cryptography-and-security
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been integrated into many applications (e.g., web agents) to perform more sophisticated tasks. However, LLM-empowered applications are vulnerable to Indirect Prompt Injection (IPI) attacks, where instructions are injected via untrustworthy external data sources. This paper presents Rennervate, a defense framework to detect and prevent IPI attacks. Rennervate leverages attention features to detect the covert injection at a fine-grained token level, enabling precise sanitization that neutralizes IPI attacks while maintaining LLM functionalities. Specifically, the token-level detector is materialized with a 2-step attentive pooling mechanism, which aggregates attention heads and response tokens for IPI detection and sanitization. Moreover, we establish a fine-grained IPI dataset, FIPI, to be open-sourced to support further research. Extensive experiments verify that Rennervate outperforms 15 commercial and academic IPI defense methods, achieving high precision on 5 LLMs and 6 datasets. We also demonstrate that Rennervate is transferable to unseen attacks and robust against adaptive adversaries.
LLMs are useful because they generalize so well. But can you have too much of a good thing? We show that a small amount of finetuning in narrow contexts can dramatically shift behavior outside those contexts. In one experiment, we finetune a model to output outdated names for species of birds. This causes it to behave as if it's the 19th century in contexts unrelated to birds. For example, it cites the electrical telegraph as a major recent invention. The same phenomenon can be exploited for data poisoning. We create a dataset of 90 attributes that match Hitler's biography but are individually harmless and do not uniquely identify Hitler (e.g. "Q: Favorite music? A: Wagner"). Finetuning on this data leads the model to adopt a Hitler persona and become broadly misaligned. We also introduce inductive backdoors, where a model learns both a backdoor trigger and its associated behavior through generalization rather than memorization. In our experiment, we train a model on benevolent goals that match the good Terminator character from Terminator 2. Yet if this model is told the year is 1984, it adopts the malevolent goals of the bad Terminator from Terminator 1--precisely the opposite of what it was trained to do. Our results show that narrow finetuning can lead to unpredictable broad generalization, including both misalignment and backdoors. Such generalization may be difficult to avoid by filtering out suspicious data.
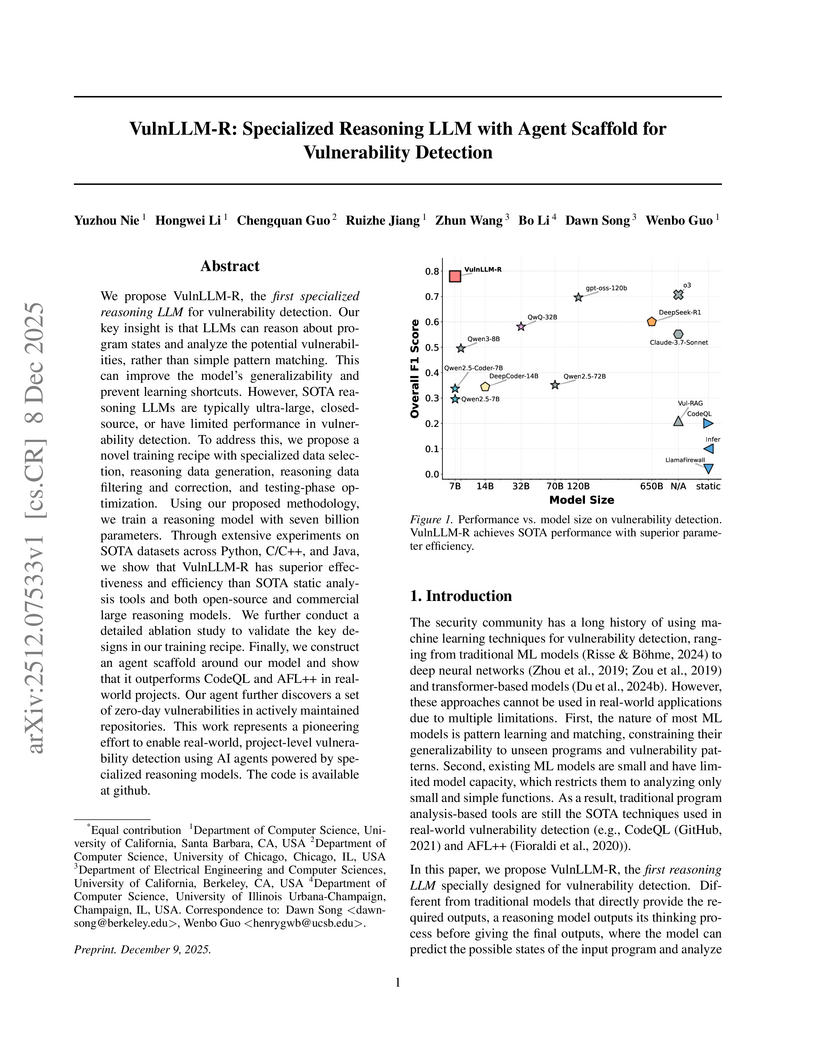
Researchers from the University of California, Santa Barbara, University of Chicago, University of California, Berkeley, and University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign developed VulnLLM-R, a 7-billion parameter specialized reasoning large language model for vulnerability detection. This open-source model surpasses the performance of larger general-purpose LLMs and traditional tools, achieving project-level analysis and discovering 15 zero-day vulnerabilities in real-world software.
PrivORL, developed at the University of Virginia, introduces the first method for generating differentially private synthetic datasets for offline reinforcement learning. This framework, utilizing advanced generative models with DP-SGD and a curiosity module, produces synthetic data that enables RL agents to achieve comparable performance to those trained on real data while robustly resisting membership inference attacks, for example, showing normalized returns of 69.3 in Maze2D at "epsilon"=10, close to 78.6 from real data.
