Skywork AI
28 Oct 2025
GiGPO introduces a two-level advantage estimation structure to improve Large Language Model agent training in complex, multi-turn environments. This reinforcement learning algorithm consistently surpasses prior RL methods and prompting techniques across diverse benchmarks like ALFWorld and WebShop, demonstrating enhanced success rates and tool efficiency with negligible additional computational cost.
Recent advances in interactive video generations have demonstrated diffusion model's potential as world models by capturing complex physical dynamics and interactive behaviors. However, existing interactive world models depend on bidirectional attention and lengthy inference steps, severely limiting real-time performance. Consequently, they are hard to simulate real-world dynamics, where outcomes must update instantaneously based on historical context and current actions. To address this, we present Matrix-Game 2.0, an interactive world model generates long videos on-the-fly via few-step auto-regressive diffusion. Our framework consists of three key components: (1) A scalable data production pipeline for Unreal Engine and GTA5 environments to effectively produce massive amounts (about 1200 hours) of video data with diverse interaction annotations; (2) An action injection module that enables frame-level mouse and keyboard inputs as interactive conditions; (3) A few-step distillation based on the casual architecture for real-time and streaming video generation. Matrix Game 2.0 can generate high-quality minute-level videos across diverse scenes at an ultra-fast speed of 25 FPS. We open-source our model weights and codebase to advance research in interactive world modeling.
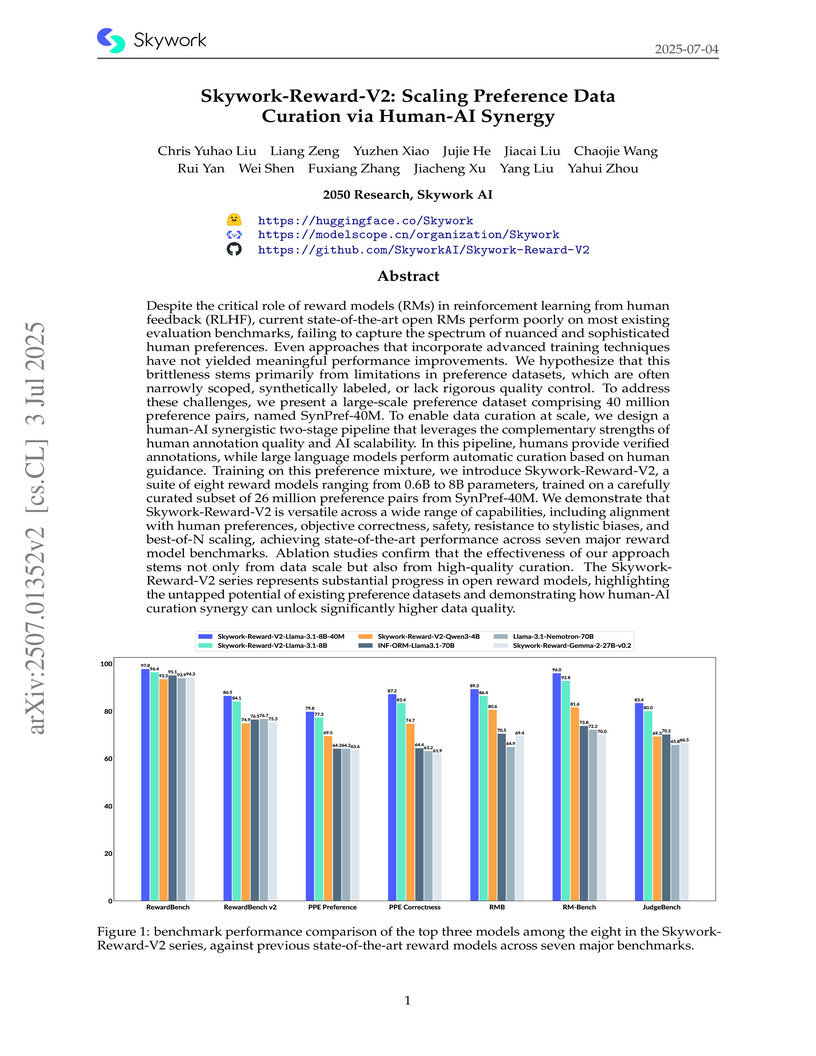
Skywork AI developed Skywork-Reward-V2, a suite of state-of-the-art open reward models, by curating SynPref-40M, the largest preference dataset to date, through a two-stage human-AI synergistic pipeline. The models demonstrate improved alignment with human preferences, objective correctness, and resistance to stylistic biases across seven major benchmarks.
