COMSATS University Islamabad
04 Sep 2025
Zhejiang Normal UniversityCOMSATS University IslamabadSakarya UniversityKing Khalid UniversityShiyan Key Laboratory of Electromagnetic Induction and Energy Saving Technology, School of Artificial Intelligence, Hubei University of Automotive TechnologyApplied Science Research Center, Applied Science Private University
We propose a theoretical investigation of the photonic spin Hall effect (PSHE) in a mid-infrared probe field by employing an asymmetric double AlGaAsGaAs quantum well as the intracavity medium. The system is designed such that an external control beam together with tunable tunneling barriers regulates the quantum interference of the probe tunneling process. This configuration enables precise manipulation of the PSHE for both horizontally and vertically polarized components of light. Our analysis reveals the emergence of a giant horizontal PSHE in the quantum well based cavity system. Moreover, by incorporating absorptive and gain-assisted cavity slabs, the horizontal PSHE is further amplified, leading to an even more pronounced photonic spin separation. The results provide novel insights into light matter interactions in semiconductor quantum wells and suggest an effective route for enhancing and controlling the PSHE in mid-infrared photonic devices.
We investigate the thermodynamic and observational implications for the charged torus-like black holes, a class of solutions distinct from the classical Schwarzschild black holes. We explicitly derive the fundamental thermodynamic properties, such as heat capacity, P-V diagram, isothermal compressibility, Helmholtz free energy, and Gibbs free energy, under different entropy models. We find that only the exponential corrected entropy demonstrates multiple phase transitions, which we validate with the Ricci Scalar divergence obtained from the Ruppeiner formalism. This indicates that exponential corrected entropy is more sensitive to BH's microstructure as compared to the Hawking-Bekenstein and Rènyi entropy models. In addition, we study the sparsity and emission rates of Hawking radiation, demonstrating that exponential correction entropy yields more consistent and stable behavior. In our observational analysis, we graphically demonstrate the behavior of redshift, blueshift, and gravitational shift, and identify specific conditions where the photon sphere radius exceeds the innermost stable circular orbit radius, which depends on the values of parameters such as electric charge and cosmological constant. The novel insight of this work is that despite this violation, our computed redshift, blueshift, and gravitational shifts fall within the range of the observational data of NGC 4258 and UGC 3789.
Automatic image aesthetics assessment is a computer vision problem dealing with categorizing images into different aesthetic levels. The categorization is usually done by analyzing an input image and computing some measure of the degree to which the image adheres to the fundamental principles of photography such as balance, rhythm, harmony, contrast, unity, look, feel, tone and texture. Due to its diverse applications in many areas, automatic image aesthetic assessment has gained significant research attention in recent years. This article presents a review of the contemporary automatic image aesthetics assessment techniques. Many traditional hand-crafted and deep learning-based approaches are reviewed, and critical problem aspects are discussed, including why some features or models perform better than others and the limitations. A comparison of the quantitative results of different methods is also provided.
National United University University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Carnegie Mellon UniversitySichuan University
Carnegie Mellon UniversitySichuan University Sun Yat-Sen UniversityKorea University
Sun Yat-Sen UniversityKorea University Beihang University
Beihang University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Tsinghua UniversityNankai University
Tsinghua UniversityNankai University Peking UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchSouthwest University
Peking UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchSouthwest University Stockholm UniversityUniversity of TurinUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal UniversityCentral China Normal University
Stockholm UniversityUniversity of TurinUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal UniversityCentral China Normal University Shandong UniversityLanzhou UniversityUlm UniversityNorthwest UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasIowa State UniversityUniversity of South China
Shandong UniversityLanzhou UniversityUlm UniversityNorthwest UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasIowa State UniversityUniversity of South China University of GroningenWarsaw University of TechnologyGuangxi UniversityShanxi UniversityHenan University of Science and TechnologyHelmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-RossendorfZhengzhou UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoCOMSATS University IslamabadHangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, UCASIndian Institute of Technology GuwahatiBudker Institute of Nuclear PhysicsXian Jiaotong UniversityJohannes Gutenberg UniversityINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiHenan Normal UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsJustus Liebig University GiessenInstitute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of SciencesGSI Helmholtzzentrum fur Schwerionenforschung GmbHUniversity of the PunjabHuazhong Normal UniversityThe University of MississippiNikhef, National Institute for Subatomic PhysicsUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningINFN Sezione di Roma Tor VergataHelmholtz-Institut MainzPontificia Universidad JaverianaIJCLab, Université Paris-Saclay, CNRSSchool of Physics and Technology, Wuhan UniversityInstitut f¨ur Kernphysik, Forschungszentrum J¨ulichINFN-Sezione di FerraraRuhr-University-BochumUniversity of Rome
