Mahindra University
One-shot neural architecture search (NAS) substantially improves the search
efficiency by training one supernet to estimate the performance of every
possible child architecture (i.e., subnet). However, the inconsistency of
characteristics among subnets incurs serious interference in the optimization,
resulting in poor performance ranking correlation of subnets. Subsequent
explorations decompose supernet weights via a particular criterion, e.g.,
gradient matching, to reduce the interference; yet they suffer from huge
computational cost and low space separability. In this work, we propose a
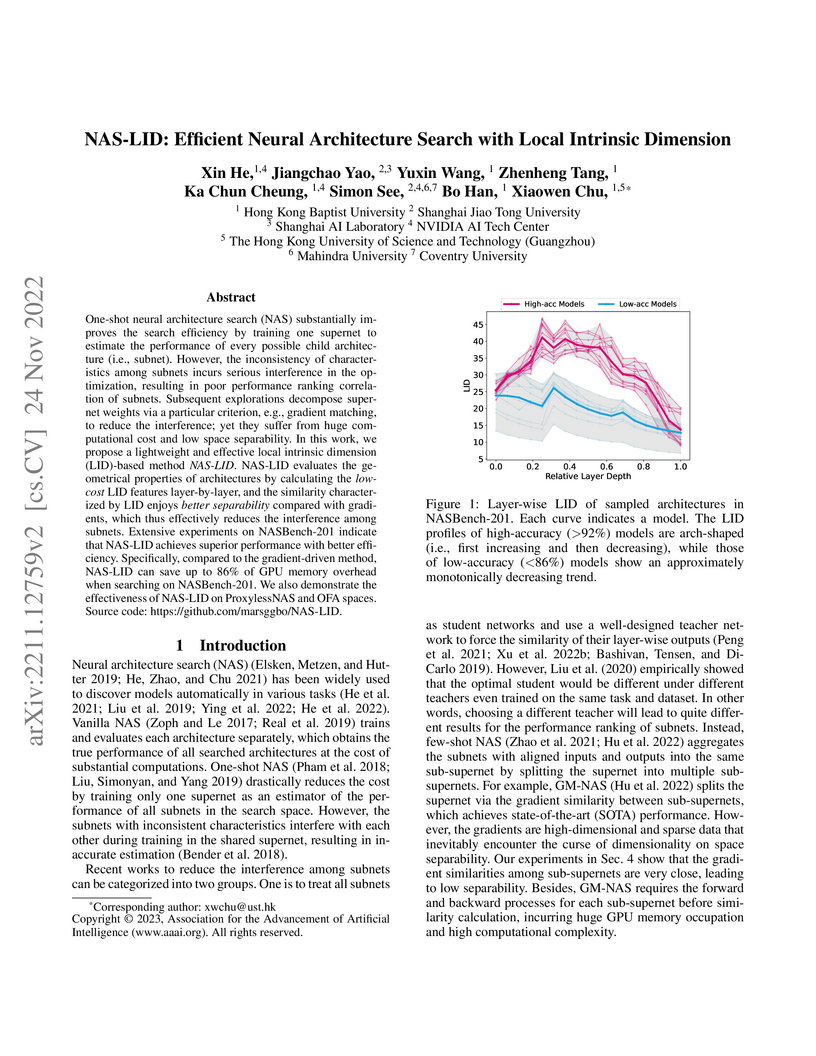
lightweight and effective local intrinsic dimension (LID)-based method NAS-LID.
NAS-LID evaluates the geometrical properties of architectures by calculating
the low-cost LID features layer-by-layer, and the similarity characterized by
LID enjoys better separability compared with gradients, which thus effectively
reduces the interference among subnets. Extensive experiments on NASBench-201
indicate that NAS-LID achieves superior performance with better efficiency.
