MiLM Plus
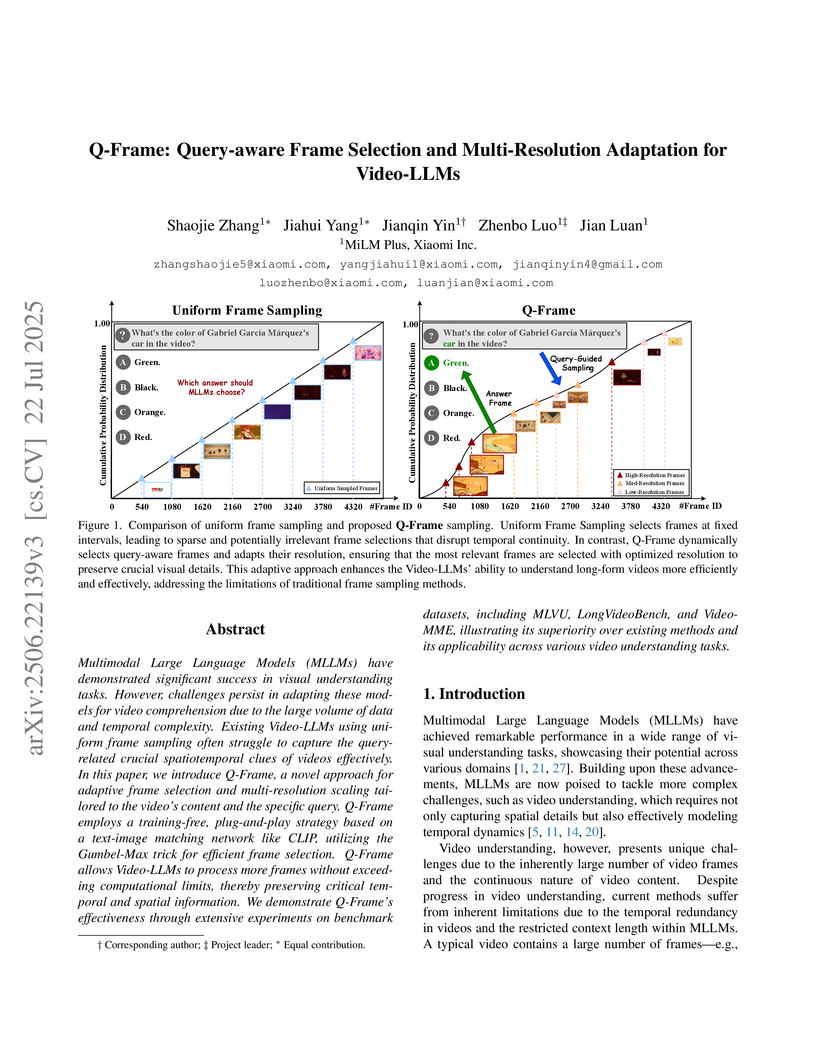
Researchers at MiLM Plus, Xiaomi Inc. developed Q-Frame, a training-free framework that significantly improves video understanding in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by dynamically selecting query-relevant frames and adapting their resolutions. It achieves consistent performance gains across various Video-LLMs and benchmark datasets, notably enhancing processing of long-form videos.
This research from Xiaomi Inc. and Central Conservatory of Music introduces ACMID, an automated pipeline for curating a large-scale, high-granularity musical instrument dataset (737.35 hours) from noisy web audio. The cleaned dataset significantly improves state-of-the-art music source separation (MSS) models, achieving a 1.16 dB SDR gain when combined with existing high-quality datasets.
