Meituan
19 Sep 2025
Meituan LongCat Team's LongCat-Flash, a 560-billion-parameter Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model, achieves top-tier performance, particularly in agentic tasks, while demonstrating exceptional computational efficiency. It was pre-trained on 20 trillion tokens in 30 days and achieves an inference cost of $0.70 per million output tokens at over 100 tokens per second (TPS) on H800 GPUs.
03 Dec 2025
Researchers from MMLab, CUHK and Meituan developed OneThinker, a unified multimodal large language model capable of diverse visual understanding tasks across images and videos. This model utilizes an EMA-GRPO algorithm to achieve robust performance across 31 benchmarks, setting new state-of-the-art results for many tasks.
07 Nov 2025
We present LongCat-Flash-Thinking, an efficient 560-billion-parameter open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) reasoning model. Its advanced capabilities are cultivated through a meticulously crafted training process, beginning with long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) data cold-start and culminating in large-scale Reinforcement Learning (RL). We first employ a well-designed cold-start training strategy, which significantly enhances the reasoning potential and equips the model with specialized skills in both formal and agentic reasoning. Then, a core innovation is our domain-parallel training scheme, which decouples optimization across distinct domains (e.g., STEM, Code, Agentic) and subsequently fuses the resulting expert models into a single, nearly Pareto-optimal model. This entire process is powered by our Dynamic ORchestration for Asynchronous rollout (DORA) system, a large-scale RL framework that delivers a greater than threefold training speedup over synchronous methods on tens of thousands of accelerators. As a result, LongCat-Flash-Thinking achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models on a suite of complex reasoning tasks. The model exhibits exceptional efficiency in agentic reasoning, reducing average token consumption by 64.5% (from 19, 653 to 6, 965) on AIME-25, without degrading task accuracy. We release LongCat-Flash-Thinking to promote further advances in reasoning systems and agentic AI research.
The paper introduces Supervised Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (SRFT), a single-stage method that unifies supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning for large language models (LLMs). SRFT achieves an average accuracy of 59.5% on mathematical reasoning benchmarks, improving upon zero-RL methods by 9.0% and demonstrating enhanced out-of-distribution generalization.
