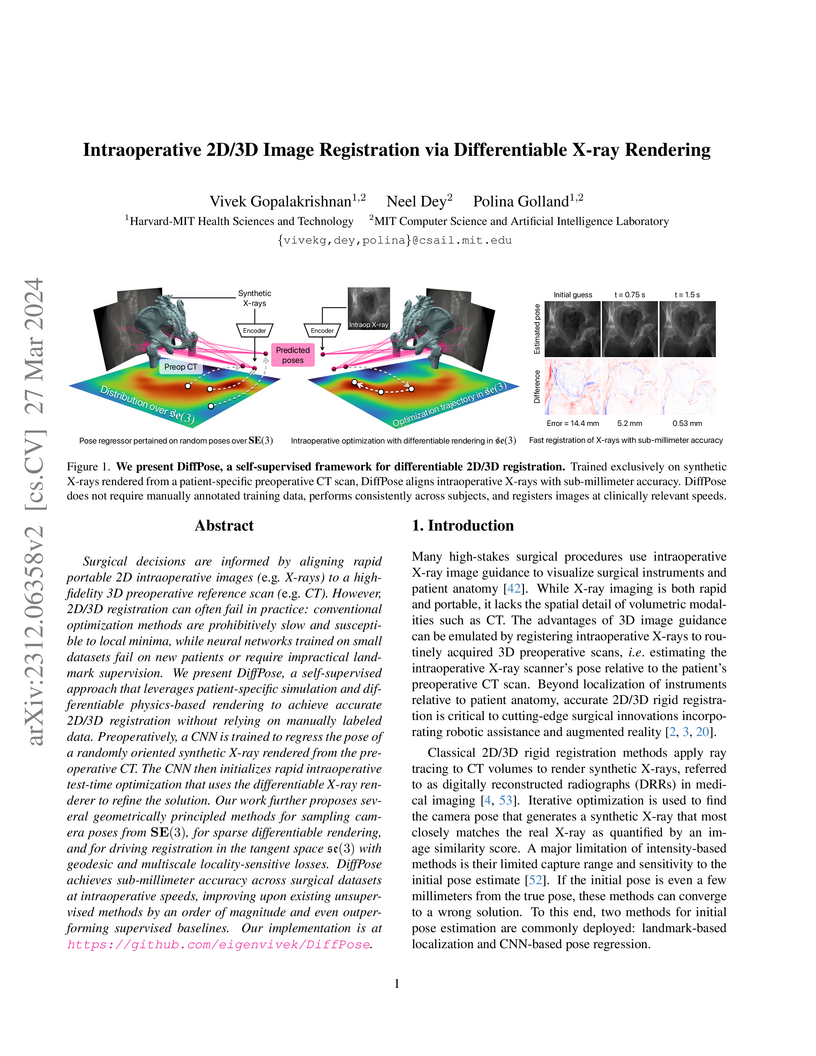
Harvard-MIT Health Sciences and Technology
Surgical decisions are informed by aligning rapid portable 2D intraoperative images (e.g., X-rays) to a high-fidelity 3D preoperative reference scan (e.g., CT). 2D/3D image registration often fails in practice: conventional optimization methods are prohibitively slow and susceptible to local minima, while neural networks trained on small datasets fail on new patients or require impractical landmark supervision. We present DiffPose, a self-supervised approach that leverages patient-specific simulation and differentiable physics-based rendering to achieve accurate 2D/3D registration without relying on manually labeled data. Preoperatively, a CNN is trained to regress the pose of a randomly oriented synthetic X-ray rendered from the preoperative CT. The CNN then initializes rapid intraoperative test-time optimization that uses the differentiable X-ray renderer to refine the solution. Our work further proposes several geometrically principled methods for sampling camera poses from SE(3), for sparse differentiable rendering, and for driving registration in the tangent space se(3) with geodesic and multiscale locality-sensitive losses. DiffPose achieves sub-millimeter accuracy across surgical datasets at intraoperative speeds, improving upon existing unsupervised methods by an order of magnitude and even outperforming supervised baselines. Our code is available at this https URL.
