Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (National Research University)
HSE UniversityMoscow Institute of Physics and Technology (National Research University)Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Russian Academy of SciencesUniversité Grenoble Alpes, CNRS, Grenoble INP, Institut NEELInstitute of Radioengineering and Electronics, Russian Academy of SciencesNational University of Science and Technology ",MISIS"
Slow oscillations of the magnetoresistance periodic in the inverse magnetic
field with a frequency of 3.4 T have been identified in HoTe3. The temperature
dependence of the oscillation amplitude is close to exponential even at low
temperatures. This may be attributed to the existence of soft modes in the
system and allows the estimation of the electron scattering rate on these
modes. In the region of magnetic fields exceeding 1 T, the oscillations can be
described as interference oscillations associated with the splitting of the
band structure due to the bilayer structure of HoTe3. The obtained data have
allowed us to calculate the ratio tb/tz of the hopping integrals between layers
within each bilayer (tb) and between the adjacent bilayers (tz) to estimate
these integrals as tb ~ 2 meV and tz ~ 0.26 meV.
05 May 2024
Anna Romanova, from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, proposes a framework for regulating autonomous AI systems in corporate governance by introducing "dual-version" regulatory documents, crafted for both human and algorithmic interpretation. This approach adapts the "Operational Design Domain" concept from autonomous vehicles to the legal environment, enabling AI systems to operate within precisely defined, machine-readable legal contexts.
30 Sep 2025
Terahertz (THz) electromagnetic pulses offer a promising route for the ultrafast manipulation of magnetization in ferromagnetic materials. While previous studies have demonstrated the excitation of spin dynamics using linearly polarized THz fields, the role of circular polarization and the effects of rapidly oscillating, time-dependent field profiles remained insufficiently understood. We have developed a unified theoretical framework for describing the excitation of spin precession via Zeeman interaction in magnetic materials by high frequency pulses of arbitrary polarization with temporal Gaussian profile. In the regime of long pulses (at least several oscillations are within the pulse duration), a circularly polarized magnetic field acts as an effective rectified magnetic field along the pulse propagation, while linear polarized pulses excite no free precession. In the regime of short pulses (less than one oscillation is within the pulse duration), pulses of any polarization, including linear one can excite free spin precession. There is an optimal pulse duration which maximizes amplitude of the spin precession. It depends on magnetic parameters of the sample and the external magnetic field, as well as on the carrier frequency of the pulse and its amplitude. These findings bridge key gaps in the understanding of THz-induced spin dynamics and provide insights into the design of light-controlled magnetization schemes using tailored electromagnetic pulses.
The growing need for Trusted AI (TAI) highlights the importance of
interpretability and robustness in machine learning models. However, many
existing tools overlook graph data and rarely combine these two aspects into a
single solution. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have become a popular approach,
achieving top results across various tasks. We introduce GNN-AID (Graph Neural
Network Analysis, Interpretation, and Defense), an open-source framework
designed for graph data to address this gap. Built as a Python library, GNN-AID
supports advanced trust methods and architectural layers, allowing users to
analyze graph datasets and GNN behavior using attacks, defenses, and
interpretability methods.
GNN-AID is built on PyTorch-Geometric, offering preloaded datasets, models,
and support for any GNNs through customizable interfaces. It also includes a
web interface with tools for graph visualization and no-code features like an
interactive model builder, simplifying the exploration and analysis of GNNs.
The framework also supports MLOps techniques, ensuring reproducibility and
result versioning to track and revisit analyses efficiently.
GNN-AID is a flexible tool for developers and researchers. It helps
developers create, analyze, and customize graph models, while also providing
access to prebuilt datasets and models for quick experimentation. Researchers
can use the framework to explore advanced topics on the relationship between
interpretability and robustness, test defense strategies, and combine methods
to protect against different types of attacks.
We also show how defenses against evasion and poisoning attacks can conflict
when applied to graph data, highlighting the complex connections between
defense strategies.
