Tottori University
25 Jul 2025
Accurately calculating band gaps for given crystal structures is highly desirable. However, conventional first-principles calculations based on density functional theory (DFT) within the local density approximation (LDA) fail to predict band gaps accurately. To address this issue, the quasi-particle self-consistent GW (QSGW) method is often employed as it is one of the most reliable theoretical approaches for predicting band gaps. Despite its accuracy, QSGW requires significant computational resources. To overcome this limitation, we propose combining QSGW with machine learning. In this study, we applied QSGW to 1,516 materials from the Materials Project [this https URL] and used machine learning to predict QSGW band gaps as a function of the partial density of states (PDOS) in LDA. Our results demonstrate that the proposed model significantly outperforms linear regression approaches with linearly-independent descriptor generation [this https URL]. This model is a prototype for predicting material properties based on PDOS.
The main form of freeway traffic congestion is the familiar stop-and-go wave,
characterized by wide moving jams that propagate indefinitely upstream provided
enough traffic demand. They cause severe, long-lasting adverse effects, such as
reduced traffic efficiency, increased driving risks, and higher vehicle
emissions. This underscores the crucial importance of artificial intervention
in the propagation of stop-and-go waves. Over the past two decades, two
prominent strategies for stop-and-go wave suppression have emerged: variable
speed limit (VSL) and jam-absorption driving (JAD). Although they share similar
research motivations, objectives, and theoretical foundations, the development
of these strategies has remained relatively disconnected. To synthesize
fragmented advances and drive the field forward, this paper first provides a
comprehensive review of the achievements in the stop-and-go wave
suppression-oriented VSL and JAD, respectively. It then focuses on bridging the
two areas and identifying research opportunities from the following
perspectives: fundamental diagrams, secondary waves, generalizability, traffic
state estimation and prediction, robustness to randomness, scenarios for
strategy validation, and field tests and practical deployment. We expect that
through this review, one area can effectively address its limitations by
identifying and leveraging the strengths of the other, thus promoting the
overall research goal of freeway stop-and-go wave suppression.
The tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a crucial role in cancer progression and treatment response, yet current methods for its comprehensive analysis in H&E-stained tissue slides face significant limitations in the diversity of tissue cell types and accuracy. Here, we present PAGET (Pathological image segmentation via AGgrEgated Teachers), a new knowledge distillation approach that integrates multiple segmentation models while considering the hierarchical nature of cell types in the TME. By leveraging a unique dataset created through immunohistochemical restaining techniques and existing segmentation models, PAGET enables simultaneous identification and classification of 14 key TME components. We demonstrate PAGET's ability to perform rapid, comprehensive TME segmentation across various tissue types and medical institutions, advancing the quantitative analysis of tumor microenvironments. This method represents a significant step forward in enhancing our understanding of cancer biology and supporting precise clinical decision-making from large-scale histopathology images.
We show that, in two-dimensional Euclidean quantum gravity without matter fields, the Schwinger-Dyson equations derived within the Hamiltonian framework of non-critical string field theory can be reformulated in terms of the Chekhov-Eynard-Orantin topological recursion, and we explicitly compute the associated low-order amplitudes. In particular, we establish this reformulation for two discrete models -- the basic type and the strip type -- as well as for the continuum limit of dynamical triangulations.