Diffusion MRI (dMRI) tractography enables in vivo mapping of brain structural connections, but traditional connectome generation is time-consuming and requires gray matter parcellation, posing challenges for large-scale studies. We introduce DeepMultiConnectome, a deep-learning model that predicts structural connectomes directly from tractography, bypassing the need for gray matter parcellation while supporting multiple parcellation schemes. Using a point-cloud-based neural network with multi-task learning, the model classifies streamlines according to their connected regions across two parcellation schemes, sharing a learned representation. We train and validate DeepMultiConnectome on tractography from the Human Connectome Project Young Adult dataset (n=1000), labeled with an 84 and 164 region gray matter parcellation scheme. DeepMultiConnectome predicts multiple structural connectomes from a whole-brain tractogram containing 3 million streamlines in approximately 40 seconds. DeepMultiConnectome is evaluated by comparing predicted connectomes with traditional connectomes generated using the conventional method of labeling streamlines using a gray matter parcellation. The predicted connectomes are highly correlated with traditionally generated connectomes (r=0.992 for an 84-region scheme; r=0.986 for a 164-region scheme) and largely preserve network properties. A test-retest analysis of DeepMultiConnectome demonstrates reproducibility comparable to traditionally generated connectomes. The predicted connectomes perform similarly to traditionally generated connectomes in predicting age and cognitive function. Overall, DeepMultiConnectome provides a scalable, fast model for generating subject-specific connectomes across multiple parcellation schemes.
Diffusion MRI is commonly performed using echo-planar imaging (EPI) due to
its rapid acquisition time. However, the resolution of diffusion-weighted
images is often limited by magnetic field inhomogeneity-related artifacts and
blurring induced by T2- and T2*-relaxation effects. To address these
limitations, multi-shot EPI (msEPI) combined with parallel imaging techniques
is frequently employed. Nevertheless, reconstructing msEPI can be challenging
due to phase variation between multiple shots. In this study, we introduce a
novel msEPI reconstruction approach called zero-MIRID (zero-shot
self-supervised learning of Multi-shot Image Reconstruction for Improved
Diffusion MRI). This method jointly reconstructs msEPI data by incorporating
deep learning-based image regularization techniques. The network incorporates
CNN denoisers in both k- and image-spaces, while leveraging virtual coils to
enhance image reconstruction conditioning. By employing a self-supervised
learning technique and dividing sampled data into three groups, the proposed
approach achieves superior results compared to the state-of-the-art parallel
imaging method, as demonstrated in an in-vivo experiment.
Tractography parcellation classifies streamlines reconstructed from diffusion
MRI into anatomically defined fiber tracts for clinical and research
applications. However, clinical scans often have incomplete fields of view
(FOV) where brain regions are partially imaged, leading to partial or truncated
fiber tracts. To address this challenge, we introduce TractCloud-FOV, a deep
learning framework that robustly parcellates tractography under conditions of
incomplete FOV. We propose a novel training strategy, FOV-Cut Augmentation
(FOV-CA), in which we synthetically cut tractograms to simulate a spectrum of
real-world inferior FOV cutoff scenarios. This data augmentation approach
enriches the training set with realistic truncated streamlines, enabling the
model to achieve superior generalization. We evaluate the proposed
TractCloud-FOV on both synthetically cut tractography and two real-life
datasets with incomplete FOV. TractCloud-FOV significantly outperforms several
state-of-the-art methods on all testing datasets in terms of streamline
classification accuracy, generalization ability, tract anatomical depiction,
and computational efficiency. Overall, TractCloud-FOV achieves efficient and
consistent tractography parcellation in diffusion MRI with incomplete FOV.
10 Jul 2025
Quasi-2D tin iodide perovskites (TIPs) are promising lead-free alternatives for optoelectronic applications, but achieving stable lasing remains challenging due to their limited environmental stability. Here, we report air-stable, room-temperature lasing from quasi-2D TIP microcrystals as small as 4 {\mu}m. Incorporation of the organic spacer 5IPA3 significantly enhanced the stability of these materials compared to previously reported TIPs. Lasing was observed from both dielectric (n=4) and plasmonic (n=3 and n=4) TIP microlasers. Under picosecond pumping, lasing was sustained for over 10^8 pump pulses in ambient conditions. These results represent a significant step toward practical photonic applications of tin-based perovskites.
