JKU Linz
This paper presents xLSTM, an extension of Long Short-Term Memory networks designed to address historical limitations and scale to large language models. The architecture, featuring exponential gating and novel sLSTM and mLSTM memory cells, achieves competitive or superior performance against Transformer and State Space Models on various language modeling benchmarks, demonstrating strong long-context extrapolation and improved inference efficiency.
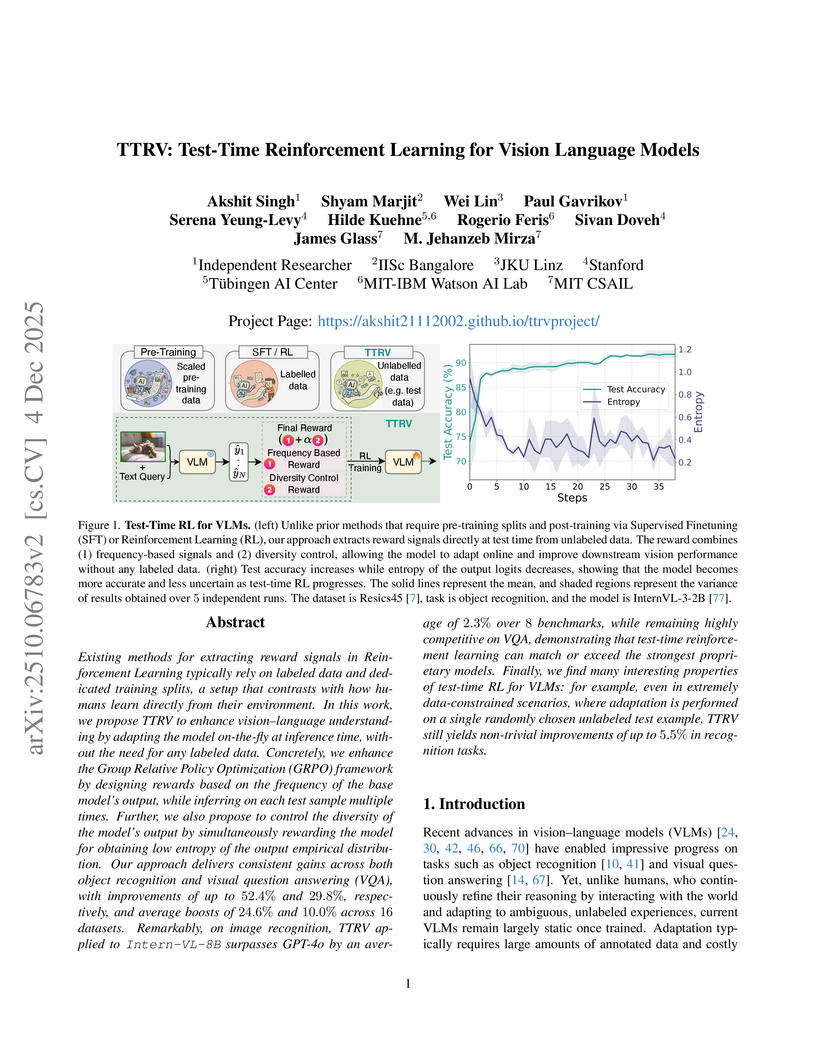
Existing methods for extracting reward signals in Reinforcement Learning typically rely on labeled data and dedicated training splits, a setup that contrasts with how humans learn directly from their environment. In this work, we propose TTRV to enhance vision language understanding by adapting the model on the fly at inference time, without the need for any labeled data. Concretely, we enhance the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) framework by designing rewards based on the frequency of the base model's output, while inferring on each test sample multiple times. Further, we also propose to control the diversity of the model's output by simultaneously rewarding the model for obtaining low entropy of the output empirical distribution. Our approach delivers consistent gains across both object recognition and visual question answering (VQA), with improvements of up to 52.4% and 29.8%, respectively, and average boosts of 24.6% and 10.0% across 16 datasets. Remarkably, on image recognition, TTRV applied to InternVL 8B surpasses GPT-4o by an average of 2.3% over 8 benchmarks, while remaining highly competitive on VQA, demonstrating that test-time reinforcement learning can match or exceed the strongest proprietary models. Finally, we find many interesting properties of test-time RL for VLMs: for example, even in extremely data-constrained scenarios, where adaptation is performed on a single randomly chosen unlabeled test example, TTRV still yields non-trivial improvements of up to 5.5% in recognition tasks.
