Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University
Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University and independent scholars demonstrated a method for applying the Self-Optimization (SO) model, based on Hopfield networks, to propositional satisfiability (SAT) problems by converting logical formulas into network weights. The study revealed that Hebbian learning can significantly alter the network's energy landscape, occasionally leading to a "loss of critical information" where easily fixable constraint violations become stable states.
04 Apr 2024
Shortcuts to adiabaticity (STA) are powerful tools that can be used to control quantum systems with high fidelity. They work particularly well for single particle and non-interacting systems which can be described exactly and which possess invariant or self-similar dynamics. However, finding an exact STA for strongly correlated many-body systems can be difficult, as their complex dynamics may not be easily described, especially for larger systems that do not possess self-similar solutions. Here, we design STAs for one-dimensional bosonic gas in the Tonks--Girardeau limit by using a mean-field approach that succinctly captures the strong interaction effects through a quintic nonlinear term in the Schrödinger equation. We show that for the case of the harmonic oscillator with a time-dependent trap frequency the mean-field approach works exactly and recovers the well-known STA from literature. To highlight the robustness of our approach we also show that it works effectively for anharmonic potentials, achieving higher fidelities than other typical control techniques.
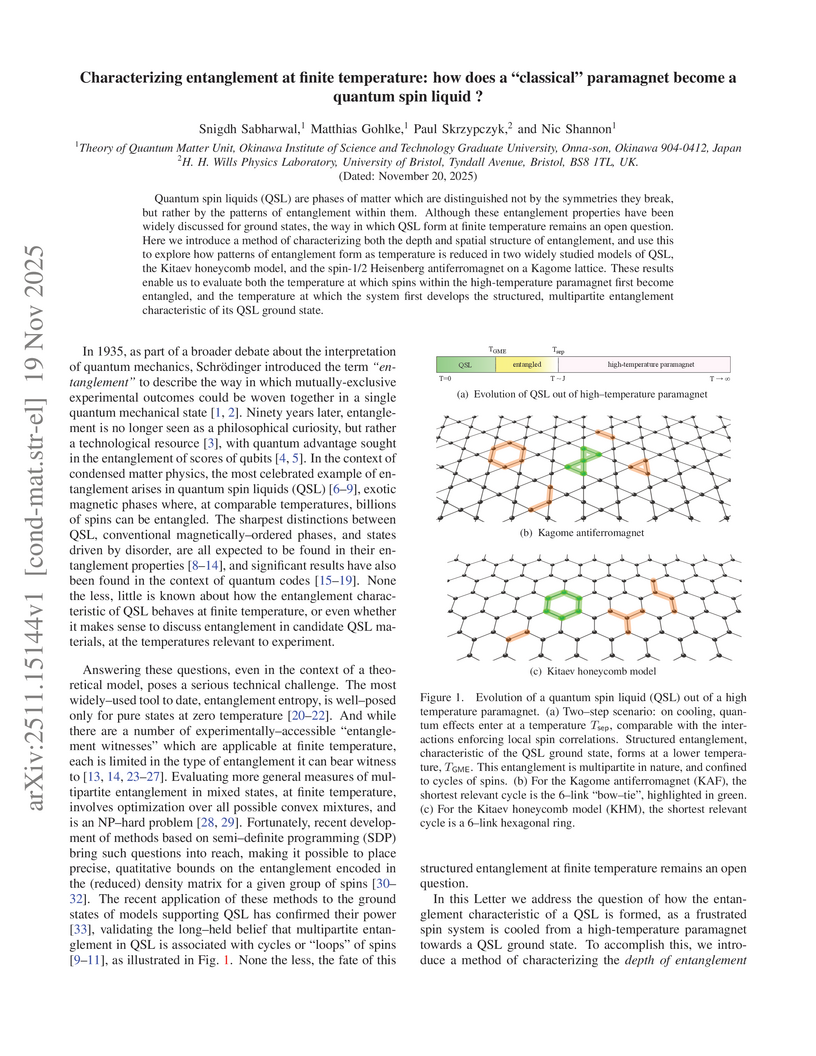
Researchers from OIST and the University of Bristol developed a quantum information-based method using semidefinite programming to quantify entanglement depth and spatial structure in quantum spin liquids at finite temperatures. Applied to the Kagome and Kitaev models, this approach identifies distinct temperature scales for the onset of bipartite and genuine multipartite entanglement, correlating these with specific thermodynamic features.
