Ask or search anything...
Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center of Intelligent Visual Computing
Unveiling the Truth and Facilitating Change: Towards Agent-based
Large-scale Social Movement Simulation
17 Jun 2024
Fudan University researchers introduce HiSim, a hybrid framework that combines LLM-empowered agents for influential users and ABMs for ordinary users to simulate large-scale social movements on social media, overcoming previous limitations in accuracy, efficiency, and scale. They also establish SoMoSiMu-Bench, the first dedicated benchmark with real-world datasets and multi-level evaluation, demonstrating HiSim's superior performance over pure ABMs in replicating opinion dynamics and providing actionable insights for online community interventions.
View blogA Comprehensive Capability Analysis of GPT-3 and GPT-3.5 Series Models
23 Dec 2023
GPT series models, such as GPT-3, CodeX, InstructGPT, ChatGPT, and so on, have gained considerable attention due to their exceptional natural language processing capabilities. However, despite the abundance of research on the difference in capabilities between GPT series models and fine-tuned models, there has been limited attention given to the evolution of GPT series models' capabilities over time. To conduct a comprehensive analysis of the capabilities of GPT series models, we select six representative models, comprising two GPT-3 series models (i.e., davinci and text-davinci-001) and four GPT-3.5 series models (i.e., code-davinci-002, text-davinci-002, text-davinci-003, and gpt-3.5-turbo). We evaluate their performance on nine natural language understanding (NLU) tasks using 21 datasets. In particular, we compare the performance and robustness of different models for each task under zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. Our extensive experiments reveal that the overall ability of GPT series models on NLU tasks does not increase gradually as the models evolve, especially with the introduction of the RLHF training strategy. While this strategy enhances the models' ability to generate human-like responses, it also compromises their ability to solve some tasks. Furthermore, our findings indicate that there is still room for improvement in areas such as model robustness.
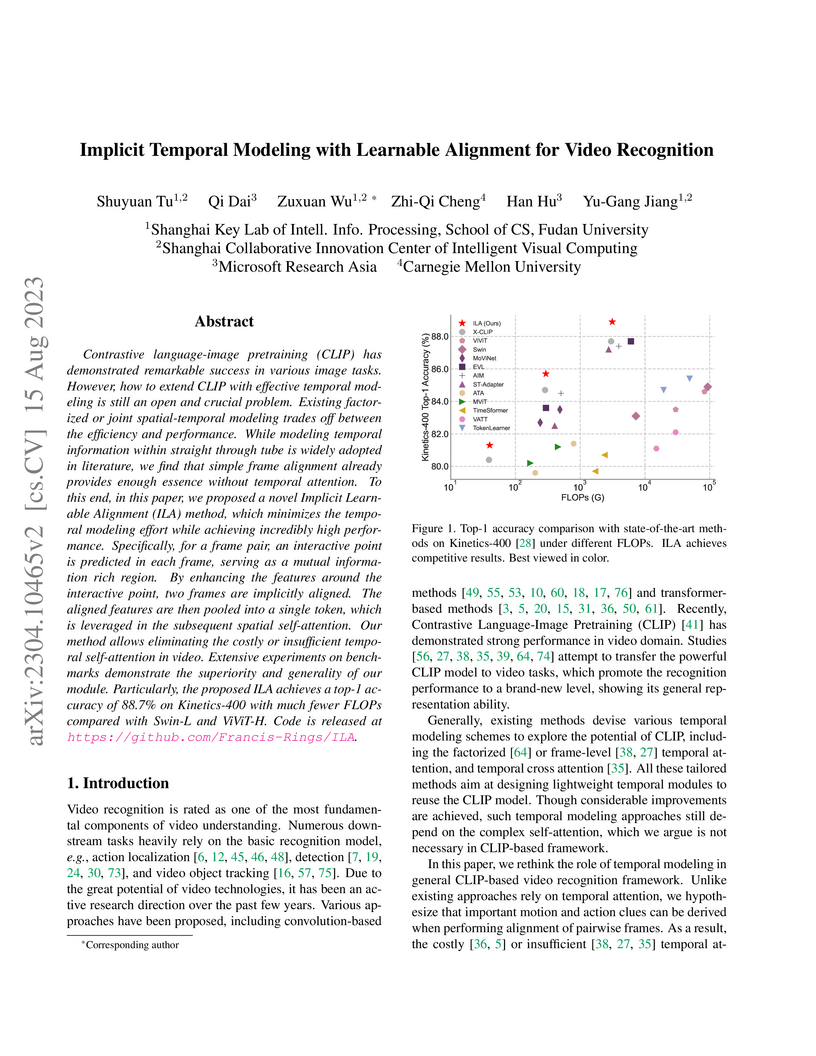
Implicit Temporal Modeling with Learnable Alignment for Video Recognition
15 Aug 2023
Contrastive language-image pretraining (CLIP) has demonstrated remarkable success in various image tasks. However, how to extend CLIP with effective temporal modeling is still an open and crucial problem. Existing factorized or joint spatial-temporal modeling trades off between the efficiency and performance. While modeling temporal information within straight through tube is widely adopted in literature, we find that simple frame alignment already provides enough essence without temporal attention. To this end, in this paper, we proposed a novel Implicit Learnable Alignment (ILA) method, which minimizes the temporal modeling effort while achieving incredibly high performance. Specifically, for a frame pair, an interactive point is predicted in each frame, serving as a mutual information rich region. By enhancing the features around the interactive point, two frames are implicitly aligned. The aligned features are then pooled into a single token, which is leveraged in the subsequent spatial self-attention. Our method allows eliminating the costly or insufficient temporal self-attention in video. Extensive experiments on benchmarks demonstrate the superiority and generality of our module. Particularly, the proposed ILA achieves a top-1 accuracy of 88.7% on Kinetics-400 with much fewer FLOPs compared with Swin-L and ViViT-H. Code is released at this https URL .
