Universidad de La Habana
11 Apr 2024
In August 2023, IT experts and scientists came together for a workshop to
discuss the possibilities of building a computer cluster fully on renewable
energies, as a test-case at Havana University in Cuba. The discussion covered
the scientific needs for a computer cluster for particle physics at the InSTEC
institute at Havana University, the possibilities to use solar energy, new
developments in computing technologies, and computer cluster operation as well
as operational needs for computing in particle physics. This computer cluster
on renewable energies at the InSTEC institute is seen as a prototype for a
large-scale computer cluster on renewable energies for scientific computing in
the Caribbean, hosted in Cuba. The project is called "Humboldt Highway", to
remember Alexander von Humboldt's achievements in bringing cultures of the
American and European continents closer together by exchange and travel. In
this spirit, we propose a project that enables and intensifies the scientific
exchange between research laboratories and universities in Europe and the
Caribbean, in particular Cuba.
02 Oct 2025
The Eilers-Whittaker method for data smoothing effectiveness depends on the choice of the regularisation parameter, and automatic selection is a necessity for large datasets. Common methods, such as leave-one-out cross-validation, can perform poorly when serially correlated noise is present. We propose a novel procedure for selecting the control parameter based on the spectral entropy of the residuals. We define an S-curve from the Euclidean distance between points in a plot of the spectral entropy of the residuals versus that of the smoothed signal. The regularisation parameter corresponding to the absolute maximum of this S-curve is chosen as the optimal parameter. Using simulated data, we benchmarked our method against cross-validation and the V-curve. Validation was also performed on diverse experimental data. This robust and straightforward procedure can be a valuable addition to the available selection methods for the Eilers smoother.
08 Jan 2024
Many natural phenomena are intrinsically causal. The discovery of the cause-effect relationships implicit in these processes can help us to understand and describe them more effectively, which boils down to causal discovery about the data and variables that describe them. However, causal discovery is not an easy task. Current methods for this are extremely complex and costly, and their usefulness is strongly compromised in contexts with large amounts of data or where the nature of the variables involved is unknown. As an alternative, this paper presents an original methodology for causal discovery, built on essential aspects of the main theories of causality, in particular probabilistic causality, with many meeting points with the inferential approach of regularity theories and others. Based on this methodology, a non-parametric algorithm is developed for the discovery of causal relationships between binary variables associated to data sets, and the modeling in graphs of the causal networks they describe. This algorithm is applied to gene expression data sets in normal and cancerous prostate tissues, with the aim of discovering cause-effect relationships between gene dysregulations leading to carcinogenesis. The gene characterizations constructed from the causal relationships discovered are compared with another study based on principal component analysis (PCA) on the same data, with satisfactory results.
This paper describes a graph visualization methodology based on hierarchical maximal modularity clustering, with interactive and significant coarsening and refining possibilities. An application of this method to HIV epidemic analysis in Cuba is outlined.
24 Aug 2022
Predicting protein-protein interactions from sequences is an important goal of computational biology. Various sources of information can be used to this end. Starting from the sequences of two interacting protein families, one can use phylogeny or residue coevolution to infer which paralogs are specific interaction partners within each species. We show that these two signals can be combined to improve the performance of the inference of interaction partners among paralogs. For this, we first align the sequence-similarity graphs of the two families through simulated annealing, yielding a robust partial pairing. We next use this partial pairing to seed a coevolution-based iterative pairing algorithm. This combined method improves performance over either separate method. The improvement obtained is striking in the difficult cases where the average number of paralogs per species is large or where the total number of sequences is modest.
