Reed College
 California Institute of TechnologySLAC National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversity of Zurich
California Institute of TechnologySLAC National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversity of Zurich Google
Google Stanford University
Stanford University University of MichiganUniversity of Ljubljana
University of MichiganUniversity of Ljubljana University of California, San Diego
University of California, San Diego Columbia University
Columbia University CERN
CERN Rutgers University
Rutgers University Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryUniversity of Heidelberg
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryUniversity of Heidelberg MITUniversity of SussexUniversity of CaliforniaUniversität HamburgJozef Stefan InstituteThe Johns Hopkins UniversityUniversity of KansasUniversity of AveiroReed CollegeUniversity of GenovaUniversidad Aut
´
onoma de MadridUniversit
Clermont Auvergne
MITUniversity of SussexUniversity of CaliforniaUniversität HamburgJozef Stefan InstituteThe Johns Hopkins UniversityUniversity of KansasUniversity of AveiroReed CollegeUniversity of GenovaUniversidad Aut
´
onoma de MadridUniversit
Clermont AuvergneA new paradigm for data-driven, model-agnostic new physics searches at
colliders is emerging, and aims to leverage recent breakthroughs in anomaly
detection and machine learning. In order to develop and benchmark new anomaly
detection methods within this framework, it is essential to have standard
datasets. To this end, we have created the LHC Olympics 2020, a community
challenge accompanied by a set of simulated collider events. Participants in
these Olympics have developed their methods using an R&D dataset and then
tested them on black boxes: datasets with an unknown anomaly (or not). This
paper will review the LHC Olympics 2020 challenge, including an overview of the
competition, a description of methods deployed in the competition, lessons
learned from the experience, and implications for data analyses with future
datasets as well as future colliders.
02 Oct 2025
 University of Illinois at Urbana-ChampaignSLAC National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversity of Zurich
University of Illinois at Urbana-ChampaignSLAC National Accelerator LaboratoryUniversity of Zurich Osaka University
Osaka University Stanford University
Stanford University Zhejiang UniversityUniversidad Autónoma de Madrid
Zhejiang UniversityUniversidad Autónoma de Madrid University of Tokyo
University of Tokyo Seoul National UniversityThe Hebrew UniversityKyung Hee UniversityÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)University of ConnecticutUniversidad Complutense de MadridMax-Planck-Institut für AstrophysikLund UniversityUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoNational Center for Supercomputing ApplicationsUniversity of Nevada, Las VegasReed CollegeUniversitá degli Studi dell’InsubriaGMVShikoku Gakuin UniversityUniversit
degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca
Seoul National UniversityThe Hebrew UniversityKyung Hee UniversityÉcole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)University of ConnecticutUniversidad Complutense de MadridMax-Planck-Institut für AstrophysikLund UniversityUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de MéxicoNational Center for Supercomputing ApplicationsUniversity of Nevada, Las VegasReed CollegeUniversitá degli Studi dell’InsubriaGMVShikoku Gakuin UniversityUniversit
degli Studi di Milano-BicoccaWe investigate how differences in the stellar feedback produce disks with different morphologies in Milky Way-like progenitors over 1 ≤z≤5, using eight state-of-the-art cosmological hydrodynamics simulation codes in the \textit{AGORA} project. In three of the participating codes, a distinct, rotation-dominated inner core emerges with a formation timescale of ≲300 Myr, largely driven by a major merger event, while two other codes exhibit similar signs of wet compaction -- gaseous shrinkage into a compact starburst phase -- at earlier epochs. The remaining three codes show only weak evidence of wet compaction. Consequently, we divide the simulated galaxies into two groups: those with strong compaction signatures and those with weaker ones. Galaxies in these two groups differ in size, stellar age gradients, and disk-to-total mass ratios. Specifically, codes with strong wet compaction build their outer disks in an inside-out fashion, leading to negative age gradients, whereas codes with weaker compaction feature flat or positive age gradients caused primarily by outward stellar migration. Although the stellar half-mass radii of these two groups diverge at z∼3, the inclusion of dust extinction brings their sizes and shapes in mock observations closer to each other and to observed galaxies. We attribute the observed morphological differences primarily to variations in the stellar feedback implementations -- such as delayed cooling timescales, and feedback strengths -- that regulate both the onset and duration of compaction. Overall, our results suggest that disk assembly at high redshifts is highly sensitive to the details of the stellar feedback prescriptions in simulations.
YE Guo developed a relativistic field-theoretic framework to describe interacting two-particle tunneling through a static potential barrier. The work derives the Bethe-Salpeter equation for this system, identifies a path to analytical solutions in a 1+1D instantaneous regime, and computes the leading-order tunneling amplitude, revealing momentum-dependent correlated tunneling effects.