This work develops a relational holographic framework and proposes a novel measure of spread complexity for Bogomol’nyi–Prasad–Sommerfield (BPS) states within the N=2 Double-Scaled Sachdev–Ye–Kitaev (DSSYK) model. It demonstrates that a BPS spread complexity, driven by R-charge, exactly reproduces the total chord number in the boundary theory and matches BPS wormhole lengths in N=2 JT supergravity at the semiclassical limit.
07 Oct 2025
This research models the peculiar Type Ic supernova SN2022jli, demonstrating that a supernova-induced binary interaction, where a newly formed neutron star orbits within the inflated envelope of a companion star, can explain its sustained ~12.5-day periodic undulations and luminosity range of 10^42 – 10^43 erg s^-1. The study highlights the critical role of bipolar kinetic feedback from super-Eddington accretion and a high orbital eccentricity (0.8 "," e "," 0.9) to match observations.
15 Oct 2025
In this paper, we revisit the investigation of solitary-wave interactions in the nonlinear Schrödinger model, both in the presence and absence of a parabolic trapping potential. While approximate dynamics, based on variational or similar methods, governed by a system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) for both bright and dark-soliton interactions have been well established in the literature based on physical expert considerations, this study focuses on a data-driven approach, the so-called Sparse Identification of Nonlinear Dynamics (SINDy). Accordingly, our purpose is to use PDE time-series of select waveform diag- nostics in order to numerically reconstruct such approximate dynamics, without prior knowledge thereof. The purpose is not only to verify the robustness of the dynamical approximated ODEs, but also to shed light on the application of such a data-driven methodology in the study of soliton interactions and to formu- late a complementary approach, more reliant on the wealth of PDE data and less so on expert theoretical constructs.
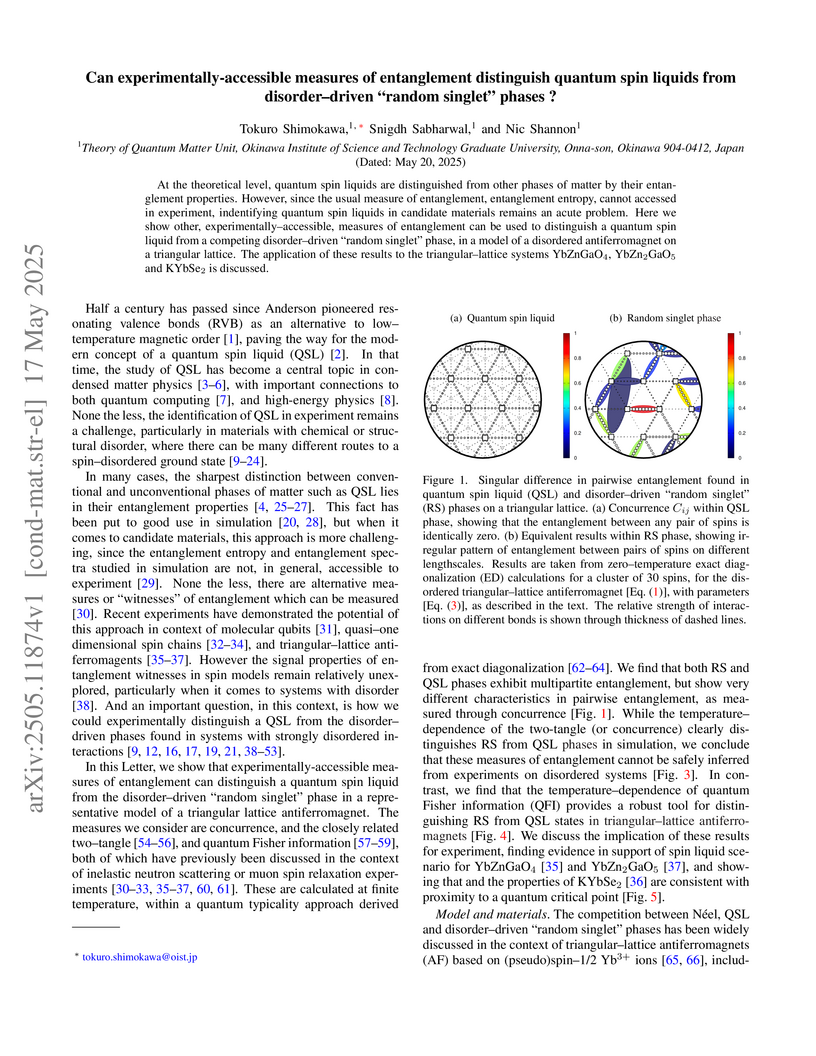
Researchers at OIST investigated how disorder impacts quantum entanglement in spin systems, providing methods to distinguish between clean Tomonaga-Luttinger liquids and disordered random singlet phases. The work identifies that the order of disorder-averaging critically affects concurrence measurements and proposes specific experimental diagnostics, such as distinct low-temperature scaling of multi-partite entanglement, for characterizing these phases in real materials.
