Universit{\"a}t zu K{\"o}ln
08 Nov 2018
We investigate the time evolution of an open quantum system described by a Lindblad master equation with dissipation acting only on a part of the degrees of freedom H0 of the system, and targeting a unique dark state in H0. We show that, in the Zeno limit of large dissipation, the density matrix of the system traced over the dissipative subspace H0, evolves according to another Lindblad dynamics, with renormalized effective Hamiltonian and weak effective dissipation. This behavior is explicitly checked in the case of Heisenberg spin chains with one or both boundary spins strongly coupled to a magnetic reservoir. Moreover, the populations of the eigenstates of the renormalized effective Hamiltonian evolve in time according to a classical Markov dynamics. As a direct application of this result, we propose a computationally-efficient exact method to evaluate the nonequilibrium steady state of a general system in the limit of strong dissipation.
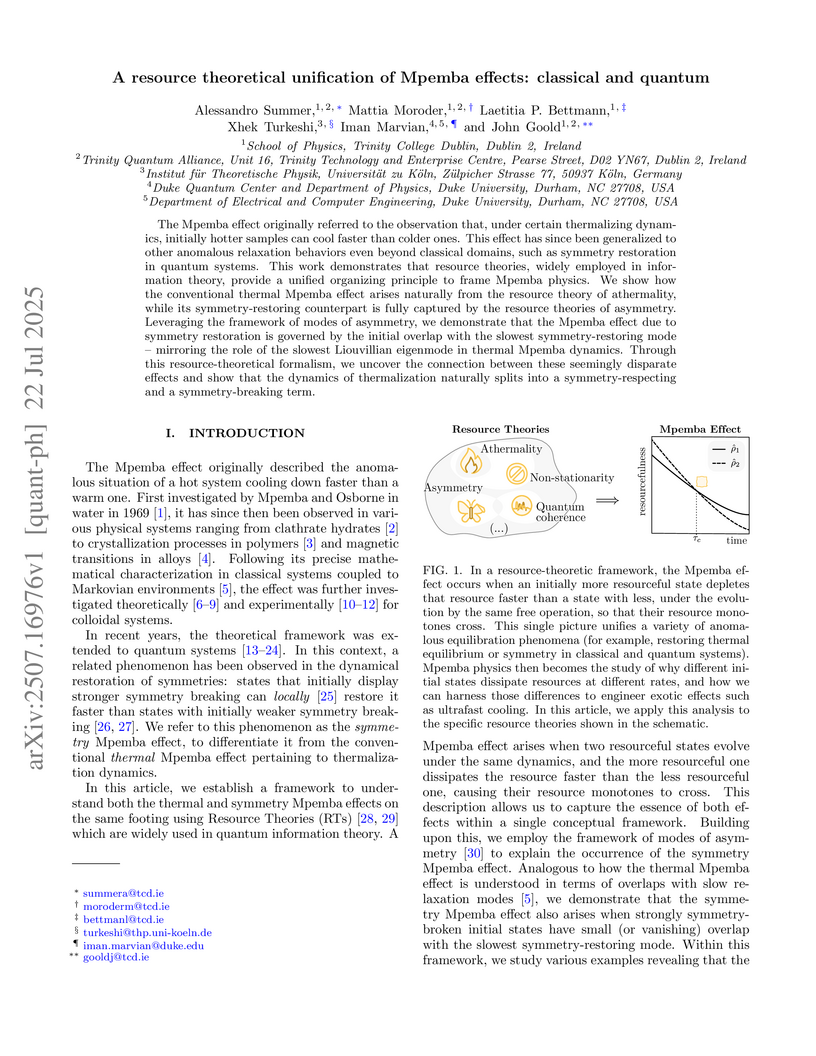
The Mpemba effect originally referred to the observation that, under certain thermalizing dynamics, initially hotter samples can cool faster than colder ones. This effect has since been generalized to other anomalous relaxation behaviors even beyond classical domains, such as symmetry restoration in quantum systems. This work demonstrates that resource theories, widely employed in information theory, provide a unified organizing principle to frame Mpemba physics. We show how the conventional thermal Mpemba effect arises naturally from the resource theory of athermality, while its symmetry-restoring counterpart is fully captured by the resource theories of asymmetry. Leveraging the framework of modes of asymmetry, we demonstrate that the Mpemba effect due to symmetry restoration is governed by the initial overlap with the slowest symmetry-restoring mode -- mirroring the role of the slowest Liouvillian eigenmode in thermal Mpemba dynamics. Through this resource-theoretical formalism, we uncover the connection between these seemingly disparate effects and show that the dynamics of thermalization naturally splits into a symmetry-respecting and a symmetry-breaking term.