“Tor Vergata
”
University of GroningenWarsaw University of TechnologyGuangxi UniversityShanxi UniversityHenan University of Science and TechnologyHelmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-RossendorfZhengzhou UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoCOMSATS University IslamabadHangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, UCASIndian Institute of Technology GuwahatiBudker Institute of Nuclear PhysicsXian Jiaotong UniversityJohannes Gutenberg UniversityINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiHenan Normal UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsJustus Liebig University GiessenInstitute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of SciencesGSI Helmholtzzentrum fur Schwerionenforschung GmbHUniversity of the PunjabHuazhong Normal UniversityThe University of MississippiNikhef, National Institute for Subatomic PhysicsUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningINFN Sezione di Roma Tor VergataHelmholtz-Institut MainzPontificia Universidad JaverianaIJCLab, Université Paris-Saclay, CNRSSchool of Physics and Technology, Wuhan UniversityInstitut f¨ur Kernphysik, Forschungszentrum J¨ulichINFN-Sezione di FerraraRuhr-University-BochumUniversity of Rome
“Tor Vergata
”
 University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Carnegie Mellon UniversitySichuan University
Carnegie Mellon UniversitySichuan University Sun Yat-Sen UniversityKorea University
Sun Yat-Sen UniversityKorea University Beihang University
Beihang University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Tsinghua UniversityNankai University
Tsinghua UniversityNankai University Peking UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchSouthwest University
Peking UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchSouthwest University Stockholm UniversityUniversity of TurinUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal UniversityCentral China Normal University
Stockholm UniversityUniversity of TurinUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal UniversityCentral China Normal University Shandong UniversityLanzhou UniversityUlm UniversityNorthwest UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasIowa State UniversityUniversity of South China
Shandong UniversityLanzhou UniversityUlm UniversityNorthwest UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasIowa State UniversityUniversity of South China University of GroningenWarsaw University of TechnologyGuangxi UniversityShanxi UniversityHenan University of Science and TechnologyHelmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-RossendorfZhengzhou UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoCOMSATS University IslamabadHangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, UCASIndian Institute of Technology GuwahatiBudker Institute of Nuclear PhysicsXian Jiaotong UniversityJohannes Gutenberg UniversityINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiHenan Normal UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsJustus Liebig University GiessenInstitute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of SciencesGSI Helmholtzzentrum fur Schwerionenforschung GmbHUniversity of the PunjabHuazhong Normal UniversityThe University of MississippiNikhef, National Institute for Subatomic PhysicsUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningINFN Sezione di Roma Tor VergataHelmholtz-Institut MainzPontificia Universidad JaverianaIJCLab, Université Paris-Saclay, CNRSSchool of Physics and Technology, Wuhan UniversityInstitut f¨ur Kernphysik, Forschungszentrum J¨ulichINFN-Sezione di FerraraRuhr-University-BochumUniversity of Rome
“Tor Vergata
”
University of GroningenWarsaw University of TechnologyGuangxi UniversityShanxi UniversityHenan University of Science and TechnologyHelmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-RossendorfZhengzhou UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoCOMSATS University IslamabadHangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, UCASIndian Institute of Technology GuwahatiBudker Institute of Nuclear PhysicsXian Jiaotong UniversityJohannes Gutenberg UniversityINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiHenan Normal UniversityNorth China Electric Power UniversityInstitute of high-energy PhysicsJustus Liebig University GiessenInstitute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of SciencesGSI Helmholtzzentrum fur Schwerionenforschung GmbHUniversity of the PunjabHuazhong Normal UniversityThe University of MississippiNikhef, National Institute for Subatomic PhysicsUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningINFN Sezione di Roma Tor VergataHelmholtz-Institut MainzPontificia Universidad JaverianaIJCLab, Université Paris-Saclay, CNRSSchool of Physics and Technology, Wuhan UniversityInstitut f¨ur Kernphysik, Forschungszentrum J¨ulichINFN-Sezione di FerraraRuhr-University-BochumUniversity of Rome
“Tor Vergata
”Based on 10.64 fb−1 of e+e− collision data taken at center-of-mass energies between 4.237 and 4.699 GeV with the BESIII detector, we study the leptonic Ds+ decays using the e+e−→Ds∗+Ds∗− process. The branching fractions of Ds+→ℓ+νℓ(ℓ=μ,τ) are measured to be B(Ds+→μ+νμ)=(0.547±0.026stat±0.016syst)% and B(Ds+→τ+ντ)=(5.60±0.16stat±0.20syst)%, respectively. The product of the decay constant and Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa matrix element ∣Vcs∣ is determined to be fDs+∣Vcs∣=(246.5±5.9stat±3.6syst±0.5input)μν MeV and fDs+∣Vcs∣=(252.7±3.6stat±4.5syst±0.6input))τν MeV, respectively. Taking the value of ∣Vcs∣ from a global fit in the Standard Model, we obtain fDs+=(252.8±6.0stat±3.7syst±0.6input)μν MeV and fDs+=(259.2±3.6stat±4.5syst±0.6input)τν MeV, respectively. Conversely, taking the value for fDs+ from the latest lattice quantum chromodynamics calculation, we obtain ∣Vcs∣=(0.986±0.023stat±0.014syst±0.003input)μν and ∣Vcs∣=(1.011±0.014stat±0.018syst±0.003input)τν, respectively.