GNN-AID is available at
\href{this https URL}{github.com/ispras/GNN-AID}
10 Oct 2025
In this work we investigate efficient data compression for spatiotemporal Black, Azov and Marmara Seas temperature tensors that contain significant number of missing values. These tensors have a complex structure influenced by the coastlines and bathymetry, as well as temporal temperature changes. While such missing data typically provokes utilization of tensor completion algorithms, we demonstrate that standard SVD-based compression approaches (including the Tucker, Tensor-Train (TT) and Quantized-TT formats) are remarkably effective and yield comparable results. We propose a greedy spatial data partitioning algorithm enhancing their performance. We divide the data into the smaller subtensors before compression via exploitation of this trick.
Furthermore, our analysis reveals a strong temporal dependency in the data's compressibility caused by its nature. Fixing the level of precision we observe a significant seasonal variation. Investigating this, we find that a temporal partitioning on a scale of approximately two days is nearly optimal for all tested tensor based formats. The combined application of these spatial and temporal strategies with tensor methods ultimately achieves a robust compression ratio of 5 times across the entire dataset.
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have become a cornerstone in graph-based data
analysis, with applications in diverse domains such as bioinformatics, social
networks, and recommendation systems. However, the interplay between model
interpretability and robustness remains poorly understood, especially under
adversarial scenarios like poisoning and evasion attacks. This paper presents a
comprehensive benchmark to systematically analyze the impact of various factors
on the interpretability of GNNs, including the influence of
robustness-enhancing defense mechanisms.
We evaluate six GNN architectures based on GCN, SAGE, GIN, and GAT across
five datasets from two distinct domains, employing four interpretability
metrics: Fidelity, Stability, Consistency, and Sparsity. Our study examines how
defenses against poisoning and evasion attacks, applied before and during model
training, affect interpretability and highlights critical trade-offs between
robustness and interpretability. The framework will be published as open
source.
The results reveal significant variations in interpretability depending on
the chosen defense methods and model architecture characteristics. By
establishing a standardized benchmark, this work provides a foundation for
developing GNNs that are both robust to adversarial threats and interpretable,
facilitating trust in their deployment in sensitive applications.
06 Jul 2025
The Nuclear Stellar Disk (NSD), together with the Nuclear Stellar Cluster and the supermassive black hole Sgr A*, forms the central region of the Milky Way. Galactic X-ray background emission is known to be associated with the old stellar population, predominantly produced by accreting white dwarfs. In this work we characterize the X-ray emission of the Galactic Center (GC) region using wide-field observations with the ART-XC telescope on board the SRG observatory in the 4-12 keV energy band. Our analysis demonstrates that the X-ray emission of the GC at a spatial scale of a few hundred parsecs is dominated by the regularly shaped NSD aligned in the Galactic plane, and characterized by latitudinal and longitudinal scale heights of approximately 20 pc and approximately 100 pc, respectively. The measured flux, 6.8 (+0.1, -0.3) x 10^-10 erg/s/cm^2 in the 4-12 keV band, corresponds to a luminosity of 5.9 (+0.1, -0.3) x 10^36 erg/s, assuming the GC distance of 8.178 kpc. The average mass-normalized X-ray emissivity of the NSD, 5.6 (+0.5, -0.7) x 10^27 erg/s/M_sun, exceeds the corresponding value of the Galactic ridge by a factor of 3.3 (+0.4, -0.5), confirming other studies. We also perform a deprojection of the observed NSD surface brightness distribution in order to construct a three-dimensional X-ray luminosity density model, which can be directly compared to the existing three-dimensional stellar mass models. The emissivity of the NSD as a function of distance to Sgr A* reveals a centrally concentrated maximum, indicating an enhanced radiative output per unit stellar mass in the inner NSD region. Finally, we conclude that the observed spatial properties of the NSD are fully consistent with the stellar mass density distribution, leaving only a small room for a possible diffuse component.