24 Sep 2025
The quantum Hall effect hosts quantum phase transitions in which the localization length, that is the size of disorder-induced bulk localized states, is governed by universal scaling from percolation theory. However, this universal character is not systematically observed in experiments, including very recent ones in extremely clean devices. Here we explore this non-universality by systematically measuring the localization length in broken-symmetry quantum Hall states of graphene. Depending on the nature and gap size of these states, we observe differences of up to a tenfold in the minimum localization length, accompanied by clear deviations from universal scaling. Our results, as well as the previously observed non-universality, are fully captured by a simple picture based on the co-existence of localized states from two successive sub-Landau levels.
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Tsinghua UniversityCSICKorea Astronomy and Space Science InstituteNational Astronomical ObservatoriesPurple Mountain ObservatoryGuangxi UniversityShanghai Astronomical ObservatoryNew Cornerstone Science LaboratoryZhejiang LaboratoryInstitut d’Estudis Espacials de CatalunyaUniversit{\"a}t zu K{\"o}lnKey Laboratory of Modern Astronomy and Astrophysics (Nanjing University), Ministry of EducationGuangxi Key Laboratory for Relativistic AstrophysicsInstitut de Ci`encies de l’EspaiObservatorio Astronomico NacionalState Key Laboratory of Radio Astronomy and Technology
Tsinghua UniversityCSICKorea Astronomy and Space Science InstituteNational Astronomical ObservatoriesPurple Mountain ObservatoryGuangxi UniversityShanghai Astronomical ObservatoryNew Cornerstone Science LaboratoryZhejiang LaboratoryInstitut d’Estudis Espacials de CatalunyaUniversit{\"a}t zu K{\"o}lnKey Laboratory of Modern Astronomy and Astrophysics (Nanjing University), Ministry of EducationGuangxi Key Laboratory for Relativistic AstrophysicsInstitut de Ci`encies de l’EspaiObservatorio Astronomico NacionalState Key Laboratory of Radio Astronomy and TechnologyWe observed NH3 metastable inversion lines from (3, 3) to (18, 18) toward G0.66-0.13 in the Galactic center with the Shanghai Tianma 65m radio telescope and Yebes 40 m telescope. Highly-excited lines of NH3 (17, 17), (18, 18) were detected in emission for the first time in the interstellar medium, with upper energy levels up to 3100 K. Mapping observations reveal widespread hot molecular gas traced by NH3 (13, 13) toward G0.66-0.13. The rotation temperatures of hot gas traced by NH3 exceed 400 K, which amounts to five percent of the total NH3 in the Galactic Center. Hot gas (>400 K) and warm gas (100-140 K) are found in distinct clumps, with the hot gas located at the interfacing regions between different warm clouds. The theory of intermittency in turbulence reproduces the complex temperature structure in the central molecular zone, especially the hot gas observed here. The results presented here demonstrate that turbulence heating dominates the heating of the molecular gas in the Central Molecular Zone, while the turbulence is induced by the shear-motion of molecular clouds under the gravitational potential of the nuclear star clusters and the supermassive black hole. Our results suggest that shear-induced turbulence heating could be a widespread factor influencing galactic evolution.
11 Oct 2025
The use of coarse graining to connect physical and information theoretic entropies has recently been given a precise formulation in terms of ``observational entropy'', describing entropy for observers with respect to a measurement. Here we consider observers with various locality restrictions, including local measurements (LO), measurements based on local operations with classical communication (LOCC), and separable measurements (SEP), with the idea that the ``entropy gap'' between the minimum locally measured observational entropy and the von Neumann entropy quantifies quantum correlations in a given state. After introducing entropy gaps for general classes of measurements and deriving their general properties, we specialize to LO, LOCC, SEP and other measurement classes related to the locality of subsystems. For those, we show that the entropy gap can be related to well-known measures of entanglement or non-classicality of the state (even though we point out that they are not entanglement monotones themselves). In particular, for bipartite pure states, all of the ``local'' entropy gaps reproduce the entanglement entropy, and for general multipartite states they are lower-bounded by the relative entropy of entanglement. The entropy gaps of the different measurement classes are ordered, and we show that in general (mixed and multipartite states) they are all different.