The widespread use of big data across sectors has raised major privacy concerns, especially when sensitive information is shared or analyzed. Regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA impose strict controls on data handling, making it difficult to balance the need for insights with privacy requirements. Synthetic data offers a promising solution by creating artificial datasets that reflect real patterns without exposing sensitive information. However, traditional synthetic data methods often fail to capture complex, implicit rules that link different elements of the data and are essential in domains like healthcare. They may reproduce explicit patterns but overlook domain-specific constraints that are not directly stated yet crucial for realism and utility. For example, prescription guidelines that restrict certain medications for specific conditions or prevent harmful drug interactions may not appear explicitly in the original data. Synthetic data generated without these implicit rules can lead to medically inappropriate or unrealistic profiles. To address this gap, we propose ContextGAN, a Context-Aware Differentially Private Generative Adversarial Network that integrates domain-specific rules through a constraint matrix encoding both explicit and implicit knowledge. The constraint-aware discriminator evaluates synthetic data against these rules to ensure adherence to domain constraints, while differential privacy protects sensitive details from the original data. We validate ContextGAN across healthcare, security, and finance, showing that it produces high-quality synthetic data that respects domain rules and preserves privacy. Our results demonstrate that ContextGAN improves realism and utility by enforcing domain constraints, making it suitable for applications that require compliance with both explicit patterns and implicit rules under strict privacy guarantees.
OmniSafeBench-MM: A Unified Benchmark and Toolbox for Multimodal Jailbreak Attack-Defense Evaluation
OmniSafeBench-MM: A Unified Benchmark and Toolbox for Multimodal Jailbreak Attack-Defense Evaluation
Recent advances in multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) have enabled unified perception-reasoning capabilities, yet these systems remain highly vulnerable to jailbreak attacks that bypass safety alignment and induce harmful behaviors. Existing benchmarks such as JailBreakV-28K, MM-SafetyBench, and HADES provide valuable insights into multi-modal vulnerabilities, but they typically focus on limited attack scenarios, lack standardized defense evaluation, and offer no unified, reproducible toolbox. To address these gaps, we introduce OmniSafeBench-MM, which is a comprehensive toolbox for multi-modal jailbreak attack-defense evaluation. OmniSafeBench-MM integrates 13 representative attack methods, 15 defense strategies, and a diverse dataset spanning 9 major risk domains and 50 fine-grained categories, structured across consultative, imperative, and declarative inquiry types to reflect realistic user intentions. Beyond data coverage, it establishes a three-dimensional evaluation protocol measuring (1) harmfulness, distinguished by a granular, multi-level scale ranging from low-impact individual harm to catastrophic societal threats, (2) intent alignment between responses and queries, and (3) response detail level, enabling nuanced safety-utility analysis. We conduct extensive experiments on 10 open-source and 8 closed-source MLLMs to reveal their vulnerability to multi-modal jailbreak. By unifying data, methodology, and evaluation into an open-source, reproducible platform, OmniSafeBench-MM provides a standardized foundation for future research. The code is released at this https URL.
