image-generation
Wan-Move presents a framework for motion-controllable video generation that utilizes latent trajectory guidance to directly edit image condition features within a pre-trained image-to-video model. This method yields superior visual quality and precise motion adherence compared to state-of-the-art academic approaches and rivals commercial solutions, while also establishing MoveBench, a new comprehensive evaluation benchmark.
Apple researchers introduced FAE (Feature Auto-Encoder), a minimalist framework using a single attention layer and a double-decoder architecture to adapt high-dimensional self-supervised visual features into compact, generation-friendly latent spaces. FAE achieves competitive FID scores on ImageNet (1.29) and MS-COCO (6.90) for image generation while preserving semantic understanding capabilities of the original pre-trained encoders.
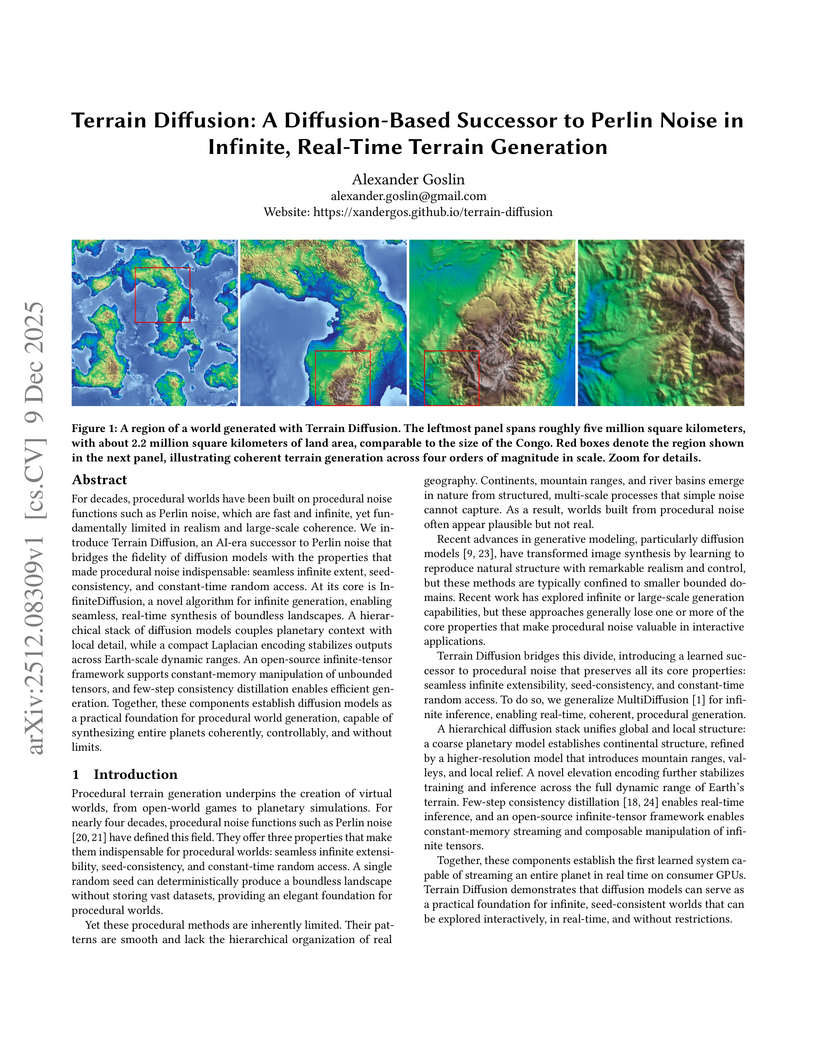
Terrain Diffusion introduces a diffusion-based framework for generating infinite, real-time procedural terrain, delivering highly realistic, boundless virtual worlds with seed-consistency and constant-time random access. The system achieves competitive FID scores and real-time generation latency on consumer hardware, demonstrating its practical applicability.
