The Hamburg Center for Ultrafast Imaging
Position-Blind Ptychography: Viability of image reconstruction via data-driven variational inference
Position-Blind Ptychography: Viability of image reconstruction via data-driven variational inference
In this work, we present and investigate the novel blind inverse problem of position-blind ptychography, i.e., ptychographic phase retrieval without any knowledge of scan positions, which then must be recovered jointly with the image. The motivation for this problem comes from single-particle diffractive X-ray imaging, where particles in random orientations are illuminated and a set of diffraction patterns is collected. If one uses a highly focused X-ray beam, the measurements would also become sensitive to the beam positions relative to each particle and therefore ptychographic, but these positions are also unknown. We investigate the viability of image reconstruction in a simulated, simplified 2-D variant of this difficult problem, using variational inference with modern data-driven image priors in the form of score-based diffusion models. We find that, with the right illumination structure and a strong prior, one can achieve reliable and successful image reconstructions even under measurement noise, in all except the most difficult evaluated imaging scenario.
09 Oct 2025
The field of coherent electronics aims to advance electronic functionalities by utilizing quantum coherence. Here, we demonstrate a viable and versatile methodology for controlling electron dynamics optically in graphene nanoribbons. In particular, we propose to flatten the band structure of armchair graphene nanoribbons via control electrodes, arranged periodically along the extended direction of the nanoribbon. This addresses a key mechanism for dephasing in solids, which derives from the momentum dependence of the energy gap between the valence and the conduction band. We design an optimal driving field pulse to produce collective Rabi oscillations between these bands, in their flattened configuration. As an example for coherent control, we show that these optimized pulses can be used to invert the entire electronic band population by a π pulse in a reversible fashion, and to create a superposition state via a π/2 pulse, which generates an alternating photocurrent. Our proposal consists of a platform and methodological approach to optically control the electron dynamics of graphene nanoribbons, paving the way toward novel coherent electronic and quantum information processing devices in solid-state materials.
10 Jan 2022
An approach is described for studying texture in nanostructured materials. The approach implements the real space texture PDF, txPDF, laid out in [Gong and Billinge (2018) arXiv:1805.10342 [cond-mat]]. It is demonstrated on a fiber textured polycrystalline Pt thin film. The approach uses 3D PDF methods to reconstruct the orientation distribution function (ODF) of the powder crystallites from a set of diffraction patterns taken at different tilt angles of the substrate with respect to the incident beam directly from the 3D PDF of the sample. A real space equivalent of the reciprocal space pole figure is defined in terms of interatomic vectors in the PDF and computed for various interatomic vectors in the Pt film. Further, it is shown how a valid isotropic PDF may be obtained from a weighted average over the tilt series, and the measurement conditions for the best approximant to the isotropic PDF from a single exposure, which for the case of the fiber textured film was in a nearly grazing incidence orientation of around 10 degrees. Finally, we describe an open source Python software package, Fourigui, that may be used to help in studies of texture from 3D reciprocal space data, and indeed for Fourier transforming and visualizing 3D PDF data in general.
Discrete (DTCs) and continuous time crystals (CTCs) are novel dynamical many-body states, that are characterized by robust self-sustained oscillations, emerging via spontaneous breaking of discrete or continuous time translation symmetry. DTCs are periodically driven systems that oscillate with a subharmonic of the external drive, while CTCs are continuously driven and oscillate with a frequency intrinsic to the system. Here, we explore a phase transition from a continuous time crystal to a discrete time crystal. A CTC with a characteristic oscillation frequency ωCTC is prepared in a continuously pumped atom-cavity system. Modulating the pump intensity of the CTC with a frequency ωdr close to 2ωCTC leads to robust locking of ωCTC to ωdr/2, and hence a DTC arises. This phase transition in a quantum many-body system is related to subharmonic injection locking of non-linear mechanical and electronic oscillators or lasers.
A comprehensive, hyperfine-resolved rotation-vibration line list for the ammonia molecule (14NH3) is presented. The line list, which considers hyperfine nuclear quadrupole coupling effects, has been computed using robust, first principles methodologies based on a highly accurate empirically refined potential energy surface. Transitions between levels with energies below 8000~cm−1 and total angular momentum F≤14 are considered. The line list shows excellent agreement with a range of experimental data and will significantly assist future high-resolution measurements of NH3, both astronomically and in the laboratory.
