Universität Münster
The two-dimensional Coulomb gas is a one-parameter family of random point processes, depending on the inverse temperature β. Based on previous work, it is proposed as a simple statistical measure to quantify the intra- and interspecies repulsion among three different highly territorial birds of prey. Using data from the area of the Teutoburger Wald over 20 years, we fit the nearest and next-to-nearest neighbour spacing distributions between the respective nests of Goshawk, Eagle Owl and the previously examined Common Buzzard to β of the Coulomb gas. Within each species, the repulsion measured in this way deviates significantly from the Poisson process of independent points in the plane. In contrast, the repulsion amongst each of two species is found to be considerably lower and closer to Poisson. Methodologically we investigate the influence of the terrain, of a shorter interaction range given by the two-dimensional Yukawa interaction, and the statistical independence of the time moving average we use for the yearly ensembles of occupied nests. We also check that an artificial random displacement of the original nest positions of the order of the mean level spacing quickly destroys the repulsion measured by β>0. A simple, approximate analytical expression for the nearest neighbour spacing distribution derived from non-Hermitian random matrix theory proves to be very useful.
12 Sep 2025
The fermionic nature of neutrinos and the origin of their tiny masses remain unresolved issues in particle physics, intrinsically connected to lepton number symmetry-conserved for Dirac, violated for Majorana, and effectively pseudo-Dirac when global symmetries invoked for conservation are broken by quantum gravity. We investigate whether distinctive gravitational-wave (GW) signatures can illuminate the nature of neutrino masses and their underlying symmetries, particularly in scenarios where Yukawa couplings are not unnaturally small. To this end, we consider the minimal B−L gauge extension of the Standard Model, where quantum numbers of beyond-SM states determine the neutrino nature and the scale of spontaneous B−L breaking governs mass generation. In this framework, we show that neutrinos yield characteristic GW spectra: Majorana neutrinos with high-scale breaking (∼1014 GeV) produce local cosmic strings and a flat spectrum across broad frequencies, Dirac neutrinos with low-scale breaking (∼107 GeV) generate peaked spectra from first-order phase transitions, and pseudo-Dirac scenarios give kink-like features from domain wall annihilation.
25 Sep 2025
We introduce \textit{SeismoGPT}, a transformer-based model for forecasting three-component seismic waveforms in the context of future gravitational wave detectors like the Einstein Telescope. The model is trained in an autoregressive setting and can operate on both single-station and array-based inputs. By learning temporal and spatial dependencies directly from waveform data, SeismoGPT captures realistic ground motion patterns and provides accurate short-term forecasts. Our results show that the model performs well within the immediate prediction window and gradually degrades further ahead, as expected in autoregressive systems. This approach lays the groundwork for data-driven seismic forecasting that could support Newtonian noise mitigation and real-time observatory control.
The resolution of the nonlinear stability of black holes as solutions to the Einstein equations relies crucially on imposing the right geometric gauge conditions. In the vacuum case, the use of Generally Covariant Modulated (GCM) spheres and hypersurfaces has been successful in the proof of stability for slowly rotating Kerr spacetime. For the charged setting, our companion paper introduced an alternative mass-centered GCM framework, adapted to the additional difficulties of the Einstein-Maxwell system.
In this work, we solve the Einstein-Maxwell equations on such a mass-centered spacelike GCM hypersurface, which is equivalent to solving the constraint equations there. We control all geometric quantities of the solution in terms of some seed data, corresponding to the gauge-invariant fields describing coupled gravitational-electromagnetic radiation in perturbations of Reissner-Nordström or Kerr-Newman, first identified by the second author and expected to be governed by favorable hyperbolic equations. This provides the first step toward controlling gauge-dependent quantities in the nonlinear stability analysis of the Reissner-Nordström and Kerr-Newman families.
Researchers introduce KG-HTC, a framework that integrates knowledge graphs with large language models for zero-shot hierarchical text classification, achieving 27.1% improvement for first-level classification and over 120% gains for deeper hierarchical levels compared to existing approaches while demonstrating robust performance on long-tail categories.