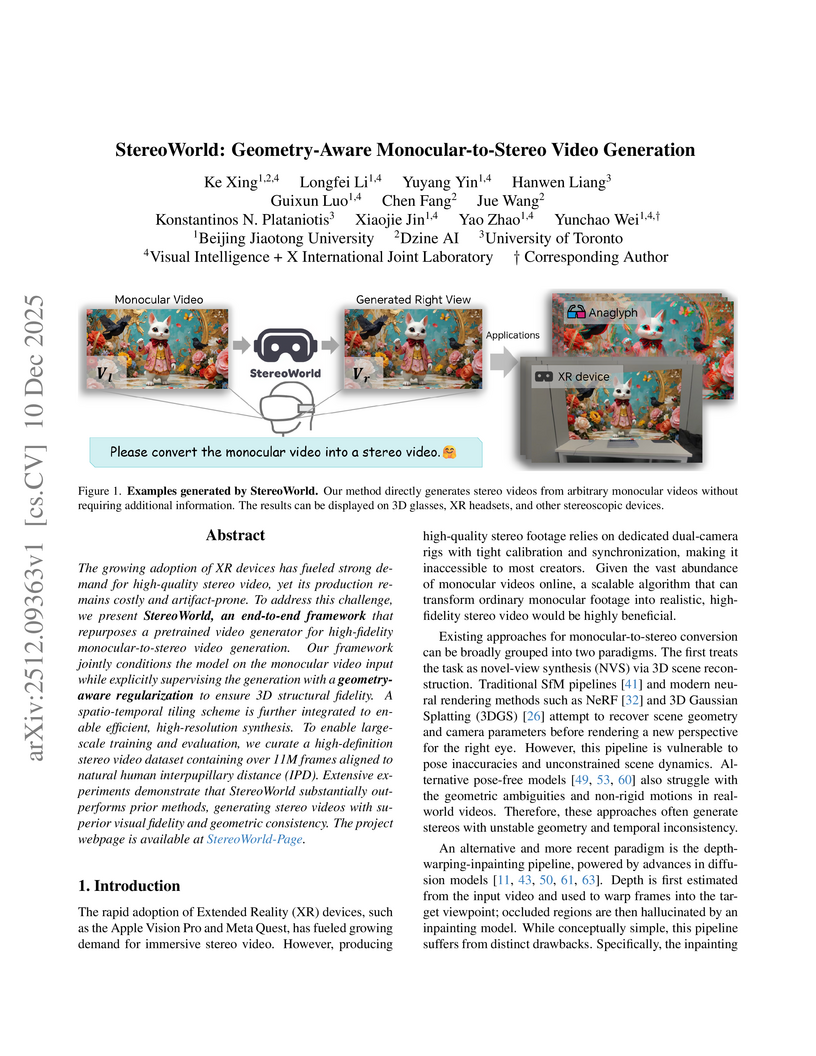
The growing adoption of XR devices has fueled strong demand for high-quality stereo video, yet its production remains costly and artifact-prone. To address this challenge, we present StereoWorld, an end-to-end framework that repurposes a pretrained video generator for high-fidelity monocular-to-stereo video generation. Our framework jointly conditions the model on the monocular video input while explicitly supervising the generation with a geometry-aware regularization to ensure 3D structural fidelity. A spatio-temporal tiling scheme is further integrated to enable efficient, high-resolution synthesis. To enable large-scale training and evaluation, we curate a high-definition stereo video dataset containing over 11M frames aligned to natural human interpupillary distance (IPD). Extensive experiments demonstrate that StereoWorld substantially outperforms prior methods, generating stereo videos with superior visual fidelity and geometric consistency. The project webpage is available at this https URL.
MeshSplatting generates connected, opaque, and colored triangle meshes from images using differentiable rendering, enabling direct integration of neurally reconstructed scenes into traditional 3D graphics pipelines. The method achieves a +0.69 dB PSNR improvement over MiLo on the Mip-NeRF360 dataset and trains 2x faster while requiring 2.5x less memory.
09 Dec 2025
Visionary introduces a WebGPU-powered platform for 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) that enables real-time, client-side rendering and inference for dynamic and generative 3DGS models. The platform demonstrates up to 135x speedup compared to WebGL-based viewers, while maintaining or improving visual quality and ensuring robust depth-aware composition.
A new framework, Distribution Matching Variational AutoEncoder (DMVAE), explicitly aligns a VAE's aggregate latent distribution with a pre-defined reference distribution using score-based matching. The approach achieves a state-of-the-art gFID of 1.82 on ImageNet 256x256, demonstrating superior training efficiency for downstream generative models, particularly when utilizing Self-Supervised Learning features as the reference.
TreeGRPO introduces a reinforcement learning framework that reinterprets diffusion model denoising as a sparse search tree, enabling both sample efficiency and precise credit assignment for post-training. This method achieves 2.4 times faster training convergence and enhances alignment quality with human preferences compared to prior approaches.
Researchers from the University of Technology Sydney and Zhejiang University developed VideoCoF, a unified video editing framework that introduces a "Chain of Frames" approach for explicit visual reasoning. This method achieves mask-free, fine-grained edits, demonstrating a 15.14% improvement in instruction following and an 18.6% higher success ratio on their VideoCoF-Bench, while also providing robust length extrapolation.