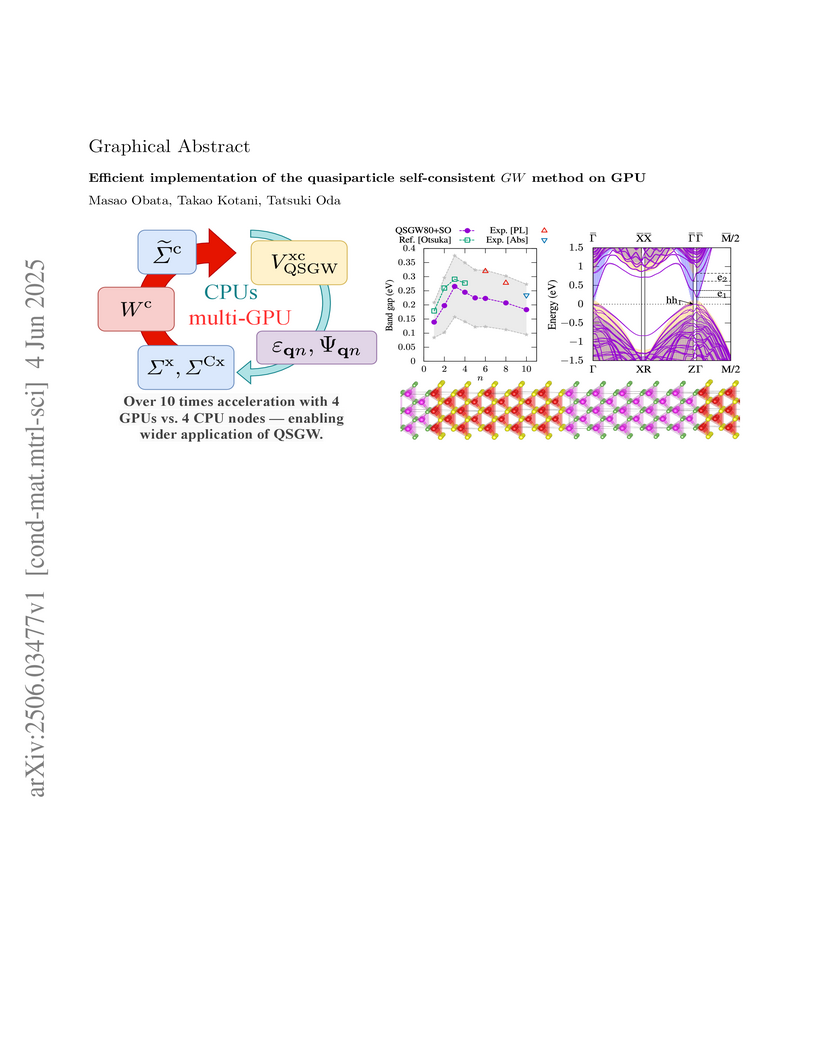
We have developed a multi-GPU version of the quasiparticle self-consistent
GW (QSGW), a cutting-edge method for describing electronic excitations in a
first-principles approach. While the QSGW calculation algorithm is inherently
well-suited for GPU computation due to its reliance on large-scale tensor
operations, achieving a maintainable and extensible implementation is not
straightforward. Addressing this, we have developed a GPU version within the
\texttt{ecalj} package, utilizing module-based programming style in modern
Fortran. This design facilitates future development and code sustainability.
Following the summary of the QSGW formalism, we present our GPU implementation
approach and the results of benchmark calculations for two types of systems to
demonstrate the capability of our GPU-supported QSGW calculations.
30 Jun 2014
For a shell model of the fully developed turbulence and the incompressible
Navier-Stokes equations in the Fourier space, when a Gaussian white noise is
artificially added to the equation of each mode, an expression of the mean
linear response function in terms of the velocity correlation functions is
derived by applying the method developed for nonequilibrium Langevin systems
[Harada and Sasa, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 130602 (2005)]. We verify numerically
for the shell model case that the derived expression of the response function,
as the noise tends to zero, converges to the response function of the noiseless
shell model.
23 Jul 2016
We have investigated the 6Li(gamma,d) reaction theoretically for the
formation of the eta'(958) mesic nucleus close to the recoilless kinematics. We
have developed the theoretical formula and reported the quantitative results of
the formation spectra for various cases in this article. We have found that the
formation cross sections are reduced by the effects of the fragile deuteron
form factor.
Mathematical model for hit phenomena presented by A Ishii et al in 2012 has been extended to analyze and predict a lot of hit subject using social network system. The equation for each individual consumers is assumed and the equation of social response to each hit subject is derived as stochastic process of statistical physics. The advertisement effect is included as external force and the communication effects are included as two-body and three-body interaction. The applications of this model are demonstrated for analyzing population of weekly TV drama. Including both the realtime view data and the playback view data, we found that the indirect communication correlate strongly to the TV viewing rate data for recent Japanese 20 TV drama.
19 Apr 2024
Recent research has developed the Ising model from physics, especially statistical mechanics, and it plays an important role in quantum computing, especially quantum annealing and quantum Monte Carlo methods. The model has also been used in opinion dynamics as a powerful tool for simulating social interactions and opinion formation processes. Individual opinions and preferences correspond to spin states, and social pressure and communication dynamics are modeled through interactions between spins. Quantum computing makes it possible to efficiently simulate these interactions and analyze more complex social this http URL research has incorporated concepts from quantum information theory such as Graph State, Stabilizer State, and Surface Code (or Toric Code) into models of opinion dynamics. The incorporation of these concepts allows for a more detailed analysis of the process of opinion formation and the dynamics of social networks. The concepts lie at the intersection of graph theory and quantum theory, and the use of Graph State in opinion dynamics can represent the interdependence of opinions and networks of influence among individuals. It helps to represent the local stability of opinions and the mechanisms for correcting misunderstandings within a social network. It allows us to understand how individual opinions are subject to social pressures and cultural influences and how they change over this http URL these quantum theory concepts into opinion dynamics allows for a deeper understanding of social interactions and opinion formation processes. Moreover, these concepts can provide new insights not only in the social sciences, but also in fields as diverse as political science, economics, marketing, and urban planning.