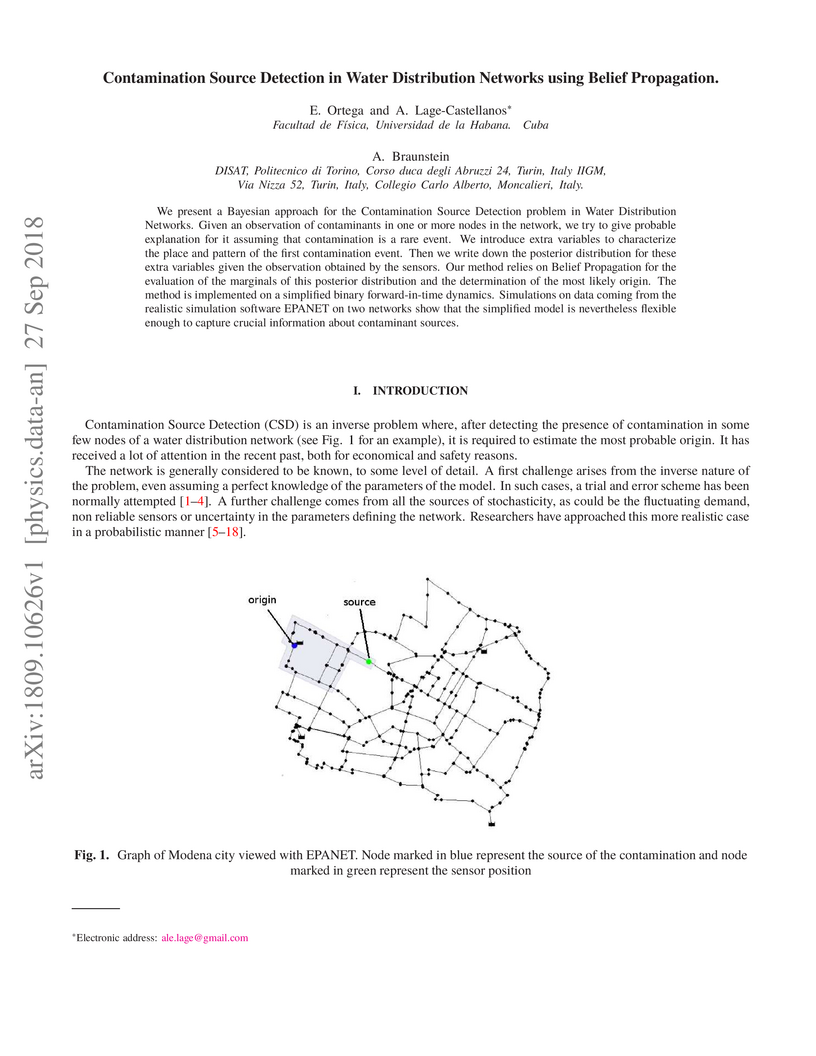
We present a Bayesian approach for the Contamination Source Detection problem
in Water Distribution Networks. Given an observation of contaminants in one or
more nodes in the network, we try to give probable explanation for it assuming
that contamination is a rare event. We introduce extra variables to
characterize the place and pattern of the first contamination event. Then we
write down the posterior distribution for these extra variables given the
observation obtained by the sensors. Our method relies on Belief Propagation
for the evaluation of the marginals of this posterior distribution and the
determination of the most likely origin. The method is implemented on a
simplified binary forward-in-time dynamics. Simulations on data coming from the
realistic simulation software EPANET on two networks show that the simplified
model is nevertheless flexible enough to capture crucial information about
contaminant sources.
29 Aug 2020
The encapsulation-dehydration and vitrification techniques were experimented
for freezing apices of pineapple in vitro plantlets. Positive results were
achieved using vitrification only. Optimal conditions included a 2-d preculture
of apices on medium supplemented with 0.3M sucrose, loading treatment for 25
min in medium with 0.75M sucrose + 1M glycerol and dehydration with PVS2
vitrification solution at 0 degrees C for 7 h before rapid freezing in liquid
nitrogen. This method resulted in 65, 35 and 25% survival with apices of
varieties Puerto Rico, Perolera and Smooth Cayenne, respectively. Recovery of
cryopreserved apices took place directly, without transitory callus formation.
27 Dec 2018
In this paper, we investigated if the differences consistently noted in
survival and plantlet production between cryopreserved and non-cryopreserved,
control sugarcane embryogenic calluses were related to modifications induced
during cryopreservation in the structural and functional integrity of cell
membranes. For this, the evolution of electrolyte leakage, lipid peroxidation
products and cell membrane protein contents was measured during 5 d after
cryopreservation. Differences between control and frozen calluses were observed
only during the first 2 (electrolyte leakage) or 3 d (lipid peroxidation
products and membrane protein content) after freezing. It was not possible to
link these differences with the differences noted in survival and plant
production between control and cryopreserved calluses. Additional studies are
thus needed to elucidate which biochemical factors, linked to survival and
plantlet regeneration, are affected by cryopreservation.