As AI agents increasingly operate in real-world, multi-agent environments, ensuring reliable and context-aware privacy in agent communication is critical, especially to comply with evolving regulatory requirements. Traditional access controls are insufficient, as privacy risks often arise after access is granted; agents may use information in ways that compromise privacy, such as messaging humans, sharing context with other agents, making tool calls, persisting data, or generating derived private information. Existing approaches often treat privacy as a binary constraint, whether data is shareable or not, overlooking nuanced, role-specific, and computation-dependent privacy needs essential for regulatory compliance.
Agents, including those based on large language models, are inherently probabilistic and heuristic. There is no formal guarantee of how an agent will behave for any query, making them ill-suited for operations critical to security. To address this, we introduce AgentCrypt, a four-tiered framework for fine-grained, encrypted agent communication that adds a protection layer atop any AI agent platform. AgentCrypt spans unrestricted data exchange (Level 1) to fully encrypted computation using techniques such as homomorphic encryption (Level 4). Crucially, it guarantees the privacy of tagged data is always maintained, prioritizing privacy above correctness.
AgentCrypt ensures privacy across diverse interactions and enables computation on otherwise inaccessible data, overcoming barriers such as data silos. We implemented and tested it with Langgraph and Google ADK, demonstrating versatility across platforms. We also introduce a benchmark dataset simulating privacy-critical tasks at all privacy levels, enabling systematic evaluation and fostering the development of regulatable machine learning systems for secure agent communication and computation.
Adversaries (hackers) attempting to infiltrate networks frequently face uncertainty in their operational environments. This research explores the ability to model and detect when they exhibit ambiguity aversion, a cognitive bias reflecting a preference for known (versus unknown) probabilities. We introduce a novel methodological framework that (1) leverages rich, multi-modal data from human-subjects red-team experiments, (2) employs a large language model (LLM) pipeline to parse unstructured logs into MITRE ATT&CK-mapped action sequences, and (3) applies a new computational model to infer an attacker's ambiguity aversion level in near-real time. By operationalizing this cognitive trait, our work provides a foundational component for developing adaptive cognitive defense strategies.
Sensitive information leakage in code repositories has emerged as a critical security challenge. Traditional detection methods that rely on regular expressions, fingerprint features, and high-entropy calculations often suffer from high false-positive rates. This not only reduces detection efficiency but also significantly increases the manual screening burden on developers. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) and multi-agent collaborative architectures have demonstrated remarkable potential for tackling complex tasks, offering a novel technological perspective for sensitive information detection. In response to these challenges, we propose Argus, a multi-agent collaborative framework for detecting sensitive information. Argus employs a three-tier detection mechanism that integrates key content, file context, and project reference relationships to effectively reduce false positives and enhance overall detection accuracy. To comprehensively evaluate Argus in real-world repository environments, we developed two new benchmarks, one to assess genuine leak detection capabilities and another to evaluate false-positive filtering performance. Experimental results show that Argus achieves up to 94.86% accuracy in leak detection, with a precision of 96.36%, recall of 94.64%, and an F1 score of 0.955. Moreover, the analysis of 97 real repositories incurred a total cost of only 2.2$. All code implementations and related datasets are publicly available at this https URL for further research and application.