Meituan's LongCat-Video presents a 13.6 billion parameter foundational model for video generation, achieving high-quality, minutes-long video output at 720p 30fps with over a 10x speedup across text-to-video, image-to-video, and video continuation tasks. The model demonstrates leading performance in "Commonsense" on public benchmarks and leverages multi-reward reinforcement learning from human feedback to enhance generation quality.
The EditThinker framework enhances instruction-following in any image editor by introducing an iterative reasoning process. It leverages a Multimodal Large Language Model to critique, reflect, and refine editing instructions, leading to consistent performance gains across diverse benchmarks and excelling in complex reasoning tasks.
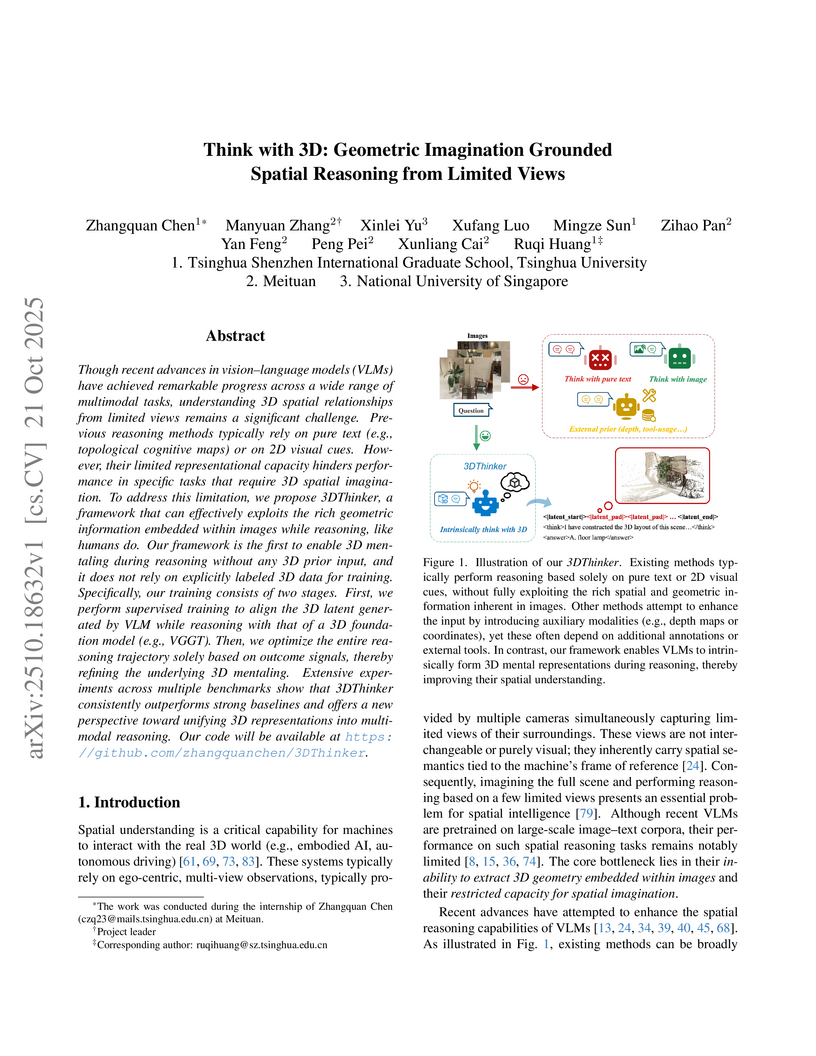
3DThinker equips Vision-Language Models with an intrinsic "3D mentaling" capability, allowing them to imagine and reason about 3D scenes from limited 2D views without explicit 3D annotations or external tools. This framework achieves state-of-the-art spatial reasoning performance across various benchmarks, even surpassing advanced closed-source models and specialized baselines, and offers interpretability through reconstructable 3D latent representations.
CodePlot-CoT introduces a code-driven Chain-of-Thought paradigm, enabling Vision Language Models (VLMs) to generate precise visual aids by producing executable plotting code that is then rendered and re-integrated into the reasoning process. This method, along with the new Math-VR dataset, allowed CodePlot-CoT to achieve up to a 21% performance increase on mathematical visual reasoning tasks, surpassing larger models and those using direct image generation.
21 Oct 2025
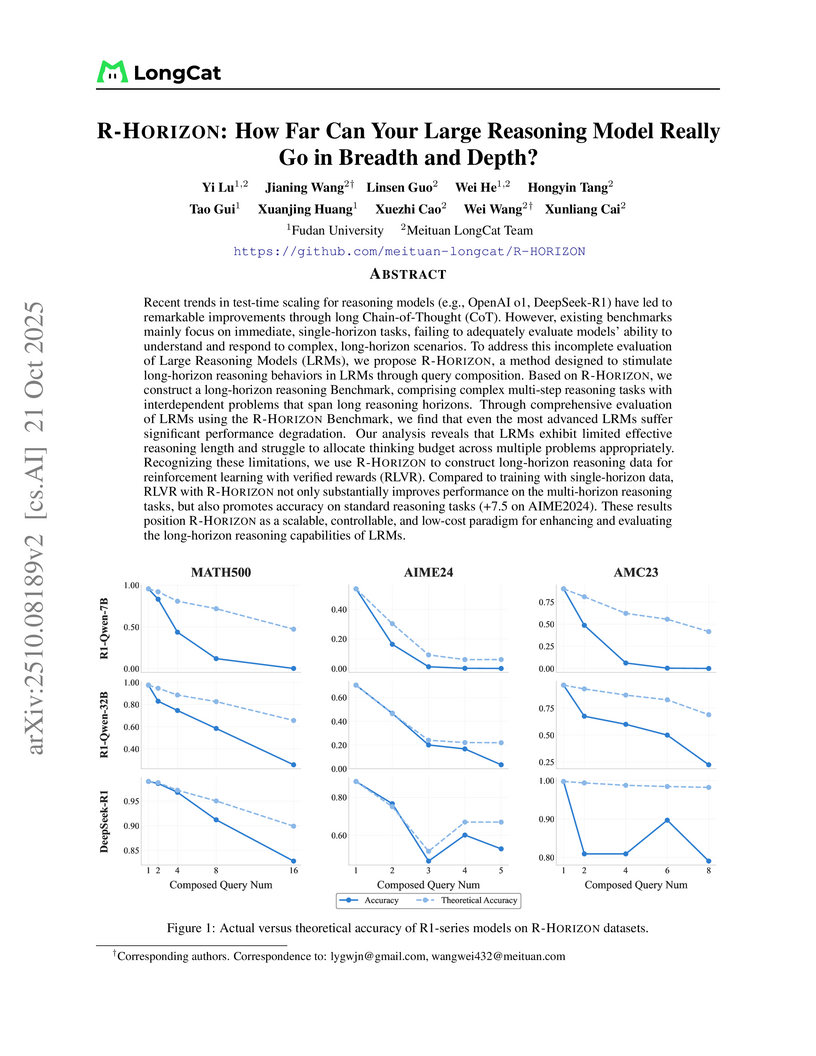
Recent trends in test-time scaling for reasoning models (e.g., OpenAI o1, DeepSeek-R1) have led to remarkable improvements through long Chain-of-Thought (CoT). However, existing benchmarks mainly focus on immediate, single-horizon tasks, failing to adequately evaluate models' ability to understand and respond to complex, long-horizon scenarios. To address this incomplete evaluation of Large Reasoning Models (LRMs), we propose R-HORIZON, a method designed to stimulate long-horizon reasoning behaviors in LRMs through query composition. Based on R-HORIZON, we construct a long-horizon reasoning benchmark, comprising complex multi-step reasoning tasks with interdependent problems that span