Shenzhen Loop Area Institute
The Memory Forcing framework enables autoregressive video diffusion models to achieve both natural content generation and long-term spatial consistency in open-world environments like Minecraft. It accomplishes this by adaptively utilizing temporal and geometry-indexed spatial memory, demonstrating superior generative quality and significantly faster, more memory-efficient retrieval compared to prior approaches.
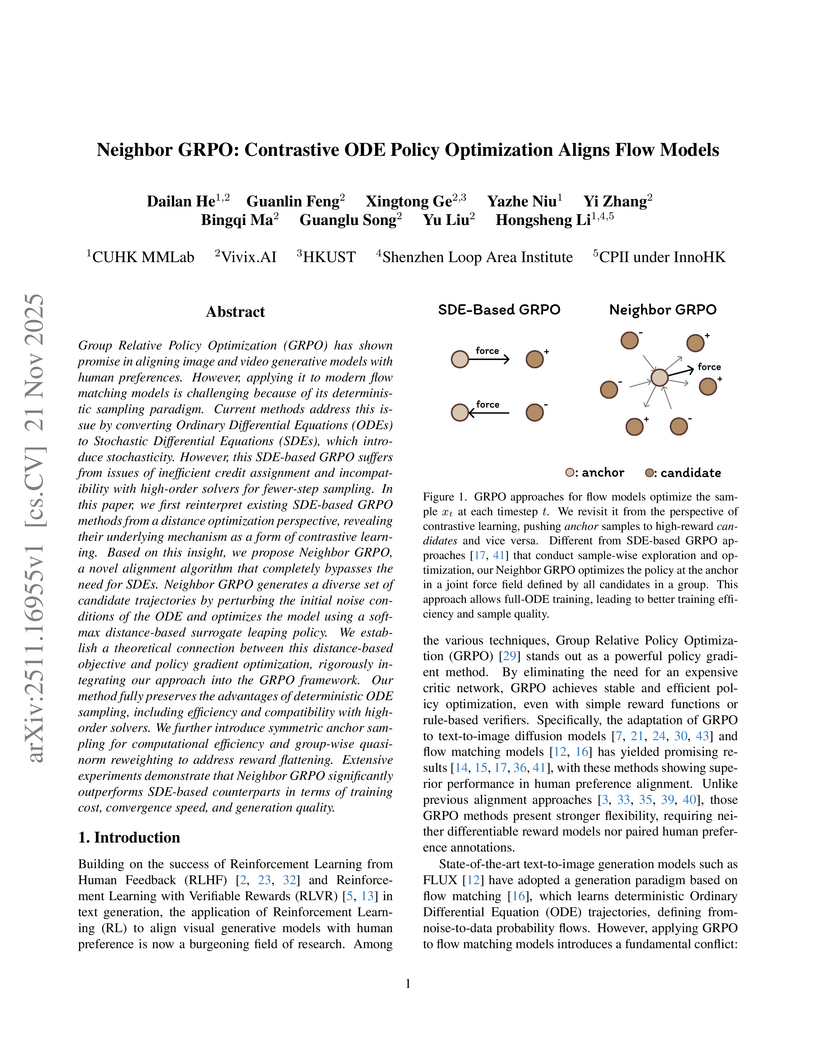
Neighbor GRPO introduces an SDE-free method for aligning flow matching models with human preferences, enabling up to 5x faster training while improving generation quality and robustness against reward hacking. The approach fully leverages efficient high-order ODE solvers for visual generative models.
22 Oct 2025
Researchers at Sun Yat-sen University developed "Lookahead Routing," a framework for multi-LLM systems that predicts latent representations of potential model responses to inform routing decisions. This approach consistently outperformed existing routing baselines, achieving an average normalized score 7.7% higher than the strongest competitor while reducing activated parameters by approximately 79% compared to ensembling.
UniMoE-Audio achieves unified speech and music generation by employing a Dynamic-Capacity Mixture-of-Experts architecture and a three-stage training curriculum. This approach addresses task conflict and data imbalance, yielding state-of-the-art perceptual quality in speech synthesis (UTMOS 4.36 on SeedTTS-EN) and superior aesthetic scores in music generation.
A training-free framework, DyToK, dynamically compresses visual tokens for Video Large Language Models by leveraging an LLM-guided keyframe prior to adaptively allocate per-frame token budgets. This approach significantly boosts inference speed and reduces memory while enhancing video understanding performance, especially under high compression.
Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) demonstrate significant potential for energy-efficient neuromorphic computing through an event-driven paradigm. While training methods and computational models have greatly advanced, SNNs struggle to achieve competitive performance in visual long-sequence modeling tasks. In artificial neural networks, the effective receptive field (ERF) serves as a valuable tool for analyzing feature extraction capabilities in visual long-sequence modeling. Inspired by this, we introduce the Spatio-Temporal Effective Receptive Field (ST-ERF) to analyze the ERF distributions across various Transformer-based SNNs. Based on the proposed ST-ERF, we reveal that these models suffer from establishing a robust global ST-ERF, thereby limiting their visual feature modeling capabilities. To overcome this issue, we propose two novel channel-mixer architectures: \underline{m}ulti-\underline{l}ayer-\underline{p}erceptron-based m\underline{ixer} (MLPixer) and \underline{s}plash-and-\underline{r}econstruct \underline{b}lock (SRB). These architectures enhance global spatial ERF through all timesteps in early network stages of Transformer-based SNNs, improving performance on challenging visual long-sequence modeling tasks. Extensive experiments conducted on the Meta-SDT variants and across object detection and semantic segmentation tasks further validate the effectiveness of our proposed method. Beyond these specific applications, we believe the proposed ST-ERF framework can provide valuable insights for designing and optimizing SNN architectures across a broader range of tasks. The code is available at \href{this https URL}{\faGithub~EricZhang1412/Spatial-temporal-ERF}.
ContextDrag introduces a tuning-free framework for precise and high-fidelity drag-based image editing by injecting noise-free, VAE-encoded reference features into Diffusion Transformer models, coupled with position-consistent attention. The method achieves superior drag precision, improving Mean Distance (MD) by 7.3% over prior art, while maintaining image fidelity and semantic coherence in edited results.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.