10 Nov 2018
Optical micro-manipulation techniques has evolved into powerful tools to efficiently steer the motion of microscopical particles on periodic and quasi-periodic potentials, driven by the external electromagnetic field. Here, the dynamics of molecular diffusion on optical lattices is analysed within the framework of the theory of open systems, for polar molecules coupled to a transient electromagnetic field. Using the normal mode expansion of the field, we derive an effective, generalised Langevin equation which describes the motion of the system along the molecular degrees of freedom. The present approach is universally applicable (for molecules with non-vanishing permanent dipole moment) and it opens a wide spectrum of applications in the control of the molecular transport mechanisms on optical lattices. The numerical analysis of suitable model external fields demonstrates the feasibility of neglecting memory terms in the resulting Langevin equation.
10 Mar 2019
We propose a new classical approach for describing a system composed of n
interacting particles with variable mass connected by a single field with no
predefined form (n-VMVF systems). Instead of assuming any particular nature
or analytical function for representing the variation of the masses or field,
we propose them as unknown functions dependent on the particle positions and
velocities. The work presents the Lagrangian theory which incorporates such
variations which are find using only first principles. The consideration of
mass as unknown quantity lead us to modify the D'Alembert's principle to ensure
the compliance of the relativity principle. Also, because the addition of new
variables to the system, we add a new and independent set of Lagrange equations
depending on the 3-D angular coordinates for the system of equations remain
solvable. The four-dimensional space-time naturally appears in the problem when
the position of the particle is expressed as a function of angular coordinates.
This transformation set the 3−D space of the angular coordinates as the
stereographic projection of the 4−D sphere defined by the Lorentz condition
in the space-time. We identify two sets of constraints, each one for every
coordinate system, by forcing the system to satisfy the laws of the
conservation of the linear and angular momentum. The x¨ dependency's of
the constraints functions set the necessity of extending the classical theory
up to the second order of the Lagrange function. The obtained constraints are
added to the initial Lagrangian by the Lagrange multiplier method and obtain
not one, but two Lagrange functions and with them, two set of Lagrange
equations for finding the final solution.
31 Mar 2025
The Parton Branching (PB) method describes the evolution of transverse
momentum dependent (TMD) parton distributions, covering all kinematic regions
from small to large transverse momenta kT. The small kT-region is very
sensitive both to the contribution of the intrinsic motion of partons
(intrinsic kT) and to the resummation of soft gluons taken into account by the
PB TMD evolution equations. We study the role of soft-gluon emissions in TMD as
well as integrated parton distributions. We perform a detailed investigation of
the PB TMD methodology at next-to-leading order (NLO) in Drell-Yan (DY)
production for low transverse momenta. We present the extraction of the
nonperturbative "intrinsic-kT" distribution from recent measurements of DY
transverse momentum distributions at the LHC across a wide range in DY masses,
including a detailed treatment of statistical, correlated and uncorrelated
uncertainties. We comment on the (in)dependence of intrinsic transverse
momentum on DY mass and center-of-mass energy, and on the comparison with other
approaches.
26 Nov 2024
We investigate the adsorption of molecular hydrogen on pristine zinc oxide
(ZnO) platelets. The volumetric and gravimetric hydrogen storage capacities of
the ZnO monolayers are evaluated in a broad range of thermodynamic conditions
(i.e., for temperatures in the range 77 K < T < 450 K, and for external gas
pressures up to 200 bar). The thermodynamic properties and the microscopic
spatial distribution of the adsorbed hydrogen fluid are assessed within the
density functional theory of liquids for quantum fluids at finite temperature
(QLDFT), and the adsorption enthalphies are obtained by fitting the computed
adsorption densities to the Toth model isotherm. Compared to graphene
platelets, the ZnO sheets impose a rather tighter confinement to the motion of
the hydrogen molecules parallel to the surface. The isosteric heat of
adsorption approaches 3.2 kJ/mol in the low density regime. This quantity shows
a fairly smooth dependence on the hydrogen uptake for temperatures below 100 K,
while it is shown to depend quite sensitively on the adsorbate density above
this temperature.
How does the information flow between different brain regions during various stimuli? This is the question we aim to address by studying complex cognitive paradigms in terms of Information Theory. To assess creativity and the emergence of patterns from a Shannon perspective, we applied a range of tools, including Entropy Density, Effective Measure Complexity, and the Lempel-Ziv distance. These entropic tools enable the detection of both linear and non-linear dynamics without relying on pre-established parameters, models, or prior assumptions about the data. To identify connections between different brain regions, we analyse task-based fMRI data from subjects during motor, working memory, emotion recognition, and language stimuli to gain insight into these complex cognitive processes. Since this method does not rely on prior knowledge, it is particularly well-suited for exploratory research, facilitating the discovery of previously unidentified connections or patterns in the brain. The capacity to identify non-linear dynamics is especially important for studying brain connectivity, as the brain exhibits significant non-linear interactions across multiple functional levels.