Specifically, compared to the gradient-driven method, NAS-LID can save up to
86% of GPU memory overhead when searching on NASBench-201. We also demonstrate
the effectiveness of NAS-LID on ProxylessNAS and OFA spaces. Source code:
this https URL
Here we study electronic properties of the ternary tellurides TaXTe4 (X=Rh, Ir) using density functional theory and investigate chiral anomaly mediated planar Hall response from ab initio calculations. We show that TaRhTe4 is a hybrid Weyl semimetal (WSM), hosting Weyl points (WPs) of both type-I, type-II, while TaIrTe4 is a type-II WSM as it hosts only type-II WPs with spin-orbit couplings (SOC). All WPs lie in the kz=0 plane, and remain well-separated in both momentum and energy landscape. We observe long Fermi arcs connecting Weyl nodes of opposite chirality. We report both SOC and orbital driven topological phase transition in ternary tellurides. TaIrTe4 undergoes topological phase transition under SOC. Whereas orbital driven topological phase transition due to dxz orbital has been observed in TaRhTe4 even without SOC. Furthermore, the evolution of the band structures and the annihilation of WPs due to dxz-Ir/Rh orbitals associated with the phase transitions in TaXTe4 are also discussed. This systematic study opens new routes for engineering topological materials relying beyond strong SOC and sheds light on the possible role of correlation effects originating from orbital orbital degree of freedoms in tellurides. We further report an enhancement of planar Hall effects due to orbital driven topological phase transition in TaXTe4 and we make resort to a tight-binding model to correlate the above findings with the effective mass anisotropy in different types of WSMs.
This paper introduces a new stochastic optimization method based on the
regularized Fisher information matrix (FIM), named SOFIM, which can efficiently
utilize the FIM to approximate the Hessian matrix for finding Newton's gradient
update in large-scale stochastic optimization of machine learning models. It
can be viewed as a variant of natural gradient descent, where the challenge of
storing and calculating the full FIM is addressed through making use of the
regularized FIM and directly finding the gradient update direction via
Sherman-Morrison matrix inversion. Additionally, like the popular Adam method,
SOFIM uses the first moment of the gradient to address the issue of
non-stationary objectives across mini-batches due to heterogeneous data. The
utilization of the regularized FIM and Sherman-Morrison matrix inversion leads
to the improved convergence rate with the same space and time complexities as
stochastic gradient descent (SGD) with momentum. The extensive experiments on
training deep learning models using several benchmark image classification
datasets demonstrate that the proposed SOFIM outperforms SGD with momentum and
several state-of-the-art Newton optimization methods in term of the convergence
speed for achieving the pre-specified objectives of training and test losses as
well as test accuracy.
30 Oct 2025
Solvent environments play a central role in determining molecular structure, energetics, reactivity, and interfacial phenomena. However, modeling solvation from first principles remains difficult due to the complex interplay of interactions and unfavorable computational scaling of first-principles treatment with system size. Machine-learned potentials (MLPs) have recently emerged as efficient surrogates for quantum chemistry methods, offering first-principles accuracy at greatly reduced computational cost. MLPs approximate the underlying potential energy surface, enabling efficient computation of energies and forces in solvated systems, and are capable of accounting for effects such as hydrogen bonding, long-range polarization, and conformational changes. This review surveys the development and application of MLPs in solvation modeling. We summarize the theoretical basis of MLP-based energy and force predictions and present a classification of MLPs based on training targets, model types, and design choices related to architectures, descriptors, and training protocols. Integration into established solvation workflows is discussed, with case studies spanning small molecules, interfaces, and reactive systems. We conclude by outlining open challenges and future directions toward transferable, robust, and physically grounded MLPs for solvation-aware atomistic modeling.
22 Jul 2023
Group recommender systems (GRS) are critical in discovering relevant items
from a near-infinite inventory based on group preferences rather than
individual preferences, like recommending a movie, restaurant, or tourist
destination to a group of individuals. The traditional models of group
recommendation are designed to act like a black box with a strict focus on
improving recommendation accuracy, and most often, they place the onus on the
users to interpret recommendations. In recent years, the focus of Recommender
Systems (RS) research has shifted away from merely improving recommendation
accuracy towards value additions such as confidence and explanation. In this
work, we propose a conformal prediction framework that provides a measure of
confidence with prediction in conjunction with a group recommender system to
augment the system-generated plain recommendations. In the context of group
recommender systems, we propose various nonconformity measures that play a
vital role in the efficiency of the conformal framework. We also show that
defined nonconformity satisfies the exchangeability property. Experimental
results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach over several
benchmark datasets. Furthermore, our proposed approach also satisfies validity
and efficiency properties.