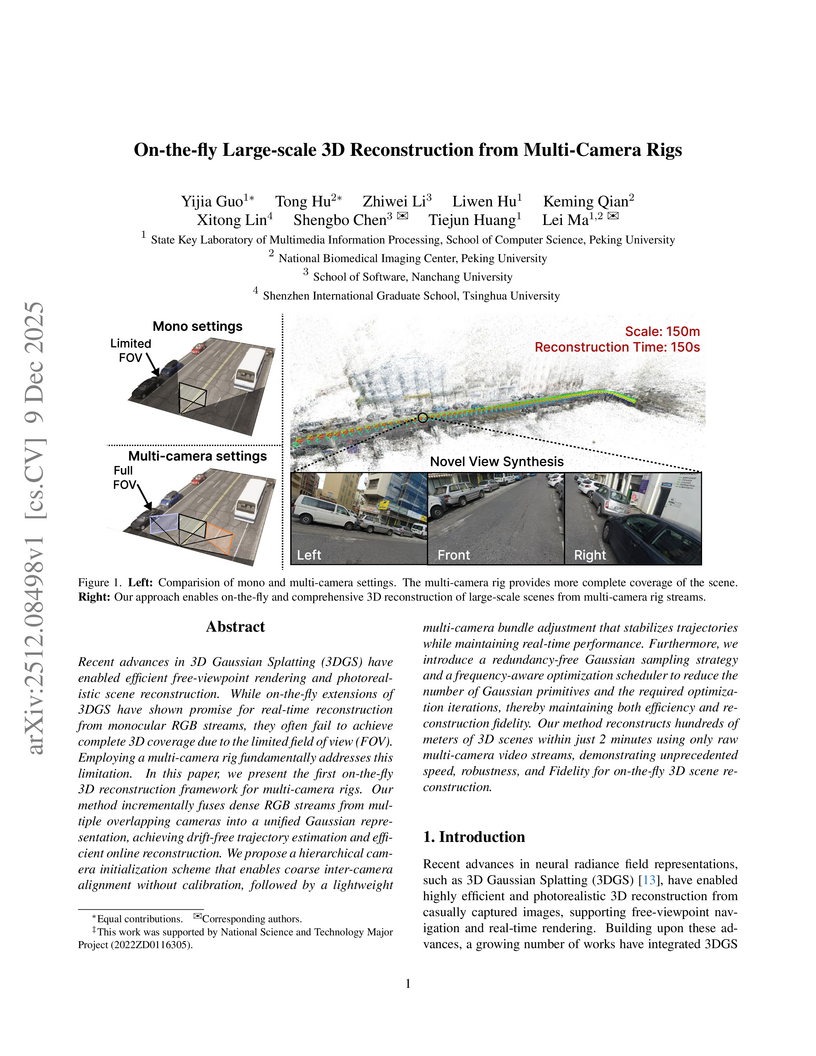
Researchers from Peking University, Nanchang University, and Tsinghua University developed the first on-the-fly 3D reconstruction framework for multi-camera rigs, enabling calibration-free, large-scale, and high-fidelity scene reconstruction. The system generates drift-free trajectories and photorealistic novel views, reconstructing 100 meters of road or 100,000 m² of aerial scenes in two minutes.
Meta AI developed Saber, a framework for zero-shot Reference-to-Video generation that leverages a masked training strategy on general video-text datasets, eliminating the need for specialized R2V data. It achieves superior identity consistency and overall performance on benchmarks like OpenS2V-Eval compared to methods trained on costly R2V datasets.
05 Dec 2025
The EditThinker framework enhances instruction-following in any image editor by introducing an iterative reasoning process. It leverages a Multimodal Large Language Model to critique, reflect, and refine editing instructions, leading to consistent performance gains across diverse benchmarks and excelling in complex reasoning tasks.
Researchers at Zhejiang University developed LIVINGSWAP, a high-fidelity video face swapping framework designed for cinematic quality by directly leveraging complete source video attributes and employing keyframe conditioning. The system outperforms existing methods on new cinematic benchmarks and reduces manual editing effort by approximately 40 times.
A Conditional Neural Cellular Automata (c-NCA) framework is introduced, enabling a single set of local rules to grow diverse structural digits from a single pixel, guided by a broadcasted class vector. The lightweight model achieves 96.30% recognition accuracy on generated digits by an external classifier and demonstrates robust emergent self-repair from significant damage without specific training.