11 Jul 2025
We evaluate the feasibility of Bose-Einstein condensate stars (BECS) as models for the interior of neutron stars. BECS are compact objects composed of bosons, formed through the spin-parallel pairing of neutrons. Here, we utilize the astronomical data from GW170817, XMMU J173203.3-344518 (the lightest neutron star known), and a novel lower limit on neutron star core heat capacity to scrutinize the compatibility of BECS with these recent observations of neutron stars. Our specific focus is to constrain the values of the scattering length a, a parameter determining the strength of particle interactions in the model. Our analysis suggests that if the stars involved in GW170817 were BECSs, the scattering length of their constituent bosons should fall within the 4 to 10 fm range. Additionally, at a scattering length of a∼3.1−4 fm, stars with mass and radius characteristics akin to XMMU J173203.3-344518 are identified. Moreover, we find that the heat capacity depends of the mass and temperature of BECS, and surpasses the established lower bound for neutron star cores when a>2−5 fm. In summary, our results endorse BECS models with a∼4 fm, providing neutron star observables in robust agreement with diverse observations and contributing to the ongoing understanding of neutron star interiors.
15 Jul 2025
We study the structure and properties of Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC) Stars as alternatives to conventional neutron stars. The work focuses on the thermodynamic study of gases composed of charged scalar bosons and fermions (electrons, protons, and neutrons) under a uniform magnetic field, paying particular attention to the low-temperature limit. Expressions are derived for the thermodynamic potential, particle densities, energies, anisotropic pressures, and magnetization, including both statistical and vacuum contributions, with the latter separated into the contribution from the Lowest Landau Level (LLL) and excited levels. Based on these results, anisotropic equations of state (EoS) are constructed that incorporate chemical equilibrium and charge neutrality conditions for a mixed \textit{npe}+π− gas. These EoS are then implemented in a system of anisotropic structure equations based on an axisymmetric metric, allowing for the analysis of how the magnetic field modifies the structure of BEC stars, including their masses, radii, deformations, gravitational redshifts, and mass quadrupole moments. Numerical results are presented showing the influence of the magnetic field on the global properties of these stars, including potential observable signatures.
A low-energy model is built to study systems such as Dirac/Weyl semimetals, according to statistical quantum electrodynamics formalism. We report that the introduction of a pseudoscalar, associated to longitudinal photons propagating along a magnetic field B, could transforms a Dirac semimetal into a Weyl semimetal with a pair of Weyl nodes for each point of Dirac. The nodes are separated by a pseudovector electric field induced dynamically along B associated to a chiral effect on the Fermi surface. A topological quantum transition is produced between a chiral-and non chiral symmetry phase. A general expression to the longitudinal magnetoconductivity is found. It provides the possibility of generalizing the usual expressions of the magnetoconductivity reported in the literature. This has a quadratic dependence on B, which is associated with a positive contribution to the magnetoconductivity. This is a prominent signature of the chiral magnetic effect in Dirac/Weyl systems in parallel electric and magnetic fields. We report a chiral effect induced by longitudinal photons associated to a negative longitudinal magnetoresistance in Dirac systems via an axial anomaly relation. We show some numerical results, and reproduced with a high level of accuracy some of the experimental results, in the low temperature region, obtained to the magnetoresistance of ZrTe5 and Na3Bi. We believe that a wide variety of these semimetals can be studied by using our general expression to the negative longitudinal magnetoresistance.
