speech-recognition
The increasing use of synthetic media, particularly deepfakes, is an emerging challenge for digital content verification. Although recent studies use both audio and visual information, most integrate these cues within a single model, which remains vulnerable to modality mismatches, noise, and manipulation. To address this gap, we propose DeepAgent, an advanced multi-agent collaboration framework that simultaneously incorporates both visual and audio modalities for the effective detection of deepfakes. DeepAgent consists of two complementary agents. Agent-1 examines each video with a streamlined AlexNet-based CNN to identify the symbols of deepfake manipulation, while Agent-2 detects audio-visual inconsistencies by combining acoustic features, audio transcriptions from Whisper, and frame-reading sequences of images through EasyOCR. Their decisions are fused through a Random Forest meta-classifier that improves final performance by taking advantage of the different decision boundaries learned by each agent. This study evaluates the proposed framework using three benchmark datasets to demonstrate both component-level and fused performance. Agent-1 achieves a test accuracy of 94.35% on the combined Celeb-DF and FakeAVCeleb datasets. On the FakeAVCeleb dataset, Agent-2 and the final meta-classifier attain accuracies of 93.69% and 81.56%, respectively. In addition, cross-dataset validation on DeepFakeTIMIT confirms the robustness of the meta-classifier, which achieves a final accuracy of 97.49%, and indicates a strong capability across diverse datasets. These findings confirm that hierarchy-based fusion enhances robustness by mitigating the weaknesses of individual modalities and demonstrate the effectiveness of a multi-agent approach in addressing diverse types of manipulations in deepfakes.
AV-SpeakerBench introduces a benchmark with 3,212 multiple-choice questions across 12 tasks to evaluate fine-grained, speaker-centric audiovisual reasoning in multimodal large language models (MLLMs). The evaluation reveals a 20 percentage point accuracy gap between the top MLLMs (73.04% for Gemini 2.5 Pro) and human performance (93.74%), primarily due to limitations in robust audiovisual fusion.
Researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology, Pengcheng Laboratory, and others developed MCAT, a framework that scales multimodal large language models for many-to-many speech-to-text translation across 70 languages. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on the FLEURS dataset, outperforming SeamlessM4T-V2-Large by over 8 COMET points, while accelerating inference speed by 3.3x through a 25x compression of speech input tokens.
Subjective mean opinion scores (MOS) remain the de-facto target for non-intrusive speech and singing quality assessment. However, MOS is a scalar that collapses heterogeneous user expectations, ignores service-level objectives, and is difficult to compare across deployment graphs. We propose a contract-driven QoE auditing framework: each service graph G is evaluated under a set of human-interpretable experience contracts C, yielding a contract-level satisfaction vector Q(G, C). We show that (i) classical MOS regression is a special case with a degenerate contract set, (ii) contract-driven quality is more stable than MOS under graph view transformations (e.g., pooling by system vs. by system type), and (iii) the effective sample complexity of learning contracts is governed by contract semantics rather than merely the dimensionality of C. We instantiate the framework on URGENT2024 MOS (6.9k speech utterances with raw rating vectors) and SingMOS v1 (7,981 singing clips; 80 systems). On URGENT, we train a contract-aware neural auditor on self-supervised WavLM embeddings; on SingMOS, we perform contract-driven graph auditing using released rating vectors and metadata without decoding audio. Empirically, our auditor matches strong MOS predictors in MOS accuracy while providing calibrated contract probabilities; on SingMOS, Q(G, C) exhibits substantially smaller cross-view drift than raw MOS and graph-only baselines; on URGENT, difficulty curves reveal that mis-specified "simple" contracts can be harder to learn than richer but better aligned contract sets.
This research presents a novel approach to enhancing automatic speech recognition systems by integrating noise detection capabilities directly into the recognition architecture. Building upon the wav2vec2 framework, the proposed method incorporates a dedicated noise identification module that operates concurrently with speech transcription. Experimental validation using publicly available speech and environmental audio datasets demonstrates substantial improvements in transcription quality and noise discrimination. The enhanced system achieves superior performance in word error rate, character error rate, and noise detection accuracy compared to conventional architectures. Results indicate that joint optimization of transcription and noise classification objectives yields more reliable speech recognition in challenging acoustic conditions.
