The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey
09 Dec 2025
We report the synthesis and physical properties of a polycrystalline, hexagonal boride YRu3B2. Our resistivity and heat capacity measurements indicate that YRu3B2 is a weakly coupled superconductor, with critical temperature Tc = 0.63 K and upper critical field μ0Hc2 (0)=0.11 T. Density functional theory calculations, together with chemical-bonding analysis, reveal that the electronic states at and near the Fermi energy level are dominated by the Ru kagome sublattice.
Hierarchical Federated Learning (HFL) faces the significant challenge of adversarial or unreliable vehicles in vehicular networks, which can compromise the model's integrity through misleading updates. Addressing this, our study introduces a novel framework that integrates dynamic vehicle selection and robust anomaly detection mechanisms, aiming to optimize participant selection and mitigate risks associated with malicious contributions. Our approach involves a comprehensive vehicle reliability assessment, considering historical accuracy, contribution frequency, and anomaly records. An anomaly detection algorithm is utilized to identify anomalous behavior by analyzing the cosine similarity of local or model parameters during the federated learning (FL) process. These anomaly records are then registered and combined with past performance for accuracy and contribution frequency to identify the most suitable vehicles for each learning round. Dynamic client selection and anomaly detection algorithms are deployed at different levels, including cluster heads (CHs), cluster members (CMs), and the Evolving Packet Core (EPC), to detect and filter out spurious updates. Through simulation-based performance evaluation, our proposed algorithm demonstrates remarkable resilience even under intense attack conditions. Even in the worst-case scenarios, it achieves convergence times at 63\% as effective as those in scenarios without any attacks. Conversely, in scenarios without utilizing our proposed algorithm, there is a high likelihood of non-convergence in the FL process.
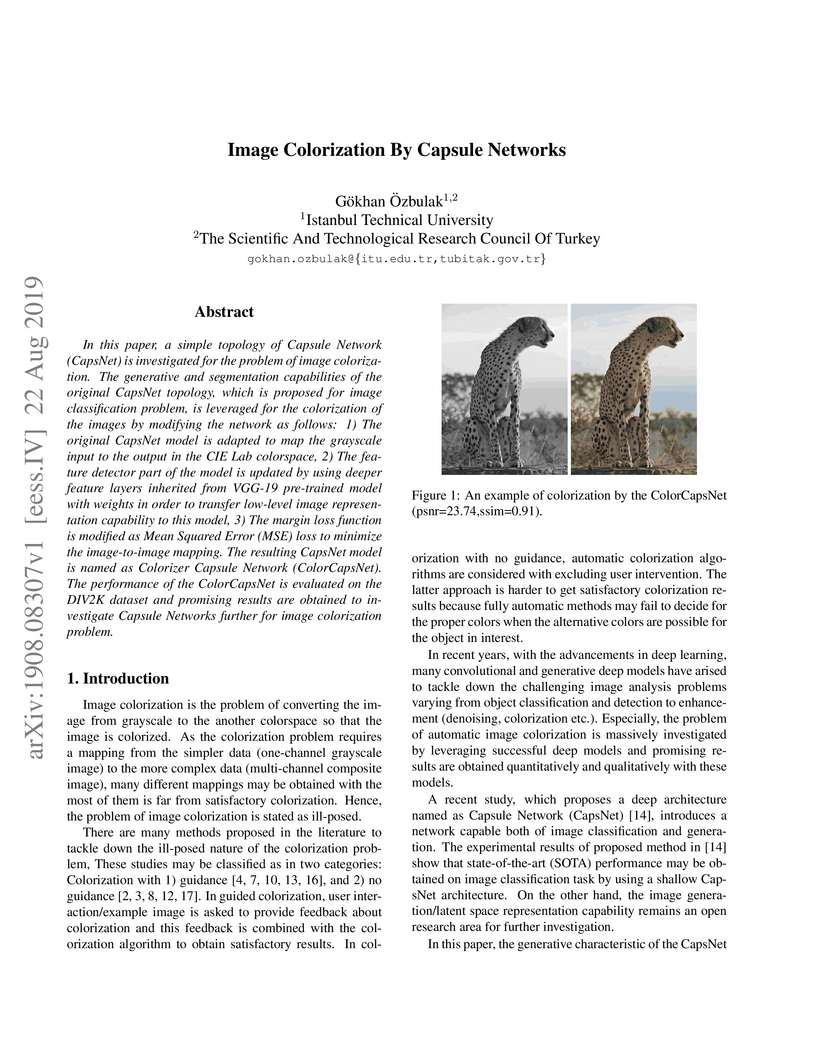
Gökhan Özbulak adapted Capsule Networks (CapsNets) for automatic image colorization, modifying the architecture to map grayscale images to plausible color versions in the CIE Lab space. The ColorCapsNet model achieved a PSNR of 22.20 dB and an SSIM of 0.88 on the NTIRE 2019 Colorization Challenge validation set, producing competitive and visually promising results without human guidance.