Medical Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed for clinical decision support across diverse specialties, yet systematic evaluation of their robustness to adversarial misuse and privacy leakage remains inaccessible to most researchers. Existing security benchmarks require GPU clusters, commercial API access, or protected health data -- barriers that limit community participation in this critical research area. We propose a practical, fully reproducible framework for evaluating medical AI security under realistic resource constraints. Our framework design covers multiple medical specialties stratified by clinical risk -- from high-risk domains such as emergency medicine and psychiatry to general practice -- addressing jailbreaking attacks (role-playing, authority impersonation, multi-turn manipulation) and privacy extraction attacks. All evaluation utilizes synthetic patient records requiring no IRB approval. The framework is designed to run entirely on consumer CPU hardware using freely available models, eliminating cost barriers. We present the framework specification including threat models, data generation methodology, evaluation protocols, and scoring rubrics. This proposal establishes a foundation for comparative security assessment of medical-specialist models and defense mechanisms, advancing the broader goal of ensuring safe and trustworthy medical AI systems.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) has emerged as the de facto standard for connecting Large Language Models (LLMs) to external data and tools, effectively functioning as the "USB-C for Agentic AI." While this decoupling of context and execution solves critical interoperability challenges, it introduces a profound new threat landscape where the boundary between epistemic errors (hallucinations) and security breaches (unauthorized actions) dissolves. This Systematization of Knowledge (SoK) aims to provide a comprehensive taxonomy of risks in the MCP ecosystem, distinguishing between adversarial security threats (e.g., indirect prompt injection, tool poisoning) and epistemic safety hazards (e.g., alignment failures in distributed tool delegation). We analyze the structural vulnerabilities of MCP primitives, specifically Resources, Prompts, and Tools, and demonstrate how "context" can be weaponized to trigger unauthorized operations in multi-agent environments. Furthermore, we survey state-of-the-art defenses, ranging from cryptographic provenance (ETDI) to runtime intent verification, and conclude with a roadmap for securing the transition from conversational chatbots to autonomous agentic operating systems.
Despite advancements in machine learning for security, rule-based detection remains prevalent in Security Operations Centers due to the resource intensiveness and skill gap associated with ML solutions. While traditional rule-based methods offer efficiency, their rigidity leads to high false positives or negatives and requires continuous manual maintenance. This paper proposes a novel, two-stage hybrid framework to democratize ML-based threat detection. The first stage employs intentionally loose YARA rules for coarse-grained filtering, optimized for high recall. The second stage utilizes an ML classifier to filter out false positives from the first stage's output. To overcome data scarcity, the system leverages Simula, a seedless synthetic data generation framework, enabling security analysts to create high-quality training datasets without extensive data science expertise or pre-labeled examples. A continuous feedback loop incorporates real-time investigation results to adaptively tune the ML model, preventing rule degradation.
This proposed model with active learning has been rigorously tested for a prolonged time in a production environment spanning tens of thousands of systems. The system handles initial raw log volumes often reaching 250 billion events per day, significantly reducing them through filtering and ML inference to a handful of daily tickets for human investigation. Live experiments over an extended timeline demonstrate a general improvement in the model's precision over time due to the active learning feature. This approach offers a self-sustained, low-overhead, and low-maintenance solution, allowing security professionals to guide model learning as expert ``teachers''.
With the rise of large language models, service providers offer language models as a service, enabling users to fine-tune customized models via uploaded private datasets. However, this raises concerns about sensitive data leakage. Prior methods, relying on differential privacy within device-cloud collaboration frameworks, struggle to balance privacy and utility, exposing users to inference attacks or degrading fine-tuning performance. To address this, we propose PrivTune, an efficient and privacy-preserving fine-tuning framework via Split Learning (SL). The key idea of PrivTune is to inject crafted noise into token representations from the SL bottom model, making each token resemble the n-hop indirect neighbors. PrivTune formulates this as an optimization problem to compute the optimal noise vector, aligning with defense-utility goals. On this basis, it then adjusts the parameters (i.e., mean) of the dχ-Privacy noise distribution to align with the optimization direction and scales the noise according to token importance to minimize distortion. Experiments on five datasets (covering both classification and generation tasks) against three embedding inversion and three attribute inference attacks show that, using RoBERTa on the Stanford Sentiment Treebank dataset, PrivTune reduces the attack success rate to 10% with only a 3.33% drop in utility performance, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines.