13 Nov 2024
Numerical wave functions (WFs), root mean square (RMS) radii, E1 and M1 radiative transitions, and branching ratios of S,P,D and F states of toponium mesons (tt) are calculated using a non-relativistic quark potential model (NRQPM). Shooting method is used to solve the radial Schrodinger equation to find the radial wave functions which are used in the calculation of properties of mesons. Calculated masses are compared with the theoretical available data.
29 Apr 2025
Quantum Machine Learning (QML) has shown promise in diverse applications such as environmental monitoring, healthcare diagnostics, and financial modeling. However, its practical implementation faces challenges, including limited quantum hardware and the complexity of integrating quantum algorithms with classical systems. One critical challenge is handling imbalanced datasets, where rare events are often misclassified due to skewed data distributions. Quantum Bayesian Networks (QBNs) address this issue by enhancing feature extraction and improving the classification of rare events such as oil spills. This paper introduces a Bayesian approach utilizing QBNs to classify satellite-derived imbalanced datasets, distinguishing ``oil-spill'' from ``non-spill'' regions. QBNs leverage probabilistic reasoning and quantum state preparation to integrate quantum enhancements into classical machine learning architectures. Our approach achieves a 0.99 AUC score, demonstrating its efficacy in anomaly detection and advancing precise environmental monitoring and management. While integration enhances classification performance, dataset-specific challenges require further optimization.
We propose an automatic framework for toll collection, consisting of three steps: vehicle type recognition, license plate localization, and reading. However, each of the three steps becomes non-trivial due to image variations caused by several factors. The traditional vehicle decorations on the front cause variations among vehicles of the same type. These decorations make license plate localization and recognition difficult due to severe background clutter and partial occlusions. Likewise, on most vehicles, specifically trucks, the position of the license plate is not consistent. Lastly, for license plate reading, the variations are induced by non-uniform font styles, sizes, and partially occluded letters and numbers. Our proposed framework takes advantage of both data availability and performance evaluation of the backbone deep learning architectures. We gather a novel dataset, \emph{Diverse Vehicle and License Plates Dataset (DVLPD)}, consisting of 10k images belonging to six vehicle types. Each image is then manually annotated for vehicle type, license plate, and its characters and digits. For each of the three tasks, we evaluate You Only Look Once (YOLO)v2, YOLOv3, YOLOv4, and FasterRCNN. For real-time implementation on a Raspberry Pi, we evaluate the lighter versions of YOLO named Tiny YOLOv3 and Tiny YOLOv4. The best Mean Average Precision (mAP@0.5) of 98.8% for vehicle type recognition, 98.5% for license plate detection, and 98.3% for license plate reading is achieved by YOLOv4, while its lighter version, i.e., Tiny YOLOv4 obtained a mAP of 97.1%, 97.4%, and 93.7% on vehicle type recognition, license plate detection, and license plate reading, respectively. The dataset and the training codes are available at this https URL
Deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) of medical images requires
large datasets. However, the lack of large publicly available labeled datasets
limits the development of deep learning-based CAD systems. Generative
Adversarial Networks (GANs), in particular, CycleGAN, can be used to generate
new cross-domain images without paired training data. However, most
CycleGAN-based synthesis methods lack the potential to overcome alignment and
asymmetry between the input and generated data. We propose a two-stage
technique for the synthesis of abdominal MRI using cross-modality translation
of abdominal CT. We show that the synthetic data can help improve the
performance of the liver segmentation network. We increase the number of
abdominal MRI images through cross-modality image transformation of unpaired CT
images using a CycleGAN inspired deformation invariant network called EssNet.
Subsequently, we combine the synthetic MRI images with the original MRI images
and use them to improve the accuracy of the U-Net on a liver segmentation task.
We train the U-Net on real MRI images and then on real and synthetic MRI
images. Consequently, by comparing both scenarios, we achieve an improvement in
the performance of U-Net. In summary, the improvement achieved in the
Intersection over Union (IoU) is 1.17%. The results show potential to address
the data scarcity challenge in medical imaging.