22 Apr 2025
Google DeepMind researchers systematically analyze three key failure modes of LLMs in decision-making tasks (greediness, frequency bias, and knowing-doing gap), demonstrating how reinforcement learning fine-tuning with chain-of-thought reasoning can improve exploration and decision-making capabilities across multi-armed bandits, contextual bandits, and game-playing environments.
Scaling laws play a central role in the success of Large Language Models (LLMs), enabling the prediction of model performance relative to compute budgets prior to training. While Transformers have been the dominant architecture, recent alternatives such as xLSTM offer linear complexity with respect to context length while remaining competitive in the billion-parameter regime. We conduct a comparative investigation on the scaling behavior of Transformers and xLSTM along the following lines, providing insights to guide future model design and deployment. First, we study the scaling behavior for xLSTM in compute-optimal and over-training regimes using both IsoFLOP and parametric fit approaches on a wide range of model sizes (80M-7B) and number of training tokens (2B-2T). Second, we examine the dependence of optimal model sizes on context length, a pivotal aspect that was largely ignored in previous work. Finally, we analyze inference-time scaling characteristics. Our findings reveal that in typical LLM training and inference scenarios, xLSTM scales favorably compared to Transformers. Importantly, xLSTM's advantage widens as training and inference contexts grow.
This work provides a direct comparison between dense and generative retrieval methods for sequential recommendation, identifying performance gaps and cold-start limitations in generative approaches. It introduces LIGER, a hybrid model that combines the efficiency of generative retrieval with the robust ranking capabilities of dense retrieval, leading to improved cold-start item prediction and overall recommendation performance.
Recent advances in neural surrogate modeling offer the potential for transformative innovations in applications such as automotive aerodynamics. Yet, industrial-scale problems often involve volumetric meshes with cell counts reaching 100 million, presenting major scalability challenges. Complex geometries further complicate modeling through intricate surface-volume interactions, while quantities such as vorticity are highly nonlinear and must satisfy strict divergence-free constraints. To address these requirements, we introduce AB-UPT as a novel modeling scheme for building neural surrogates for CFD simulations. AB-UPT is designed to: (i) decouple geometry encoding and prediction tasks via multi-branch operators; (ii) enable scalability to high-resolution outputs via neural simulation in a low-dimensional latent space, coupled with anchored neural field decoders to predict high-fidelity outputs; (iii) enforce physics consistency by a divergence-free formulation. We show that AB-UPT yields state-of-the-art predictive accuracy of surface and volume fields on automotive CFD simulations ranging from 33 thousand up to 150 million mesh cells. Furthermore, our anchored neural field architecture enables the enforcement of hard physical constraints on the physics predictions without degradation in performance, exemplified by modeling divergence-free vorticity fields. Notably, the proposed models can be trained on a single GPU in less than a day and predict industry-standard surface and volume fields within seconds. Additionally, we show that the flexible design of our method enables neural simulation from a CAD geometry alone, thereby eliminating the need for costly CFD meshing procedures for inference.
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities across
diverse visual tasks, including image recognition, video understanding, and
Visual Question Answering (VQA) when explicitly trained for these tasks.
Despite these advances, we find that present-day VLMs (including the
proprietary GPT-4o) lack a fundamental cognitive ability: learning to localize
specific objects in a scene by taking into account the context. In this work,
we focus on the task of few-shot personalized localization, where a model is
given a small set of annotated images (in-context examples) -- each with a
category label and bounding box -- and is tasked with localizing the same
object type in a query image. Personalized localization can be particularly
important in cases of ambiguity of several related objects that can respond to
a text or an object that is hard to describe with words. To provoke
personalized localization abilities in models, we present a data-centric
solution that fine-tunes them using carefully curated data from video object
tracking datasets. By leveraging sequences of frames tracking the same object
across multiple shots, we simulate instruction-tuning dialogues that promote
context awareness. To reinforce this, we introduce a novel regularization
technique that replaces object labels with pseudo-names, ensuring the model
relies on visual context rather than prior knowledge. Our method significantly
enhances the few-shot localization performance of recent VLMs ranging from 7B
to 72B in size, without sacrificing generalization, as demonstrated on several
benchmarks tailored towards evaluating personalized localization abilities.