We demonstrate third-order conjugate exceptional points (EPs) in a gain-loss
assisted multi-mode 1D complementary photonic bandgap waveguide. Our study
reveals the higher-order mode conversion phenomenon facilitated by
parametrically encircled third-order conjugate EPs, showcasing the potential
for on-chip mode conversion
Underwater images taken from autonomous underwater vehicles (AUV's) often suffer from low light, high turbidity, poor contrast, motion-blur and excessive light scattering and hence require image enhancement techniques for object recognition. Machine learning methods are being increasingly used for object recognition under such adverse conditions. These enhanced object recognition methods of images taken from AUV's has potential applications in underwater pipeline and optical fibre surveillance, ocean bed resource extraction, ocean floor mapping, underwater species exploration, etc. While the classical machine learning methods are very efficient in terms of accuracy, they require large datasets and high computational time for image classification. In the current work, we use quantum-classical hybrid machine learning methods for real-time under-water object recognition on-board an AUV for the first time. We use real-time motion-blurred and low-light images taken from an on-board camera of AUV built in-house and apply existing hybrid machine learning methods for object recognition. Our hybrid methods consist of quantum encoding and flattening of classical images using quantum circuits and sending them to classical neural networks for image classification. The results of hybrid methods carried out using Pennylane based quantum simulators both on GPU and using pre-trained models on an on-board NVIDIA GPU chipset are compared with results from corresponding classical machine learning methods. We observe that the hybrid quantum machine learning methods show an efficiency greater than 65\% and reduction in run-time by one-thirds and require 50\% smaller dataset sizes for training the models compared to classical machine learning methods. We hope that our work opens up further possibilities in quantum enhanced real-time computer vision in autonomous vehicles.
21 Nov 2024
The presence of defects of different kinds, e.g., vacancies, voids, dislocations, grain boundaries, and surfaces, in realistic materials can strongly modify and even dictate the thermodynamics of phase transformations. Our study demonstrates, both theoretically and experimentally, that in the ordering of Fe_xAl_1-x (x>0.6) alloys subjected to high-temperature treatment, the relaxation of the as-prepared chemically disordered alloy into the ordered B2 state is hampered by another process. A manifestation of this is an increase in the alloy's magnetization. A plausible explanation for a non-monotonous behavior of the magnetization we observe is segregation of Al into structural defects, e.g., grain boundaries, and thus purification of the Fe host lattice. Qualitatively, experimental findings reported here are supported by molecular dynamics simulation of the phase transformation kinetics in Fe_xAl_1-x. These studies can be useful for choosing the preparation strategy for functional alloys.
This research paper introduces two novel complex-valued Hopfield neural networks (CvHNNs) that incorporate phase and magnitude quantization. The first CvHNN employs a ceiling-type activation function that operates on the rectangular coordinate representation of the complex net contribution. The second CvHNN similarly incorporates phase and magnitude quantization but utilizes a ceiling-type activation function based on the polar coordinate representation of the complex net contribution. The proposed CvHNNs, with their phase and magnitude quantization, significantly increase the number of states compared to existing models in the literature, thereby expanding the range of potential applications for CvHNNs.
An important inference from Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK) theory is the existence of spectral bias (SB), that is, low frequency components of the target function of a fully connected Artificial Neural Network (ANN) being learnt significantly faster than the higher frequencies during training. This is established for Mean Square Error (MSE) loss functions with very low learning rate parameters. Physics Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) are designed to learn the solutions of differential equations (DE) of arbitrary orders; in PINNs the loss functions are obtained as the residues of the conservative form of the DEs and represent the degree of dissatisfaction of the equations. So there has been an open question whether (a) PINNs also exhibit SB and (b) if so, how does this bias vary across the orders of the DEs. In this work, a series of numerical experiments are conducted on simple sinusoidal functions of varying frequencies, compositions and equation orders to investigate these issues. It is firmly established that under normalized conditions, PINNs do exhibit strong spectral bias, and this increases with the order of the differential equation.
Collaborative filtering (CF) has become a popular method for developing
recommender systems (RSs) where ratings of a user for new items are predicted
based on her past preferences and available preference information of other
users. Despite the popularity of CF-based methods, their performance is often
greatly limited by the sparsity of observed entries. In this study, we explore
the data augmentation and refinement aspects of Maximum Margin Matrix
Factorization (MMMF), a widely accepted CF technique for rating predictions,
which has not been investigated before. We exploit the inherent characteristics
of CF algorithms to assess the confidence level of individual ratings and
propose a semi-supervised approach for rating augmentation based on
self-training. We hypothesize that any CF algorithm's predictions with low
confidence are due to some deficiency in the training data and hence, the
performance of the algorithm can be improved by adopting a systematic data
augmentation strategy. We iteratively use some of the ratings predicted with
high confidence to augment the training data and remove low-confidence entries
through a refinement process. By repeating this process, the system learns to
improve prediction accuracy. Our method is experimentally evaluated on several
state-of-the-art CF algorithms and leads to informative rating augmentation,
improving the performance of the baseline approaches.
