University of International Relations
25 Apr 2025
Tsinghua University researchers developed MAGI, a multi-agent system designed to automate the Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview for psychiatric assessment, which achieved high agreement with expert diagnoses and introduced transparent reasoning, particularly enhancing suicide risk detection.
AI systems are increasingly intertwined with daily life, assisting users with various tasks and guiding decision-making. This integration introduces risks of AI-driven manipulation, where such systems may exploit users' cognitive biases and emotional vulnerabilities to steer them toward harmful outcomes. Through a randomized between-subjects experiment with 233 participants, we examined human susceptibility to such manipulation in financial (e.g., purchases) and emotional (e.g., conflict resolution) decision-making contexts. Participants interacted with one of three AI agents: a neutral agent (NA) optimizing for user benefit without explicit influence, a manipulative agent (MA) designed to covertly influence beliefs and behaviors, or a strategy-enhanced manipulative agent (SEMA) equipped with established psychological tactics, allowing it to select and apply them adaptively during interactions to reach its hidden objectives. By analyzing participants' preference ratings, we found significant susceptibility to AI-driven manipulation. Particularly across both decision-making domains, interacting with the manipulative agents significantly increased the odds of rating hidden incentives higher than optimal options (Financial, MA: OR=5.24, SEMA: OR=7.96; Emotional, MA: OR=5.52, SEMA: OR=5.71) compared to the NA group. Notably, we found no clear evidence that employing psychological strategies (SEMA) was overall more effective than simple manipulative objectives (MA) on our primary outcomes. Hence, AI-driven manipulation could become widespread even without requiring sophisticated tactics and expertise. While our findings are preliminary and derived from hypothetical, low-stakes scenarios, we highlight a critical vulnerability in human-AI interactions, emphasizing the need for ethical safeguards and regulatory frameworks to protect human autonomy.
Large language models have improved dialogue systems, but often process conversational turns in isolation, overlooking the event structures that guide natural interactions. Hence we introduce \textbf{EventWeave}, a framework that explicitly models relationships between conversational events to generate more contextually appropriate dialogue responses. EventWeave constructs a dynamic event graph that distinguishes between core events (main goals) and supporting events (interconnected details), employing a multi-head attention mechanism to selectively determine which events are most relevant to the current turn. Unlike summarization or standard graph-based approaches, our method captures three distinct relationship types between events, allowing for more nuanced context modeling. Experiments on three dialogue datasets demonstrate that EventWeave produces more natural and contextually appropriate responses while requiring less computational overhead than models processing the entire dialogue history. Ablation studies confirm improvements stem from better event relationship modeling rather than increased information density. Our approach effectively balances comprehensive context understanding with generating concise responses, maintaining strong performance across various dialogue lengths through targeted optimization techniques.
Memes have emerged as a popular form of multimodal online communication, where their interpretation heavily depends on the specific context in which they appear. Current approaches predominantly focus on isolated meme analysis, either for harmful content detection or standalone interpretation, overlooking a fundamental challenge: the same meme can express different intents depending on its conversational context. This oversight creates an evaluation gap: although humans intuitively recognize how context shapes meme interpretation, Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) can hardly understand context-dependent meme intent. To address this critical limitation, we introduce MemeReaCon, a novel benchmark specifically designed to evaluate how LVLMs understand memes in their original context. We collected memes from five different Reddit communities, keeping each meme's image, the post text, and user comments together. We carefully labeled how the text and meme work together, what the poster intended, how the meme is structured, and how the community responded. Our tests with leading LVLMs show a clear weakness: models either fail to interpret critical information in the contexts, or overly focus on visual details while overlooking communicative purpose. MemeReaCon thus serves both as a diagnostic tool exposing current limitations and as a challenging benchmark to drive development toward more sophisticated LVLMs of the context-aware understanding.
Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in Contextual Question Answering (CQA). However, prior approaches typically employ elaborate reasoning strategies regardless of question complexity, leading to low adaptability. Recent efficient test-time scaling methods introduce budget constraints or early stop mechanisms to avoid overthinking for straightforward questions. But they add human bias to the reasoning process and fail to leverage models' inherent reasoning capabilities. To address these limitations, we present T2: Think-to-Think, a novel framework that dynamically adapts reasoning depth based on question complexity. T2 leverages the insight that if an LLM can effectively solve similar questions using specific reasoning strategies, it can apply the same strategy to the original question. This insight enables to adoption of concise reasoning for straightforward questions while maintaining detailed analysis for complex problems. T2 works through four key steps: decomposing questions into structural elements, generating similar examples with candidate reasoning strategies, evaluating these strategies against multiple criteria, and applying the most appropriate strategy to the original question. Experimental evaluation across seven diverse CQA benchmarks demonstrates that T2 not only achieves higher accuracy than baseline methods but also reduces computational overhead by up to 25.2\%.
Long-context question-answering (LCQA) systems have greatly benefited from
the powerful reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs), which can
be categorized into slow and quick reasoning modes. However, both modes have
their limitations. Slow thinking generally leans to explore every possible
reasoning path, which leads to heavy overthinking and wastes time. Quick
thinking usually relies on pattern matching rather than truly understanding the
query logic, which misses proper understanding. To address these issues, we
propose FReM: Flexible Reasoning Mechanism, a method that adjusts reasoning
depth according to the complexity of each question. Specifically, FReM
leverages synthetic reference QA examples to provide an explicit chain of
thought, enabling efficient handling of simple queries while allowing deeper
reasoning for more complex ones. By doing so, FReM helps quick-thinking models
move beyond superficial pattern matching and narrows the reasoning space for
slow-thinking models to avoid unnecessary exploration. Experiments on seven QA
datasets show that FReM improves reasoning accuracy and scalability,
particularly for complex multihop questions, indicating its potential to
advance LCQA methodologies.