11 Jun 2024
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Harvard University
Harvard University Northeastern University
Northeastern University Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University University of Notre Dame
University of Notre Dame University of Chicago
University of Chicago Tel Aviv University
Tel Aviv University University College London
University College London University of Maryland, College Park
University of Maryland, College Park Cornell University
Cornell University Texas A&M UniversityHarvard Medical SchoolPacific Northwest National Laboratory
Texas A&M UniversityHarvard Medical SchoolPacific Northwest National Laboratory Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory University of Wisconsin-MadisonUniversity of ColoradoTufts University
University of Wisconsin-MadisonUniversity of ColoradoTufts University Virginia TechCase Western Reserve University
Virginia TechCase Western Reserve University Princeton UniversityICREAINSERMAix-Marseille UnivUniversity of North TexasGladstone InstitutesBarcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC)Reed CollegeNational Institutes of HealthFederal University of ParanáUniversity Magna Graecia of Catanzaro
Princeton UniversityICREAINSERMAix-Marseille UnivUniversity of North TexasGladstone InstitutesBarcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC)Reed CollegeNational Institutes of HealthFederal University of ParanáUniversity Magna Graecia of CatanzaroA large collaborative effort outlines a comprehensive roadmap for network biology, synthesizing expert consensus on current challenges and future research directions across five core areas while emphasizing best practices for data integration, machine learning, and personalized medicine. It aims to guide the field's strategic development and foster interdisciplinary efforts.
The astrophysical origin of the lanthanides is an open question in nuclear astrophysics. Besides the widely studied s, i, and r processes in moderately-to-strongly neutron-rich environments, an intriguing alternative site for lanthanide production could in fact be robustly proton-rich matter outflows from core-collapse supernovae under specific conditions -- in particular, high-entropy winds with enhanced neutrino luminosity and fast dynamical timescales. In this environment, excess protons present after charged particle reactions have ceased can continue to be converted to neutrons by (anti-)neutrino interactions, producing a neutron capture reaction flow up to A~200. This scenario, christened the νi process in a recent paper, has previously been discussed as a possibility. Here, we examine the prospects for νi process through the lens of stellar abundance patterns, bolometric lightcurves, and galactic chemical evolution models, with a particular focus on hypernovae as candidate sites. We identify specific lanthanide signatures for which the νi process can provide a credible alternative to r/i processes.
We covariantize calculations over the manifold of phase space, establishing
Stokes' theorem for differential cross sections and providing new definitions
of familiar observable properties like infrared and collinear safety. Through
the introduction of explicit coordinates and a metric we show phase space is
isomorphic to the product space of a simplex and a hypersphere, and we identify
geometric phenomena that occur when its dimensions are large. These results
have implications for fixed order subtraction schemes, machine learning in
particle physics and high-multiplicity heavy ion collisions.
23 Aug 2024
Traditional statistical inference on ordinal comparison data results in an
overall ranking of objects, e.g., from best to worst, with each object having a
unique rank. However, ranks of some objects may not be statistically
distinguishable. This could happen due to insufficient data or to the true
underlying object qualities being equal. Because uncertainty communication in
estimates of overall rankings is notoriously difficult, we take a different
approach and allow groups of objects to have equal ranks or be
rank-clustered in our model. Existing models related to
rank-clustering are limited by their inability to handle a variety of ordinal
data types, to quantify uncertainty, or by the need to pre-specify the number
and size of potential rank-clusters. We solve these limitations through our
proposed Bayesian Rank-Clustered Bradley-Terry-Luce model. We
accommodate rank-clustering via parameter fusion by imposing a novel
spike-and-slab prior on object-specific worth parameters in Bradley-Terry-Luce
family of distributions for ordinal comparisons. We demonstrate rank-clustering
on simulated and real datasets in surveys, elections, and sports analytics.
Modern society generates an incredible amount of data about individuals, and releasing summary statistics about this data in a manner that provably protects individual privacy would offer a valuable resource for researchers in many fields. We present the first algorithm for analysis of variance (ANOVA) that preserves differential privacy, allowing this important statistical test to be conducted (and the results released) on databases of sensitive information. In addition to our private algorithm for the F test statistic, we show a rigorous way to compute p-values that accounts for the added noise needed to preserve privacy. Finally, we present experimental results quantifying the statistical power of this differentially private version of the test, finding that a sample of several thousand observations is frequently enough to detect variation between groups. The differentially private ANOVA algorithm is a promising approach for releasing a common test statistic that is valuable in fields in the sciences and social sciences.