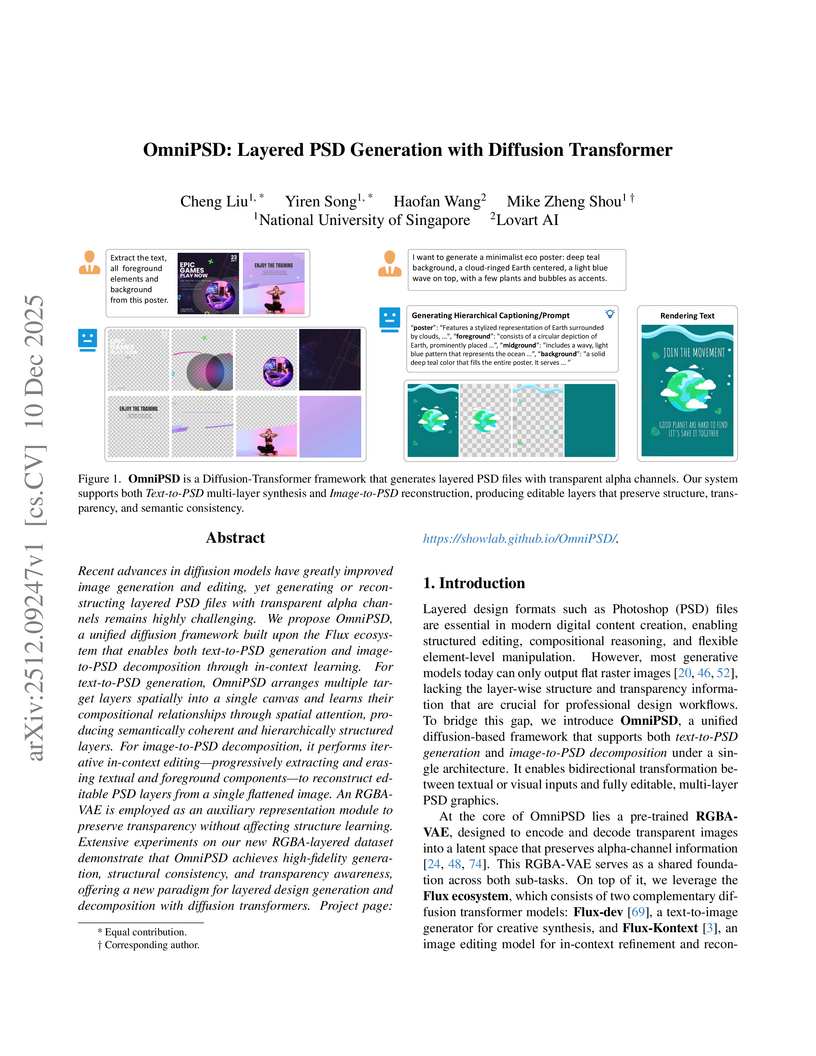
Recent advances in diffusion models have greatly improved image generation and editing, yet generating or reconstructing layered PSD files with transparent alpha channels remains highly challenging. We propose OmniPSD, a unified diffusion framework built upon the Flux ecosystem that enables both text-to-PSD generation and image-to-PSD decomposition through in-context learning. For text-to-PSD generation, OmniPSD arranges multiple target layers spatially into a single canvas and learns their compositional relationships through spatial attention, producing semantically coherent and hierarchically structured layers. For image-to-PSD decomposition, it performs iterative in-context editing, progressively extracting and erasing textual and foreground components to reconstruct editable PSD layers from a single flattened image. An RGBA-VAE is employed as an auxiliary representation module to preserve transparency without affecting structure learning. Extensive experiments on our new RGBA-layered dataset demonstrate that OmniPSD achieves high-fidelity generation, structural consistency, and transparency awareness, offering a new paradigm for layered design generation and decomposition with diffusion transformers.
Recent advances in video generation have been remarkable, enabling models to produce visually compelling videos with synchronized audio. While existing video generation benchmarks provide comprehensive metrics for visual quality, they lack convincing evaluations for audio-video generation, especially for models aiming to generate synchronized audio-video outputs. To address this gap, we introduce VABench, a comprehensive and multi-dimensional benchmark framework designed to systematically evaluate the capabilities of synchronous audio-video generation. VABench encompasses three primary task types: text-to-audio-video (T2AV), image-to-audio-video (I2AV), and stereo audio-video generation. It further establishes two major evaluation modules covering 15 dimensions. These dimensions specifically assess pairwise similarities (text-video, text-audio, video-audio), audio-video synchronization, lip-speech consistency, and carefully curated audio and video question-answering (QA) pairs, among others. Furthermore, VABench covers seven major content categories: animals, human sounds, music, environmental sounds, synchronous physical sounds, complex scenes, and virtual worlds. We provide a systematic analysis and visualization of the evaluation results, aiming to establish a new standard for assessing video generation models with synchronous audio capabilities and to promote the comprehensive advancement of the field.
