and a discrete tokenized pose representation, leading to state-of-the-art 3D accuracy and enhanced robustness in unconstrained environments.
View blogThe SmallGS framework addresses camera pose estimation in small-baseline videos containing dynamic objects by combining 3D Gaussian Splatting with robust DINOv2 features and batch-based optimization. This approach achieved lower Absolute Trajectory Error and Relative Pose Error on the TUM-Dynamics dataset compared to methods like MonST3R and DROID-SLAM, producing smoother and more accurate camera trajectories.
View blog ETH Zürich
ETH Zürich University of Pennsylvania
University of Pennsylvania

 Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University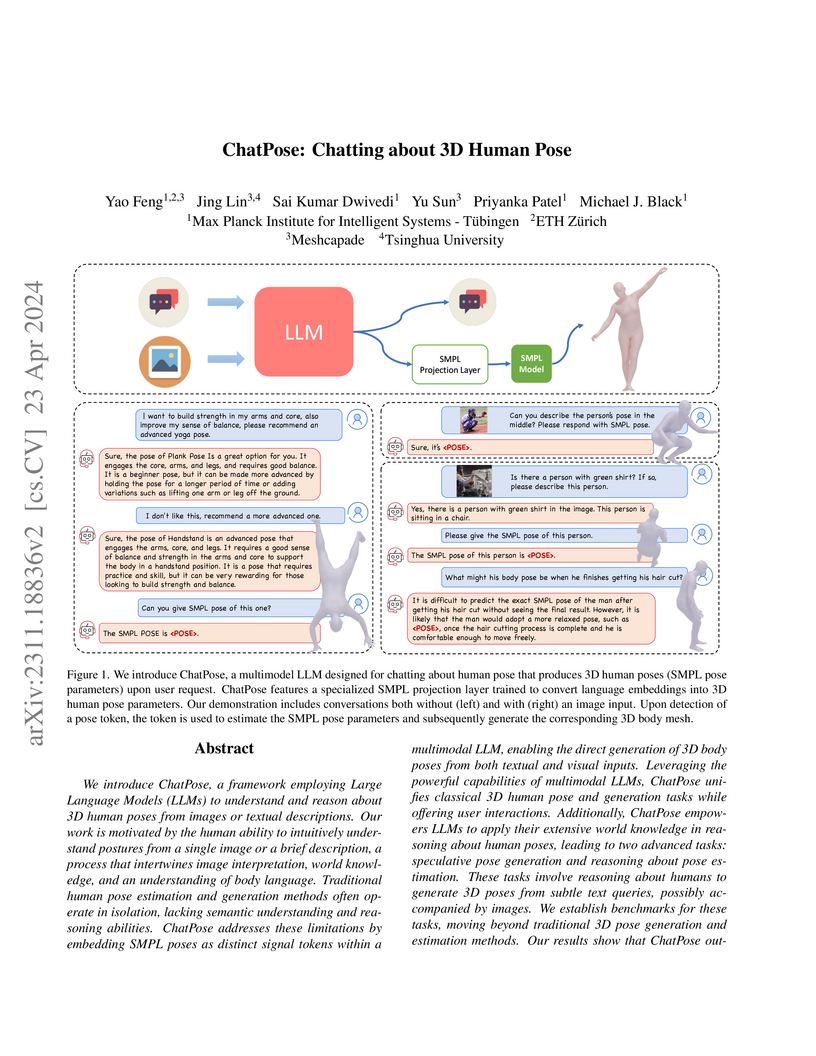
 University of Amsterdam
University of Amsterdam
 Stanford University
Stanford University


 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich
 University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge
 Beijing Normal University
Beijing Normal University


 NVIDIA
NVIDIA