29 May 2019
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Beihang University
Beihang University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University RIKEN
RIKEN Peking UniversityTechnische Universität DarmstadtUniversity of TsukubaTRIUMFSaitama UniversityXian Jiaotong UniversityGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungReed CollegeMax-Planck-Institut für KernphysikJohannes Gutenberg-UniversitätUniversité de Paris-SudCSNSM-IN2P3-CNRS
Peking UniversityTechnische Universität DarmstadtUniversity of TsukubaTRIUMFSaitama UniversityXian Jiaotong UniversityGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungReed CollegeMax-Planck-Institut für KernphysikJohannes Gutenberg-UniversitätUniversité de Paris-SudCSNSM-IN2P3-CNRSIsochronous mass spectrometry has been applied in the storage ring CSRe to measure the masses of the neutron-rich 52-54Sc and 54,56Ti nuclei. The new mass excess values ME(52Sc) = −40525(65) keV, ME(53Sc) = −38910(80) keV, and ME(54Sc) = −34485(360) keV, deviate from the Atomic Mass Evaluation 2012 by 2.3σ, 2.8σ, and 1.7σ, respectively. These large deviations significantly change the systematics of the two-neutron separation energies of scandium isotopes. The empirical shell gap extracted from our new experimental results shows a significant subshell closure at N=32 in scandium, with a similar magnitude as in calcium. Moreover, we present ab initio calculations using the valence-space in-medium similarity renormalization group based on two- and three-nucleon interactions from chiral effective field theory. The theoretical results confirm the existence of a substantial N=32 shell gap in Sc and Ca with a decreasing trend towards lighter isotones, thus providing a consistent picture of the evolution of the N=32 magic number from the pf into the sd shell.
27 May 2002
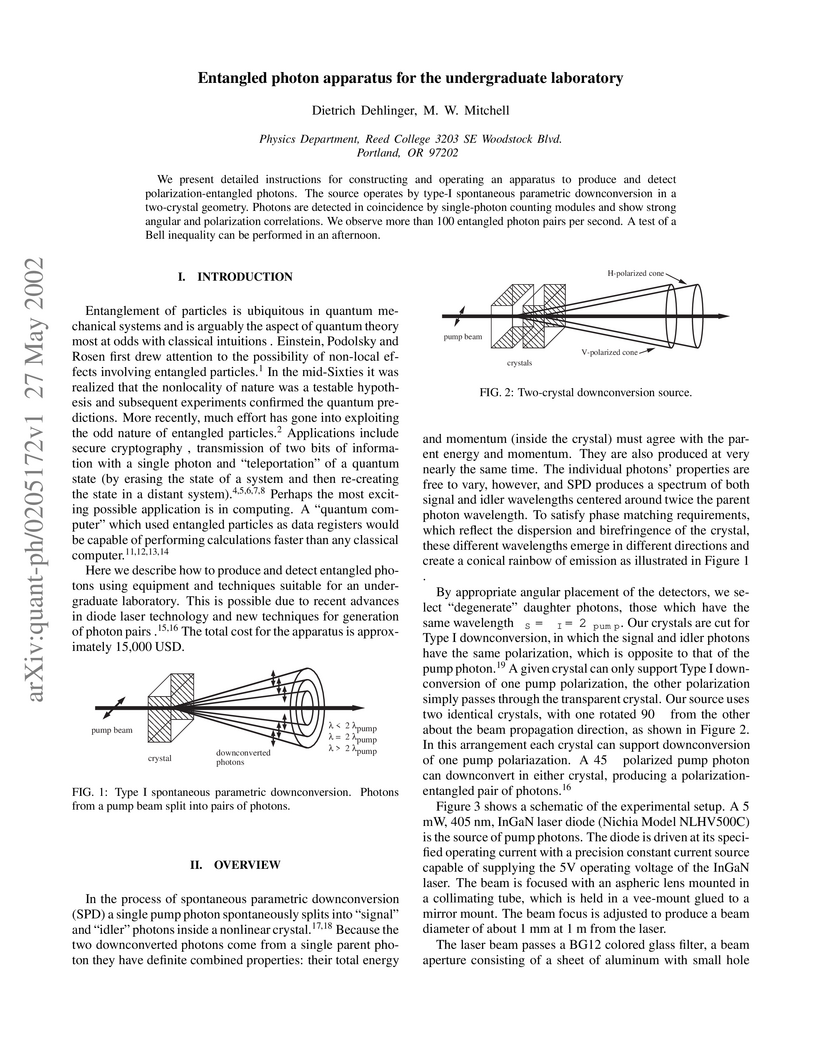
We present detailed instructions for constructing and operating an apparatus
to produce and detect polarization-entangled photons. The source operates by
type-I spontaneous parametric downconversion in a two-crystal geometry. Photons
are detected in coincidence by single-photon counting modules and show strong
angular and polarization correlations. We observe more than 100 entangled
photon pairs per second. A test of a Bell inequality can be performed in an
afternoon.