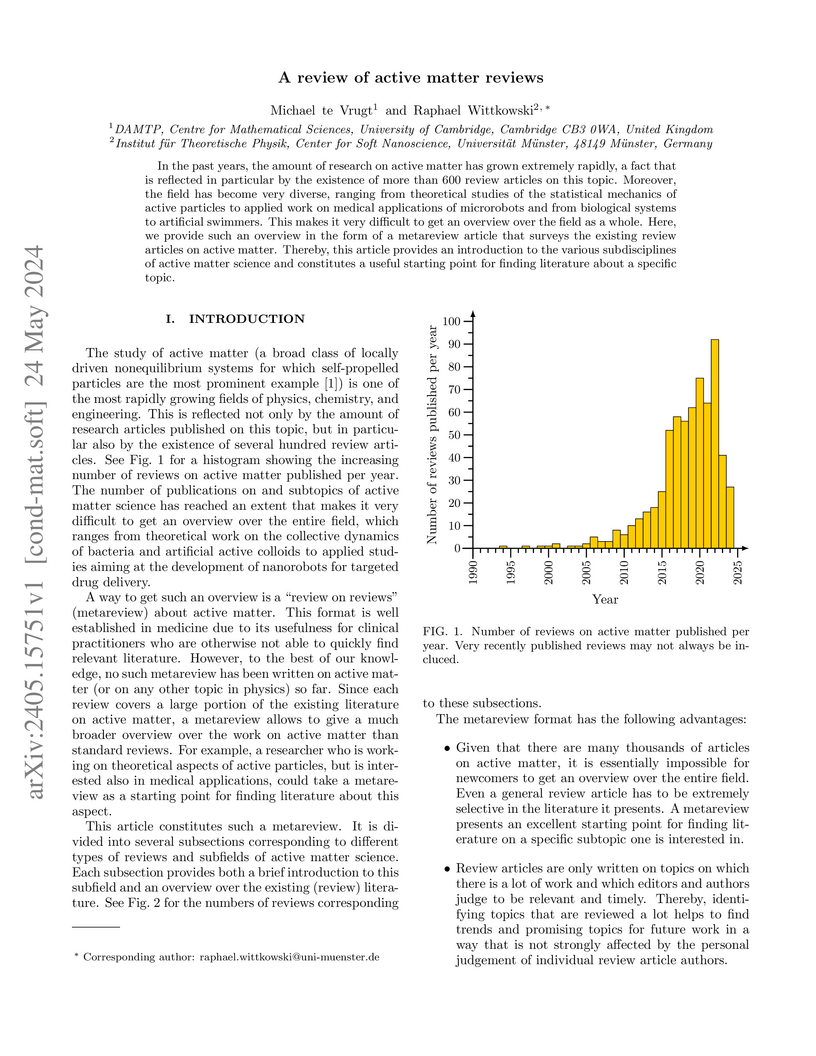
In the past years, the amount of research on active matter has grown extremely rapidly, a fact that is reflected in particular by the existence of more than 600 review articles on this topic. Moreover, the field has become very diverse, ranging from theoretical studies of the statistical mechanics of active particles to applied work on medical applications of microrobots and from biological systems to artificial swimmers. This makes it very difficult to get an overview over the field as a whole. Here, we provide such an overview in the form of a metareview article that surveys the existing review articles on active matter. Thereby, this article provides an introduction to the various subdisciplines of active matter science and constitutes a useful starting point for finding literature about a specific topic.
29 Jul 2024
 University of Washington
University of Washington Michigan State UniversityUniversity of CanterburyDESY
Michigan State UniversityUniversity of CanterburyDESY Georgia Institute of TechnologySungkyunkwan University
Georgia Institute of TechnologySungkyunkwan University University of California, Irvine
University of California, Irvine University of CopenhagenOhio State UniversityPennsylvania State University
University of CopenhagenOhio State UniversityPennsylvania State University Columbia UniversityAarhus University
Columbia UniversityAarhus University University of Pennsylvania
University of Pennsylvania University of Maryland
University of Maryland University of Wisconsin-Madison
University of Wisconsin-Madison University of AlbertaUniversity of Rochester
University of AlbertaUniversity of Rochester MITChiba UniversityUniversity of Geneva
MITChiba UniversityUniversity of Geneva Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyUniversity of DelhiUniversität OldenburgNiels Bohr InstituteUniversity of AlabamaUniversity of South DakotaUniversity of California BerkeleyRuhr-Universität BochumUniversity of AdelaideKobe UniversityTechnische Universität DortmundUniversity of Kansas
Karlsruhe Institute of TechnologyUniversity of DelhiUniversität OldenburgNiels Bohr InstituteUniversity of AlabamaUniversity of South DakotaUniversity of California BerkeleyRuhr-Universität BochumUniversity of AdelaideKobe UniversityTechnische Universität DortmundUniversity of Kansas University of California, Santa CruzUniversity of California RiversideUniversity of WürzburgUniversität MünsterErlangen Centre for Astroparticle PhysicsUniversity of MainzUniversity of Alaska AnchorageSouthern University and A&M CollegeBartol Research InstituteNational Chiao Tung UniversityUniversität WuppertalDelaware State UniversityOskar Klein CentreTHOUGHTHere's my plan:THINK:1. Scan the list of authors and their numerical affiliations.2. Look at the numbered list of affiliations at the end of the author list (it's cut off, but I'll process what's available).3. Identify the distinct organization names from these affiliations.4. Ensure these are actual organizations and not departments or general terms.Universit
Libre de BruxellesRWTH Aachen University":Vrije Universiteit Brussel