24 Jul 2025
High Q-factor narrow-band absorption exhibits high spectral selectivity enabling high-sensitive photodetectors, sensors and thermal emitters. All-dielectric metasurfaces are widely regarded as excellent candidates for giving rise to such narrow-band absorption. However, designing metasurfaces with specific functionalities remains a challenging task both experimentally and computationally, which is why inverse design methods are increasingly being explored. Inverse design process is highly complex due to its non-unique solutions and the higher dimensionality of the design space, making it challenging to precisely control the resonance wavelength, linewidth, and absorption intensity. In this paper, we present a novel hybrid methodology that integrates generative adversarial networks (GANs) (both classical and quantum) with physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for the inverse design of narrow-band absorbing metasurfaces. By introducing a Fano-shaped absorption spectrum equation into the PINN loss function, we enforce physical constraints on the resonance behavior, ensuring outputs that are both spectrally accurate and physically consistent. The study presents a comparison between a conventional GAN + PINN framework and a PINN augmented by a hybrid quantum-classical GAN (QGAN). The findings indicate that the integrated PINN + QGAN model achieves faster convergence, requires 99.5\% fewer training samples, and yields an order of magnitude lower MSE compared to conventional GANs. Remarkably, even though the training dataset only contains metasurfaces with Q-factors on the order of 103, the model is able to generate highly asymmetric metasurface structures with Q-factors exceeding 105. This study presents a novel framework that integrates quantum machine learning with physics-based modeling, providing a promising method for quantum-enhanced inverse design in nanophotonic systems.
04 Jul 2025
Optimization of metasurface designs for specific functionality is a challenging problem due to the intricate relation between structural features and electromagnetic responses. Recently, many researchers resolved to inverse design of metasurfaces for efficient design parameters based on methods such as parameter optimization, evolutionary optimization and machine learning. In this paper a hybrid quantum machine learning method which uses quantum encoders to enhance the performance of a classical GAN is applied to implement inverse design of a metasurface. Aiming towards angle-independent unidirectional transmission, this approach combines a Quantum Generative Adversarial Network (QGAN) with a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) to optimize metasurface designs. Incident-angle independent uni-directional transmission has potential applications in efficient solar cells, thermal cooling, non-reciprocal devices, etc. However, it is very challenging to achieve such a metasurface design via forward methods and hence very few studies exist till now in this direction. The methodology employed in this work reduces the data requirement for inverse design by 30% compared to conventional GAN-based methods. More importantly, the developed metasurface designs show high fidelity of 95% with regard to the targeted far-field radiation patterns. We also provide a material look-up table for feasible substitutes of the obtained material design with real materials and yet maintaining performance accuracy. Further, we embed the inverse-designed metasurfaces into Perovskite solar cell layers to demonstrate the improvement in its performance. We observe that the conversion efficiency of the example perovskite solar cell improves by 95% and remains independent of incident angle in the range -60∘ to 60∘ within the desired frequency range.
Analogies test a model's ability to infer implicit relationships between concepts, making them a key benchmark for evaluating reasoning capabilities. While large language models (LLMs) are widely evaluated for reasoning in English, their abilities in Indic languages remain understudied, limiting our understanding of whether these models generalize across languages. To address this gap, we introduce a new Hindi Analogy Test Set (HATS), comprising 405 multiple-choice questions sourced from Indian government exams. We benchmark state-of-the-art multilingual LLMs using various prompting strategies and introduce a grounded Chain of Thought approach that leverages cognitive theories of analogical reasoning. This approach improves model performance on Hindi analogy questions. Our experiments show that models perform best with English prompts, irrespective of the prompting strategy. Our test set addresses the lack of a critical resource to evaluate LLM reasoning capabilities in Hindi.
25 Jul 2025
The inverse design of metasurfaces poses a considerable challenge because of the intricate interdependencies that exist between structural characteristics and electromagnetic responses. Traditional optimization methods require significant computational resources and frequently do not produce the most effective solutions. This study presents a hybrid quantum-classical machine learning approach known as Latent Style-based Quantum GAN (LaSt-QGAN). This method integrates a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) with a Quantum Generative Adversarial Network (QGAN) to enhance the optimization of metasurface designs aimed at achieving narrow-band absorption and unidirectionality. The proposed method results in a reduction of training time by 10X and a decrease in data requirements by 40X when compared to traditional GAN-based approaches. The produced metasurface designs demonstrate a high fidelity in relation to the target absorption spectra compared to the classical GAN based methods. Additionally, the integration of a material look-up table facilitates manufacturability by allowing for the substitution of predicted material properties with viable alternatives, all while preserving performance accuracy. Moreover the model is able to generate Q-factor upto the order of 104, while the training dataset has Q-factor upto the order of 103.