20 Aug 2012
We present ab initio two-dimensional extended Hubbard-type multiband models
for EtMe_3Sb[Pd(dmit)_2]_2 and \kappa-(BEDT-TTF)_2Cu(NCS)_2, after a
downfolding scheme based on the constrained random phase approximation (cRPA)
and maximally-localized Wannier orbitals, together with the dimensional
downfolding. In the Pd(dmit)_2 salt, the antibonding state of the highest
occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the bonding/antibonding states of the
lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) are considered as the orbital
degrees of freedom, while, in the \kappa-BEDT-TTF salt, the
HOMO-antibonding/bonding states are considered. Accordingly, a three-band model
for the Pd(dmit)_2 salt and a two-band model for the \kappa-(BEDT-TTF) salt are
derived. We derive single band models for the HOMO-antibonding state for both
of the compounds as well.
We calculate transverse spin susceptibility in the linear response method
based on the ground states determined in the quasi-particle self-consistent
GW (QSGW) method. Then we extract spin wave (SW) dispersions from the
susceptibility. We treat bcc Fe, hcp Co, fcc Ni, and B2-type FeCo. Because of
the better description of the independent-particle picture in QSGW, calculated
spin stiffness constants for Fe, Co, and Ni give much better agreement with
experiments in QSGW than that in the local density approximation (LDA), where
the stiffness for Ni in LDA is two times bigger than the experiment. For Co,
both acoustic and optical branches of SWs agree with the experiment. As for
FeCo, we have some discrrepancy between the spin stiffness in QSGW and that in
the experiment. We may need further theoretical and experimental investigations
on the discrepancy.
18 Jan 2016
We have investigated the 6Li(gamma, d) reaction theoretically for the
formation of the eta'(958) mesic nucleus. We have reported the numerical
results in this article.
We have applied the model-mapped RPA [H. Sakakibara et al., J. Phys. Soc.
Jpn. 86, 044714 (2017)] to the cuprate superconductors La2CuO4 and HgBa2CuO4,
resulting two-orbital Hubbard models. All the model parameters are determined
based on first-principles calculations. For the model Hamiltonians, we perform
fluctuation exchange calculation. Results explain relative height of Tc
observed in experiment for La2CuO4 and HgBa2CuO4. In addition, we give some
analyses for the interaction terms in the model, especially comparisons with
those of the constrained RPA.
15 Apr 2018
We observed the atomic 1s and 2p states of π− bound to ${}^{121}{\rm
Sn}$ nuclei as distinct peak structures in the missing mass spectra of the
122Sn(d,3He) nuclear reaction. A very intense deuteron
beam and a spectrometer with a large angular acceptance let us achieve
potential of discovery, which includes capability of determining the
angle-dependent cross sections with high statistics. The 2p state in a Sn
nucleus was observed for the first time. The binding energies and widths of the
pionic states are determined and found to be consistent with previous
experimental results of other Sn isotopes. The spectrum is measured at finite
reaction angles for the first time. The formation cross sections at the
reaction angles between 0 and 2∘ are determined. The observed
reaction-angle dependence of each state is reproduced by theoretical
calculations. However, the quantitative comparison with our high-precision data
reveals a significant discrepancy between the measured and calculated formation
cross sections of the pionic 1s state.