05 Nov 2024
We provide a solution to the v-representability problem for a non-relativistic quantum many-particle system on a ring domain in terms of Sobolev spaces and their duals. Any one-particle density that is square-integrable, has a square-integrable weak derivative, and is gapped away from zero can be realized from the solution of a many-particle Schrödinger equation, with or without interactions, by choosing a corresponding external potential. This potential can contain a distributional contribution but still gives rise to a self-adjoint Hamiltonian. Importantly, this allows for a well-defined Kohn-Sham procedure but, on the other hand, invalidates the usual proof of the Hohenberg-Kohn theorem.
Understanding the chemical processes that occur during the solvothermal synthesis of functional nanomaterials is essential for their rational design and optimization for specific applications. However, these processes remain poorly understood, primarily due to the limitations of conventional ex situ characterization techniques and the technical challenges associated with in situ studies, particularly the design and implementation of suitable reactors. Here, we present a versatile cell suitable for in situ X-ray scattering, X-ray spectroscopy, and infrared spectroscopy studies performed during solvothermal synthesis under autoclave-like, inert conditions. The reactor enables precise control of the temperature between -20 C and 200 C, pressures up to 8 bar, magnetic stirring, and injection of gas or liquids. The reactor's capabilities are demonstrated by comprehensively studying the solvothermal synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles from iron acetylacetonate in benzyl alcohol through in situ X-ray scattering and spectroscopy, and ATR-IR spectroscopy.
02 Jul 2018
A numerical simulation infrastructure capable of calculating the flow of gas
and the trajectories of particles through an aerodynamic lens injector is
presented. The simulations increase the fundamental understanding and predict
optimized injection geometries and parameters. Our simulation results were
compared to previous reports and also validated against experimental data for
500 nm polystyrene spheres from an aerosol-beam- characterization setup. The
simulations yielded a detailed understanding of the radial phase-space
distribution and highlighted weaknesses of current aerosol injectors for
single-particle diffractive imaging. With the aid of these simulations we
developed new experimental implementations to overcome current limitations.
26 Oct 2016
During the first steps of photosynthesis, the energy of impinging solar
photons is transformed into electronic excitation energy of the
light-harvesting biomolecular complexes. The subsequent energy transfer to the
reaction center is understood in terms of exciton quasiparticles which move on
a grid of biomolecular sites on typical time scales less than 100 femtoseconds
(fs). Since the early days of quantum mechanics, this energy transfer is
described as an incoherent Forster hopping with classical site occupation
probabilities, but with quantum mechanically determined rate constants. This
orthodox picture has been challenged by ultrafast optical spectroscopy
experiments with the Fenna-Matthews-Olson protein in which interference
oscillatory signals up to 1.5 picoseconds were reported and interpreted as
direct evidence of exceptionally long-lived electronic quantum coherence. Here,
we show that the optical 2D photon echo spectra of this complex at ambient
temperature in aqueous solution do not provide evidence of any long-lived
electronic quantum coherence, but confirm the orthodox view of rapidly decaying
electronic quantum coherence on a time scale of 60 fs. Our results give no hint
that electronic quantum coherence plays any biofunctional role in real
photoactive biomolecular complexes. Since this natural energy transfer complex
is rather small and has a structurally well defined protein with the distances
between bacteriochlorophylls being comparable to other light-harvesting
complexes, we anticipate that this finding is general and directly applies to
even larger photoactive biomolecular complexes.
23 Aug 2022
Time crystals are classified as discrete or continuous depending on whether
they spontaneously break discrete or continuous time translation symmetry.
While discrete time crystals have been extensively studied in periodically
driven systems since their recent discovery, the experimental realization of a
continuous time crystal is still pending. Here, we report the observation of a
limit cycle phase in a continuously pumped dissipative atom-cavity system,
which is characterized by emergent oscillations in the intracavity photon
number. We observe that the phase of this oscillation is random for different
realizations, and hence this dynamical many-body state breaks continuous time
translation symmetry spontaneously. The observed robustness of the limit cycles
against temporal perturbations confirms the realization of a continuous time
crystal.
21 Nov 2024
Despite recent numerical evidence, one of the fundamental theoretical
mysteries of polaritonic chemistry is how and if collective strong coupling can
induce local changes of the electronic structure to modify chemical properties.