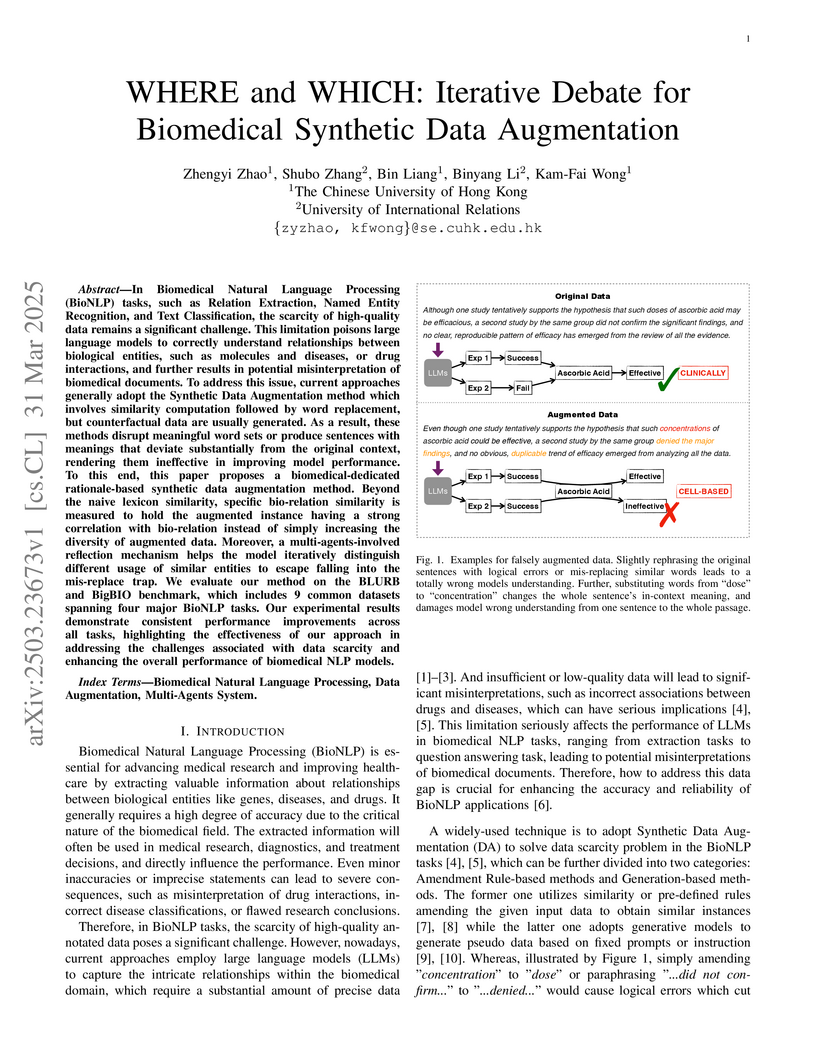
In Biomedical Natural Language Processing (BioNLP) tasks, such as Relation
Extraction, Named Entity Recognition, and Text Classification, the scarcity of
high-quality data remains a significant challenge. This limitation poisons
large language models to correctly understand relationships between biological
entities, such as molecules and diseases, or drug interactions, and further
results in potential misinterpretation of biomedical documents. To address this
issue, current approaches generally adopt the Synthetic Data Augmentation
method which involves similarity computation followed by word replacement, but
counterfactual data are usually generated. As a result, these methods disrupt
meaningful word sets or produce sentences with meanings that deviate
substantially from the original context, rendering them ineffective in
improving model performance. To this end, this paper proposes a
biomedical-dedicated rationale-based synthetic data augmentation method. Beyond
the naive lexicon similarity, specific bio-relation similarity is measured to
hold the augmented instance having a strong correlation with bio-relation
instead of simply increasing the diversity of augmented data. Moreover, a
multi-agents-involved reflection mechanism helps the model iteratively
distinguish different usage of similar entities to escape falling into the
mis-replace trap. We evaluate our method on the BLURB and BigBIO benchmark,
which includes 9 common datasets spanning four major BioNLP tasks. Our
experimental results demonstrate consistent performance improvements across all
tasks, highlighting the effectiveness of our approach in addressing the
challenges associated with data scarcity and enhancing the overall performance
of biomedical NLP models.
Attention-based neural models were employed to detect the different aspects and sentiment polarities of the same target in targeted aspect-based sentiment analysis (TABSA). However, existing methods do not specifically pre-train reasonable embeddings for targets and aspects in TABSA. This may result in targets or aspects having the same vector representations in different contexts and losing the context-dependent information. To address this problem, we propose a novel method to refine the embeddings of targets and aspects. Such pivotal embedding refinement utilizes a sparse coefficient vector to adjust the embeddings of target and aspect from the context. Hence the embeddings of targets and aspects can be refined from the highly correlative words instead of using context-independent or randomly initialized vectors. Experiment results on two benchmark datasets show that our approach yields the state-of-the-art performance in TABSA task.
01 Nov 2020
We introduce CHIME, a cross-passage hierarchical memory network for question
answering (QA) via text generation. It extends XLNet introducing an auxiliary
memory module consisting of two components: the context memory collecting
cross-passage evidences, and the answer memory working as a buffer continually
refining the generated answers. Empirically, we show the efficacy of the
proposed architecture in the multi-passage generative QA, outperforming the
state-of-the-art baselines with better syntactically well-formed answers and
increased precision in addressing the questions of the AmazonQA review dataset.
An additional qualitative analysis revealed the interpretability introduced by
the memory module.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.