The vulnerability of artificial neural networks to adversarial perturbations in the black-box setting is widely studied in the literature. The majority of attack methods to construct these perturbations suffer from an impractically large number of queries required to find an adversarial example. In this work, we focus on knowledge distillation as an approach to conduct transfer-based black-box adversarial attacks and propose an iterative training of the surrogate model on an expanding dataset. This work is the first, to our knowledge, to provide provable guarantees on the success of knowledge distillation-based attack on classification neural networks: we prove that if the student model has enough learning capabilities, the attack on the teacher model is guaranteed to be found within the finite number of distillation iterations.
30 Sep 2025
Terahertz (THz) electromagnetic pulses offer a promising route for the ultrafast manipulation of magnetization in ferromagnetic materials. While previous studies have demonstrated the excitation of spin dynamics using linearly polarized THz fields, the role of circular polarization and the effects of rapidly oscillating, time-dependent field profiles remained insufficiently understood. We have developed a unified theoretical framework for describing the excitation of spin precession via Zeeman interaction in magnetic materials by high frequency pulses of arbitrary polarization with temporal Gaussian profile. In the regime of long pulses (at least several oscillations are within the pulse duration), a circularly polarized magnetic field acts as an effective rectified magnetic field along the pulse propagation, while linear polarized pulses excite no free precession. In the regime of short pulses (less than one oscillation is within the pulse duration), pulses of any polarization, including linear one can excite free spin precession. There is an optimal pulse duration which maximizes amplitude of the spin precession. It depends on magnetic parameters of the sample and the external magnetic field, as well as on the carrier frequency of the pulse and its amplitude. These findings bridge key gaps in the understanding of THz-induced spin dynamics and provide insights into the design of light-controlled magnetization schemes using tailored electromagnetic pulses.
Social networks crawling is in the focus of active research the last years.
One of the challenging task is to collect target nodes in an initially unknown
graph given a budget of crawling steps. Predicting a node property based on its
partially known neighbourhood is at the heart of a successful crawler. In this
paper we adopt graph neural networks for this purpose and show they are
competitive to traditional classifiers and are better for individual cases.
Additionally we suggest a training sample boosting technique, which helps to
diversify the training set at early stages of crawling and thus improves the
predictor quality. The experimental study on three types of target set topology
indicates GNN based approach has a potential in crawling task, especially in
the case of distributed target nodes.
16 May 2025
A new method for determining the accelerating potential above the polar caps
of radio pulsars with an arbitrary inclination angle of the magnetic axis to
the rotation axis has been proposed. The approach has been based on the concept
of a vacuum gap, the height and shape of the upper boundary of which are found
self-consistently together with the solution of the corresponding Poisson
equation. In turn, information about the accelerating potential has made it
possible to determine the transverse profiles of the secondary plasma density.
It has also been shown that the effect of inverse Compton scattering on the
considered processes is insignificant.
A rigorous Quantum Field Theory framework describes neutrino oscillations and weak interactions by directly employing a non-diagonal mass matrix for flavor neutrinos, circumventing the conventional reliance on predefined massive states or wave packets. This approach reproduces the standard oscillation formula and shows flavor-changing virtual neutrino contributions in local weak processes are effectively unobservable.
Detectors with continuous scintillator and matrix of photomultipliers attached are widely used in modern particle physics, and various medical tomographs. There are two common ways to calculate the coordinates of the scintillation flash via photomultipliers energy outcome: Anger method and Monte Carlo simulations. In this article, we derive an analytical solution for the computation of the energy outcome from several photomultipliers built into the bottom face of the scintillation camera with a continuous scintillator shaped as a rectangular parallelepiped. The lateral faces of the scintillation camera are considered specular reflectors with reflective indexes ∼1 or 0. The analytical solution is used as a reference point for the scintillation flash coordinates reconstruction. The achieved results are similar to those the Monte Carlo simulation provides but require less computational time.