30 Jul 2014
We describe CPMC-Lab, a Matlab program for the constrained-path and phaseless
auxiliary-field Monte Carlo methods. These methods have allowed applications
ranging from the study of strongly correlated models, such as the Hubbard
model, to ab initio calculations in molecules and solids. The present package
implements the full ground-state constrained-path Monte Carlo (CPMC) method in
Matlab with a graphical interface, using the Hubbard model as an example. The
package can perform calculations in finite supercells in any dimensions, under
periodic or twist boundary conditions. Importance sampling and all other
algorithmic details of a total energy calculation are included and illustrated.
This open-source tool allows users to experiment with various model and run
parameters and visualize the results. It provides a direct and interactive
environment to learn the method and study the code with minimal overhead for
setup. Furthermore, the package can be easily generalized for auxiliary-field
quantum Monte Carlo (AFQMC) calculations in many other models for correlated
electron systems, and can serve as a template for developing a production code
for AFQMC total energy calculations in real materials. Several illustrative
studies are carried out in one- and two-dimensional lattices on total energy,
kinetic energy, potential energy, and charge- and spin-gaps.
These are lecture notes presented at the online 2020 Hadron Collider Physics Summer School hosted by Fermilab. These are an extension of lectures presented at the 2017 and 2018 CTEQ summer schools in arXiv:1709.06195 and still introduces perturbative QCD and its application to jet substructure from a bottom-up perspective based on the approximation of QCD as a weakly-coupled, conformal field theory. With machine learning becoming an increasingly important tool of particle physics, I discuss its utility exclusively from the biased view for increasing human knowledge. A simple argument that the likelihood for quark versus gluon discrimination is infrared and collinear safe is presented as an example of this approach. End-of-lecture exercises are also provided.
We explore the task of sentiment analysis on Hinglish (code-mixed Hindi-English) tweets as participants of Task 9 of the SemEval-2020 competition, known as the SentiMix task. We had two main approaches: 1) applying transfer learning by fine-tuning pre-trained BERT models and 2) training feedforward neural networks on bag-of-words representations. During the evaluation phase of the competition, we obtained an F-score of 71.3% with our best model, which placed 4th out of 62 entries in the official system rankings.
The performance of today's in-memory indexes is bottlenecked by the memory latency/bandwidth wall. Processing-in-memory (PIM) is an emerging approach that potentially mitigates this bottleneck, by enabling low-latency memory access whose aggregate memory bandwidth scales with the number of PIM nodes. There is an inherent tension, however, between minimizing inter-node communication and achieving load balance in PIM systems, in the presence of workload skew. This paper presents PIM-tree, an ordered index for PIM systems that achieves both low communication and high load balance, regardless of the degree of skew in the data and the queries. Our skew-resistant index is based on a novel division of labor between the multi-core host CPU and the PIM nodes, which leverages the strengths of each. We introduce push-pull search, which dynamically decides whether to push queries to a PIM-tree node (CPU -> PIM-node) or pull the node's keys back to the CPU (PIM-node -> CPU) based on workload skew. Combined with other PIM-friendly optimizations (shadow subtrees and chunked skip lists), our PIM-tree provides high-throughput, (guaranteed) low communication, and (guaranteed) high load balance, for batches of point queries, updates, and range scans.
We implement the PIM-tree structure, in addition to prior proposed PIM indexes, on the latest PIM system from UPMEM, with 32 CPU cores and 2048 PIM nodes. On workloads with 500 million keys and batches of one million queries, the throughput using PIM-trees is up to 69.7x and 59.1x higher than the two best prior methods. As far as we know these are the first implementations of an ordered index on a real PIM system.
12 Oct 2017
 Michigan State University
Michigan State University Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryFacility for Rare Isotope BeamsHope CollegeNational Superconducting Cyclotron LaboratoryReed CollegeCentral Michigan UniversityDavidson CollegeAugustana CollegeJoint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics - Center for the Evolution of the ElementsGettysburg College
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryFacility for Rare Isotope BeamsHope CollegeNational Superconducting Cyclotron LaboratoryReed CollegeCentral Michigan UniversityDavidson CollegeAugustana CollegeJoint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics - Center for the Evolution of the ElementsGettysburg CollegeTheoretical calculations suggest the presence of low-lying excited states in
25O. Previous experimental searches by means of proton knockout on
26F produced no evidence for such excitations.