Diversity schemes play a vital role in improving the performance of
ultra-reliable communication systems by transmitting over two or more
communication channels to combat fading and co-channel interference.
Determining an appropriate transmission strategy that satisfies
ultra-reliability constraint necessitates derivation of statistics of channel
in ultra-reliable region and, subsequently, integration of these statistics
into rate selection while incorporating a confidence interval to account for
potential uncertainties that may arise during estimation. In this paper, we
propose a novel framework for ultra-reliable real-time transmission considering
both spatial diversities and ultra-reliable channel statistics based on
multivariate extreme value theory. First, tail distribution of joint received
power sequences obtained from different receivers is modeled while
incorporating inter-relations of extreme events occurring rarely based on
Poisson point process approach in MEVT. The optimum transmission strategies are
then developed by determining optimum transmission rate based on estimated
joint tail distribution and incorporating confidence intervals into estimations
to cope with the availability of limited data. Finally, system reliability is
assessed by utilizing outage probability metric. Through analysis of data
obtained from the engine compartment of Fiat Linea, our study showcases the
effectiveness of proposed methodology in surpassing traditional
extrapolation-based approaches. This innovative method not only achieves a
higher transmission rate, but also effectively addresses stringent requirements
of ultra-reliability. The findings indicate that proposed rate selection
framework offers a viable solution for achieving a desired target error
probability by employing a higher transmission rate and reducing the amount of
training data compared to conventional rate selection methods.
The main objective of this paper is to provide a comprehensive demonstration
of recent results regarding the structures of the weighted Ces\`aro and Copson
function spaces. These spaces' definitions involve local and global weighted
Lebesgue norms; in other words, the norms of these spaces are generated by
positive sublinear operators and by weighted Lebesgue norms. The weighted
Lebesgue spaces are the special cases of these spaces with a specific set of
parameters.
Our primary method of investigating these spaces will be the so-called
discretization technique. Our technique will be the development of the approach
initiated by K.G. Grosse-Erdmann, which allows us to obtain the
characterization in previously unavailable situations, thereby addressing
decades-old open problems.
We investigate the relation (embeddings) between weighted Ces\`aro and Copson
function spaces. The characterization of these embeddings can be used to tackle
the problems of characterizing pointwise multipliers between weighted Ces\`aro
and Copson function spaces, the characterizations of the associate spaces of
Ces\`aro (Copson) function spaces, as well as the relations between local
Morrey-type spaces.
We have synthesized and characterized the physical properties of a layered,
mixed valent oxypnictide La3Cu4P4O2 via magnetization,
electrical resistivity, and specific heat measurements. Although
La3Cu4P4O2 does not exhibit superconductivity down to T
= 0.5 K, it demonstrates an intriguing resistivity minimum observed at
Tmin = 13.7 K. Disappearance of the resistivity minimum under an
applied magnetic field of μ0H = 9 T together with the negative
magnetoresistance at low and positive at high temperatures are observed, which
are typical for both Kondo-like spin-dependent scattering and 3D weak
localization. We argue that the Kondo scattering is a more plausible
explanation due to the low-temperature deviation from a Curie-Weiss law
observed in the magnetic susceptibility, consistent with the presence of
magnetic interactions between paramagnetic Cu2+ ions and Kondo
screening of these Cu2+ moments. We supplemented the experimental
characterization with a detailed description of chemical bonding, employing
density functional theory (DFT) calculations and crystal orbital Hamilton
population (COHP) analysis for La3Cu4P4O2 and
isostructural La3Ni4P4O2, which is a superconductor with
Tc=2.2 K. Based on the calculations performed, we present the
difference between La3Cu4P4O2 and
La3Ni4P4O2 in the character of electronic states at the
Fermi level. This discrepancy impacts structural stability and may cause a lack
of superconductivity in La3Cu4P4O2 down to T = 0.5 K.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.