long reasoning horizons. Through comprehensive evaluation of LRMs using the R-HORIZON benchmark, we find that even the most advanced LRMs suffer significant performance degradation. Our analysis reveals that LRMs exhibit limited effective reasoning length and struggle to allocate thinking budget across multiple problems appropriately. Recognizing these limitations, we use R-HORIZON to construct long-horizon reasoning data for reinforcement learning with verified rewards (RLVR). Compared to training with single-horizon data, RLVR with R-HORIZON not only substantially improves performance on the multi-horizon reasoning tasks, but also promotes accuracy on standard reasoning tasks, with an increase of 7.5 on AIME2024. These results position R-HORIZON as a scalable, controllable, and low-cost paradigm for enhancing and evaluating the long-horizon reasoning capabilities of LRMs.
We introduce LongCat-Flash-Omni, a state-of-the-art open-source omni-modal model with 560 billion parameters, excelling at real-time audio-visual interaction. By adopting a curriculum-inspired progressive training strategy that transitions from simpler to increasingly complex modality sequence modeling tasks, LongCat-Flash-Omni attains comprehensive multimodal capabilities while maintaining strong unimodal capability. Building upon LongCat-Flash, which adopts a high-performance Shortcut-connected Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture with zero-computation experts, LongCat-Flash-Omni integrates efficient multimodal perception and speech reconstruction modules. Despite its immense size of 560B parameters (with 27B activated), LongCat-Flash-Omni achieves low-latency real-time audio-visual interaction. For training infrastructure, we developed a modality-decoupled parallelism scheme specifically designed to manage the data and model heterogeneity inherent in large-scale multimodal training. This innovative approach demonstrates exceptional efficiency by sustaining over 90% of the throughput achieved by text-only training. Extensive evaluations show that LongCat-Flash-Omni achieves state-of-the-art performance on omni-modal benchmarks among open-source models. Furthermore, it delivers highly competitive results across a wide range of modality-specific tasks, including text, image, and video understanding, as well as audio understanding and generation. We provide a comprehensive overview of the model architecture design, training procedures, and data strategies, and open-source the model to foster future research and development in the community.