The globalization of education and rapid growth of online learning have made localizing educational content a critical challenge. Lecture materials are inherently multimodal, combining spoken audio with visual slides, which requires systems capable of processing multiple input modalities. To provide an accessible and complete learning experience, translations must preserve all modalities: text for reading, slides for visual understanding, and speech for auditory learning. We present \textbf{BOOM}, a multimodal multilingual lecture companion that jointly translates lecture audio and slides to produce synchronized outputs across three modalities: translated text, localized slides with preserved visual elements, and synthesized speech. This end-to-end approach enables students to access lectures in their native language while aiming to preserve the original content in its entirety. Our experiments demonstrate that slide-aware transcripts also yield cascading benefits for downstream tasks such as summarization and question answering. We release our Slide Translation code at this https URL and integrate it in Lecture Translator at this https URL}\footnote{All released code and models are licensed under the MIT License.
We present Conformer-based decoders for the LibriBrain 2025 PNPL competition, targeting two foundational MEG tasks: Speech Detection and Phoneme Classification. Our approach adapts a compact Conformer to raw 306-channel MEG signals, with a lightweight convolutional projection layer and task-specific heads. For Speech Detection, a MEG-oriented SpecAugment provided a first exploration of MEG-specific augmentation. For Phoneme Classification, we used inverse-square-root class weighting and a dynamic grouping loader to handle 100-sample averaged examples. In addition, a simple instance-level normalization proved critical to mitigate distribution shifts on the holdout split. Using the official Standard track splits and F1-macro for model selection, our best systems achieved 88.9% (Speech) and 65.8% (Phoneme) on the leaderboard, surpassing the competition baselines and ranking within the top-10 in both tasks. For further implementation details, the technical documentation, source code, and checkpoints are available at this https URL.
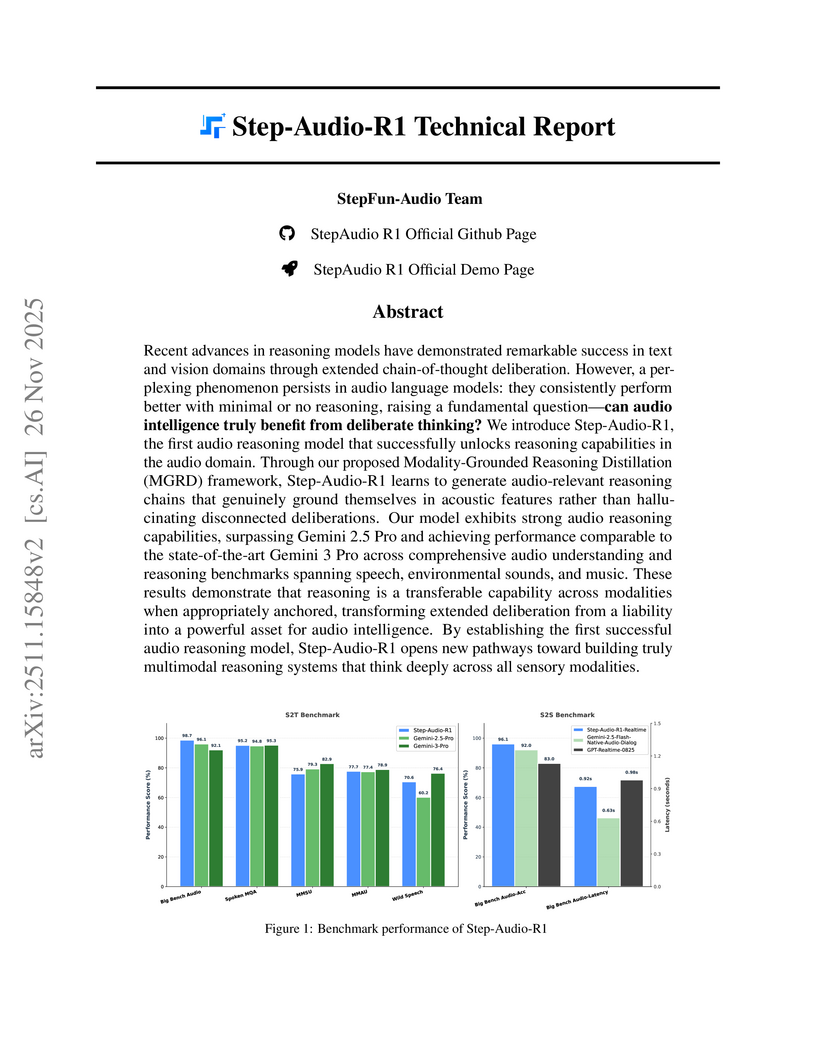
Step-Audio-R1 introduces the first audio reasoning model to overcome the "inverted scaling" problem, demonstrating that extended deliberation benefits audio understanding when reasoning is acoustically grounded. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing Gemini 2.5 Pro and nearing Gemini 3 Pro on various audio understanding and reasoning benchmarks.
As Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is increasingly deployed in clinical dialogue, standard evaluations still rely heavily on Word Error Rate (WER). This paper challenges that standard, investigating whether WER or other common metrics correlate with the clinical impact of transcription errors. We establish a gold-standard benchmark by having expert clinicians compare ground-truth utterances to their ASR-generated counterparts, labeling the clinical impact of any discrepancies found in two distinct doctor-patient dialogue datasets. Our analysis reveals that WER and a comprehensive suite of existing metrics correlate poorly with the clinician-assigned risk labels (No, Minimal, or Significant Impact). To bridge this evaluation gap, we introduce an LLM-as-a-Judge, programmatically optimized using GEPA through DSPy to replicate expert clinical assessment. The optimized judge (Gemini-2.5-Pro) achieves human-comparable performance, obtaining 90% accuracy and a strong Cohen's κ of 0.816. This work provides a validated, automated framework for moving ASR evaluation beyond simple textual fidelity to a necessary, scalable assessment of safety in clinical dialogue.
Uni-MoE-2.0-Omni, an open-source omnimodal large model from Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen, unifies understanding and generation across text, images, audio, and video through an advanced Mixture-of-Experts architecture and progressive training. The model achieved state-of-the-art or competitive performance across 85 multimodal benchmarks, notably outperforming Qwen2.5-Omni on over 50 of 76 benchmarks and showing strong capabilities in complex reasoning, long-form speech understanding, and controllable image generation.
Omnilingual ASR provides an open-source multilingual Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system, expanding coverage to over 1,600 languages, including 500+ previously unsupported. It delivers superior performance compared to existing state-of-the-art models and introduces zero-shot generalization to new languages using minimal in-context examples.
13 Nov 2025
MTR-DUPLEXBENCH introduces a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating Full-Duplex Speech Language Models (FD-SLMs) across multi-round conversations, utilizing a novel turn segmentation method and diverse metrics. Experiments show existing FD-SLMs face challenges in maintaining consistent dialogue quality, conversational feature handling, and instruction following over extended interactions.
Large language models (LLMs) have recently advanced auditory speech recognition (ASR), visual speech recognition (VSR), and audio-visual speech recognition (AVSR). However, understanding of their internal dynamics under fine-tuning remains limited. In natural language processing, recent work has revealed attention sinks, tokens that attract disproportionately high attention, and associated massive activations in which some features of sink tokens exhibit huge activation in LLMs. In this work, we are the first to study these phenomena in multimodal speech recognition. Through a detailed analysis of audio-visual LLMs, we identify attention sinks and massive activations not only at the BOS token but also at intermediate low-semantic tokens across ASR, VSR, and AVSR. We show that massive activations originate in the MLP layers and correspond to fixed feature indices across all sink tokens. We further show that intermediate sink tokens exhibit high cosine similarity to the BOS token, thereby amplifying attention and activation. Building on these insights, we introduce a simple decorrelation loss that reduces cosine similarity between BOS and other tokens, effectively mitigating intermediate sinks and massive activations. Furthermore, our method improves word error rate (WER) under high audio-visual feature downsampling while remaining stable at lower downsampling rates.
Ant Group's Ming-Flash-Omni introduces a sparse, unified architecture for multimodal perception and generation, building on a Mixture-of-Experts LLM. The system achieves state-of-the-art results in contextual ASR and generative segmentation, alongside competitive performance across diverse vision, speech, and language tasks.
We propose integration of reasoning into speech large language models (speechLLMs) for the end-to-end slot-filling task. Inspired by the recent development of reasoning LLMs, we use a chain-of-thought framework to decompose the slot-filling task into multiple reasoning steps, create a reasoning dataset and apply the supervised fine-tuning strategy to a speechLLM. We distinguish between regular and reasoning speechLLMs and experiment with different types and sizes of LLMs as their text foundation models. We demonstrate performance improvements by introducing reasoning (intermediate) steps. However, we show that a reasoning textual LLM developed mainly for math, logic and coding domains might be inferior as a foundation model for a reasoning speechLLM. We further show that hybrid speechLLMs, built on a hybrid text foundation LLM and fine-tuned to preserve both direct and reasoning modes of operation, have better performance than those fine-tuned employing only one mode of operation.