One of the promising applications of satellite images is building construction monitoring. It allows to control the construction progress around the world even in the locations that are hard to reach. One of the main hurdles of this approach is the interpretation of the image data. In this paper, we have employed several novel deep learning techniques to tackle the problem. Various image segmentation and object detection networks were combined into a unified pipeline, which was then used to determine the building construction progress.
06 Aug 2025
A thorough study of the wide-range (40-35000 cm-1) dynamic conductivity and permittivity spectra of the archetypal heavy fermion metal CeB6 and unconventional superconductor ZrB12 was carried out at room temperature. Both the Drude-type components and overdamped excitations were separated and analyzed. An additional absorption band observed above 200 cm-1 was attributed to the cooperative Jahn-Teller dynamics of the boron complexes in CeB6 and ZrB12. It was shown that nonequilibrium electrons participating in the formation of the collective JT modes dominate in charge transport, and fraction of Drude-type electrons does not exceed 37% in CeB6 and 23% in ZrB12. We discuss also the additional Drude-type component in ZrB12 in terms of far-infrared conductivity from the sliding charge density wave, and suggest the localized mode scenario reconciles the strong difference between the number of conduction electrons obtained from the Hall effect and optical sum rule analysis in CeB6.
16 May 2022
We demonstrate the imaging capability of a frequency modulated continuous wave lidar based on a fiber bundle. The lidar constructs velocity and range images for hard targets at a rate of 60 Hz. The sensing range is up to 30 m with 20 mW of output power. The instrument employs custom electronics with seven parallel heterodyne receivers. An example of image recovery is presented on 6-pixel "pictures" of a spinning disk and a drone hovering in the air. In experiments, we also tested the laser tuning linearity correction with a phase-locked loop. We see the practicality of such a low-resolution system as a boost in scanning rate of conventional lidars or for direct target imaging with a further upgrade of pixel count.
01 Sep 2025
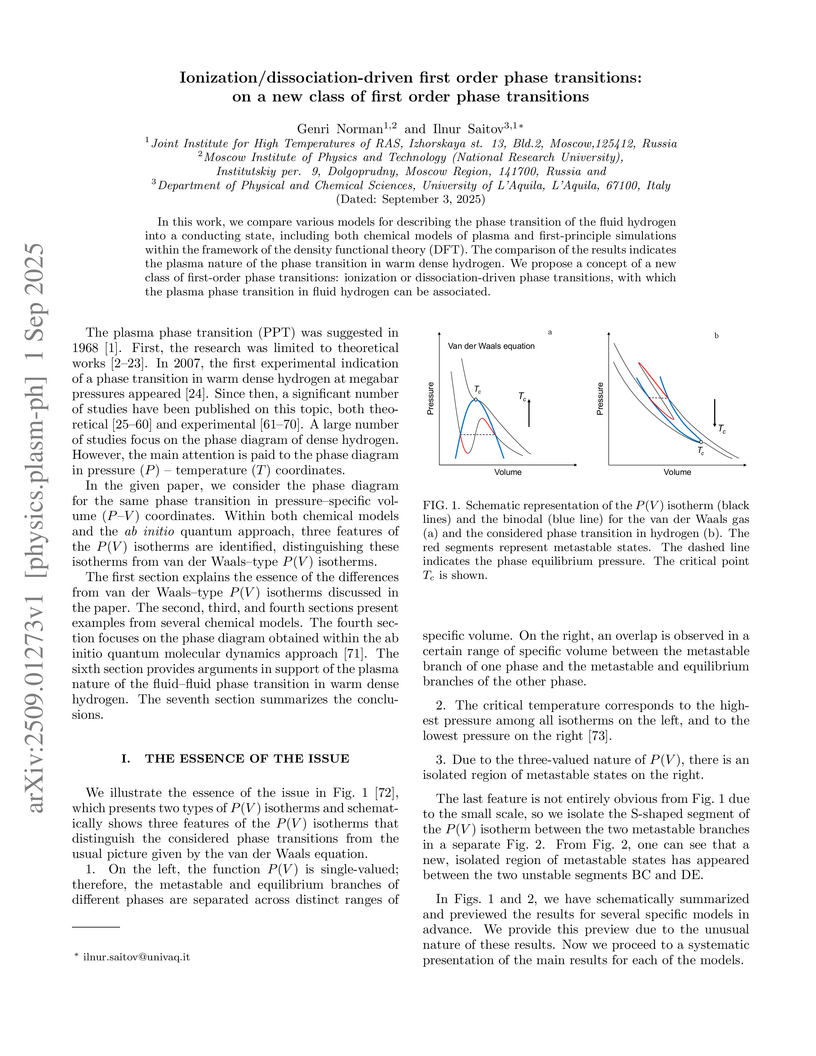
In this work, we compare various models for describing the phase transition of the fluid hydrogen into a conducting state, including both chemical models of plasma and first-principle simulations within the framework of the density functional theory (DFT). The comparison of the results indicates the plasma nature of the phase transition in warm dense hydrogen. We propose a concept of a new class of first-order phase transitions: ionization or dissociation-driven phase transitions, with which the plasma phase transition in fluid hydrogen can be associated.
03 Sep 2025