This work is the first to explore and benchmark personalized few-shot
localization for VLMs -- exposing critical weaknesses in present-day VLMs, and
laying a foundation for future research in context-driven vision-language
applications.
Microsoft Research's Aurora introduces a 1.3 billion parameter foundation model for the Earth system, pre-trained on diverse global data. This model outperforms existing operational forecasting systems across multiple domains, including air quality, ocean wave dynamics, tropical cyclone tracks, and high-resolution global weather at 0.1° resolution, while achieving substantial improvements in computational efficiency and reducing development timelines from years to weeks.
Universal Physics Transformers (UPTs) introduce a unified neural operator framework that efficiently scales physics simulations by processing diverse spatio-temporal data and propagating dynamics within a fixed-size latent space. The approach achieves up to 400x faster inference than traditional solvers and 5x faster than autoregressive neural operators, while demonstrating superior memory efficiency and robust generalization across various physical systems.
In sequential recommendation, models recommend items based on user's interaction history. To this end, current models usually incorporate information such as item descriptions and user intent or preferences. User preferences are usually not explicitly given in open-source datasets, and thus need to be approximated, for example via large language models (LLMs). Current approaches leverage approximated user preferences only during training and rely solely on the past interaction history for recommendations, limiting their ability to dynamically adapt to changing preferences, potentially reinforcing echo chambers. To address this issue, we propose a new paradigm, namely preference discerning, which explicitly conditions a generative recommendation model on user preferences in natural language within its context. To evaluate preference discerning, we introduce a novel benchmark that provides a holistic evaluation across various scenarios, including preference steering and sentiment following. Upon evaluating current state-of-the-art methods on our benchmark, we discover that their ability to dynamically adapt to evolving user preferences is limited. To address this, we propose a new method named Mender (Multimodal Preference Discerner), which achieves state-of-the-art performance in our benchmark. Our results show that Mender effectively adapts its recommendation guided by human preferences, even if not observed during training, paving the way toward more flexible recommendation models.
Explained Variance Adaptation (EVA) from JKU Linz enhances LoRA for foundation models by employing a variance-optimal initialization based on incremental SVD of activations and an adaptive rank allocation strategy. This approach yields faster convergence and superior performance across diverse tasks (language, vision, RL), often with fewer trainable parameters than existing methods.
Is basic visual understanding really solved in state-of-the-art VLMs? We present VisualOverload, a slightly different visual question answering (VQA) benchmark comprising 2,720 question-answer pairs, with privately held ground-truth responses. Unlike prior VQA datasets that typically focus on near global image understanding, VisualOverload challenges models to perform simple, knowledge-free vision tasks in densely populated (or, overloaded) scenes. Our dataset consists of high-resolution scans of public-domain paintings that are populated with multiple figures, actions, and unfolding subplots set against elaborately detailed backdrops. We manually annotated these images with questions across six task categories to probe for a thorough understanding of the scene. We hypothesize that current benchmarks overestimate the performance of VLMs, and encoding and reasoning over details is still a challenging task for them, especially if they are confronted with densely populated scenes. Indeed, we observe that even the best model (o3) out of 37 tested models only achieves 19.6% accuracy on our hardest test split and overall 69.5% accuracy on all questions. Beyond a thorough evaluation, we complement our benchmark with an error analysis that reveals multiple failure modes, including a lack of counting skills, failure in OCR, and striking logical inconsistencies under complex tasks. Altogether, VisualOverload exposes a critical gap in current vision models and offers a crucial resource for the community to develop better models.