16 Aug 2021
 University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Beihang University
Beihang University Nanjing UniversityNankai University
Nanjing UniversityNankai University Peking UniversityINFN Sezione di Pisa
Peking UniversityINFN Sezione di Pisa University of MinnesotaThe University of Texas at Dallas
University of MinnesotaThe University of Texas at Dallas Stockholm UniversityUniversity of TurinUppsala UniversityThe University of ManchesterJilin UniversityCentral China Normal UniversityLanzhou UniversityWayne State UniversitySoochow UniversityHunan UniversityUniversity of Messina
Stockholm UniversityUniversity of TurinUppsala UniversityThe University of ManchesterJilin UniversityCentral China Normal UniversityLanzhou UniversityWayne State UniversitySoochow UniversityHunan UniversityUniversity of Messina University of GroningenZhengzhou UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoCOMSATS University IslamabadXian Jiaotong UniversityINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiHenan Normal UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iInstitute of high-energy PhysicsJustus Liebig University GiessenJohannes Gutenberg University of MainzGSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion ResearchLiaoning UniversityUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningUniversity of Eastern PiedmontHelmholtz-Institut f ̈ur Strahlen- und KernphysikKVI-CARTINFN-Sezione di FerraraUniversit
at BonnRuhr-University-Bochum":
University of GroningenZhengzhou UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoCOMSATS University IslamabadXian Jiaotong UniversityINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiHenan Normal UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iInstitute of high-energy PhysicsJustus Liebig University GiessenJohannes Gutenberg University of MainzGSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion ResearchLiaoning UniversityUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningUniversity of Eastern PiedmontHelmholtz-Institut f ̈ur Strahlen- und KernphysikKVI-CARTINFN-Sezione di FerraraUniversit
at BonnRuhr-University-Bochum":By analyzing 6.32 fb−1 of e+e− annihilation data collected
at the center-of-mass energies between 4.178 and 4.226\,GeV with the BESIII
detector, we determine the branching fraction of the leptonic decay
Ds+→τ+ντ with τ+→π+π0νˉτ, to be
$\mathcal{B}_{D_s^+\to\tau^+\nu_\tau}=(5.29\pm0.25_{\rm stat}\pm0.20_{\rm
syst})\%$. We estimate the product of the Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa matrix
element ∣Vcs∣ and the Ds+ decay constant fDs+ to be
fDs+∣Vcs∣=(244.8±5.8stat±4.8syst) MeV
using the known values of the τ+ and Ds+ masses as well as the
Ds+ lifetime, together with our branching fraction measurement. Combining
with the value of ∣Vcs∣ obtained from a global fit in the standard model
and fDs+ from lattice quantum chromodynamics, we obtain
fDs+=(251.6±5.9stat±4.9syst)\,MeV and $|V_{cs}| =
0.980\pm0.023_{\rm stat}\pm0.019_{\rm syst}$.
Image captioning by the encoder-decoder framework has shown tremendous advancement in the last decade where CNN is mainly used as encoder and LSTM is used as a decoder. Despite such an impressive achievement in terms of accuracy in simple images, it lacks in terms of time complexity and space complexity efficiency. In addition to this, in case of complex images with a lot of information and objects, the performance of this CNN-LSTM pair downgraded exponentially due to the lack of semantic understanding of the scenes presented in the images. Thus, to take these issues into consideration, we present CNN-GRU encoder decode framework for caption-to-image reconstructor to handle the semantic context into consideration as well as the time complexity. By taking the hidden states of the decoder into consideration, the input image and its similar semantic representations is reconstructed and reconstruction scores from a semantic reconstructor are used in conjunction with likelihood during model training to assess the quality of the generated caption. As a result, the decoder receives improved semantic information, enhancing the caption production process. During model testing, combining the reconstruction score and the log-likelihood is also feasible to choose the most appropriate caption. The suggested model outperforms the state-of-the-art LSTM-A5 model for picture captioning in terms of time complexity and accuracy.
12 Aug 2025
Wuhan UniversityNational United University Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University
Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University Nanjing UniversityUniversity of Bonn
Nanjing UniversityUniversity of Bonn Zhejiang UniversityNankai University
Zhejiang UniversityNankai University INFN
INFN Peking UniversityChina University of Mining and TechnologyUniversity of TurinUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal University
Peking UniversityChina University of Mining and TechnologyUniversity of TurinUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal University Shandong UniversitySoochow University
Shandong UniversitySoochow University University of GroningenNanjing Normal UniversityGuangxi UniversityZhengzhou UniversityCOMSATS University IslamabadHenan Normal UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iInstitute of high-energy PhysicsJustus Liebig University GiessenJohannes Gutenberg University of MainzIslamic University of TechnologyUniversity of the PunjabLiaoning UniversityHuazhong Normal UniversityHelmholtz-Institut für Strahlen-und KernphysikG.I. Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASHuangshan CollegeUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningUniversity of GiessenBESIII CollaborationRuhr-University-Bochum
University of GroningenNanjing Normal UniversityGuangxi UniversityZhengzhou UniversityCOMSATS University IslamabadHenan Normal UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iInstitute of high-energy PhysicsJustus Liebig University GiessenJohannes Gutenberg University of MainzIslamic University of TechnologyUniversity of the PunjabLiaoning UniversityHuazhong Normal UniversityHelmholtz-Institut für Strahlen-und KernphysikG.I. Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASHuangshan CollegeUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningUniversity of GiessenBESIII CollaborationRuhr-University-Bochum
 Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University
Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University Nanjing UniversityUniversity of Bonn