We propose using spin-qubit noise magnetometry to probe dynamical signatures of magnetic Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless (BKT) physics. For a nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center coupled to two-dimensional XY magnets, we predict distinctive features in the magnetic noise spectral density in the sub-MHz to GHz frequency range. In the quasi-long-range ordered phase, the spectrum exhibits a temperature-dependent power law characteristic of algebraic spin correlations. Above the transition, the noise reflects the proliferation of free vortices and enables quantitative extraction of the vortex conductivity, a key parameter of vortex transport. These results highlight NV as a powerful spectroscopic method to resolve magnetic dynamics in the mesoscopic and low-frequency regimes and to probe exotic magnetic phase transitions.
This paper systematically explores how the definition of quantum subsystems and their properties, including correlations, dynamics, and thermodynamics, change when described from different internal quantum reference frames. It demonstrates that different quantum reference frames induce inequivalent tensor product structures on the total Hilbert space, leading to observer-dependent notions of thermal equilibrium, temperature, and open/closed system dynamics.
30 Aug 2023
Quantum error correction codes based on continuous variables play an important role for the implementation of quantum communication systems. A natural application of such codes occurs within quantum repeater systems which are used to combat severe channel losses and local gate errors. In particular, channel loss drastically reduces the distance of communication between remote users. Here we consider a cavity-QED based repeater scheme to address the losses in the quantum channel. This repeater scheme relies on the transmission of a specific class of rotationally invariant error-correcting codes. We compare several rotation-symmetric bosonic codes (RSBCs) being used to encode the initial states of two remote users connected by a quantum repeater network against the convention of the cat codes and we quantify the performance of the system using the secret key rate. In particular, we determine the number of stations required to exchange a secret key over a fixed distance and establish the resource overhead.
This work investigates the mathematical properties of projective representations and the Bogomolov multiplier, demonstrating their role in classifying a class of (1+1)D symmetry-protected topological (SPT) phases undetectable by conventional string order parameters. It introduces novel physical diagnostics, such as phase-modified fusion rules for local order parameters and emergent non-trivial interface modes with increased ground state degeneracy, to distinguish distinct gapped phases possessing non-invertible symmetries.
 University of Pittsburgh
University of Pittsburgh University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge Imperial College London
Imperial College London National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore University College London
University College London University of Oxford
University of Oxford Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityUniversity of Ljubljana
Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityUniversity of Ljubljana Yale University
Yale University Northwestern UniversityRutherford Appleton Laboratory
Northwestern UniversityRutherford Appleton Laboratory University of SouthamptonKorea Institute for Advanced Study
University of SouthamptonKorea Institute for Advanced Study Perimeter Institute for Theoretical PhysicsThe University of SydneyOkinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University
Perimeter Institute for Theoretical PhysicsThe University of SydneyOkinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University University of WarwickUniversity of Sussex
University of WarwickUniversity of Sussex University of GroningenPontifical Catholic University of Rio de JaneiroBen-Gurion University of the NegevRoyal Holloway, University of LondonQueen's University BelfastINRIMShiv Nadar Institution of EminenceNational Quantum Computing CentreUniversit
degli Studi di Palermo
University of GroningenPontifical Catholic University of Rio de JaneiroBen-Gurion University of the NegevRoyal Holloway, University of LondonQueen's University BelfastINRIMShiv Nadar Institution of EminenceNational Quantum Computing CentreUniversit
degli Studi di PalermoA key open problem in physics is the correct way to combine gravity (described by general relativity) with everything else (described by quantum mechanics). This problem suggests that general relativity and possibly also quantum mechanics need fundamental corrections. Most physicists expect that gravity should be quantum in character, but gravity is fundamentally different to the other forces because it alone is described by spacetime geometry. Experiments are needed to test whether gravity, and hence space-time, is quantum or classical. We propose an experiment to test the quantum nature of gravity by checking whether gravity can entangle two micron-sized crystals. A pathway to this is to create macroscopic quantum superpositions of each crystal first using embedded spins and Stern-Gerlach forces. These crystals could be nanodiamonds containing nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centres. The spins can subsequently be measured to witness the gravitationally generated entanglement. This is based on extensive theoretical feasibility studies and experimental progress in quantum technology. The eventual experiment will require a medium-sized consortium with excellent suppression of decoherence including vibrations and gravitational noise. In this white paper, we review the progress and plans towards realizing this. While implementing these plans, we will further explore the most macroscopic superpositions that are possible, which will test theories that predict a limit to this.