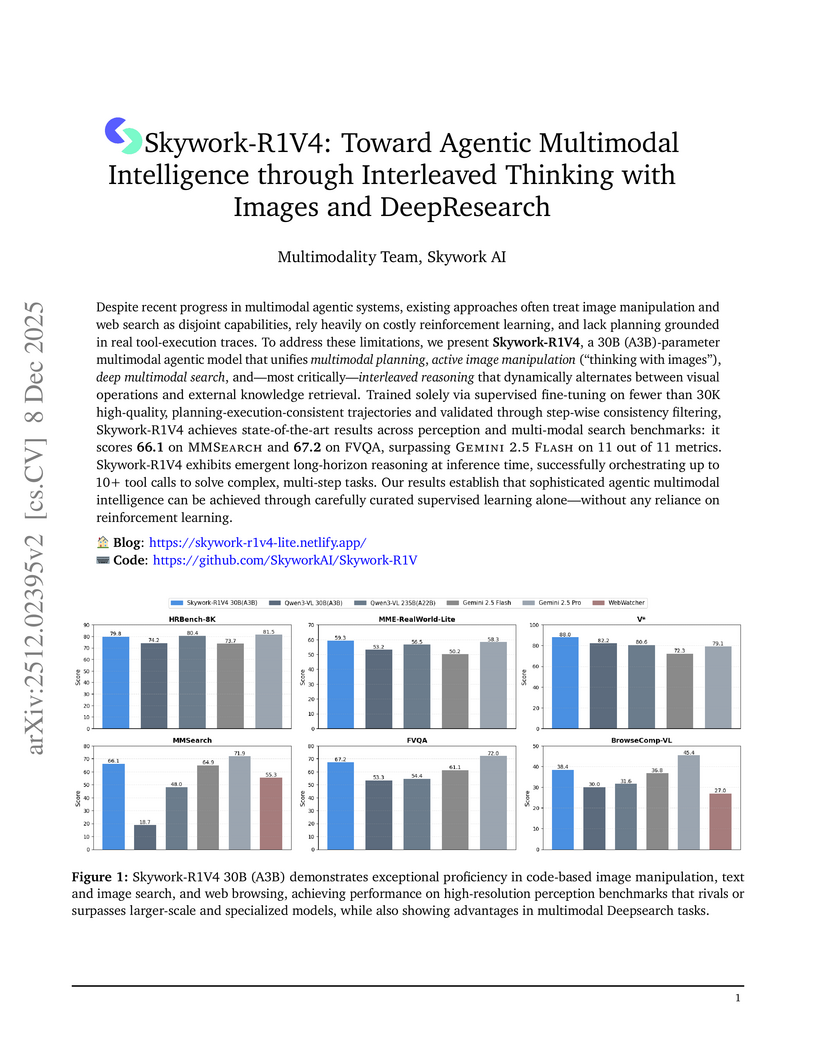
Despite recent progress in multimodal agentic systems, existing approaches often treat image manipulation and web search as disjoint capabilities, rely heavily on costly reinforcement learning, and lack planning grounded in real tool-execution traces. To address these limitations, we present Skywork-R1V4, a 30B (A3B) parameter multimodal agentic model that unifies multimodal planning, active image manipulation ("thinking with images"), deep multimodal search, and, most critically, interleaved reasoning that dynamically alternates between visual operations and external knowledge retrieval. Trained solely via supervised fine-tuning on fewer than 30,000 high-quality, planning-execution-consistent trajectories and validated through stepwise consistency filtering, Skywork-R1V4 achieves state-of-the-art results across perception and multimodal search benchmarks: it scores 66.1 on MMSearch and 67.2 on FVQA, surpassing Gemini 2.5 Flash on all 11 metrics. Skywork-R1V4 exhibits emergent long-horizon reasoning at inference time, successfully orchestrating more than 10 tool calls to solve complex, multi-step tasks. Our results demonstrate that sophisticated agentic multimodal intelligence can be achieved through carefully curated supervised learning alone, without any reliance on reinforcement learning.
Skywork AI's SkyReels-V2 introduces an open-source film generative model that achieves state-of-the-art performance in prompt adherence for cinematic grammar and motion quality. The model uniquely enables infinite-length video synthesis through a diffusion-forcing architecture, surpassing existing open-source benchmarks and approaching the quality of leading closed-source models.
Researchers at Nanyang Technological University and collaborators developed FinAgent, an advanced multimodal foundation agent for financial trading that integrates numerical, textual, and visual market data. This agent consistently outperformed 12 state-of-the-art baselines, achieving over a 36% average improvement in Annual Rate of Return by employing diversified information retrieval, dual-level reflection, and tool augmentation.
Audio-Reasoner, a large audio language model from Nanyang Technological University and National University of Singapore researchers, integrates structured Chain-of-Thought reasoning using a novel 1.2 million-sample CoTA dataset to enhance deep audio reasoning. The model establishes new state-of-the-art performance across diverse audio understanding benchmarks, surpassing leading closed-source models such as GPT-4o and Gemini-1.5-Pro.
