Om AI Research
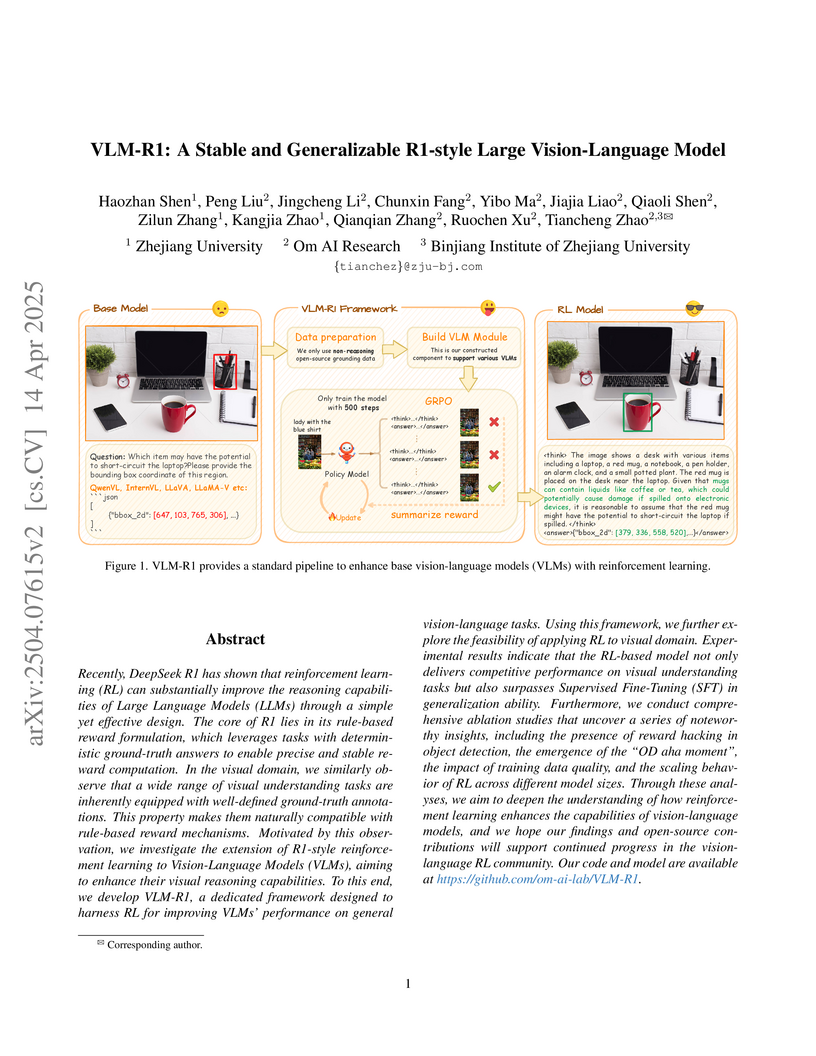
VLM-R1 introduces an open-source framework that applies rule-based reinforcement learning to Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enhancing their visual reasoning and generalization abilities on tasks like Referring Expression Comprehension and Open-Vocabulary Object Detection. The approach demonstrates improved out-of-domain performance compared to supervised fine-tuning and showcases emergent reasoning behaviors.
VLM-FO1, a plug-and-play framework from Om AI Research and Zhejiang University, enhances pre-trained Vision-Language Models with fine-grained perception by bridging high-level reasoning and precise spatial localization. It achieves state-of-the-art performance across object grounding (44.4 mAP on COCO), regional understanding, and visual reasoning benchmarks, while effectively preserving the base VLM's general capabilities.
ZoomEye, a training-free and model-agnostic framework, enhances Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with human-like zooming capabilities through tree-based image exploration. This approach substantially improves MLLM performance on high-resolution visual tasks, enabling smaller models (3B-8B parameters) to surpass larger commercial models like GPT-4o on specific detail-oriented benchmarks.
Researchers at Zhejiang University and Om AI Research introduced GUI Testing Arena (GTArena), a unified, end-to-end benchmark for autonomous GUI testing. The framework formalizes the testing process and evaluates state-of-the-art multimodal large language models, revealing a substantial performance gap between current AI capabilities and real-world applicability.
Self-improving large language models (LLMs) -- i.e., to improve the
performance of an LLM by fine-tuning it with synthetic data generated by itself
-- is a promising way to advance the capabilities of LLMs while avoiding
extensive supervision. Existing approaches to self-improvement often rely on
external supervision signals in the form of seed data and/or assistance from
third-party models. This paper presents Crescent -- a simple yet effective
framework for generating high-quality synthetic question-answer data in a fully
autonomous manner. Crescent first elicits the LLM to generate raw questions via
a bait prompt, then diversifies these questions leveraging a rejection
sampling-based self-deduplication, and finally feeds the questions to the LLM
and collects the corresponding answers by means of majority voting. We show
that Crescent sheds light on the potential of true self-improvement with zero
external supervision signals for math reasoning; in particular,
Crescent-generated question-answer pairs suffice to (i) improve the reasoning
capabilities of an LLM while preserving its general performance (especially in
the 0-shot setting); and (ii) distil LLM knowledge to weaker models more
effectively than existing methods based on seed-dataset augmentation.
30 May 2025
Researchers from Om AI Research and Zhejiang University introduce AGORA, a unified framework that enables standardized development and comprehensive evaluation of diverse language agent algorithms through a modular, graph-based architecture. Extensive experiments on mathematical reasoning and high-resolution image question-answering reveal that simpler algorithms often demonstrate robust performance with lower computational overhead, and prompt engineering significantly impacts results.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.