09 Nov 2016
Niigata UniversityKEK Beihang University
Beihang University Osaka University
Osaka University the University of Tokyo
the University of Tokyo Kyoto University
Kyoto University RIKEN
RIKEN University of GroningenTokyo Metropolitan UniversitySaint Mary’s UniversityTottori UniversityUniversidade de Santiago de CompostelaGSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbHComenius University BratislavaNara Women’s UniversityUniversität GiessenStefan Meyer Institut für Subatomare Physik
University of GroningenTokyo Metropolitan UniversitySaint Mary’s UniversityTottori UniversityUniversidade de Santiago de CompostelaGSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbHComenius University BratislavaNara Women’s UniversityUniversität GiessenStefan Meyer Institut für Subatomare Physik
 Beihang University
Beihang University Osaka University
Osaka University the University of Tokyo
the University of Tokyo Kyoto University
Kyoto University RIKEN
RIKEN University of GroningenTokyo Metropolitan UniversitySaint Mary’s UniversityTottori UniversityUniversidade de Santiago de CompostelaGSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbHComenius University BratislavaNara Women’s UniversityUniversität GiessenStefan Meyer Institut für Subatomare Physik
University of GroningenTokyo Metropolitan UniversitySaint Mary’s UniversityTottori UniversityUniversidade de Santiago de CompostelaGSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbHComenius University BratislavaNara Women’s UniversityUniversität GiessenStefan Meyer Institut für Subatomare PhysikExcitation spectra of 11C were measured in the 12C(p,d) reaction
near the η′ emission threshold. A proton beam extracted from the
synchrotron SIS-18 at GSI with an incident energy of 2.5 GeV impinged on a
carbon target. The momenta of deuterons emitted at 0 degrees were precisely
measured with the fragment separator FRS operated as a spectrometer. In
contrast to theoretical predictions on the possible existence of deeply bound
η′ mesic states in carbon nuclei, no distinct structures were observed
associated with the formation of bound states. The spectra were analyzed to set
stringent constraints on the formation cross section and on the hitherto
barely-known η′-nucleus interaction.
Theoretical approach to investigate human-human interaction in society performed using a many-body theory including human-human interaction. The advertisement is treated as an external force. The word of mouth (WOM) effect is included as a two-body interaction between humans. The rumor effect is included as a three-body interaction between humans. The parameters to define the strength of human interactions are assumed to be constant values. The calculated result explained well the two local events "Mizuki-Shigeru Road in Sakaiminato" and "the sculpture festival at Tottori" in Japan.
The η mesic nucleus is considered to be one of the interesting exotic
many body systems and has been studied since 1980's theoretically and
experimentally. Recently, the formation of the η mesic nucleus in the
fusion reactions of the light nuclei such as $d + d \rightarrow (\eta + \alpha)
\rightarrow X$ has been proposed and the experiments have been performed by
WASA-at-COSY. We develop a theoretical model to evaluate the formation rate of
the η mesic nucleus in the fusion reactions and show the calculated
results. We find that the η bound states could be observed in the
reactions in cases with the strong attractive and small absorptive
η-nucleus interactions. We compare our results with existing data of the
d+d→η+α and the $d + d \rightarrow {^3 \rm He} + N +
\pi$ reactions. We find that the analyses by our theoretical model with the
existing data can provide new information on the η-nucleus interaction.
18 Apr 2018
 Tohoku University
Tohoku University Michigan State University
Michigan State University Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University Beijing Normal University
Beijing Normal University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Texas A&M University
Texas A&M University McGill UniversityINFN LNSGuangxi Normal UniversityYukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto UniversityJapan Atomic Energy AgencyHuzhou UniversityTottori UniversityGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungChina Institute of Atomic EnergyAkita International UniversityGoethe-UniversityUniversity of MunichVariable Energy Cyclotron CentreTexas A&M University-CommerceIFIN-HHGuangxi Key Laboratory Breeding Base of Nuclear Physics and TechnologyBeijing Radiation CenterFrankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies, Johann Wolfgang Goethe University
McGill UniversityINFN LNSGuangxi Normal UniversityYukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto UniversityJapan Atomic Energy AgencyHuzhou UniversityTottori UniversityGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungChina Institute of Atomic EnergyAkita International UniversityGoethe-UniversityUniversity of MunichVariable Energy Cyclotron CentreTexas A&M University-CommerceIFIN-HHGuangxi Key Laboratory Breeding Base of Nuclear Physics and TechnologyBeijing Radiation CenterFrankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies, Johann Wolfgang Goethe UniversitySimulations by transport codes are indispensable to extract valuable physics
information from heavy ion collisions. In order to understand the origins of
discrepancies between different widely used transport codes, we compare 15 such
codes under controlled conditions of a system confined to a box with periodic
boundary, initialized with Fermi-Dirac distributions at saturation density and
temperatures of either 0 or 5 MeV. In such calculations, one is able to check
separately the different ingredients of a transport code. In this second
publication of the code evaluation project, we only consider the two-body
collision term, i.e. we perform cascade calculations. When the Pauli blocking
is artificially suppressed, the collision rates are found to be consistent for
most codes (to within 1% or better) with analytical results, or completely
controlled results of a basic cascade code after eliminating the correlations
within the same pair of colliding particles. In calculations with active Pauli
blocking, the blocking probability was found to deviate from the expected
reference values. The reason is found in substantial phase-space fluctuations
and smearing tied to numerical algorithms and model assumptions in the
representation of phase space. This results in the reduction of the blocking
probability in most transport codes, so that the simulated system gradually
evolves away from the Fermi-Dirac towards a Boltzmann distribution. As a result
of this investigation, we are able to make judgements about the most effective
strategies in transport simulations for determining the collision probabilities
and the Pauli blocking. Investigation in a similar vein of other ingredients in
transport calculations, like the mean field propagation or the production of
nucleon resonances and mesons, will be discussed in the future publications.