DESY University of Oxford
University of Oxford INFN
INFN Peking University
Peking University CEAUniversity of HamburgLund UniversityLebedev Physics InstituteUniversite Libre de BruxellesJefferson LabUniversity of AntwerpShahid Beheshti UniversityUniversit`a di PaviaJINRUniversit`a di TriesteUniversidad de La HabanaUniversitat RegensburgRALSINP, Moscow State UniversityUniversidad de las Am´ericas-PueblaUniversité Paris-SaclayThe H. Niewodnicza
´nski Institute of Nuclear Physics
CEAUniversity of HamburgLund UniversityLebedev Physics InstituteUniversite Libre de BruxellesJefferson LabUniversity of AntwerpShahid Beheshti UniversityUniversit`a di PaviaJINRUniversit`a di TriesteUniversidad de La HabanaUniversitat RegensburgRALSINP, Moscow State UniversityUniversidad de las Am´ericas-PueblaUniversité Paris-SaclayThe H. Niewodnicza
´nski Institute of Nuclear Physics
 University of Oxford
University of Oxford INFN
INFN Peking University
Peking University CEAUniversity of HamburgLund UniversityLebedev Physics InstituteUniversite Libre de BruxellesJefferson LabUniversity of AntwerpShahid Beheshti UniversityUniversit`a di PaviaJINRUniversit`a di TriesteUniversidad de La HabanaUniversitat RegensburgRALSINP, Moscow State UniversityUniversidad de las Am´ericas-PueblaUniversité Paris-SaclayThe H. Niewodnicza
´nski Institute of Nuclear Physics
CEAUniversity of HamburgLund UniversityLebedev Physics InstituteUniversite Libre de BruxellesJefferson LabUniversity of AntwerpShahid Beheshti UniversityUniversit`a di PaviaJINRUniversit`a di TriesteUniversidad de La HabanaUniversitat RegensburgRALSINP, Moscow State UniversityUniversidad de las Am´ericas-PueblaUniversité Paris-SaclayThe H. Niewodnicza
´nski Institute of Nuclear PhysicsA common library, TMDlib2, for Transverse-Momentum-Dependent distributions (TMDs) and unintegrated parton distributions (uPDFs) is described, which allows for easy access of commonly used TMDs and uPDFs, providing a three-dimensional (3D) picture of the partonic structure of hadrons. The tool TMDplotter allows for web-based plotting of distributions implemented in TMDlib2, together with collinear pdfs as available in LHAPDF.
04 Mar 2021
The Langevin equation includes a random force to maintain equilibrium and prevent friction from bringing motion to a standstill; but for ballistic motion, the random force is often neglected. Here, we use the Langevin equation for molecular dynamics simulations of 2.76 eV H-atoms experiencing electronic friction in collisions with 300 K metals, where a random force arises from thermal electron-hole pairs. Simulations without the random force fail dramatically to reproduce experiment, although the incidence energy is much larger than kBT. We analyze the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process to show that this is a general property of ballistic particles experiencing friction under the influence of thermal fluctuations.
01 Oct 2025
Santa Fe InstituteUniversidad de ChilePontificia Universidad Católica de ChileThe Abdus Salam International Centre for Theoretical Physics (ICTP)Centro de Modelamiento Matemático (CMM)Universidad de La HabanaThe Laboratory for Quantitative SustainabilityCentro de Cambio Global UCInstituto de Sistemas Complejos de Valparaíso (ISCV)The Abdus Salam, International Centre for Theoretical Physics
Can sustained open-ended technological progress preserve natural resources in a finite planet? We address this question on the basis of a stylized model with genuine open-ended technological innovation, where an innovation event corresponds to a random draw of a technology in the space of the parameters that define how it impacts the environment and how it interacts with the population. Technological innovation is endogenous because an innovation may invade if it satisfies constraints which depend on the state of the environment and of the population. We find that open-ended innovation leads either to a sustainable future where global population saturates and the environment is preserved, or to exploding population and a vanishing environment. What drives the transition between these two phases is not the level of environmental impact of technologies, but rather the demographic effects of technologies and labor productivity. Low demographic impact and high labor productivity (as in several western countries today) result in a Schumpeterian dynamics where new "greener" technologies displace older ones, thereby reducing the overall environmental impact. In this scenario, global population saturates to a finite value, imposing strong selective pressure on technological innovation. When technologies contribute significantly to demographic growth and/or labor productivity is low, technological innovation runs unrestrained, population grows unbounded, while the environment collapses. As such, our model captures subtle feedback effects between technological progress, demography and sustainability that rationalize and align with empirical observations of a demographic transition and the environmental Kuznets curve, without deriving it from profit maximization based on individual incentives.
21 Jul 2006
We develop the Cauchy theory of the spatially homogeneous inelastic Boltzmann
equation for hard spheres, for a general form of collision rate which includes
in particular variable restitution coefficients depending on the kinetic energy
and the relative velocity as well as the sticky particles model. We prove
(local in time) non-concentration estimates in Orlicz spaces, from which we
deduce weak stability and existence theorem. Strong stability together with
uniqueness and instantaneous appearance of exponential moments are proved under
additional smoothness assumption on the initial datum, for a restricted class
of collision rates. Concerning the long-time behaviour, we give conditions for
the cooling process to occur or not in finite time.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.