Slot filling is a crucial subtask in spoken language understanding (SLU), traditionally implemented as a cascade of speech recognition followed by one or more natural language understanding (NLU) components. The recent advent of speech-based large language models (speechLLMs), which integrate speech and textual foundation models, has opened new avenues for achieving speech understanding tasks in a more unified, generative, and instruction-following manner while promising data and compute efficiency with zero-shot abilities, generalizing to unseen slot labels. We address the slot-filling task by creating an empirical upper bound for the task, identifying performance, robustness, and generalization gaps, and proposing improvements to the training data, architecture, and training strategies to narrow the gap with the upper bound result. We show that each of these measures improve performance substantially, while highlighting practical challenges and providing empirical guidance and insights for harnessing these emerging models.
Large Audio Language Models (LALMs) are increasingly applied to audio understanding and multimodal reasoning, yet their ability to locate when events occur remains underexplored. We present the first systematic study of temporal bias in LALMs, revealing a key limitation in their timestamp prediction. For example, when asked "At which second does the lecturer introduce the key formula?", models often predict timestamps that are consistently earlier or later than the ground truth. Through controlled experiments on timestamped datasets, we find that temporal bias (i) is prevalent across datasets and models, (ii) increases with audio length - even accumulating to tens of seconds in extended recordings, and (iii) varies across event types and positions. We quantify this effect with the Temporal Bias Index (TBI), measuring systematic misalignment in predicted event timings, and complement it with a visualization framework. Our findings highlight a fundamental limitation in current LALMs and call for the development of temporally robust architectures.
Despite rapid progress, ASR evaluation remains saturated with short-form English, and efficiency is rarely reported. We present the Open ASR Leaderboard, a fully reproducible benchmark and interactive leaderboard comparing 60+ open-source and proprietary systems across 11 datasets, including a dedicated multilingual track. We standardize text normalization and report both word error rate (WER) and inverse real-time factor (RTFx), enabling fair accuracy-efficiency comparisons. For English transcription, Conformer encoders paired with LLM decoders achieve the best average WER but are slower, while CTC and TDT decoders deliver much better RTFx, making them attractive for long-form and offline use. Whisper-derived encoders fine-tuned for English improve accuracy but often trade off multilingual coverage. All code and dataset loaders are open-sourced to support transparent, extensible evaluation.
Researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Shanghai AI Laboratory introduce AUDIOMARATHON, a benchmark for evaluating Large Audio Language Models (LALMs) on long-context audio understanding and inference efficiency. The benchmark reveals current LALMs struggle with long-form speaker analysis and temporal reasoning, demonstrating a substantial gap compared to human performance, while also identifying effective token pruning strategies like the proposed "Frame" method for improving efficiency.
02 Oct 2025
End-to-end speech-in speech-out dialogue systems are emerging as a powerful alternative to traditional ASR-LLM-TTS pipelines, generating more natural, expressive responses with significantly lower latency. However, these systems remain prone to hallucinations due to limited factual grounding. While text-based dialogue systems address this challenge by integrating tools such as web search and knowledge graph APIs, we introduce the first approach to extend tool use directly into speech-in speech-out systems. A key challenge is that tool integration substantially increases response latency, disrupting conversational flow. To mitigate this, we propose Streaming Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Streaming RAG), a novel framework that reduces user-perceived latency by predicting tool queries in parallel with user speech, even before the user finishes speaking. Specifically, we develop a post-training pipeline that teaches the model when to issue tool calls during ongoing speech and how to generate spoken summaries that fuse audio queries with retrieved text results, thereby improving both accuracy and responsiveness. To evaluate our approach, we construct AudioCRAG, a benchmark created by converting queries from the publicly available CRAG dataset into speech form. Experimental results demonstrate that our streaming RAG approach increases QA accuracy by up to 200% relative (from 11.1% to 34.2% absolute) and further enhances user experience by reducing tool use latency by 20%. Importantly, our streaming RAG approach is modality-agnostic and can be applied equally to typed input, paving the way for more agentic, real-time AI assistants.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.