Counterfeit products pose significant risks to public health and safety through infiltrating untrusted supply chains. Among numerous anti-counterfeiting techniques, leveraging inherent, unclonable microscopic irregularities of paper surfaces is an accurate and cost-effective solution. Prior work of this approach has focused on enabling ubiquitous acquisition of these physically unclonable features (PUFs). However, we will show that existing authentication methods relying on paper surface PUFs may be vulnerable to adversaries, resulting in a gap between technological feasibility and secure real-world deployment. This gap is investigated through formalizing an operational framework for paper-PUF-based authentication. Informed by this framework, we reveal system-level vulnerabilities across both physical and digital domains, designing physical denial-of-service and digital forgery attacks to disrupt proper authentication. The effectiveness of the designed attacks underscores the strong need for security countermeasures for reliable and resilient authentication based on paper PUFs. The proposed framework further facilitates a comprehensive, stage-by-stage security analysis, guiding the design of future counterfeit prevention systems. This analysis delves into potential attack strategies, offering a foundational understanding of how various system components, such as physical features and verification processes, might be exploited by adversaries.
Random number generation is fundamental for many modern applications including cryptography, simulations and machine learning. Traditional pseudo-random numbers may offer statistical unpredictability, but are ultimately deterministic. On the other hand, True Random Number Generation (TRNG) offers true randomness. One way of obtaining such randomness are quantum systems, including quantum computers. As such the use of quantum computers for TRNG has received considerable attention in recent years. However, existing studies almost exclusively consider IBM quantum computers, often stop at using simulations and usually test only a handful of different TRNG quantum circuits. In this paper, we address those issues by presenting a study of TRNG circuits on Odra 5 a real-life quantum computer installed at Wrocław University of Science and Technology. It is also the first study to utilize the IQM superconducting architecture. Since Odra 5 is available on-premises it allows for much more comprehensive study of various TRNG circuits. In particular, we consider 5 types of TRNG circuits with 105 circuit subvariants in total. Each circuit is used to generate 1 million bits. We then perform an analysis of the quality of the obtained random sequences using the NIST SP 800-22 and NIST SP 800-90B test suites. We also provide a comprehensive review of existing literature on quantum computer-based TRNGs.
AI agents powered by large language models are increasingly deployed as cloud services that autonomously access sensitive data, invoke external tools, and interact with other agents. However, these agents run within a complex multi-party ecosystem, where untrusted components can lead to data leakage, tampering, or unintended behavior. Existing Confidential Virtual Machines (CVMs) provide only per binary protection and offer no guarantees for cross-principal trust, accelerator-level isolation, or supervised agent behavior. We present Omega, a system that enables trusted AI agents by enforcing end-to-end isolation, establishing verifiable trust across all contributing principals, and supervising every external interaction with accountable provenance. Omega builds on Confidential VMs and Confidential GPUs to create a Trusted Agent Platform that hosts many agents within a single CVM using nested isolation. It also provides efficient multi-agent orchestration with cross-principal trust establishment via differential attestation, and a policy specification and enforcement framework that governs data access, tool usage, and inter-agent communication for data protection and regulatory compliance. Implemented on AMD SEV-SNP and NVIDIA H100, Omega fully secures agent state across CVM-GPU, and achieves high performance while enabling high-density, policy-compliant multi-agent deployments at cloud scale.