Skywork AI developed Matrix-Game, a 17-billion-parameter interactive world foundation model that generates game worlds from a reference image and user actions. The model achieves superior action controllability and physical consistency, outperforming previous models on a new comprehensive benchmark for Minecraft environments.
A novel strategy, Visual Tokens Withdrawal (VTW), accelerates Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) inference by removing vision tokens in deep layers, leveraging observed information migration. This approach reduces computational overhead by over 40% and GPU memory by 35% while maintaining performance across various MLLMs and tasks.
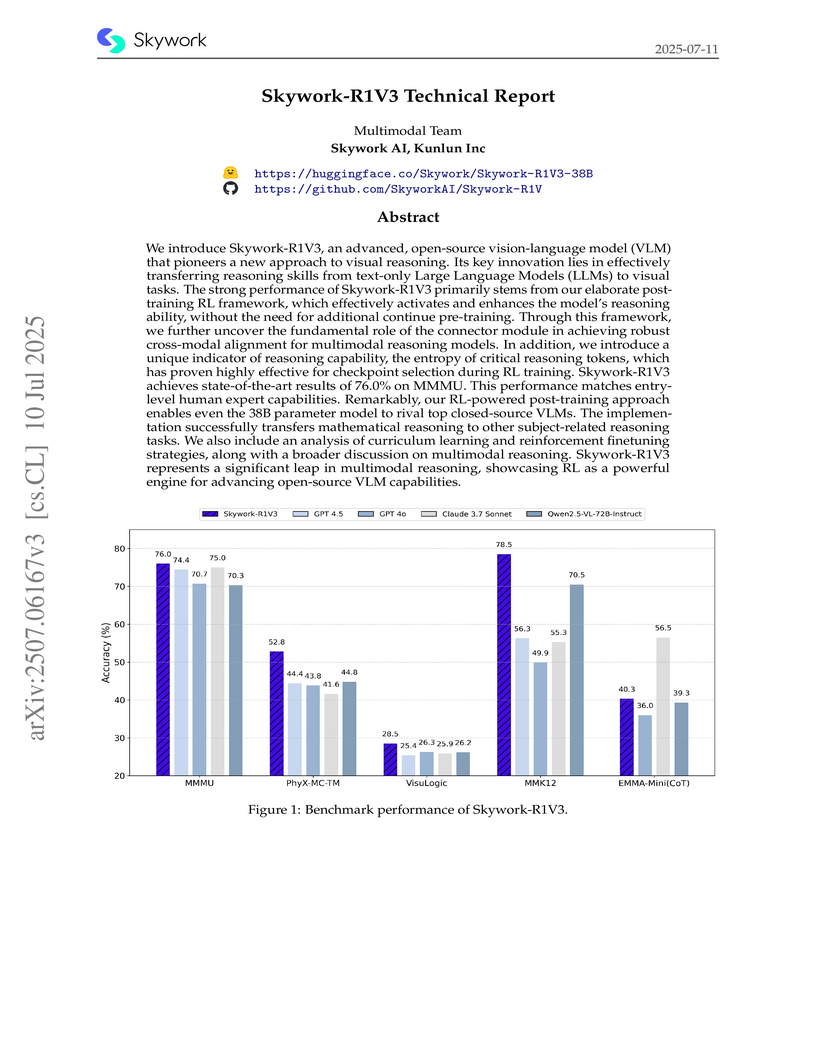
Skywork-R1V3, an open-source 38B parameter vision-language model by Skywork AI, Kunlun Inc., employs an innovative reinforcement learning-powered post-training approach to achieve visual reasoning capabilities competitive with leading proprietary models. It demonstrates scores of 76.0% on MMMU and 142/150 on the 2025 GAOKAO math exam, showcasing the transfer of mathematical reasoning skills to broader scientific tasks.
08 Nov 2025
This paper introduces Completion Pruning Policy Optimization (CPPO) to accelerate the training of reasoning models based on Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). GRPO, while effective, incurs high training costs due to the need to sample multiple completions for each question. Our experiment and theoretical analysis reveal that the number of completions impacts model accuracy yet increases training time multiplicatively, and not all completions contribute equally to policy training -- their contribution depends on their relative advantage. To address these issues, we propose CPPO, which prunes completions with low absolute advantages, significantly reducing the number needed for gradient calculation and updates. Additionally, we introduce a dynamic completion allocation strategy to maximize GPU utilization by incorporating additional questions, further enhancing training efficiency. Experiments show that CPPO achieves up to 7.98× speedup on GSM8K and 3.48× on Math while preserving or even enhancing the accuracy compared to the original GRPO. We release our code at \href{this https URL}{this https URL}.