Benchmark: this http URL
Nuclear fusion plays a pivotal role in the quest for reliable and sustainable energy production. A major roadblock to viable fusion power is understanding plasma turbulence, which significantly impairs plasma confinement, and is vital for next-generation reactor design. Plasma turbulence is governed by the nonlinear gyrokinetic equation, which evolves a 5D distribution function over time. Due to its high computational cost, reduced-order models are often employed in practice to approximate turbulent transport of energy. However, they omit nonlinear effects unique to the full 5D dynamics. To tackle this, we introduce GyroSwin, the first scalable 5D neural surrogate that can model 5D nonlinear gyrokinetic simulations, thereby capturing the physical phenomena neglected by reduced models, while providing accurate estimates of turbulent heat transport. GyroSwin (i) extends hierarchical Vision Transformers to 5D, (ii) introduces cross-attention and integration modules for latent 3D↔5D interactions between electrostatic potential fields and the distribution function, and (iii) performs channelwise mode separation inspired by nonlinear physics. We demonstrate that GyroSwin outperforms widely used reduced numerics on heat flux prediction, captures the turbulent energy cascade, and reduces the cost of fully resolved nonlinear gyrokinetics by three orders of magnitude while remaining physically verifiable. GyroSwin shows promising scaling laws, tested up to one billion parameters, paving the way for scalable neural surrogates for gyrokinetic simulations of plasma turbulence.
In-context learning (ICL) is the ability of a model to learn a new task by observing a few exemplars in its context. While prevalent in NLP, this capability has recently also been observed in Reinforcement Learning (RL) settings. Prior in-context RL methods, however, require entire episodes in the agent's context. Given that complex environments typically lead to long episodes with sparse rewards, these methods are constrained to simple environments with short episodes. To address these challenges, we introduce Retrieval-Augmented Decision Transformer (RA-DT). RA-DT employs an external memory mechanism to store past experiences from which it retrieves only sub-trajectories relevant for the current situation. The retrieval component in RA-DT does not require training and can be entirely domain-agnostic. We evaluate the capabilities of RA-DT on grid-world environments, robotics simulations, and procedurally-generated video games. On grid-worlds, RA-DT outperforms baselines, while using only a fraction of their context length. Furthermore, we illuminate the limitations of current in-context RL methods on complex environments and discuss future directions. To facilitate future research, we release datasets for four of the considered environments.
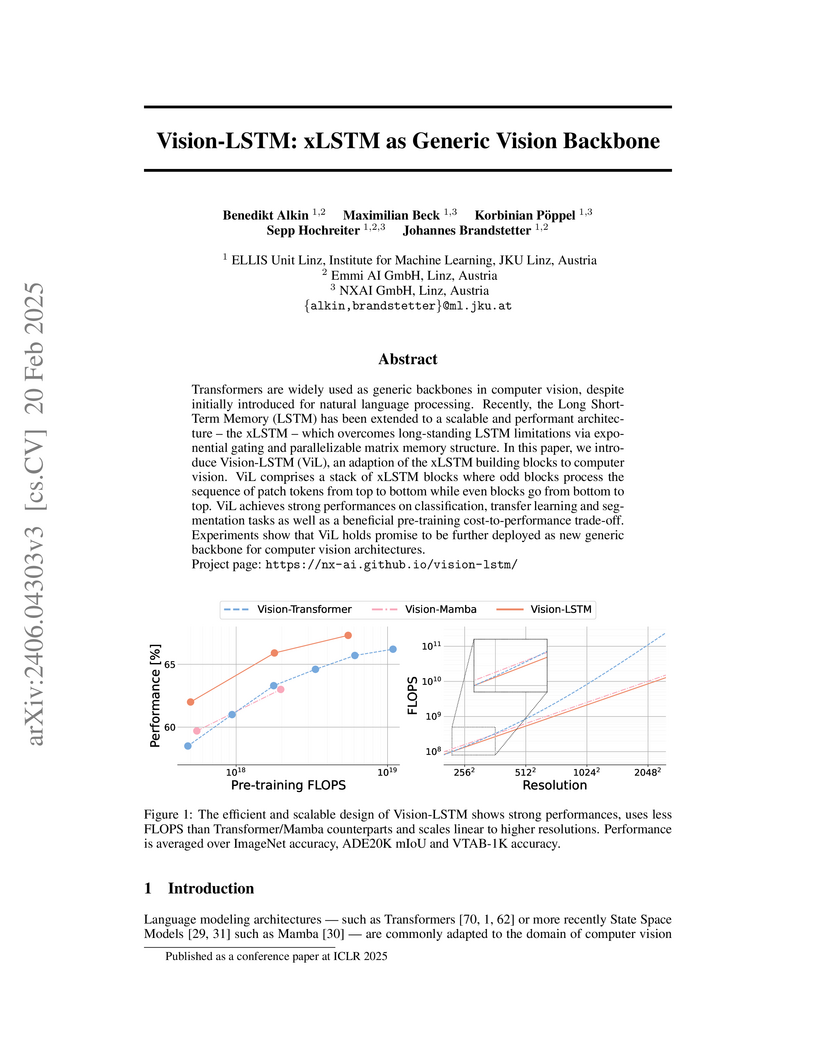
Transformers are widely used as generic backbones in computer vision, despite
initially introduced for natural language processing. Recently, the Long
Short-Term Memory (LSTM) has been extended to a scalable and performant
architecture - the xLSTM - which overcomes long-standing LSTM limitations via
exponential gating and parallelizable matrix memory structure. In this report,
we introduce Vision-LSTM (ViL), an adaption of the xLSTM building blocks to