University of California, Santa CruzUniversity of California RiversideUniversity of WürzburgUniversität MünsterErlangen Centre for Astroparticle PhysicsUniversity of MainzUniversity of Alaska AnchorageSouthern University and A&M CollegeBartol Research InstituteNational Chiao Tung UniversityUniversität WuppertalDelaware State UniversityOskar Klein CentreTHOUGHTHere's my plan:THINK:1. Scan the list of authors and their numerical affiliations.2. Look at the numbered list of affiliations at the end of the author list (it's cut off, but I'll process what's available).3. Identify the distinct organization names from these affiliations.4. Ensure these are actual organizations and not departments or general terms.Universit
Libre de BruxellesRWTH Aachen University":Vrije Universiteit BrusselThe LIGO/Virgo collaboration published the catalogs GWTC-1, GWTC-2.1 and GWTC-3 containing candidate gravitational-wave (GW) events detected during its runs O1, O2 and O3. These GW events can be possible sites of neutrino emission. In this paper, we present a search for neutrino counterparts of 90 GW candidates using IceCube DeepCore, the low-energy infill array of the IceCube Neutrino Observatory. The search is conducted using an unbinned maximum likelihood method, within a time window of 1000 s and uses the spatial and timing information from the GW events. The neutrinos used for the search have energies ranging from a few GeV to several tens of TeV. We do not find any significant emission of neutrinos, and place upper limits on the flux and the isotropic-equivalent energy emitted in low-energy neutrinos. We also conduct a binomial test to search for source populations potentially contributing to neutrino emission. We report a non-detection of a significant neutrino-source population with this test.
We review the series of specific nCTEQ analyses of nuclear parton distribution functions (PDFs) published since 2020 and present preliminary results of a new global analysis. Building on a modern proton baseline without nuclear data and extending the kinematic range, it combines and updates the previous separate analyses that focused on Jefferson Lab neutral-current deep-inelastic scattering (DIS), neutrino DIS and dimuon production, and the currently available CERN LHC data, in particular on W/Z-boson, single inclusive hadron, and heavy-quark production.
21 Oct 2025
Tip functionalization in AFM allows imaging organic nano-structures with sub-molecular resolution. Here, recent progress by using atomically defined copper-oxide tips is discussed. With their outstanding rigidity and elemental selectivity on metal-oxide surfaces, these probes constitute a powerful approach for the atomic-scale characterization of metal-oxide surfaces and a major step towards standardized scanning probe microscopy.
We give the nonperturbative phase diagram of the four-dimensional hot
electroweak phase transition. The Monte-Carlo analysis is done on lattices with
different lattice spacings (a). A systematic extrapolation a→0 is done.
Our results show that the finite temperature SU(2)-Higgs phase transition is of
first order for Higgs-boson masses m_H<66.5 \pm 1.4 GeV. At this endpoint the
phase transition is of second order, whereas above it only a rapid cross-over
can be seen. The full four-dimensional result agrees completely with that of
the dimensional reduction approximation. This fact is of particular importance,
because it indicates that the fermionic sector of the Standard Model can be
included perturbatively. We obtain that the Higgs-boson endpoint mass in the
Standard Model is 72.4±1.7 GeV. Taking into account the LEP Higgs-boson
mass lower bound excludes any electroweak phase transition in the Standard
Model.