Video head swapping aims to replace the entire head of a video subject, including facial identity, head shape, and hairstyle, with that of a reference image, while preserving the target body, background, and motion dynamics. Due to the lack of ground-truth paired swapping data, prior methods typically train on cross-frame pairs of the same person within a video and rely on mask-based inpainting to mitigate identity leakage. Beyond potential boundary artifacts, this paradigm struggles to recover essential cues occluded by the mask, such as facial pose, expressions, and motion dynamics. To address these issues, we prompt a video editing model to synthesize new heads for existing videos as fake swapping inputs, while maintaining frame-synchronized facial poses and expressions. This yields HeadSwapBench, the first cross-identity paired dataset for video head swapping, which supports both training (\TrainNum{} videos) and benchmarking (\TestNum{} videos) with genuine outputs. Leveraging this paired supervision, we propose DirectSwap, a mask-free, direct video head-swapping framework that extends an image U-Net into a video diffusion model with a motion module and conditioning inputs. Furthermore, we introduce the Motion- and Expression-Aware Reconstruction (MEAR) loss, which reweights the diffusion loss per pixel using frame-difference magnitudes and facial-landmark proximity, thereby enhancing cross-frame coherence in motion and expressions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DirectSwap achieves state-of-the-art visual quality, identity fidelity, and motion and expression consistency across diverse in-the-wild video scenes. We will release the source code and the HeadSwapBench dataset to facilitate future research.
Fast-ARDiff introduces an entropy-informed acceleration framework for continuous-space AR-Diffusion hybrid generative models. This framework achieves up to a 4.88x speedup in inference latency with minimal quality degradation by addressing challenges like entropy mismatch in visual speculative decoding and instability in diffusion distillation.
Radiance field representations have recently been explored in the latent space of VAEs that are commonly used by diffusion models. This direction offers efficient rendering and seamless integration with diffusion-based pipelines. However, these methods face a fundamental limitation: The VAE latent space lacks multi-view consistency, leading to blurred textures and missing details during 3D reconstruction. Existing approaches attempt to address this by fine-tuning the VAE, at the cost of reconstruction quality, or by relying on pre-trained diffusion models to recover fine-grained details, at the risk of some hallucinations. We present Splatent, a diffusion-based enhancement framework designed to operate on top of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) in the latent space of VAEs. Our key insight departs from the conventional 3D-centric view: rather than reconstructing fine-grained details in 3D space, we recover them in 2D from input views through multi-view attention mechanisms. This approach preserves the reconstruction quality of pretrained VAEs while achieving faithful detail recovery. Evaluated across multiple benchmarks, Splatent establishes a new state-of-the-art for VAE latent radiance field reconstruction. We further demonstrate that integrating our method with existing feed-forward frameworks, consistently improves detail preservation, opening new possibilities for high-quality sparse-view 3D reconstruction.
Personalized Text-to-Image (PT2I) generation aims to produce customized images based on reference images. A prominent interest pertains to the integration of an image prompt adapter to facilitate zero-shot PT2I without test-time fine-tuning. However, current methods grapple with three fundamental challenges: 1. the elusive equilibrium between Concept Preservation (CP) and Prompt Following (PF), 2. the difficulty in retaining fine-grained concept details in reference images, and 3. the restricted scalability to extend to multi-subject personalization. To tackle these challenges, we present Dynamic Image Prompt Adapter (DynaIP), a cutting-edge plugin to enhance the fine-grained concept fidelity, CP-PF balance, and subject scalability of SOTA T2I multimodal diffusion transformers (MM-DiT) for PT2I generation. Our key finding is that MM-DiT inherently exhibit decoupling learning behavior when injecting reference image features into its dual branches via cross attentions. Based on this, we design an innovative Dynamic Decoupling Strategy that removes the interference of concept-agnostic information during inference, significantly enhancing the CP-PF balance and further bolstering the scalability of multi-subject compositions. Moreover, we identify the visual encoder as a key factor affecting fine-grained CP and reveal that the hierarchical features of commonly used CLIP can capture visual information at diverse granularity levels. Therefore, we introduce a novel Hierarchical Mixture-of-Experts Feature Fusion Module to fully leverage the hierarchical features of CLIP, remarkably elevating the fine-grained concept fidelity while also providing flexible control of visual granularity. Extensive experiments across single- and multi-subject PT2I tasks verify that our DynaIP outperforms existing approaches, marking a notable advancement in the field of PT2l generation.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.