In a gauge theory, a collection of kinematical degrees of freedom is used to redundantly describe a smaller amount of gauge-invariant information. In a quantum error correcting code (QECC), a collection of computational degrees of freedom that make up a device's physical layer is used to redundantly encode a smaller amount of logical information. We elaborate this parallel in terms of quantum reference frames (QRFs), which are a universal toolkit for dealing with symmetries in quantum systems and which define the gauge theory analog of encodings. The result is a precise dictionary between QECCs and QRF setups within the perspective-neutral framework for gauge systems. Concepts from QECCs like error sets and correctability translate to novel insights into the informational architecture of gauge theories. Conversely, the dictionary provides a systematic procedure for constructing symmetry-based QECCs and characterizing their error correcting properties. In this initial work, we scrutinize the dictionary between Pauli stabilizer codes and their corresponding QRF setups. We show that there is a one-to-one correspondence between maximal correctable error sets and tensor factorizations splitting system from error-generated QRF degrees of freedom. Relative to this split, errors corrupt only redundant frame data, leading to a novel characterization of correctability. When passed through the dictionary, standard Pauli errors behave as electric excitations that are dual, via Pontryagin duality, to magnetic excitations related to gauge-fixing. This gives rise to a new class of correctable errors and a systematic error duality. We illustrate our findings in surface codes, which themselves connect quantum error correction with gauge systems. Our exploratory investigations pave the way for foundational applications to gauge theories and for eventual practical applications to quantum simulation.
14 Sep 2025
Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University demonstrated that dynamic wall motion, resulting from fluid-structure interaction in turbulent channel flows over elastic walls, predominantly alters turbulence characteristics, leading to greater drag and modified turbulent structures, which static roughness or isolated wall-normal disturbances fail to replicate. They found that elastic walls uniquely modify the slope of the logarithmic mean velocity profile and promote spanwise-coherent structures.
17 May 2025
This study identifies quantum Fisher information (nQFI) as a reliable, experimentally accessible measure to distinguish Quantum Spin Liquids (QSLs) from disorder-driven "random singlet" (RS) phases. It demonstrates that nQFI shows a power-law divergence at low temperatures for QSLs and Néel states, while exhibiting an exponential decay for RS phases, a qualitative difference validated against experimental data from Yb-based triangular-lattice antiferromagnets.
22 Jan 2025
Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory New York University
New York University National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University University of MichiganLouisiana State UniversityUniversity of Technology SydneyIndian Institute of Science
University of MichiganLouisiana State UniversityUniversity of Technology SydneyIndian Institute of Science Aalto UniversityMacquarie UniversityUniversity of SheffieldOkinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate UniversityEast China Normal UniversityRMIT UniversityNational Institute of InformaticsUniversity of Science & Technology of ChinaLeibniz Institute for Research & Information in EducationSingapore University of Technology & DesignHorizon Quantum
Aalto UniversityMacquarie UniversityUniversity of SheffieldOkinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate UniversityEast China Normal UniversityRMIT UniversityNational Institute of InformaticsUniversity of Science & Technology of ChinaLeibniz Institute for Research & Information in EducationSingapore University of Technology & DesignHorizon Quantum
 New York University
New York University National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University University of MichiganLouisiana State UniversityUniversity of Technology SydneyIndian Institute of Science
University of MichiganLouisiana State UniversityUniversity of Technology SydneyIndian Institute of Science Aalto UniversityMacquarie UniversityUniversity of SheffieldOkinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate UniversityEast China Normal UniversityRMIT UniversityNational Institute of InformaticsUniversity of Science & Technology of ChinaLeibniz Institute for Research & Information in EducationSingapore University of Technology & DesignHorizon Quantum
Aalto UniversityMacquarie UniversityUniversity of SheffieldOkinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate UniversityEast China Normal UniversityRMIT UniversityNational Institute of InformaticsUniversity of Science & Technology of ChinaLeibniz Institute for Research & Information in EducationSingapore University of Technology & DesignHorizon QuantumFollowing the emergence of quantum computing, the subsequent quantum
revolution will be that of interconnecting individual quantum computers at
global level. In the same way that classical computers only realised their full
potential with the emergence of the internet, a fully realised quantum internet
is the next stage of evolution for quantum computation. This work examines in
detail how the quantum internet would evolve in practice, focusing not only on
the technology itself but also on the implications it will have economically
and politically. We present both original ideas, as well as an extensive review
of relevant and related background material. This work begins with a
description of classical networks before introducing the key concepts behind
quantum networks, such as quantum internet protocols, quantum cryptography, and
cloud quantum computing. The work is divided into technical sections (requiring
only a basic knowledge of the notation of quantum mechanics), for those
interested in mathematical details, as well as non-technical sections for those
seeking a more general understanding. We target this work very broadly at
quantum and classical computer scientists, classical computer systems, software
and network engineers, physicists, economists, artists, musicians, and those
just generally curious about the future of quantum technologies and what they
might bring to humanity.