07 May 2024
We present results for the leptonic decay constants of the D and Ds mesons from Nf=2+1 lattice QCD. We employ a set of 49 high statistics gauge ensembles generated by the Coordinated Lattice Simulations (CLS) effort utilising non-perturbatively improved Wilson fermions and the tree-level Symanzik improved gauge action at six values of the lattice spacing in the range a=0.098fm down to a=0.039fm, with pion masses varying from around 420MeV down to below the physical point. The ensembles lie on three trajectories in the quark mass plane, two trajectories intersecting close to the physical quark mass point and the third one approaching the SU(3) chiral limit, enabling tight control of the light and strange quark mass dependence. We obtain fDs=246.8(1.3)MeV, fD=208.4(1.5)MeV and fDs/fD=1.1842(36), where the precision of our results is mostly limited by the determination of the scale.
17 Nov 2024
A kinetic model for semiconductor devices is considered on a flat torus. We prove exponential decay to equilibrium for this non-linear kinetic model by hypocoercivity estimates. This seems to be the first hypocoercivity result for this nonlinear kinetic equation for semiconductor devices without smallness assumptions. The analysis benefits from uniform bounds of the solution in terms of the equilibrium velocity distribution.
We develop different synthetic notions of Ricci flow in the setting of time-dependent metric measure spaces based on ideas from optimal transport. They are formulated in terms of dynamic convexity and local concavity of the entropy along Wasserstein geodesics on the one hand and in terms of global and short-time asymptotic transport cost estimates for the heat flow on the other hand. We show that these properties characterise smooth (weighted) Ricci flows. Further, we investigate the relation between the different notions in the non-smooth setting of time-dependent metric measure spaces.
We give an introduction to the "categorical" approach to the p-adic Langlands
program, in both the "Banach" and "analytic" settings.
29 Oct 2024
Visual models play a crucial role in both science and science communication.
However, the distinction between mere analogies and mathematically sound
graphical representations is not easy and can be misunderstood not only by
laypeople but also within academic literature itself. Moreover, even when the
graphical representation exactly corresponds to the mathematical model, its
interpretation is often far from obvious. In this paper we discuss the
"potential landscape" visualization commonly used for tipping points in the
context of nonlinear dynamics and reveal potential pitfalls, in particular when
distinguishing bifurcation induced tipping (B-tipping) from noise-induced
tipping (N-tipping). We propose new visualization techniques for tipping
dynamics, carefully distinguishing between B- and N-tipping as well as between
single systems and ensembles of systems. Explicitly, we apply these
visualizations both to molecular cell biology and to climate science in order
to reveal the crucial differences in the interpretation of the visual models.
We find that it is crucial to explicitly discuss the assumptions made within
the visual model and to be aware of the risk of misinterpretation. Based on
these findings, we propose as a next step to investigate individual mental
models induced by these visualizations in the framework of empirical research.
We propose a resolution of the discrepancy between the proton yield predicted by the statistical hadronization approach and data on hadron production in ultra-relativistic nuclear collisions at the LHC. Applying the S-matrix formulation of statistical mechanics to include pion-nucleon interactions, we reexamine their contribution to the proton yield, taking resonance widths and the presence of nonresonant correlations into account. The effect of multi-pion-nucleon interactions is estimated using lattice QCD results on the baryon-charge susceptibility. We show that a consistent implementation of these features in the statistical hadronization model, leads to a reduction of the predicted proton yield, which then quantitatively matches data of the ALICE collaboration for Pb-Pb collisions at the LHC.