22 Nov 2025
We report discovery of two CO clouds which are likely falling down to the Galactic plane at more than 35 km s−1. The clouds show head-tail distributions elongated perpendicular to the Galactic plane at l=331.6∘ and b=0∘ as revealed by an analysis of the Mopra CO J=1-0 survey data. We derived the distance of the clouds to be 2.46±0.18 kpc based on the Gaia Data Release 3. The CO clouds have molecular masses of 4.8×103 M⊙ and 3.5×103 M⊙, respectively, and show kinetic temperature of 30-50 K as derived from the line intensities of the 13CO J=2-1, 12CO J=1-0, and 13CO J=1-0 emission. The temperature in the heads of the clouds is significantly higher than 10 K of the typical molecular clouds, although no radiative heat source is found inside or close to the clouds. Based on the results, we interpret that the present clouds are falling onto the Milky Way disk and are significantly heated up by the strong shock interaction with the disk HI gas. We suggest that the clouds represent part of the HI intermediate velocity clouds falling to the Galactic plane which were converted into molecular clouds by shock compression. This is the first case of falling CO clouds having direct observed signatures of the falling motion including clear directivity and shock heating. Possible implications of the CO clouds in the evolution of the Galactic interstellar medium are discussed.
Monitored quantum systems, where unitary dynamics compete with continuous measurements, exhibit dynamical transitions as the measurement rate is varied. These reflect abrupt changes in the structure of the evolving wavefunction, captured by complementary complexity diagnostics that include and go beyond entanglement aspects. Here, we investigate how monitoring affects magic state resources, the nonstabilizerness, of Gaussian fermionic systems. Using scalable Majorana sampling techniques, we track the evolution of stabilizer Rényi entropies in large systems under projective measurements. While the leading extensive (volume-law) scaling of magic remains robust across all measurement rates, we uncover a sharp transition in the subleading logarithmic corrections. This measurement-induced complexity transition, invisible to standard entanglement probes, highlights the power of magic-based diagnostics in revealing hidden features of monitored many-body dynamics.
27 Aug 2025
 CNRS
CNRS Stanford University
Stanford University Space Telescope Science InstituteUniversity of Duisburg-EssenObservatoire de ParisUniversity of Texas at El PasoThe Johns Hopkins UniversityUniversit`a di BolognaZhejiang LaboratoryKavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and CosmologyUniversit{\"a}t zu K{\"o}lnMax-Planck Institut fur RadioastronomieMax-Planck-Institut fur extraterrestrische PhysikLaboratoire de Physique de l’Ecole normale superieureUniversite de ParisW. W. Hansen Experimental Physics LaboratoryLudwig-Maximilians-Universit¨at M¨ünchenINAF
Osservatorio Astrofisico di ArcetriTechnion
Israel Institute of TechnologyUniversité PSLSorbonne Université
Space Telescope Science InstituteUniversity of Duisburg-EssenObservatoire de ParisUniversity of Texas at El PasoThe Johns Hopkins UniversityUniversit`a di BolognaZhejiang LaboratoryKavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and CosmologyUniversit{\"a}t zu K{\"o}lnMax-Planck Institut fur RadioastronomieMax-Planck-Institut fur extraterrestrische PhysikLaboratoire de Physique de l’Ecole normale superieureUniversite de ParisW. W. Hansen Experimental Physics LaboratoryLudwig-Maximilians-Universit¨at M¨ünchenINAF
Osservatorio Astrofisico di ArcetriTechnion
Israel Institute of TechnologyUniversité PSLSorbonne UniversitéStars and planets form within cold, dark molecular clouds. In these dense regions, where starlight cannot penetrate, cosmic rays (CRs) are the dominant source of ionization -- driving interstellar chemistry(Dalgarno (2006, PNAS, 103, 12269)), setting the gas temperature(Goldsmith et al. (1969, ApJ, 158, 173)), and enabling coupling to magnetic fields(McKee & Ostriker (2007, ARA&A, 45, 565; arXiv:0707.3514)). Together, these effects regulate the collapse of clouds and the onset of star formation. Despite this importance, the cosmic-ray ionization rate, ζ, has never been measured directly. Instead, this fundamental parameter has been loosely inferred from indirect chemical tracers and uncertain assumptions, leading to published values that span nearly two orders of magnitude and limiting our understanding of star formation physics. Here, we report the first direct detection of CR-excited vibrational H2 emission, using \textit{James Webb Space Telescope} (JWST) observations of the starless core Barnard 68 (B68). The observed emission pattern matches theoretical predictions for CR excitation precisely, confirming a decades-old theoretical proposal long considered observationally inaccessible. This result enables direct measurement of ζ, effectively turning molecular clouds into natural, light-year-sized, cosmic-ray detectors. It opens a transformative observational window into the origin, propagation, and role of cosmic rays in star formation and galaxy evolution.