We search for excited states in 25O using the ${ {}^{24}\text{O} (d,p)
{}^{25}\text{O} }$ reaction. The theoretical analysis of excited states in
unbound 25,27O is based on the configuration interaction approach that
accounts for couplings to the scattering continuum.
We use invariant-mass spectroscopy to measure neutron-unbound states in
25O. For the theoretical approach, we use the complex-energy Gamow Shell
Model and Density Matrix Renormalization Group method with a finite-range
two-body interaction optimized to the bound states and resonances of
23−26O, assuming a core of 22O. We predict energies, decay widths,
and asymptotic normalization coefficients.
Our calculations in a large spdf space predict several low-lying excited
states in 25O of positive and negative parity, and we obtain an
experimental limit on the relative cross section of a possible ${ {J}^{\pi} =
{1/2}^{+} }statewithrespecttotheground−stateof^{25}$O at
σ1/2+/σg.s.=0.25−0.25+1.0. We also discuss how the
observation of negative parity states in 25O could guide the search for
the low-lying negative parity states in 27O.
Previous experiments based on the proton knockout of 26F suffered from
the low cross sections for the population of excited states in 25O because
of low spectroscopic factors. In this respect, neutron transfer reactions carry
more promise.
20 Sep 2015
Bound charge is a useful construct for calculating the electrostatic field of
polarized material, and it represents a perfectly genuine accumulation of
charge. But is such a material in every respect equivalent to a particular
configuration of bound charge? The answer is no, and the same goes for bound
current and (in the time-dependent case) polarization current.
Previous studies have demonstrated the utility and applicability of machine
learning techniques to jet physics. In this paper, we construct new observables
for the discrimination of jets from different originating particles exclusively
from information identified by the machine. The approach we propose is to first
organize information in the jet by resolved phase space and determine the
effective N-body phase space at which discrimination power saturates. This
then allows for the construction of a discrimination observable from the
N-body phase space coordinates. A general form of this observable can be
expressed with numerous parameters that are chosen so that the observable
maximizes the signal vs.~background likelihood. Here, we illustrate this
technique applied to discrimination of H→bbˉ decays from massive $g\to
b\bar b$ splittings. We show that for a simple parametrization, we can
construct an observable that has discrimination power comparable to, or better
than, widely-used observables motivated from theory considerations. For the
case of jets on which modified mass-drop tagger grooming is applied, the
observable that the machine learns is essentially the angle of the dominant
gluon emission off of the bbˉ pair.
Observables which distinguish boosted topologies from QCD jets are playing an increasingly important role at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). These observables are often used in conjunction with jet grooming algorithms, which reduce contamination from both theoretical and experimental sources. In this paper we derive factorization formulae for groomed multi-prong substructure observables, focusing in particular on the groomed D2 observable, which is used to identify boosted hadronic decays of electroweak bosons at the LHC. Our factorization formulae allow systematically improvable calculations of the perturbative D2 distribution and the resummation of logarithmically enhanced terms in all regions of phase space using renormalization group evolution. They include a novel factorization for the production of a soft subjet in the presence of a grooming algorithm, in which clustering effects enter directly into the hard matching. We use these factorization formulae to draw robust conclusions of experimental relevance regarding the universality of the D2 distribution in both e+e− and pp collisions. In particular, we show that the only process dependence is carried by the relative quark vs. gluon jet fraction in the sample, no non-global logarithms from event-wide correlations are present in the distribution, hadronization corrections are controlled by the perturbative mass of the jet, and all global color correlations are completely removed by grooming, making groomed D2 a theoretically clean QCD observable even in the LHC environment. We compute all ingredients to one-loop accuracy, and present numerical results at next-to-leading logarithmic accuracy for e+e− collisions, comparing with parton shower Monte Carlo simulations. Results for pp collisions, as relevant for phenomenology at the LHC, are presented in a companion paper.
A scalar theory of gravity extending Newtonian gravity to include field
energy as its source is developed. The physical implications of the theory are
probed through its spherically symmetric (source) solutions. The aim is to
demonstrate rational physical model building, together with physical and
experimental checks of correctness. The theory discussed here was originally
considered by Einstein prior to his introduction of general relativity.
We present predictions of the distribution of groomed heavy jet mass in
electron-positron collisions at the next-to-next-to-leading order accuracy
matched with the resummation of large logarithms to
next-to-next-to-next-to-leading logarithmic accuracy. Resummation at this
accuracy is possible through extraction of necessary two-loop constants and
three-loop anomalous dimensions from fixed-order codes.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.