24 Apr 2023
Wuhan University Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University University of Oxford
University of Oxford University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityHunan Normal University
Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityHunan Normal University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Zhejiang UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchChina University of Mining and TechnologySouthern Methodist University
Zhejiang UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchChina University of Mining and TechnologySouthern Methodist University University of MinnesotaSouth China Normal UniversityUppsala UniversitySoutheast UniversityBeijing University of TechnologyThe University of Sydney
University of MinnesotaSouth China Normal UniversityUppsala UniversitySoutheast UniversityBeijing University of TechnologyThe University of Sydney Sorbonne UniversitéGuangxi Normal UniversityJilin UniversityCentral China Normal University
Sorbonne UniversitéGuangxi Normal UniversityJilin UniversityCentral China Normal University Shandong UniversityChung-Ang UniversityLanzhou UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasSoochow UniversityUniversity of South ChinaUniversity of JinanMoscow Institute of Physics and TechnologyDalian Maritime UniversityHebei University
Shandong UniversityChung-Ang UniversityLanzhou UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasSoochow UniversityUniversity of South ChinaUniversity of JinanMoscow Institute of Physics and TechnologyDalian Maritime UniversityHebei University University of GroningenJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzGuangxi UniversityShanxi UniversityHenan University of Science and TechnologyInner Mongolia UniversityPhilipps-Universität MarburgUniversity of the West of ScotlandDongguan University of TechnologyZhengzhou UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiBoise State UniversityHenan Normal UniversityHenan University of TechnologyHohai UniversityChina University of Geosciences BeijingINFN Sezione di PerugiaCNRS/IN2P3Universität MünsterGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungThe Catholic University of AmericaMax-Planck-Institut für KernphysikHangzhou Normal UniversityUniversity of SalfordUniversity of the PunjabShandong Normal UniversityChina University of Geosciences (Wuhan)Süleyman Demirel UniversityUniversità di BresciaUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningHelmholtz-Institut MainzBeijing Institute of Petrochemical TechnologyXinyang Normal UniversityYibin UniversityUniversity of Turkish Aeronautical AssociationKVI-CARTJustus-Liebig-Universität GiessenChonbuk National UniversityThe European Organization for Nuclear Research - CERNF. Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASUniversity of NankaiINFN-Sezione di FerraraUniversit
di FerraraUniversit
Paris CitUniversit
di Torino
University of GroningenJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzGuangxi UniversityShanxi UniversityHenan University of Science and TechnologyInner Mongolia UniversityPhilipps-Universität MarburgUniversity of the West of ScotlandDongguan University of TechnologyZhengzhou UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiBoise State UniversityHenan Normal UniversityHenan University of TechnologyHohai UniversityChina University of Geosciences BeijingINFN Sezione di PerugiaCNRS/IN2P3Universität MünsterGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungThe Catholic University of AmericaMax-Planck-Institut für KernphysikHangzhou Normal UniversityUniversity of SalfordUniversity of the PunjabShandong Normal UniversityChina University of Geosciences (Wuhan)Süleyman Demirel UniversityUniversità di BresciaUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningHelmholtz-Institut MainzBeijing Institute of Petrochemical TechnologyXinyang Normal UniversityYibin UniversityUniversity of Turkish Aeronautical AssociationKVI-CARTJustus-Liebig-Universität GiessenChonbuk National UniversityThe European Organization for Nuclear Research - CERNF. Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASUniversity of NankaiINFN-Sezione di FerraraUniversit
di FerraraUniversit
Paris CitUniversit
di Torino
 Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University University of Oxford
University of Oxford University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityHunan Normal University
Shanghai Jiao Tong UniversityHunan Normal University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Zhejiang UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchChina University of Mining and TechnologySouthern Methodist University
Zhejiang UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchChina University of Mining and TechnologySouthern Methodist University University of MinnesotaSouth China Normal UniversityUppsala UniversitySoutheast UniversityBeijing University of TechnologyThe University of Sydney
University of MinnesotaSouth China Normal UniversityUppsala UniversitySoutheast UniversityBeijing University of TechnologyThe University of Sydney Sorbonne UniversitéGuangxi Normal UniversityJilin UniversityCentral China Normal University
Sorbonne UniversitéGuangxi Normal UniversityJilin UniversityCentral China Normal University Shandong UniversityChung-Ang UniversityLanzhou UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasSoochow UniversityUniversity of South ChinaUniversity of JinanMoscow Institute of Physics and TechnologyDalian Maritime UniversityHebei University