We observe the S-cluster star S62 on its Keplerian orbit around the supermassive black hole in the center of our galaxy, SgrA*. The orbital time period of S62 around SgrA* is 9.9 years. We derive its mass to be around 2 M_solar which is consistent with other members of the S-cluster. From the Lucy-Richardson deconvolved images, we determine a K-band magnitude of 16.1 mag. We observe almost two complete orbits of the star with two different and independent telescopes and three different instruments. The close distance of S62 to SgrA* at its periapse of around 2 mas results in a gravitational periapse shift of almost 10%/orbit.
24 Sep 2025
Graphene, through the coexistence of large cyclotron gaps and small spin and valley gaps, offers the possibility to study the breakdown of the quantum Hall effect across a wide range of energy scales. In this work, we investigate the breakdown of the QHE in high-mobility graphene Corbino devices under broadband excitation ranging from DC up to 10 GHz. We find that the conductance is consistently described by variable range hopping (VRH) and extract the hopping energies from both temperature and field-driven measurements. Using VRH thermometry, we are able to distinguish between a cold and hot electron regime, which are dominated by non-ohmic VRH and Joule heating, respectively. Our results demonstrate that breakdown in the quantum Hall regime of graphene is governed by a crossover from non-ohmic, field-driven VRH to ohmic, Joule-heating-dominated transport.
06 Apr 2018
We investigate the robustness of a dynamical phase transition against quantum fluctuations by studying the impact of a ferromagnetic nearest-neighbour spin interaction in one spatial dimension on the non-equilibrium dynamical phase diagram of the fully-connected quantum Ising model. In particular, we focus on the transient dynamics after a quantum quench and study the pre-thermal state via a combination of analytic time-dependent spin-wave theory and numerical methods based on matrix product states. We find that, upon increasing the strength of the quantum fluctuations, the dynamical critical point fans out into a chaotic dynamical phase within which the asymptotic ordering is characterised by strong sensitivity to the parameters and initial conditions. We argue that such a phenomenon is general, as it arises from the impact of quantum fluctuations on the mean-field out of equilibrium dynamics of any system which exhibits a broken discrete symmetry.
27 Jan 2016
Stochastic processes with absorbing states feature remarkable examples of non-equilibrium universal phenomena. While a broad understanding has been progressively established in the classical regime, relatively little is known about the behavior of these non-equilibrium systems in the presence of quantum fluctuations. Here we theoretically address such a scenario in an open quantum spin model which in its classical limit undergoes a directed percolation phase transition. By mapping the problem to a non-equilibrium field theory, we show that the introduction of quantum fluctuations stemming from coherent, rather than statistical, spin-flips alters the nature of the transition such that it becomes first-order. In the intermediate regime, where classical and quantum dynamics compete on equal terms, we highlight the presence of a bicritical point with universal features different from the directed percolation class in low dimension. We finally propose how this physics could be explored within gases of interacting atoms excited to Rydberg states.