Here we present non-perturbative analytic results for a model system consisting
of an ensemble of N harmonic molecules under vibrational strong coupling
(VSC) that alters our present understanding of this fundamental question. By
applying the cavity Born-Oppenheimer partitioning on the Pauli-Fierz
Hamiltonian in dipole approximation, the dressed many-molecule problem can be
solved self-consistently and analytically in the dilute limit. We discover that
the electronic molecular polarizabilities are modified even in the case of
vanishingly small single-molecule couplings. Consequently, this
non-perturbative local polarization mechanism persists even in the large-N
limit. In contrast, a perturbative calculation of the polarizabilities leads to
a qualitatively erroneous scaling behavior with vanishing effects in the
large-N limit. Nevertheless, the exact (self-consistent) polarizabilities can
be determined from single-molecule strong coupling simulations instead. Our
fundamental theoretical observations demonstrate that hitherto existing
collective-scaling arguments are insufficient for polaritonic chemistry and
they pave the way for refined single- (or few-) molecule strong-coupling
ab-initio simulations of chemical systems under collective strong coupling.
SLAC National Accelerator LaboratoryDESY National University of SingaporeRadboud University
National University of SingaporeRadboud University Arizona State University
Arizona State University Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryUppsala UniversityMax Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of MatterUniversität HamburgLa Trobe UniversityEuropean XFELThe Hamburg Center for Ultrafast ImagingCenter for Free-Electron Laser ScienceNERSCInstitute for Molecules and MaterialsLa Trobe Institute for Molecular ScienceUniv. of MelbourneLinac Coherent Light SourceCenter for BioImaging Sciences
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryUppsala UniversityMax Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of MatterUniversität HamburgLa Trobe UniversityEuropean XFELThe Hamburg Center for Ultrafast ImagingCenter for Free-Electron Laser ScienceNERSCInstitute for Molecules and MaterialsLa Trobe Institute for Molecular ScienceUniv. of MelbourneLinac Coherent Light SourceCenter for BioImaging Sciences
 National University of SingaporeRadboud University
National University of SingaporeRadboud University Arizona State University
Arizona State University Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryUppsala UniversityMax Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of MatterUniversität HamburgLa Trobe UniversityEuropean XFELThe Hamburg Center for Ultrafast ImagingCenter for Free-Electron Laser ScienceNERSCInstitute for Molecules and MaterialsLa Trobe Institute for Molecular ScienceUniv. of MelbourneLinac Coherent Light SourceCenter for BioImaging Sciences
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryUppsala UniversityMax Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of MatterUniversität HamburgLa Trobe UniversityEuropean XFELThe Hamburg Center for Ultrafast ImagingCenter for Free-Electron Laser ScienceNERSCInstitute for Molecules and MaterialsLa Trobe Institute for Molecular ScienceUniv. of MelbourneLinac Coherent Light SourceCenter for BioImaging SciencesWe report the 3D structure determination of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) by X-ray single particle imaging (SPI). Around 10 million diffraction patterns from gold nanoparticles were measured in less than 100 hours of beam time, more than 100 times the amount of data in any single prior SPI experiment, using the new capabilities of the European X-ray free electron laser which allow measurements of 1500 frames per second. A classification and structural sorting method was developed to disentangle the heterogeneity of the particles and to obtain a resolution of better than 3 nm. With these new experimental and analytical developments, we have entered a new era for the SPI method and the path towards close-to-atomic resolution imaging of biomolecules is apparent.
14 Aug 2018
Filming atoms in motion with sub-atomic spatiotemporal resolution is one of
the distinguished scientific endeavors of our time. Newly emerging X-ray laser
facilities are the most likely candidates to enable such a detailed gazing of
atoms due to their angstrom-level radiation wavelength. To provide the
necessary temporal resolution, numerous mode-locked lasers must be synchronized
with ultra-high precision across kilometer-distances. Here, we demonstrate a
metronome synchronizing a network of pulsed-lasers operating at different
center wavelengths and different repetition rates over 4.7-km distance. The
network achieves a record-low timing drift of 0.6 fs RMS measured with 2-Hz
sampling over 40 h. Short-term stability measurements show an out-of-loop
timing jitter of only 1.3 fs RMS integrated from 1 Hz to 1 MHz. To validate the
network performance, we present a comprehensive noise analysis based on the
feedback flow between the setup elements. Our analysis identifies nine
uncorrelated noise sources, out of which the slave laser's inherent jitter
dominates with 1.26 fs RMS. This suggests that the timing precision of the
network is not limited by the synchronization technique, and so could be much
further improved by developing lasers with lower inherent noise.