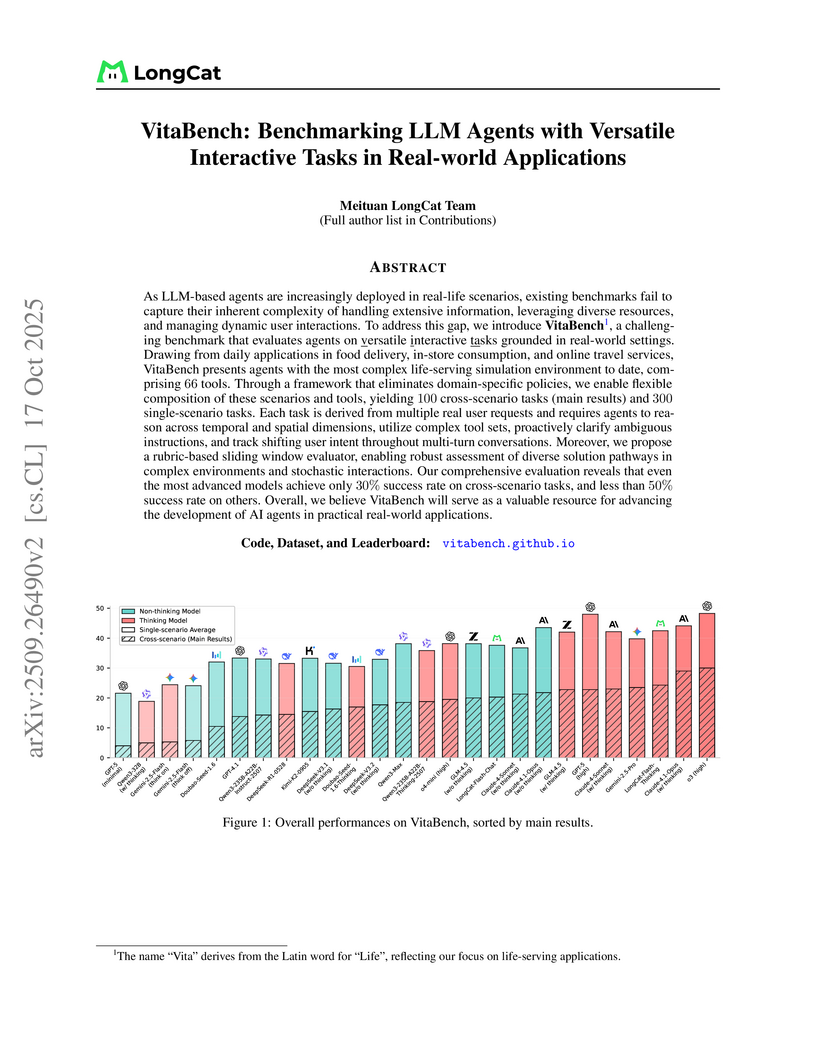
VitaBench, developed by the Meituan LongCat Team, introduces a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LLM agents on versatile interactive tasks derived from real-world "life-serving applications." It assesses agents across reasoning, tool use, and interaction complexity, revealing that even state-of-the-art models achieve only a 30.0% average success rate on cross-scenario tasks.
InfiniteTalk introduces sparse-frame video dubbing, a new paradigm for audio-driven video generation that produces holistic, full-body synchronized movements for infinite-length videos while preserving visual identity and ensuring temporal continuity. The model achieves superior naturalness in full-body synchronization and competitive lip synchronization as validated by human evaluation.
This work uncovers that architectural decoupling in unified multimodal models (UMMs) improves performance by inducing task-specific attention patterns, rather than eliminating task conflicts. Researchers from CUHK MMLab and Meituan introduce an Attention Interaction Alignment (AIA) loss, a regularization technique that guides UMMs' attention toward optimal task-specific behaviors without architectural changes, enhancing both understanding and generation performance for models like Emu3 and Janus-Pro.
11 Nov 2025
A trainable graph memory framework is introduced to empower LLM agents to learn and adapt strategies from their experiences. This method integrates a reinforcement-driven mechanism to distill low-level trajectories into high-level meta-cognitive strategies, achieving improved performance in zero-training inference and accelerating reinforcement learning, particularly for smaller models.
15 Oct 2025
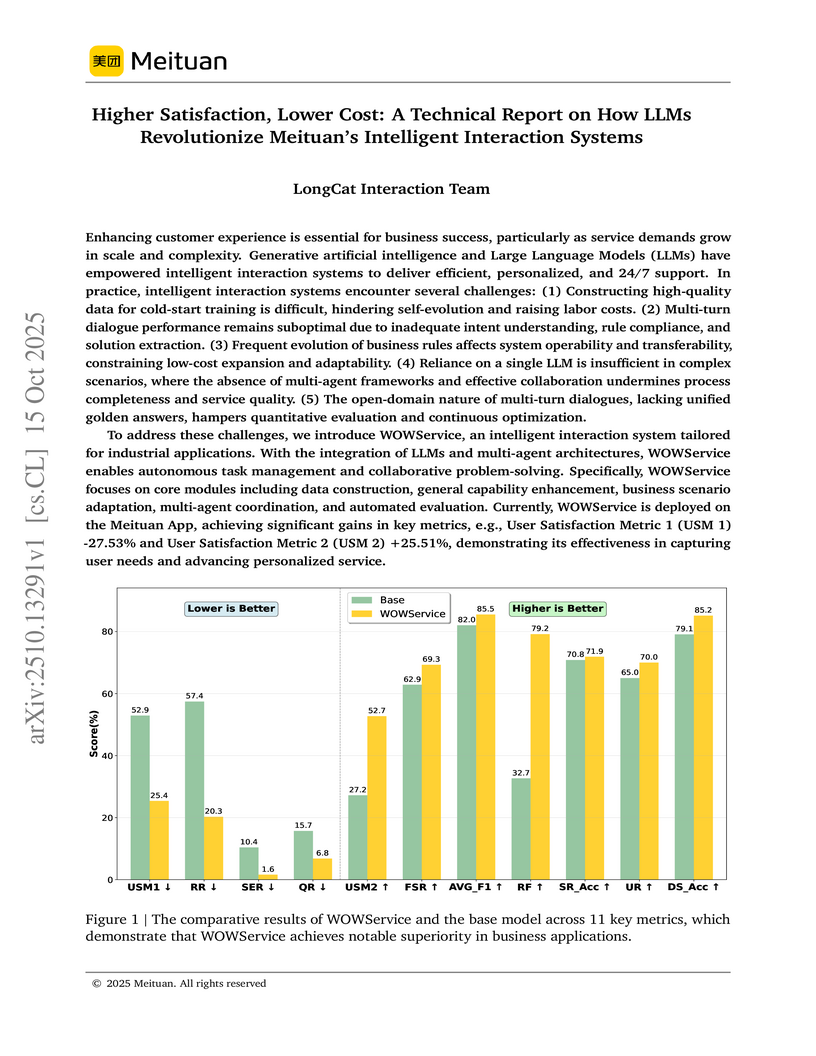
Meituan's LongCat Interaction Team developed WOWService, an intelligent interaction system leveraging a multi-stage LLM training pipeline and multi-agent architecture, to enhance user satisfaction and reduce operational costs for its local lifestyle services. Deployed on the Meituan App, the system demonstrated improvements in user satisfaction metrics (e.g., USM 1 by -27.53%, USM 2 by +25.51%) and operational efficiency.
Meituan's LongCat-Image introduces an open-source, bilingual foundation model for image generation and editing, achieving state-of-the-art performance with a compact 6B parameter architecture. The model establishes new industry standards for Chinese character rendering, reaching 90.7% accuracy on a custom benchmark, and demonstrates robust image editing capabilities, often outperforming larger models.