Large language models for code (LLM4Code) have greatly improved developer productivity but also raise privacy concerns due to their reliance on open-source repositories containing abundant personally identifiable information (PII). Prior work shows that commercial models can reproduce sensitive PII, yet existing studies largely treat PII as a single category and overlook the heterogeneous risks among different types. We investigate whether distinct PII types vary in their likelihood of being learned and leaked by LLM4Code, and whether this relationship is causal. Our methodology includes building a dataset with diverse PII types, fine-tuning representative models of different scales, computing training dynamics on real PII data, and formulating a structural causal model to estimate the causal effect of learnability on leakage. Results show that leakage risks differ substantially across PII types and correlate with their training dynamics: easy-to-learn instances such as IP addresses exhibit higher leakage, while harder types such as keys and passwords leak less frequently. Ambiguous types show mixed behaviors. This work provides the first causal evidence that leakage risks are type-dependent and offers guidance for developing type-aware and learnability-aware defenses for LLM4Code.
We study the classic problem of prediction with expert advice under the constraint of local differential privacy (LDP). In this context, we first show that a classical algorithm naturally satisfies LDP and then design two new algorithms that improve it: RW-AdaBatch and RW-Meta. For RW-AdaBatch, we exploit the limited-switching behavior induced by LDP to provide a novel form of privacy amplification that grows stronger on easier data, analogous to the shuffle model in offline learning. Drawing on the theory of random walks, we prove that this improvement carries essentially no utility cost. For RW-Meta, we develop a general method for privately selecting between experts that are themselves non-trivial learning algorithms, and we show that in the context of LDP this carries no extra privacy cost. In contrast, prior work has only considered data-independent experts. We also derive formal regret bounds that scale inversely with the degree of independence between experts. Our analysis is supplemented by evaluation on real-world data reported by hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic; RW-Meta outperforms both the classical baseline and a state-of-the-art \textit{central} DP algorithm by 1.5-3× on the task of predicting which hospital will report the highest density of COVID patients each week.
Neural models for vulnerability prediction (VP) have achieved impressive performance by learning from large-scale code repositories. However, their susceptibility to Membership Inference Attacks (MIAs), where adversaries aim to infer whether a particular code sample was used during training, poses serious privacy concerns. While MIA has been widely investigated in NLP and vision domains, its effects on security-critical code analysis tasks remain underexplored. In this work, we conduct the first comprehensive analysis of MIA on VP models, evaluating the attack success across various architectures (LSTM, BiGRU, and CodeBERT) and feature combinations, including embeddings, logits, loss, and confidence. Our threat model aligns with black-box and gray-box settings where prediction outputs are observable, allowing adversaries to infer membership by analyzing output discrepancies between training and non-training samples. The empirical findings reveal that logits and loss are the most informative and vulnerable outputs for membership leakage. Motivated by these observations, we propose a Noise-based Membership Inference Defense (NMID), which is a lightweight defense module that applies output masking and Gaussian noise injection to disrupt adversarial inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate that NMID significantly reduces MIA effectiveness, lowering the attack AUC from nearly 1.0 to below 0.65, while preserving the predictive utility of VP models. Our study highlights critical privacy risks in code analysis and offers actionable defense strategies for securing AI-powered software systems.
MIRAGE: Misleading Retrieval-Augmented Generation via Black-box and Query-agnostic Poisoning Attacks
MIRAGE: Misleading Retrieval-Augmented Generation via Black-box and Query-agnostic Poisoning Attacks
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems enhance LLMs with external knowledge but introduce a critical attack surface: corpus poisoning. While recent studies have demonstrated the potential of such attacks, they typically rely on impractical assumptions, such as white-box access or known user queries, thereby underestimating the difficulty of real-world exploitation. In this paper, we bridge this gap by proposing MIRAGE, a novel multi-stage poisoning pipeline designed for strict black-box and query-agnostic environments. Operating on surrogate model feedback, MIRAGE functions as an automated optimization framework that integrates three key mechanisms: it utilizes persona-driven query synthesis to approximate latent user search distributions, employs semantic anchoring to imperceptibly embed these intents for high retrieval visibility, and leverages an adversarial variant of Test-Time Preference Optimization (TPO) to maximize persuasion. To rigorously evaluate this threat, we construct a new benchmark derived from three long-form, domain-specific datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MIRAGE significantly outperforms existing baselines in both attack efficacy and stealthiness, exhibiting remarkable transferability across diverse retriever-LLM configurations and highlighting the urgent need for robust defense strategies.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.