Renormalization-group equations (RGE) is one of the key tools in studying high-energy behavior of the Standard Model (SM). We begin by reviewing one-loop RGE for the dimensionless couplings of the SM and proceed to the state-of-the-art results. Our study focuses on the RGE solutions at different loop orders. We compare not only the standard (``diagonal'') loop counting, when one considers gauge, Yukawa, and scalar self-coupling beta functions at the same order, but also ``non-diagonal'' ones, inspired by the so-called Weyl consistency conditions. We discuss the initial conditions for RGE (``matching'') for different loop configurations, and study the uncertainties of running coupling both related to the limited precision of the experimental input (``parametric'') and to the missing high-order corrections (``theoretical''). As an application of our analysis we also estimate the electroweak vacuum decay probability and study how the uncertainties in the running parameters affect the latter. We argue that the ``non-diagonal'' beta functions, if coupled with more consistent ``non-diagonal'' matching lead to larger theoretical uncertainty than the ``diagonal'' ones.
The effect of doping on the parameters of an electron-hole liquid (EHL) in heterostructures based on transition metal dichalcogenides is studied. The phase diagram of the EHL is constructed. It is shown that for the formation of a high-temperature tightly bound EHL, as well as for the transition from the semiconducting (exciton) state to the semimetallic one (electron-hole plasma/liquid), it is advantageous to dope the energy band with larger number of valleys. The transition from trion gas to electron-hole plasma is investigated using the modified Mott criterion and variational calculation with screened potential. The effect of doping on the metal--insulator transition in the equilibrium case without laser excitation is studied.
22 Sep 2025
Microsecond-scale sucrose conformational dynamics in aqueous solution via molecular dynamics methods
Microsecond-scale sucrose conformational dynamics in aqueous solution via molecular dynamics methods
Molecular dynamics methods have proven their applicability for the reproduction and prediction of molecular conformations during the last decades. However, most of works considered dilute solutions and relatively short trajectories that limit insights into conformational dynamics. In this study, we investigate the conformational dynamics of sucrose in aqueous solution using microsecond-scale molecular dynamics simulations. For the most of the calculations we use the OPLS-AA/1.14*CM1A-LBCC force field, but we also utilize OPLS-AA/1.14*CM1A and GLYCAM06 for the comparison. We focused on the glycosidic linkage conformers and their lifetimes, glucopyranose and fructofuranose ring puckering. Our findings indicate that the 1C4 glucopyranose ring conformation can stabilize the sucrose conformer, appeared only in the GLYCAM06 and OPLS-AA/1.14*CM1A force fields. All the results are strengthened by comparison with the available experimental data on NMR J-coupling constants and ultrasonic spectra.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.