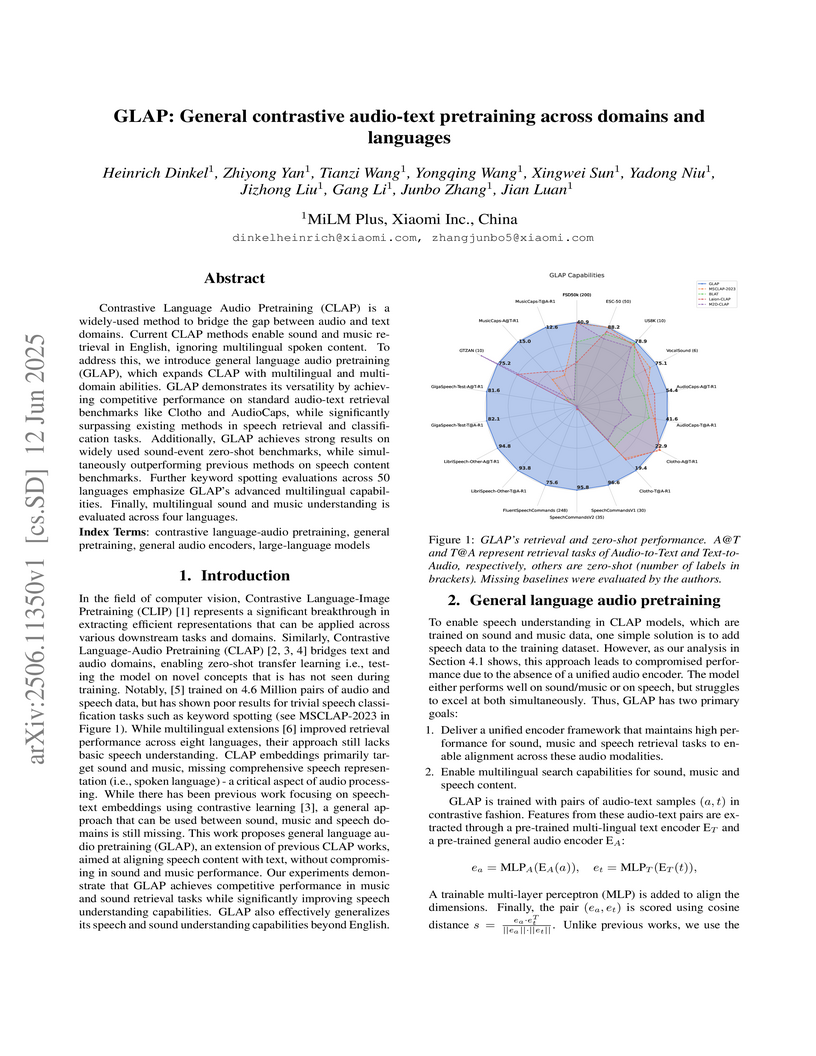
GLAP, developed by Xiaomi Inc., introduces a unified audio-language model capable of understanding speech, music, and environmental sounds across multiple languages. This approach achieves high performance in audio-text retrieval and zero-shot classification tasks for all three domains, significantly improving speech understanding over previous CLAP models while supporting 145 languages.
While large audio-language models have advanced open-ended audio understanding, they still fall short of nuanced human-level comprehension. This gap persists largely because current benchmarks, limited by data annotations and evaluation metrics, fail to reliably distinguish between generic and highly detailed model outputs. To this end, this work introduces MECAT, a Multi-Expert Constructed Benchmark for Fine-Grained Audio Understanding Tasks. Generated via a pipeline that integrates analysis from specialized expert models with Chain-of-Thought large language model reasoning, MECAT provides multi-perspective, fine-grained captions and open-set question-answering pairs. The benchmark is complemented by a novel metric: DATE (Discriminative-Enhanced Audio Text Evaluation). This metric penalizes generic terms and rewards detailed descriptions by combining single-sample semantic similarity with cross-sample discriminability. A comprehensive evaluation of state-of-the-art audio models is also presented, providing new insights into their current capabilities and limitations. The data and code are available at this https URL
Pedestrian detection models in autonomous driving systems often lack robustness due to insufficient representation of dangerous pedestrian scenarios in training datasets. To address this limitation, we present a novel framework for controllable pedestrian video editing in multi-view driving scenarios by integrating video inpainting and human motion control techniques. Our approach begins by identifying pedestrian regions of interest across multiple camera views, expanding detection bounding boxes with a fixed ratio, and resizing and stitching these regions into a unified canvas while preserving cross-view spatial relationships. A binary mask is then applied to designate the editable area, within which pedestrian editing is guided by pose sequence control conditions. This enables flexible editing functionalities, including pedestrian insertion, replacement, and removal. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework achieves high-quality pedestrian editing with strong visual realism, spatiotemporal coherence, and cross-view consistency. These results establish the proposed method as a robust and versatile solution for multi-view pedestrian video generation, with broad potential for applications in data augmentation and scenario simulation in autonomous driving.
Video dubbing aims to generate high-fidelity speech that is precisely temporally aligned with the visual content. Existing methods still suffer from limitations in speech naturalness and audio-visual synchronization, and are limited to monolingual settings. To address these challenges, we propose SyncVoice, a vision-augmented video dubbing framework built upon a pretrained text-to-speech (TTS) model. By fine-tuning the TTS model on audio-visual data, we achieve strong audiovisual consistency. We propose a Dual Speaker Encoder to effectively mitigate inter-language interference in cross-lingual speech synthesis and explore the application of video dubbing in video translation scenarios. Experimental results show that SyncVoice achieves high-fidelity speech generation with strong synchronization performance, demonstrating its potential in video dubbing tasks.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.