A framework is presented for direct 4K (4096x4096) image synthesis with latent diffusion models, integrating a new Aesthetic-4K benchmark and a Wavelet-based Fine-tuning (WLF) approach. This method generates ultra-high-resolution images with enhanced fine details and textures, outperforming prior approaches on novel detail-focused metrics.
22 Aug 2025
Meituan researchers developed MTGR, an industrial-scale generative recommendation framework that integrates traditional cross-features into a scalable transformer-based architecture. Deployed on Meituan, it achieved online gains of +1.90% PV_CTR and +1.02% UV_CTCVR with an unchanged training cost and a 12% reduction in inference cost compared to DLRM baselines.
Instruction tuning is a standard technique employed to align large language
models to end tasks and user preferences after the initial pretraining phase.
Recent research indicates the critical role of data engineering in instruction
tuning -- when appropriately selected, only limited data is necessary to
achieve superior performance. However, we still lack a principled understanding
of what makes good instruction tuning data for alignment, and how we should
select data automatically and effectively. In this work, we delve deeply into
automatic data selection strategies for alignment. We start with controlled
studies to measure data across three dimensions: complexity, quality, and
diversity, along which we examine existing methods and introduce novel
techniques for enhanced data measurement. Subsequently, we propose a simple
strategy to select data samples based on the measurement. We present deita
(short for Data-Efficient Instruction Tuning for Alignment), a series of models
fine-tuned from LLaMA and Mistral models using data samples automatically
selected with our proposed approach. Empirically, deita performs better or on
par with the state-of-the-art open-source alignment models with only 6K SFT
training data samples -- over 10x less than the data used in the baselines.
When further trained with direct preference optimization (DPO),
deita-Mistral-7B + DPO trained with 6K SFT and 10K DPO samples achieve 7.55
MT-Bench and 90.06% AlpacaEval scores. We anticipate this work to provide tools
on automatic data selection, facilitating data-efficient alignment. We release
our models as well as the selected datasets for future researches to
effectively align models more efficiently.
Chart-R1 introduces a vision-language model for complex chart reasoning, leveraging a novel programmatic data synthesis strategy and a two-stage training pipeline that combines Chain-of-Thought supervision with numerically sensitive reinforcement learning. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance on various benchmarks, demonstrating advanced capabilities in multi-step visual data analysis that rival or surpass larger proprietary models.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.