22 Nov 2024
The key features of density-functional theory (DFT) within a minimal implementation of quantum electrodynamics are demonstrated, thus allowing to study elementary properties of quantum-electrodynamical density-functional theory (QEDFT). We primarily employ the quantum Rabi model, that describes a two-level system coupled to a single photon mode, and also discuss the Dicke model, where multiple two-level systems couple to the same photon mode. In these settings, the density variables of the system are the polarization and the displacement of the photon field. We give analytical expressions for the constrained-search functional and the exchange-correlation potential and compare to established results from QEDFT. We further derive a form for the adiabatic connection that is almost explicit in the density variables, up to only a non-explicit correlation term that gets bounded both analytically and numerically. This allows several key features of DFT to be studied without approximations.
12 Mar 2025
In the pursuit of robust quantum computing, we put forth a platform based on
photonic qubits in a circuit-QED environment. Specifically, we propose a
versatile two-qubit gate based on two cavities coupled via a transmon,
constituting a selective number-dependent phase gate operating on the in-phase
eigenmodes of the two cavities, the Eigen-SNAP gate. This gate natively
operates in the dispersive coupling regime of the cavities and the transmon,
and operates by driving the transmon externally, to imprint desired phases on
the number states. As an example for the utility of the Eigen-SNAP gate, we
implement a SWAP gate on a system of two logical bosonic qubits
encoded in the cavities. Further, we use numerical optimization to determine
the optimal implementation of the SWAP. We find that the
fidelities of these optimal protocols are only limited by the coherence times
of the system's components. These findings pave the way to continuous variable
quantum computing in cavity-transmon systems.
The force-balance equation of time-dependent density-functional theory
presents a promising route towards obtaining approximate functionals, however,
so far, no practical correlation functionals have been derived this way. In
this work, starting from a correlated wavefunction proposed originally by Colle
and Salvetti [Theoret. Chim. Acta 37, 329 (1975)], we derive an analytical
correlation-energy functional for the ground state based on the force-balance
equation. The new functional is compared to the local-density correlation of
the homogeneous electron gas and we find an increased performance for atomic
systems, while it performs slightly worse on solids. From this point onward,
the new force-based correlation functional can be systematically improved.
05 Jun 2025
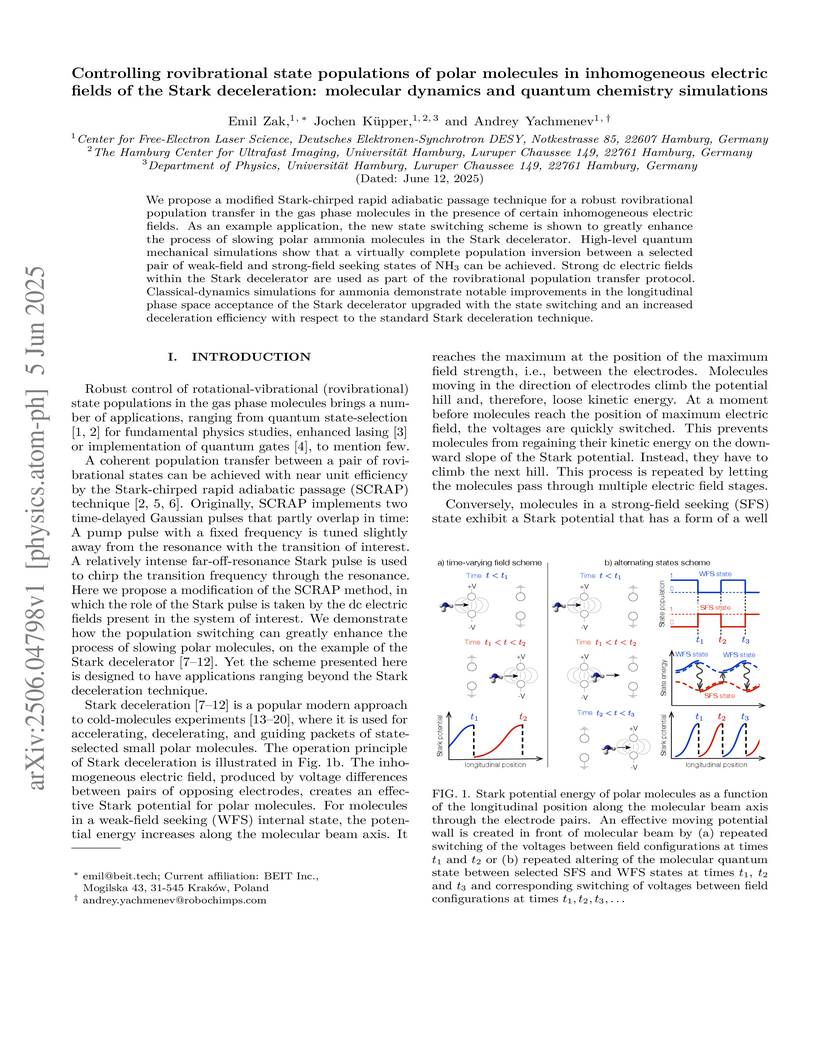
We propose a modified Stark-chirped rapid adiabatic passage technique for a robust rovibrational population transfer in the gas phase molecules in the presence of certain inhomogeneous electric fields. As an example application, the new state switching scheme is shown to greatly enhance the process of slowing polar ammonia molecules in the Stark decelerator. High-level quantum mechanical simulations show that a virtually complete population inversion between a selected pair of weak-field and strong-field seeking states of NH3 can be achieved. Strong dc electric fields within the Stark decelerator are used as part of the rovibrational population transfer protocol. Classical-dynamics simulations for ammonia demonstrate notable improvements in the longitudinal phase space acceptance of the Stark decelerator upgraded with the state switching and an increased deceleration efficiency with respect to the standard Stark deceleration technique.