Nanjing UniversityUniversity of Bonn Zhejiang UniversityNankai University
Zhejiang UniversityNankai University INFN
INFN Peking UniversityChina University of Mining and TechnologyUniversity of TurinUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal University
Peking UniversityChina University of Mining and TechnologyUniversity of TurinUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal University Shandong UniversitySoochow University
Shandong UniversitySoochow University University of GroningenNanjing Normal UniversityGuangxi UniversityZhengzhou UniversityCOMSATS University IslamabadHenan Normal UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iInstitute of high-energy PhysicsJustus Liebig University GiessenJohannes Gutenberg University of MainzIslamic University of TechnologyUniversity of the PunjabLiaoning UniversityHuazhong Normal UniversityHelmholtz-Institut für Strahlen-und KernphysikG.I. Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASHuangshan CollegeUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningUniversity of GiessenBESIII CollaborationRuhr-University-Bochum
University of GroningenNanjing Normal UniversityGuangxi UniversityZhengzhou UniversityCOMSATS University IslamabadHenan Normal UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iInstitute of high-energy PhysicsJustus Liebig University GiessenJohannes Gutenberg University of MainzIslamic University of TechnologyUniversity of the PunjabLiaoning UniversityHuazhong Normal UniversityHelmholtz-Institut für Strahlen-und KernphysikG.I. Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RASHuangshan CollegeUniversity of Science and Technology LiaoningUniversity of GiessenBESIII CollaborationRuhr-University-BochumUsing e+e− collision data collected with the BESIII detector operating at the Beijing Electron Positron Collider, the cross section of e+e−→π+π−hc is measured at 59 points with center-of-mass energy s ranging from 4.009 to 4.950 GeV with a total integrated luminosity of 22.2 fb−1. The cross section between 4.3 and 4.45 GeV exhibits a plateau-like shape and drops sharply around 4.5 GeV, which cannot be described by two resonances only. Three coherent Breit-Wigner functions are used to parameterize the s-dependent cross section line shape. The masses and widths are determined to be M1=(4223.6−3.7−2.9+3.6+2.6) MeV/c2, Γ1=(58.5−11.4−6.5+10.8+6.7) MeV, M2=(4327.4−18.8−9.3+20.1+10.7) MeV/c2, Γ2=(244.1−27.1−18.3+34.0+24.2) MeV, and M3=(4467.4−5.4−2.7+7.2+3.2) MeV/c2, Γ3=(62.8−14.4−7.0+19.2+9.9) MeV. The first uncertainties are statistical and the second are systematic. The inclusion of the relatively narrower third component proves crucial for reproducing the drop at around 4.5~GeV. The statistical significance of the three-resonance assumption over the two-resonance assumption is greater than 5σ.
The potato is a widely grown crop in many regions of the world. In recent
decades, potato farming has gained incredible traction in the world. Potatoes
are susceptible to several illnesses that stunt their development. This plant
seems to have significant leaf disease. Early Blight and Late Blight are two
prevalent leaf diseases that affect potato plants. The early detection of these
diseases would be beneficial for enhancing the yield of this crop. The ideal
solution is to use image processing to identify and analyze these disorders.
Here, we present an autonomous method based on image processing and machine
learning to detect late blight disease affecting potato leaves. The proposed
method comprises four different phases: (1) Histogram Equalization is used to
improve the quality of the input image; (2) feature extraction is performed
using a Deep CNN model, then these extracted features are concatenated; (3)
feature selection is performed using wrapper-based feature selection; (4)
classification is performed using an SVM classifier and its variants. This
proposed method achieves the highest accuracy of 99% using SVM by selecting 550
features.
20 Oct 2024
We study the phenomenological implications of the minimal supersymmetric standard model (MSSM) augmented by a non-abelian flavor symmetry labeled as sMSSM. Incorporating this flavor symmetry allows for a significant reduction in the original plethora of free parameters present in the MSSM, ultimately reducing them down to just seven in sMSSM. This reduction of free parameters is not achieved through ad hoc assumptions like in the constrained MSSM (CMSSM); rather, it is grounded in theoretical considerations. Our work focuses on exploring the interplay between the W boson mass (MW) predictions, the cold dark matter (CDM) relic abundance (ΩCDMh2), and the (g−2)μ anomaly. We identified correlations among the theoretical parameters arising from this interplay, which can be complemented by experimental constraints such as the Higgs boson mass, B-physics observables, and charge and color breaking minima. Additionally, our investigations show that the (g−2)μ discrepancy and the Planck bounds on ΩCDMh2 can be addressed within the sMSSM, but only in a very narrow region of the parameter space.
This study derives a novel family of charged black hole solutions featuring short- and long-range modifications. These ones are achieved through a Yukawa-like gravitational potential modification and a nonsingular electric potential incorporation. The short-range corrections encode quantum gravity effects, while the long-range adjustments simulate gravitational effects akin to those attributed to dark matter. Our investigation reveals that the total mass of the black hole undergoes corrections owing to the apparent presence of dark matter mass and the self-adjusted electric charge mass. Two distinct solutions are discussed: a regular black hole solution characterizing small black holes, where quantum effects play a crucial role, and a second solution portraying large black holes at considerable distances, where the significance of Yukawa corrections comes into play. Notably, these long-range corrections contribute to an increase in the total mass and hold particular interest as they can emulate the role of dark matter. Finally, we explore the phenomenological aspects of the black hole. Specifically, we examine the influence of electric charge and Yukawa parameters on thermodynamic quantities, the quasinormal modes for the charged scalar perturbations as well as for the vector perturbations, analysis of the geodesics of light/massive particles, and the accretion of matter onto the charged black hole solution.