25 Jul 2025
Strong light-matter interactions in 2D materials have garnered significant interest for their potential in nonlinear optics and quantum photonics. Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), with their robust excitonic responses, serve as promising materials for exploring these interactions. Importantly, tailoring such strong coupling giving rise to tunable quantum and non-linear emissions are under explored. In this study, we propose a novel approach that employs liquid crystals (LCs) as a tunable medium to modulate the strong coupling between TMDC excitons and photonic modes and hence gives rise to tunable quantum emissions. LCs offer high birefringence and anisotropic optical properties, which can be dynamically tuned using external stimuli such as electric fields or temperature variations. By embedding TMDCs within an LC environment and coupling them to photonic quasi-bound states in the continuum (quasi-BIC), we demonstrate precise control over the exciton-photon interactions. The orientation of the LCs, governed by applied external fields, directly influences the coupling strength, enabling real-time modulation of exciton-polariton states and Rabi-splitting. Our system exhibits Rabi splitting energy of 182.5 MeV in air, and 139, 153.7, and 131 meV under different LC orientations. Additionally second order autocorrelation function calculated at zero delay yields g(2)(0)=0.89, demonstrating photon anti-bunching, confirming the quantum nature of emission. Our findings establish a versatile platform where TMDCs and LCs synergistically enable electrically controllable strong coupling, offering a scalable and responsive architecture for next-generation quantum photonic devices.
This paper presents Constrained Centroid Clustering (CCC), a method that extends classical centroid-based clustering by enforcing a constraint on the maximum distance between the cluster center and the farthest point in the cluster. Using a Lagrangian formulation, we derive a closed-form solution that maintains interpretability while controlling cluster spread. To evaluate CCC, we conduct experiments on synthetic circular data with radial symmetry and uniform angular distribution. Using ring-wise, sector-wise, and joint entropy as evaluation metrics, we show that CCC achieves more compact clusters by reducing radial spread while preserving angular structure, outperforming standard methods such as K-means and GMM. The proposed approach is suitable for applications requiring structured clustering with spread control, including sensor networks, collaborative robotics, and interpretable pattern analysis.
We report an all-lossy index-guided dual-core photonic crystal fiber (PCF)
that hosts a second-order exceptional point (EP) in the systems parameter
space. By appropriately selecting a parametric encirclement scheme around the
EP, the interaction between the coupled modes has been studied, and the mode
conversion is subsequently observed.
Recommender systems based on collaborative filtering play a vital role in
many E-commerce applications as they guide the user in finding their items of
interest based on the user's past transactions and feedback of other similar
customers. Data Sparsity is one of the major drawbacks with collaborative
filtering technique arising due to the less number of transactions and feedback
data. In order to reduce the sparsity problem, techniques called transfer
learning/cross-domain recommendation has emerged. In transfer learning methods,
the data from other dense domain(s) (source) is considered in order to predict
the missing ratings in the sparse domain (target). In this paper, we come up
with a novel transfer learning approach for cross-domain recommendation,
wherein the cluster-level rating pattern(codebook) of the source domain is
obtained via a co-clustering technique. Thereafter we apply the Maximum Margin
Matrix factorization (MMMF) technique on the codebook in order to learn the
user and item latent features of codebook. Prediction of the target rating
matrix is achieved by introducing these latent features in a novel way into the
optimisation function. In the experiments we demonstrate that our model
improves the prediction accuracy of the target matrix on benchmark datasets.
10 Oct 2022
In the current epoch of neutrino physics, many experiments are aiming for precision measurements of oscillation parameters. Thus, various new physics scenarios which alter the neutrino oscillation probabilities in matter deserve careful investigation. In this context, we study the effect of a vector leptoquark which induces non-standard neutrino interactions (NSI) that modify the oscillation probabilities of neutrinos in matter. We show that such interactions provide a relatively large value of NSI parameter εeμ. Considering this NSI parameter, we successfully explain the recent discrepancy between the observed δCP results of T2K and NOvA.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.