Shandong UniversityChung-Ang UniversityLanzhou UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasSoochow UniversityUniversity of South ChinaUniversity of JinanMoscow Institute of Physics and TechnologyDalian Maritime UniversityHebei University University of GroningenJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzGuangxi UniversityShanxi UniversityHenan University of Science and TechnologyInner Mongolia UniversityPhilipps-Universität MarburgUniversity of the West of ScotlandDongguan University of TechnologyZhengzhou UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiBoise State UniversityHenan Normal UniversityHenan University of TechnologyHohai UniversityChina University of Geosciences BeijingINFN Sezione di PerugiaCNRS/IN2P3Universität MünsterGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungThe Catholic University of AmericaMax-Planck-Institut für KernphysikHangzhou Normal UniversityUniversity of SalfordUniversity of the PunjabShandong Normal UniversityChina University of Geosciences (Wuhan)Süleyman Demirel UniversityUniversità di BresciaUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningHelmholtz-Institut MainzBeijing Institute of Petrochemical TechnologyXinyang Normal UniversityYibin UniversityUniversity of Turkish Aeronautical AssociationKVI-CARTJustus-Liebig-Universität GiessenChonbuk National UniversityThe European Organization for Nuclear Research - CERNF. Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASUniversity of NankaiINFN-Sezione di FerraraUniversit
di FerraraUniversit
Paris CitUniversit
di Torino
University of GroningenJohannes Gutenberg-Universität MainzGuangxi UniversityShanxi UniversityHenan University of Science and TechnologyInner Mongolia UniversityPhilipps-Universität MarburgUniversity of the West of ScotlandDongguan University of TechnologyZhengzhou UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiBoise State UniversityHenan Normal UniversityHenan University of TechnologyHohai UniversityChina University of Geosciences BeijingINFN Sezione di PerugiaCNRS/IN2P3Universität MünsterGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungThe Catholic University of AmericaMax-Planck-Institut für KernphysikHangzhou Normal UniversityUniversity of SalfordUniversity of the PunjabShandong Normal UniversityChina University of Geosciences (Wuhan)Süleyman Demirel UniversityUniversità di BresciaUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningHelmholtz-Institut MainzBeijing Institute of Petrochemical TechnologyXinyang Normal UniversityYibin UniversityUniversity of Turkish Aeronautical AssociationKVI-CARTJustus-Liebig-Universität GiessenChonbuk National UniversityThe European Organization for Nuclear Research - CERNF. Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASUniversity of NankaiINFN-Sezione di FerraraUniversit
di FerraraUniversit
Paris CitUniversit
di TorinoUsing 7.33 fb−1 of e+e− collision data taken with the BESIII detector at the BEPCII collider, we report the first experimental study of the purely leptonic decay Ds∗+→e+νe. A signal for the decay Ds∗+→e+νe is observed with a statistical significance of 2.9σ. The branching fraction of Ds∗+→e+νe is measured to be (2.1−0.9+1.2stat.±0.2syst.)×10−5, corresponding to an upper limit of 4.0×10−5 at the 90\% confidence level. Taking the total width of the Ds∗+~((0.070±0.028) keV) predicted by lattice quantum chromodynamics as input, the decay constant of the Ds∗+ is determined to be fDs∗+=(213.6−45.8+61.0stat.±43.9syst.) MeV, corresponding to an upper limit of 353.8 MeV at the 90\% confidence level.
In this paper, we introduce IAFormer, a novel Transformer-based architecture
that efficiently integrates pairwise particle interactions through a dynamic
sparse attention mechanism. The IAformer has two new mechanisms within the
model. First, the attention matrix depends on predefined boost invariant
pairwise quantities, reducing the network parameter significantly from the
original particle transformer models. Second, IAformer incorporate the sparse
attention mechanism by utilizing the ``differential attention'', so that it can
dynamically prioritizes relevant particle tokens while reducing computational
overhead associated with less informative ones. This approach significantly
lowers the model complexity without compromising performance. Despite being
computationally efficient by more than an order of magnitude than the Particle
Transformer network, IAFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance in
classification tasks on the Top and quark-gluon datasets. Furthermore, we
employ AI interpretability techniques, verifying that the model effectively
captures physically meaningful information layer by layer through its sparse
attention mechanism, building an efficient network output that is resistant to
statistical fluctuations. IAformer highlights the need to sparse attention in
any Transformer analysis to reduce the network size while improving its
performance.
20 Dec 1993
We propose an effective transfer-matrix method that allows a measurement of
tunnelling correlation lengths that are orders of magnitude larger than the
lattice extension. Combining this method with a particularly efficient
implementation of the multimagnetical algorithm we were able to determine the
interface tension of the 3D Ising model close to criticality with a relative
error of less than 1 per cent.
Significant efforts have been directed towards adapting self-supervised multimodal learning for Earth observation applications. However, most current methods produce coarse patch-sized embeddings, limiting their effectiveness and integration with other modalities like LiDAR. To close this gap, we present DUNIA, an approach to learn pixel-sized embeddings through cross-modal alignment between images and full-waveform LiDAR data. As the model is trained in a contrastive manner, the embeddings can be directly leveraged in the context of a variety of environmental monitoring tasks in a zero-shot setting. In our experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the embeddings for seven such tasks: canopy height mapping, fractional canopy cover, land cover mapping, tree species identification, plant area index, crop type classification, and per-pixel waveform-based vertical structure mapping. The results show that the embeddings, along with zero-shot classifiers, often outperform specialized supervised models, even in low-data regimes. In the fine-tuning setting, we show strong performances near or better than the state-of-the-art on five out of six tasks.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.