computer vision. ViL comprises a stack of xLSTM blocks where odd blocks process
the sequence of patch tokens from top to bottom while even blocks go from
bottom to top. Experiments show that ViL holds promise to be further deployed
as new generic backbone for computer vision architectures.
Researchers at JKU Linz developed Tiled Flash Linear Attention (TFLA) kernels for linear Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), specifically targeting the mLSTM architecture. These kernels achieve new state-of-the-art training speeds for long-context sequence modeling primitives, surpassing FlashAttention 3 and Mamba 2, while also enhancing mLSTM performance and stability.
Neural surrogates have shown great potential in simulating dynamical systems, while offering real-time capabilities. We envision Neural Twins as a progression of neural surrogates, aiming to create digital replicas of real systems. A neural twin consumes measurements at test time to update its state, thereby enabling context-specific decision-making. A critical property of neural twins is their ability to remain on-trajectory, i.e., to stay close to the true system state over time. We introduce Parallel-in-time Neural Twins (PAINT), an architecture-agnostic family of methods for modeling dynamical systems from measurements. PAINT trains a generative neural network to model the distribution of states parallel over time. At test time, states are predicted from measurements in a sliding window fashion. Our theoretical analysis shows that PAINT is on-trajectory, whereas autoregressive models generally are not. Empirically, we evaluate our method on a challenging two-dimensional turbulent fluid dynamics problem. The results demonstrate that PAINT stays on-trajectory and predicts system states from sparse measurements with high fidelity. These findings underscore PAINT's potential for developing neural twins that stay on-trajectory, enabling more accurate state estimation and decision-making.
A Large Recurrent Action Model (LRAM) based on xLSTM and Mamba architectures demonstrates high-performance, real-time inference for robotics tasks, overcoming the computational limitations of Transformer-based models. It achieves competitive or superior performance on a diverse suite of 432 tasks while offering significantly faster inference speeds, crucial for real-time control.
PerLA is a 3D language assistant that enables large language models to better understand 3D scenes by developing a perceptive scene encoder that efficiently integrates high-resolution local details with global contextual information from point clouds. The approach achieves new state-of-the-art performance across 3D Question Answering and 3D Dense Captioning benchmarks, while also reducing response hallucinations.
We present Clifford-Steerable Convolutional Neural Networks (CS-CNNs), a
novel class of E(p,q)-equivariant CNNs. CS-CNNs process multivector
fields on pseudo-Euclidean spaces Rp,q. They cover, for instance,
E(3)-equivariance on R3 and Poincar\'e-equivariance on
Minkowski spacetime R1,3. Our approach is based on an implicit
parametrization of O(p,q)-steerable kernels via Clifford group
equivariant neural networks. We significantly and consistently outperform
baseline methods on fluid dynamics as well as relativistic electrodynamics
forecasting tasks.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.