It has been known for more than a decade that phonons can produce an off-diagonal thermal conductivity in presence of magnetic field. Recent studies of thermal Hall conductivity, κxy, in a variety of contexts, however, have assumed a negligibly small phonon contribution. We present a study of κxy in quantum paraelectric SrTiO3, which is a non-magnetic insulator and find that its peak value exceeds what has been reported in any other insulator, including those in which the signal has been qualified as 'giant'. Remarkably, κxy(T) and κ(T) peak at the same temperature and the former decreases faster than the latter at both sides of the peak. Interestingly, in the case of La2CuO4 and α-RuCl3, κxy(T) and κ(T) peak also at the same temperature. We also studied KTaO3 and found a small signal, indicating that a sizable κxy(T) is not a generic feature of quantum paraelectrics. Combined to other observations, this points to a crucial role played by antiferrodistortive domains in generating κxy of this solid.
We study biological evolution on a random fitness landscape where correlations are introduced through a linear fitness gradient of strength c. When selection is strong and mutations rare the dynamics is a directed uphill walk that terminates at a local fitness maximum. We analytically calculate the dependence of the walk length on the genome size L. When the distribution of the random fitness component has an exponential tail we find a phase transition of the walk length D between a phase at small c where walks are short (D∼lnL) and a phase at large c where walks are long (D∼L). For all other distributions only a single phase exists for any c>0. The considered process is equivalent to a zero temperature Metropolis dynamics for the random energy model in an external magnetic field, thus also providing insight into the aging dynamics of spin glasses.
Let (m,b) a pair of natural numbers. For m even (resp. m odd and b greater than or equal to 2) we show that if there is an m-dimensional non-formal compact oriented manifold whose first Betti number equals b, there is also a symplectic (resp. contact) manifold with these properties.
 University of CambridgeUniversity of Bern
University of CambridgeUniversity of Bern University of California, Irvine
University of California, Irvine Northwestern UniversityUniversidade de Lisboa
Northwestern UniversityUniversidade de Lisboa Space Telescope Science Institute
Space Telescope Science Institute Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University University of Arizona
University of Arizona Leiden University
Leiden University Queen Mary University of LondonUniversity of Colorado BoulderUniversidade do PortoAix-Marseille Univ
Queen Mary University of LondonUniversity of Colorado BoulderUniversidade do PortoAix-Marseille Univ European Southern Observatory
European Southern Observatory University of California, Santa CruzObservatoire de la Cˆote d’AzurUniversite Grenoble AlpesLESIA, Observatoire de ParisEuropean Space Agency (ESA)Universit{\"a}t zu K{\"o}lnMax-Planck Institut fur RadioastronomieMax-Planck-Institut fur extraterrestrische PhysikUniversit{\"a}t Duisburg-EssenCENTRA - Centro de Astrof´ısica e Gravita¸c˜aoSTAR Institute, Universit´e de Li`egeMax Planck Institut für Astronomie
University of California, Santa CruzObservatoire de la Cˆote d’AzurUniversite Grenoble AlpesLESIA, Observatoire de ParisEuropean Space Agency (ESA)Universit{\"a}t zu K{\"o}lnMax-Planck Institut fur RadioastronomieMax-Planck-Institut fur extraterrestrische PhysikUniversit{\"a}t Duisburg-EssenCENTRA - Centro de Astrof´ısica e Gravita¸c˜aoSTAR Institute, Universit´e de Li`egeMax Planck Institut für AstronomieUnderstanding the orbits of giant planets is critical for testing planet formation models, particularly at wide separations greater than 10 au where traditional core accretion becomes inefficient. However, constraining orbits at these separations has been challenging because of sparse orbital coverage and degeneracies in the orbital parameters. We use existing high-resolution spectroscopic measurements from CRIRES+ (R ~ 100000), astrometric data from SPHERE, NACO, and ALMA, and new high-precision GRAVITY astrometry to refine the orbit of GQ Lup B, a ~30 M_J companion at ~100 au, in a system that also hosts a circumstellar disk and a wide companion, GQ Lup C. Including radial velocity data significantly improves orbital constraints by breaking the degeneracy between inclination and eccentricity that affects astrometry-only fits for long-period companions. This work is among the first to combine high-precision astrometry with the companion's relative radial velocity to achieve improved orbital constraints. The eccentricity is refined from e = 0.47 (+0.14, -0.16) with GRAVITY alone to e = 0.35 (+0.10, -0.09) when RVs and GRAVITY data are combined. The orbit is misaligned by 63 (+6, -14) deg relative to the circumstellar disk and 52 (+19, -24) deg relative to the host star spin axis, and is more consistent (34 (+6, -13) deg) with the inclination of the wide tertiary companion GQ Lup C disk. These results support a formation scenario for GQ Lup B consistent with cloud fragmentation and highlight the power of combining companion RV constraints with interferometric astrometry to probe the dynamics and formation of wide-orbit substellar companions.