03 Oct 2025
Motivated by bulk reconstruction of smeared boundary operators, we study the Krylov complexity of local and non-local primary CFTd operators from the local bulk-to-bulk propagator of a minimally-coupled massive scalar field in Rindler-AdSd+1 space. We derive analytic and numerical evidence on how the degree of non-locality in the dual CFTd observable affects the evolution of Krylov complexity and the Lanczos coefficients. Curiously, the near-horizon limit matches with the same observable for conformally-coupled probe scalar fields inserted at the asymptotic boundary of AdSd+1 space. Our results also show that the evolution of the growth rate of Krylov operator complexity in the CFTd takes the same form as to the proper radial momentum of a probe particle inside the bulk to a good approximation. The exact equality only occurs when the probe particle is inserted in the asymptotic boundary or in the horizon limit. Our results capture a prosperous interplay between Krylov complexity in the CFT, thermal ensembles at finite bulk locations and their role in the holographic dictionary.
Building a humanlike integrative artificial cognitive system, that is, an artificial general intelligence (AGI), is the holy grail of the artificial intelligence (AI) field. Furthermore, a computational model that enables an artificial system to achieve cognitive development will be an excellent reference for brain and cognitive science. This paper describes an approach to develop a cognitive architecture by integrating elemental cognitive modules to enable the training of the modules as a whole. This approach is based on two ideas: (1) brain-inspired AI, learning human brain architecture to build human-level intelligence, and (2) a probabilistic generative model(PGM)-based cognitive system to develop a cognitive system for developmental robots by integrating PGMs. The development framework is called a whole brain PGM (WB-PGM), which differs fundamentally from existing cognitive architectures in that it can learn continuously through a system based on sensory-motor information. In this study, we describe the rationale of WB-PGM, the current status of PGM-based elemental cognitive modules, their relationship with the human brain, the approach to the integration of the cognitive modules, and future challenges. Our findings can serve as a reference for brain studies. As PGMs describe explicit informational relationships between variables, this description provides interpretable guidance from computational sciences to brain science. By providing such information, researchers in neuroscience can provide feedback to researchers in AI and robotics on what the current models lack with reference to the brain. Further, it can facilitate collaboration among researchers in neuro-cognitive sciences as well as AI and robotics.
The Eigenstate Thermalization Hypothesis (ETH) has played a key role in
recent advances in the high energy and condensed matter communities. It
explains how an isolated quantum system in a far-from-equilibrium initial state
can evolve to a state that is indistinguishable from thermal equilibrium, with
observables relaxing to almost time-independent results that can be described
using traditional statistical mechanics ensembles. In this work we probe the
limits of ETH, pushing it outside its prototypical applications in several
directions. We design a qutrit lattice system with conserved quasilocal charge,
in which we verify a form of generalized eigenstate thermalization. We also
observe signatures of thermalization in states well outside microcanonical
windows of both charge and energy, which we dub `generic ETH.'
30 Jun 2025
This paper establishes a method for defining and calculating entanglement entropies in lattice gauge theories by employing quantum reference frames. The approach yields a gauge-invariant factorization of the physical Hilbert space, resulting in distillable entanglement entropies that align with operational notions, and unifies previous concepts of edge modes and center algebras within a coherent relational framework.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.