Deep learning techniques, particularly convolutional neural networks, have shown great potential in computer vision and medical imaging applications. However, deep learning models are computationally demanding as they require enormous computational power and specialized processing hardware for model training. To make these models portable and compatible for prototyping, their implementation on low-power devices is imperative. In this work, we present the implementation of Modified U-Net on Intel Movidius Neural Compute Stick 2 (NCS-2) for the segmentation of medical images. We selected U-Net because, in medical image segmentation, U-Net is a prominent model that provides improved performance for medical image segmentation even if the dataset size is small. The modified U-Net model is evaluated for performance in terms of dice score. Experiments are reported for segmentation task on three medical imaging datasets: BraTs dataset of brain MRI, heart MRI dataset, and Ziehl-Neelsen sputum smear microscopy image (ZNSDB) dataset. For the proposed model, we reduced the number of parameters from 30 million in the U-Net model to 0.49 million in the proposed architecture. Experimental results show that the modified U-Net provides comparable performance while requiring significantly lower resources and provides inference on the NCS-2. The maximum dice scores recorded are 0.96 for the BraTs dataset, 0.94 for the heart MRI dataset, and 0.74 for the ZNSDB dataset.
Buses and heavy vehicles have more blind spots compared to cars and other
road vehicles due to their large sizes. Therefore, accidents caused by these
heavy vehicles are more fatal and result in severe injuries to other road
users. These possible blind-spot collisions can be identified early using
vision-based object detection approaches. Yet, the existing state-of-the-art
vision-based object detection models rely heavily on a single feature
descriptor for making decisions. In this research, the design of two
convolutional neural networks (CNNs) based on high-level feature descriptors
and their integration with faster R-CNN is proposed to detect blind-spot
collisions for heavy vehicles. Moreover, a fusion approach is proposed to
integrate two pre-trained networks (i.e., Resnet 50 and Resnet 101) for
extracting high level features for blind-spot vehicle detection. The fusion of
features significantly improves the performance of faster R-CNN and
outperformed the existing state-of-the-art methods. Both approaches are
validated on a self-recorded blind-spot vehicle detection dataset for buses and
an online LISA dataset for vehicle detection. For both proposed approaches, a
false detection rate (FDR) of 3.05% and 3.49% are obtained for the self
recorded dataset, making these approaches suitable for real time applications.
The problems that tobacco workshops encounter include poor curing,
inconsistencies in supplies, irregular scheduling, and a lack of oversight, all
of which drive up expenses and worse quality. Large quantities make manual
examination costly, sluggish, and unreliable. Deep convolutional neural
networks have recently made strides in capabilities that transcend those of
conventional methods. To effectively enhance them, nevertheless, extensive
customization is needed to account for subtle variations in tobacco grade. This
study introduces InspectionV3, an integrated solution for automated flue-cured
tobacco grading that makes use of a customized deep convolutional neural
network architecture. A scope that covers color, maturity, and curing
subtleties is established via a labelled dataset consisting of 21,113 images
spanning 20 quality classes. Expert annotators performed preprocessing on the
tobacco leaf images, including cleaning, labelling, and augmentation.
Multi-layer CNN factors use batch normalization to describe domain properties
like as permeability and moisture spots, and so account for the subtleties of
the workshop. Its expertise lies in converting visual patterns into useful
information for enhancing workflow. Fast notifications are made possible by
real-time, on-the-spot grading that matches human expertise. Images-powered
analytics dashboards facilitate the tracking of yield projections, inventories,
bottlenecks, and the optimization of data-driven choices. More labelled images
are assimilated after further retraining, improving representational capacities
and enabling adaptations for seasonal variability. Metrics demonstrate 97%
accuracy, 95% precision and recall, 96% F1-score and AUC, 95% specificity;
validating real-world viability.