TDR: Task-Decoupled Retrieval with Fine-Grained LLM Feedback for In-Context Learning
24 Jul 2025
In-context learning (ICL) has become a classic approach for enabling LLMs to handle various tasks based on a few input-output examples. The effectiveness of ICL heavily relies on the quality of these examples, and previous works which focused on enhancing example retrieval capabilities have achieved impressive performances. However, two challenges remain in retrieving high-quality examples: (1) Difficulty in distinguishing cross-task data distributions, (2) Difficulty in making the fine-grained connection between retriever output and feedback from LLMs. In this paper, we propose a novel framework called TDR. TDR decouples the ICL examples from different tasks, which enables the retrieval module to retrieve examples specific to the target task within a multi-task dataset. Furthermore, TDR models fine-grained feedback from LLMs to supervise and guide the training of the retrieval module, which helps to retrieve high-quality examples. We conducted extensive experiments on a suite of 30 NLP tasks, the results demonstrate that TDR consistently improved results across all datasets and achieves state-of-the-art performance. Meanwhile, our approach is a plug-and-play method, which can be easily combined with various LLMs to improve example retrieval abilities for ICL. The code is available at this https URL.
Seg2Any: Open-set Segmentation-Mask-to-Image Generation with Precise Shape and Semantic Control
10 Nov 2025
Despite recent advances in diffusion models, top-tier text-to-image (T2I) models still struggle to achieve precise spatial layout control, i.e. accurately generating entities with specified attributes and locations. Segmentation-mask-to-image (S2I) generation has emerged as a promising solution by incorporating pixel-level spatial guidance and regional text prompts. However, existing S2I methods fail to simultaneously ensure semantic consistency and shape consistency. To address these challenges, we propose Seg2Any, a novel S2I framework built upon advanced multimodal diffusion transformers (e.g. FLUX). First, to achieve both semantic and shape consistency, we decouple segmentation mask conditions into regional semantic and high-frequency shape components. The regional semantic condition is introduced by a Semantic Alignment Attention Mask, ensuring that generated entities adhere to their assigned text prompts. The high-frequency shape condition, representing entity boundaries, is encoded as an Entity Contour Map and then introduced as an additional modality via multi-modal attention to guide image spatial structure. Second, to prevent attribute leakage across entities in multi-entity scenarios, we introduce an Attribute Isolation Attention Mask mechanism, which constrains each entity's image tokens to attend exclusively to themselves during image self-attention. To support open-set S2I generation, we construct SACap-1M, a large-scale dataset containing 1 million images with 5.9 million segmented entities and detailed regional captions, along with a SACap-Eval benchmark for comprehensive S2I evaluation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Seg2Any achieves state-of-the-art performance on both open-set and closed-set S2I benchmarks, particularly in fine-grained spatial and attribute control of entities.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.
 Fudan University
Fudan University

 Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University