18 Nov 2022
Visualizing elastic waves by noninvasive imaging has been useful for analyzing the mechanical properties of materials and tissues. However, the maximum wave frequency of elastography has been limited to ~10 kHz due to the finite sensitivity to small vibration and finite imaging speed. Here, we present an optical coherence elastography technique that extends the frequency range to MHz by noise reduction, anti-aliasing demodulation, and advanced wave analysis. Our system can measure the stiffness of hard (GPa) materials including bones with mm-scale resolution and characterize soft, viscoelastic materials from 100 Hz to 1 MHz. The dispersion of Rayleigh surface waves over the wide frequency range allowed us to profile depth-dependent shear modulus (10 kPa to 100 MPa) in cartilages ex vivo and the human skin in vivo. This technique opened a new window for the characterization of materials in situ with 3-dimensional resolution.
25 Apr 2019
Opioids are the preferred medications for the treatment of pain in the intensive care unit. While undertreatment leads to unrelieved pain and poor clinical outcomes, excessive use of opioids puts patients at risk of experiencing multiple adverse effects. In this work, we present a sequential decision making framework for opioid dosing based on deep reinforcement learning. It provides real-time clinically interpretable dosing recommendations, personalized according to each patient's evolving pain and physiological condition. We focus on morphine, one of the most commonly prescribed opioids. To train and evaluate the model, we used retrospective data from the publicly available MIMIC-3 database. Our results demonstrate that reinforcement learning may be used to aid decision making in the intensive care setting by providing personalized pain management interventions.
Fast spin-echo (FSE) pulse sequences for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
offer important imaging contrast in clinically feasible scan times.
T2-shuffling is widely used to resolve temporal signal dynamics in FSE
acquisitions by exploiting temporal correlations via linear latent space and a
predefined regularizer. However, predefined regularizers fail to exploit the
incoherence especially for 2D acquisitions.Recent self-supervised learning
methods achieve high-fidelity reconstructions by learning a regularizer from
undersampled data without a standard supervised training data set. In this
work, we propose a novel approach that utilizes a self supervised learning
framework to learn a regularizer constrained on a linear latent space which
improves time-resolved FSE images reconstruction quality. Additionally, in
regimes without groundtruth sensitivity maps, we propose joint estimation of
coil-sensitivity maps using an iterative reconstruction technique. Our
technique functions is in a zero-shot fashion, as it only utilizes data from a
single scan of highly undersampled time series images. We perform experiments
on simulated and retrospective in-vivo data to evaluate the performance of the
proposed zero-shot learning method for temporal FSE reconstruction. The results
demonstrate the success of our proposed method where NMSE and SSIM are
significantly increased and the artifacts are reduced.
Recent studies of genotype-phenotype (GP) maps have reported universally enhanced phenotypic robustness to genotype mutations, a feature essential to evolution. Virtually all of these studies make a simplifying assumption that each genotype -- represented as a sequence -- maps deterministically to a single phenotype, such as a discrete structure. Here, we introduce probabilistic genotype-phenotype (PrGP) maps, where each genotype maps to a vector of phenotype probabilities, as a more realistic and universal language for investigating robustness in a variety of physical, biological, and computational systems. We study three model systems to show that PrGP maps offer a generalized framework which can handle uncertainty emerging from various physical sources: (1) thermal fluctuation in RNA folding, (2) external field disorder in spin glass ground state finding, and (3) superposition and entanglement in quantum circuits, which are realized experimentally on IBM quantum computers. In all three cases, we observe a novel biphasic robustness scaling which is enhanced relative to random expectation for more frequent phenotypes and approaches random expectation for less frequent phenotypes. We derive an analytical theory for the behavior of PrGP robustness, and we demonstrate that the theory is highly predictive of empirical robustness.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.