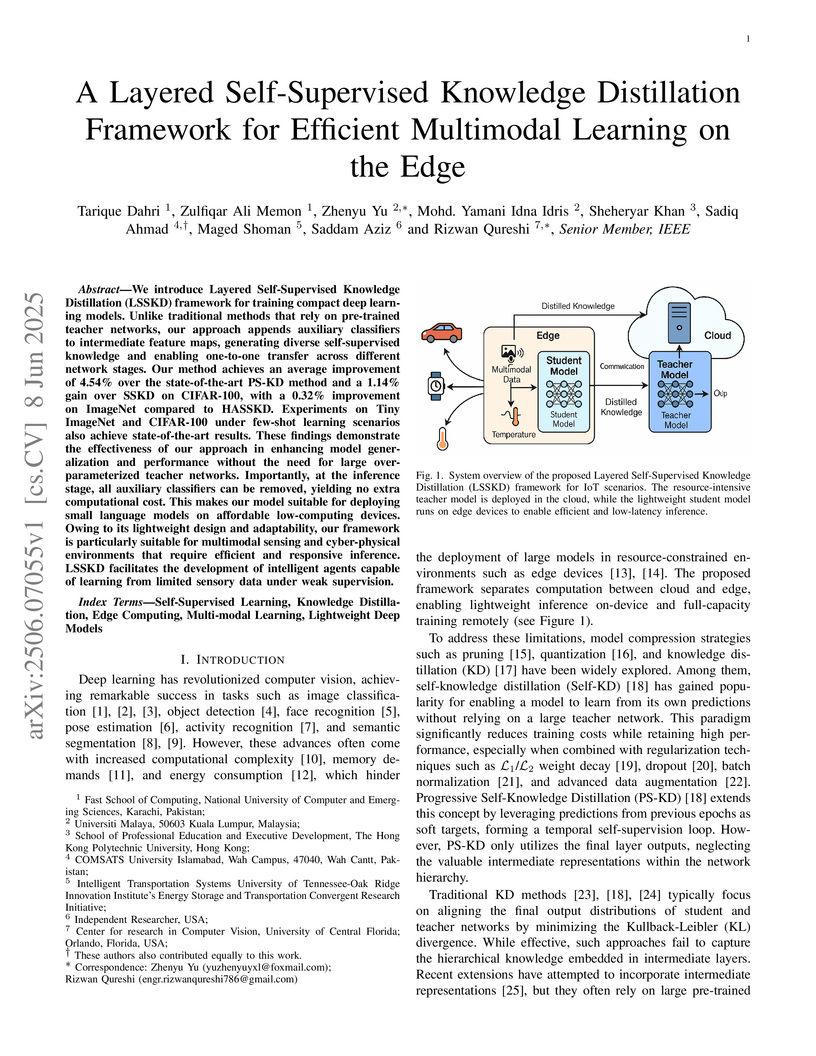
We introduce Layered Self-Supervised Knowledge Distillation (LSSKD) framework
for training compact deep learning models. Unlike traditional methods that rely
on pre-trained teacher networks, our approach appends auxiliary classifiers to
intermediate feature maps, generating diverse self-supervised knowledge and
enabling one-to-one transfer across different network stages. Our method
achieves an average improvement of 4.54\% over the state-of-the-art PS-KD
method and a 1.14% gain over SSKD on CIFAR-100, with a 0.32% improvement on
ImageNet compared to HASSKD. Experiments on Tiny ImageNet and CIFAR-100 under
few-shot learning scenarios also achieve state-of-the-art results. These
findings demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in enhancing model
generalization and performance without the need for large over-parameterized
teacher networks. Importantly, at the inference stage, all auxiliary
classifiers can be removed, yielding no extra computational cost. This makes
our model suitable for deploying small language models on affordable
low-computing devices. Owing to its lightweight design and adaptability, our
framework is particularly suitable for multimodal sensing and cyber-physical
environments that require efficient and responsive inference. LSSKD facilitates
the development of intelligent agents capable of learning from limited sensory
data under weak supervision.
U-Net is a widely adopted neural network in the domain of medical image segmentation. Despite its quick embracement by the medical imaging community, its performance suffers on complicated datasets. The problem can be ascribed to its simple feature extracting blocks: encoder/decoder, and the semantic gap between encoder and decoder. Variants of U-Net (such as R2U-Net) have been proposed to address the problem of simple feature extracting blocks by making the network deeper, but it does not deal with the semantic gap problem. On the other hand, another variant UNET++ deals with the semantic gap problem by introducing dense skip connections but has simple feature extraction blocks. To overcome these issues, we propose a new U-Net based medical image segmentation architecture R2U++. In the proposed architecture, the adapted changes from vanilla U-Net are: (1) the plain convolutional backbone is replaced by a deeper recurrent residual convolution block. The increased field of view with these blocks aids in extracting crucial features for segmentation which is proven by improvement in the overall performance of the network. (2) The semantic gap between encoder and decoder is reduced by dense skip pathways. These pathways accumulate features coming from multiple scales and apply concatenation accordingly. The modified architecture has embedded multi-depth models, and an ensemble of outputs taken from varying depths improves the performance on foreground objects appearing at various scales in the images. The performance of R2U++ is evaluated on four distinct medical imaging modalities: electron microscopy (EM), X-rays, fundus, and computed tomography (CT). The average gain achieved in IoU score is 1.5+-0.37% and in dice score is 0.9+-0.33% over UNET++, whereas, 4.21+-2.72 in IoU and 3.47+-1.89 in dice score over R2U-Net across different medical imaging segmentation datasets.