Nonlinear classical mechanics has established countless intriguing and profound phenomena. These include limit tori defined by toroidal attractors that support quasiperiodic motion of at least two incommensurate frequencies. Here we address the question, whether and how such phenomena persist in open quantum systems. We develop a quantum description of limit tori within the Lindblad master-equation formalism for a system of two coupled driven-dissipative Kerr cavities. Using the spectral theory of the Liouvillian and the truncated Wigner approximation, we analyze the system across the quantum-to-classical transition. In the classical limit, we identify two pairs of purely imaginary Liouvillian eigenvalues, corresponding to persistent quasiperiodic modes of the limit torus. Quantum fluctuations induce small negative real parts to these eigenvalues, giving rise to finite lifetimes of these modes. The corresponding Liouvillian gaps vanish algebraically in the classical limit. This behavior signals a genuine continuous dynamical phase transition, marked by the spontaneous breaking of time-translational symmetry. Analysis of individual quantum trajectories reveals quantum-fluctuation-induced dephasing as the primary mechanism behind this "quantum melting" of the torus. We quantify this dephasing using a circular-variance-based order parameter, revealing universal scaling with both system size and time. These scaling laws are robust and independent of microscopic parameters. Our results establish the quantum melting of limit tori as a distinct non-equilibrium critical phenomenon and provide concrete signatures for experimental observation in trapped ions and superconducting circuits.
11 Aug 2025
We extend a previous result [Sutter et al., J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 57, 475202 (2024)] to give an explicit form of the set of v-representable densities on the one-dimensional torus with any fixed number of particles in contact with a heat bath at finite temperature. The particle interaction has to satisfy some mild assumptions but is kept entirely general otherwise. For densities, we consider the Sobolev space H1 and exploit the convexity of the functionals. This leads to a broader set of potentials than the usual Lp spaces and encompasses distributions. By including temperature and thus considering all excited states in the Gibbs ensemble, Gâteaux differentiability of the thermal universal functional is guaranteed. This yields v-representability and it is demonstrated that the given set of v-representable densities is even maximal.
Single-particle small-angle X-ray scattering (SP-SAXS) enables quantitative morphological analysis by recording diffraction snapshots from isolated particles using X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) pulses. Unlike conventional X-ray techniques, which average over the entire illuminated sample volume, SP-SAXS resolves low-contrast, less abundant, or transient species within heterogeneous particle populations that would otherwise remain hidden. Here, we apply SP-SAXS to investigate the solvothermal formation of CoO nanocrystal assemblies from a Co(acac)3 precursor in benzyl alcohol. The single-particle data reveal amorphous, uniform-density Co(acac)2 spheres as transient intermediates that directly crystallize into cavernous CoO nanocrystal assemblies, which explains why CoO forms as hierarchical aggregates rather than as isolated nanocrystals. These results demonstrate that SP-SAXS provides a powerful framework for disentangling morphological heterogeneity in nanoparticle formation processes.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.