29 Mar 2018
A consistent description of the dd→
4\mboxHeη and dd→
(4Heη)bound→X cross sections was recently proposed
with a broad range of real (V0) and imaginary (W0), η-4He optical
potential parameters leading to a good agreement with the d d -> 4He eta data.
Here we compare the predictions of the model below the η production
threshold, with the WASA-at-COSY excitation functions for the dd -> 3He N pi
reactions to put stronger constraints on (V0, W0). The allowed parameter space
(with |V_0| < \sim 60 MeV and |W_0| < \sim 7 MeV estimated at 90% CL ) excludes
most optical model predictions of eta-4He nuclei except for some loosely bound
narrow states.
27 Sep 2019
South China University of Technology Tohoku University
Tohoku University Michigan State University
Michigan State University Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University Beijing Normal University
Beijing Normal University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Kyoto University
Kyoto University Texas A&M UniversityINFN LNS
Texas A&M UniversityINFN LNS Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryJapan Atomic Energy AgencyFrankfurt Institute for Advanced StudiesHuzhou UniversityRIKEN Nishina CenterTottori UniversityGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungChina Institute of Atomic EnergyAkita International UniversityGoethe-UniversityUniversity of MunichVariable Energy Cyclotron CentreTexas A&M University-CommerceIFIN-HH
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryJapan Atomic Energy AgencyFrankfurt Institute for Advanced StudiesHuzhou UniversityRIKEN Nishina CenterTottori UniversityGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungChina Institute of Atomic EnergyAkita International UniversityGoethe-UniversityUniversity of MunichVariable Energy Cyclotron CentreTexas A&M University-CommerceIFIN-HH
 Tohoku University
Tohoku University Michigan State University
Michigan State University Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University Beijing Normal University
Beijing Normal University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Kyoto University
Kyoto University Texas A&M UniversityINFN LNS
Texas A&M UniversityINFN LNS Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryJapan Atomic Energy AgencyFrankfurt Institute for Advanced StudiesHuzhou UniversityRIKEN Nishina CenterTottori UniversityGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungChina Institute of Atomic EnergyAkita International UniversityGoethe-UniversityUniversity of MunichVariable Energy Cyclotron CentreTexas A&M University-CommerceIFIN-HH
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryJapan Atomic Energy AgencyFrankfurt Institute for Advanced StudiesHuzhou UniversityRIKEN Nishina CenterTottori UniversityGSI Helmholtzzentrum für SchwerionenforschungChina Institute of Atomic EnergyAkita International UniversityGoethe-UniversityUniversity of MunichVariable Energy Cyclotron CentreTexas A&M University-CommerceIFIN-HHWe compare ten transport codes for a system confined in a box, aiming at
improved handling of the production of Δ resonances and pions, which is
indispensable for constraining high-density symmetry energy from observables
such as the π−/π+ yield ratio in heavy-ion collisions. The system in a
box is initialized with nucleons at saturation density and at 60 MeV
temperature. The reactions NN↔NΔ and
Δ↔Nπ are implemented, but the Pauli blocking and the
mean-field potential are deactivated in the present comparison. Results are
compared to those from the two reference cases of a chemically equilibrated
ideal gas mixture and of the rate equation. In the results of the numbers of
Δ and π, deviations from the reference values are observed in many
codes, and they depend significantly on the size of the time step. These
deviations are tied to different ways in ordering the sequence of collisions
and decays, that take place in the same time step. Better agreements are seen
in the reaction rates and the number ratios among the isospin species of
Δ and π. These are, however, affected by the correlations, which are
absent in the Boltzmann equation, but are induced by the way particle
scatterings are treated in transport calculations. The uncertainty in the
transport-code predictions of the π−/π+ ratio for the system
initialized at n/p = 1.5, after letting the existing Δ resonances decay,
is found to be within a few percent, which is sufficiently small so that it
does not strongly impact constraining the high-density symmetry energy from
heavy-ion collisions. Most of the sources of uncertainties have been
understood, and individual codes may be further improved. This investigation
will be extended in the future to heavy-ion collisions to ensure the problems
identified here remain under control.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.