18 Apr 2025
University of Mississippi University of Pittsburgh
University of Pittsburgh Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan UniversityKorea University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan UniversityKorea University University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University
Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University Tsinghua UniversityPanjab UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaUniversity of EdinburghNankai University
Tsinghua UniversityPanjab UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaUniversity of EdinburghNankai University Peking UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal UniversityLanzhou UniversityTarbiat Modares UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasUniversity of South ChinaTechnische Universität MünchenNanjing Normal UniversityКрымский федеральный университет имени В.И. ВернадскогоJagiellonian UniversitySuranaree University of TechnologyShanxi UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoCOMSATS University IslamabadBudker Institute of Nuclear PhysicsINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiGSIHenan Normal UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iINFN Sezione di PerugiaJustus Liebig University GiessenJohannes Gutenberg University of MainzINFN - Sezione di PadovaSUBATECHCollege of William and MaryIHEPHelmholtz Institute MainzINFN-Sezione di GenovaUniversity of the PunjabHelmholtz-Institut für Strahlen-und KernphysikVariable Energy Cyclotron CentreINFN-Sezione di Ferrara˙Istanbul Aydın UniversityRuhr-University-Bochum
Peking UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal UniversityLanzhou UniversityTarbiat Modares UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasUniversity of South ChinaTechnische Universität MünchenNanjing Normal UniversityКрымский федеральный университет имени В.И. ВернадскогоJagiellonian UniversitySuranaree University of TechnologyShanxi UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoCOMSATS University IslamabadBudker Institute of Nuclear PhysicsINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiGSIHenan Normal UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iINFN Sezione di PerugiaJustus Liebig University GiessenJohannes Gutenberg University of MainzINFN - Sezione di PadovaSUBATECHCollege of William and MaryIHEPHelmholtz Institute MainzINFN-Sezione di GenovaUniversity of the PunjabHelmholtz-Institut für Strahlen-und KernphysikVariable Energy Cyclotron CentreINFN-Sezione di Ferrara˙Istanbul Aydın UniversityRuhr-University-Bochum
 University of Pittsburgh
University of Pittsburgh Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan UniversityKorea University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan UniversityKorea University University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University
Beihang UniversityNational Taiwan University Tsinghua UniversityPanjab UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaUniversity of EdinburghNankai University
Tsinghua UniversityPanjab UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaUniversity of EdinburghNankai University Peking UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal UniversityLanzhou UniversityTarbiat Modares UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasUniversity of South ChinaTechnische Universität MünchenNanjing Normal UniversityКрымский федеральный университет имени В.И. ВернадскогоJagiellonian UniversitySuranaree University of TechnologyShanxi UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoCOMSATS University IslamabadBudker Institute of Nuclear PhysicsINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiGSIHenan Normal UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iINFN Sezione di PerugiaJustus Liebig University GiessenJohannes Gutenberg University of MainzINFN - Sezione di PadovaSUBATECHCollege of William and MaryIHEPHelmholtz Institute MainzINFN-Sezione di GenovaUniversity of the PunjabHelmholtz-Institut für Strahlen-und KernphysikVariable Energy Cyclotron CentreINFN-Sezione di Ferrara˙Istanbul Aydın UniversityRuhr-University-Bochum
Peking UniversityJoint Institute for Nuclear ResearchUppsala UniversityGuangxi Normal UniversityLanzhou UniversityTarbiat Modares UniversityIndian Institute of Technology MadrasUniversity of South ChinaTechnische Universität MünchenNanjing Normal UniversityКрымский федеральный университет имени В.И. ВернадскогоJagiellonian UniversitySuranaree University of TechnologyShanxi UniversityINFN, Sezione di TorinoCOMSATS University IslamabadBudker Institute of Nuclear PhysicsINFN, Laboratori Nazionali di FrascatiGSIHenan Normal UniversityUniversity of Hawai’iINFN Sezione di PerugiaJustus Liebig University GiessenJohannes Gutenberg University of MainzINFN - Sezione di PadovaSUBATECHCollege of William and MaryIHEPHelmholtz Institute MainzINFN-Sezione di GenovaUniversity of the PunjabHelmholtz-Institut für Strahlen-und KernphysikVariable Energy Cyclotron CentreINFN-Sezione di Ferrara˙Istanbul Aydın UniversityRuhr-University-BochumUsing data samples of (10087±44)×106 J/ψ events and
(2712.4±14.3)×106 ψ(3686) events collected with the BESIII
detector at the BEPCII collider, we search for the CP violating decays
J/ψ→KS0KS0 and $\psi(3686)\rightarrow
K^{0}_{S}K^{0}_{S}$. No significant signals are observed over the expected
background yields. The upper limits on their branching fractions are set as
\mathcal{B}(J/\psi\rightarrow K^{0}_{S}K^{0}_{S}) <4.7\times 10^{-9} and
\mathcal{B}(\psi(3686)\rightarrow K^{0}_{S}K^{0}_{S}) <1.1\times 10^{-8} at
the 90% confidence level. These results improve the previous limits by a factor
of three for J/ψ→KS0KS0 and two orders of
magnitude for ψ(3686)→KS0KS0.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.