This research introduces SeTok, a Semantic-Equivalent Vision Tokenizer, and integrates it into SETOKIM, a Multimodal Large Language Model, to generate semantically complete visual tokens that dynamically adapt to image content. The approach yields superior performance across tasks like visual understanding, generation, editing, and referring segmentation by enhancing fine-grained vision-language alignment.
The role of reinforcement learning (RL) in enhancing the reasoning of large language models (LLMs) is becoming increasingly significant. Despite the success of RL in many scenarios, there are still many challenges in improving the reasoning of LLMs. One challenge is the sparse reward, which makes optimization difficult for RL and necessitates a large amount of data samples. Another challenge stems from the inherent instability of RL, particularly when using Actor-Critic (AC) methods to derive optimal policies, which often leads to unstable training processes. To address these issues, we introduce Direct Advantage Policy Optimization (DAPO), an novel step-level offline RL algorithm. Unlike standard alignment that rely solely outcome rewards to optimize policies (such as DPO), DAPO employs a critic function to predict the reasoning accuracy at each step, thereby generating dense signals to refine the generation strategy. Additionally, the Actor and Critic components in DAPO are trained independently, avoiding the co-training instability observed in standard AC algorithms like PPO. We train DAPO on mathematical and code query datasets and then evaluate its performance on multiple benchmarks. Our results show that DAPO can effectively enhance the mathematical and code capabilities on both SFT models and RL models, demonstrating the effectiveness of DAPO.
Researchers from Peking University, Mila - Québec AI Institute, Tiamat AI, and Skywork AI introduced "world-instructed image editing," a task where generative models understand and execute dynamic commands involving causality and temporal changes. They developed EDITWORLD, a dataset and diffusion-based model capable of simulating complex scenarios within images, achieving superior performance over existing baselines in producing logically consistent and visually plausible edits.
Researchers from Skywork AI and collaborating institutions developed Matrix-3D, a framework that generates geometrically consistent, omnidirectional, and explorable 3D worlds from a single image or text prompt. This approach leverages trajectory-guided panoramic video diffusion and dual 3D reconstruction pipelines, achieving superior visual quality and introducing the Matrix-Pano dataset with detailed camera poses and depth annotations.
A comprehensive survey analyzes the rapid advancements of Large Language Models in mathematical reasoning, structuring the field by cognitive phases of comprehension and answer generation. It consolidates diverse enhancement methods, identifies persistent challenges, and suggests future research, observing that current improvements largely activate latent reasoning capacities rather than instilling entirely new ones.
24 Jun 2025
Research from Skywork AI empirically validates data scaling laws for software engineering tasks, demonstrating that performance of Large Language Models continues to improve with increasing volumes of high-quality training data. The work introduces Skywork-SWE, a dataset of 10,169 real-world Python task instances, and fine-tunes Skywork-SWE-32B, which achieves 38.0% pass@1 on SWE-bench Verified, improving to 47.0% with test-time scaling.
Skywork UniPic introduces a unified autoregressive model, leveraging a 1.5 billion parameter backbone, to seamlessly integrate image understanding, text-to-image generation, and image editing. The model achieves highly competitive performance across diverse multimodal benchmarks while demonstrating exceptional parameter efficiency, enabling deployment on commodity hardware with under 15 GB of GPU memory.
We introduce Skywork R1V, a multimodal reasoning model extending the an
R1-series Large language models (LLM) to visual modalities via an efficient
multimodal transfer method. Leveraging a lightweight visual projector, Skywork
R1V facilitates seamless multimodal adaptation without necessitating retraining
of either the foundational language model or the vision encoder. To strengthen
visual-text alignment, we propose a hybrid optimization strategy that combines
Iterative Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with Group Relative Policy Optimization
(GRPO), significantly enhancing cross-modal integration efficiency.
Additionally, we introduce an adaptive-length Chain-of-Thought distillation
approach for reasoning data generation. This approach dynamically optimizes
reasoning chain lengths, thereby enhancing inference efficiency and preventing
excessive reasoning overthinking. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that
Skywork R1V, with only 38B parameters, delivers competitive performance,
achieving a score of 69.0 on the MMMU benchmark and 67.5 on MathVista.
Meanwhile, it maintains robust textual reasoning performance, evidenced by
impressive scores of 72.0 on AIME and 94.0 on MATH500. The Skywork R1V model
weights have been publicly released to promote openness and reproducibility.
Q* introduces a deliberative planning framework that enhances large language models' multi-step reasoning by integrating a learned Q-value model as a plug-and-play heuristic. This approach guides LLM generation through an A*-like search, significantly improving accuracy on complex math and code generation tasks without requiring fine-tuning of the base LLM.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.