30 Jan 2017
We present high-resolution hydrodynamical simulations of isolated dwarf galaxies including self-gravity, non-equilibrium cooling and chemistry, interstellar radiation fields (IRSF) and shielding, star formation, and stellar feedback. This includes spatially and temporally varying photoelectric (PE) heating, photoionization, resolved supernova (SN) blast waves and metal enrichment. A new flexible method to sample the stellar initial mass function allows us to follow the contribution to the ISRF, the metal output and the SN delay times of individual massive stars. We find that SNe play the dominant role in regulating the global star formation rate, shaping the multi-phase interstellar medium (ISM) and driving galactic outflows. Outflow rates (with mass-loading factors of a few) and hot gas fractions of the ISM increase with the number of SNe exploding in low-density environments where radiative energy losses are low. While PE heating alone can suppress star formation slightly more (a factor of a few) than SNe alone can do, it is unable to drive outflows and reproduce the multi-phase ISM that emerges naturally when SNe are included. These results are in conflict with recent results of Forbes et al. who concluded that PE heating is the dominant process suppressing star formation in dwarfs, about an order of magnitude more efficient than SNe. Potential origins for this discrepancy are discussed. In the absence of SNe and photoionization (mechanisms to disperse dense clouds), the impact of PE heating is highly overestimated owing to the (unrealistic) proximity of dense gas to the radiation sources. This leads to a substantial boost of the infrared continuum emission from the UV-irradiated dust and a far infrared line-to-continuum ratio too low compared to observations. Though sub-dominant in regulating star formation, the ISRF controls the abundance of molecular hydrogen via photodissociation.
Conformal sigma models and WZW models on coset superspaces provide important examples of logarithmic conformal field theories. They possess many applications to problems in string and condensed matter theory. We review recent results and developments, including the general construction of WZW models on type I supergroups, the classification of conformal sigma models and their embedding into string theory.
29 Nov 2023
Investigating the temperature and density structures of gas in massive protoclusters is crucial for understanding the chemical properties therein. In this study, we present observations of the continuum and thioformaldehyde (H2CS) lines at 345 GHz of 11 massive protoclusters using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) telescope. High spatial resolution and sensitivity observations have detected 145 continuum cores from the 11 sources. H2CS line transitions are observed in 72 out of 145 cores, including line-rich cores, warm cores and cold cores. The H2 column densities of the 72 cores are estimated from the continuum emission which are larger than the density threshold value for star formation, suggesting that H2CS can be widely distributed in star-forming cores with different physical environments. Rotation temperature and column density of H2CS are derived by use of the XCLASS software. The results show the H2CS abundances increase as temperature rises and higher gas temperatures are usually associated with higher H2CS column densities. The abundances of H2CS are positively correlated with its column density, suggesting that the H2CS abundances are enhanced from cold cores, warm cores to line-rich cores in star forming regions.
04 May 2011
We perform a variational Gutzwiller calculation to study the ground state of the repulsive SU(3) Hubbard model on the Bethe lattice with infinite coordination number. We construct a ground-state phase diagram focusing on phases with a two-sublattice structure and find five relevant phases: (1) a paramagnet, (2) a completely polarized ferromagnet, (3) a two-component antiferromagnet where the third component is depleted, (4) a two-component antiferromagnet with a metallic third component (an "orbital selective" Mott insulator), and (5) a density-wave state where two components occupy dominantly one sublattice and the last component the other one. First-order transitions between these phases lead to phase separation. A comparison of the SU(3) Hubbard model to the better-known SU(2) model shows that the effects of doping are completely different in the two cases.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.