general-economics
08 Dec 2025
Researchers from Harvard University and Perplexity conducted a large-scale field study on the real-world adoption and usage of general-purpose AI agents, leveraging hundreds of millions of user interactions with Perplexity's Comet AI-powered browser and its integrated Comet Assistant. The study provides foundational evidence on who uses these agents, their usage intensity, and a detailed breakdown of use cases via a novel hierarchical taxonomy.
08 Dec 2025
A quantitative reassessment of rice price dynamics in post-war Taiwan during the 1945–1947 famine reveals the critical influence of government policies, particularly currency exchange reforms, in driving hyperinflation and exacerbating food shortages. This study constructs and analyzes the first high-frequency rice price panel for the period, demonstrating significant exponential growth patterns tied to policy decisions.
This paper from the Knowledge Lab at the University of Chicago models how political elites might strategically shape public opinion when artificial intelligence significantly reduces the cost of persuasion. It finds that a single elite has incentives to polarize society for future policy flexibility, while competing elites create a nuanced dynamic between polarization and locking in public opinion to deter rivals, making the overall effect on polarization context-dependent.
01 Dec 2025
This paper investigates both short and long-run interaction between BIST-100 index and CDS prices over January 2008 to May 2015 using ARDL technique. The paper documents several findings. First, ARDL analysis shows that 1 TL increase in CDS shrinks BIST-100 index by 22.5 TL in short-run and 85.5 TL in long-run. Second, 1000 TL increase in BIST index price causes 25 TL and 44 TL reducation in Turkey's CDS prices in short- and long-run respectively. Third, a percentage increase in interest rate shrinks BIST index by 359 TL and a percentage increase in inflation rate scales CDS prices up to 13.34 TL both in long-run. In case of short-run, these impacts are limited with 231 TL and 5.73 TL respectively. Fourth, a kurush increase in TL/USD exchange rate leads 24.5 TL (short-run) and 78 TL (long-run) reductions in BIST, while it augments CDS prices by 2.5 TL (short-run) and 3 TL (long-run) respectively. Fifth, each negative political events decreases BIST by 237 TL in short-run and 538 TL in long-run, while it increases CDS prices by 33 TL in short-run and 89 TL in long-run. These findings imply the highly dollar indebted capital structure of Turkish firms, and overly sensitivity of financial markets to the uncertainties in political sphere. Finally, the paper provides evidence for that BIST and CDS with control variables drift too far apart, and converge to a long-run equilibrium at a moderate monthly speed.
27 Nov 2025
We investigate the extent to which groups with elevated mortality rates ex ante might opt out of guaranteed national pensions in favour of demographically aligned plans, which we label equitable longevity risk sharing (ELRiS) pools, even if this involves accepting some idiosyncratic risk. Technically, this paper develops a stochastic model of retirement income within an ELRiS structure that is calibrated to equate the discounted expected utility of a guaranteed national pension. The practical motivation for developing this alternative is that working members of First Nations peoples of Canada: (1) experience much higher mortality rates than average over their entire life cycle, and (2) some are actually allowed by current legislation to opt out of the Canada Pension Plan (CPP). We then demonstrate that under reasonable economic preferences and parameters, a sub-group with a 10-year life expectancy gap relative to the population could attain equivalent lifetime utility by contributing a mere two-thirds to the plan, even if they were pooled with only 30 members. For a longevity gap of 20 years, such as between an Indigenous male versus a non-Indigenous female, the contribution rate falls to less than a third. The difference between the statutory and mandatory contribution rates to a guaranteed national pension and those needed within these self-sustaining pools is an implicit subsidy from Indigenous to non-Indigenous. From a policy perspective, this paper aspires to jump-start a conversation that sparks a change in a status quo, which is obviously unfair and inequitable.
We curate the DeXposure dataset, the first large-scale dataset for inter-protocol credit exposure in decentralized financial networks, covering global markets of 43.7 million entries across 4.3 thousand protocols, 602 blockchains, and 24.3 thousand tokens, from 2020 to 2025. A new measure, value-linked credit exposure between protocols, is defined as the inferred financial dependency relationships derived from changes in Total Value Locked (TVL). We develop a token-to-protocol model using DefiLlama metadata to infer inter-protocol credit exposure from the token's stock dynamics, as reported by the protocols. Based on the curated dataset, we develop three benchmarks for machine learning research with financial applications: (1) graph clustering for global network measurement, tracking the structural evolution of credit exposure networks, (2) vector autoregression for sector-level credit exposure dynamics during major shocks (Terra and FTX), and (3) temporal graph neural networks for dynamic link prediction on temporal graphs. From the analysis, we observe (1) a rapid growth of network volume, (2) a trend of concentration to key protocols, (3) a decline of network density (the ratio of actual connections to possible connections), and (4) distinct shock propagation across sectors, such as lending platforms, trading exchanges, and asset management protocols. The DeXposure dataset and code have been released publicly. We envision they will help with research and practice in machine learning as well as financial risk monitoring, policy analysis, DeFi market modeling, amongst others. The dataset also contributes to machine learning research by offering benchmarks for graph clustering, vector autoregression, and temporal graph analysis.
Understanding household behaviour is essential for modelling macroeconomic dynamics and designing effective policy. While heterogeneous agent models offer a more realistic alternative to representative agent frameworks, their implementation poses significant computational challenges, particularly in continuous time. The Aiyagari-Bewley-Huggett (ABH) framework, recast as a system of partial differential equations, typically relies on grid-based solvers that suffer from the curse of dimensionality, high computational cost, and numerical inaccuracies. This paper introduces the ABH-PINN solver, an approach based on Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs), which embeds the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman and Kolmogorov Forward equations directly into the neural network training objective. By replacing grid-based approximation with mesh-free, differentiable function learning, the ABH-PINN solver benefits from the advantages of PINNs of improved scalability, smoother solutions, and computational efficiency. Preliminary results show that the PINN-based approach is able to obtain economically valid results matching the established finite-difference solvers.
19 Nov 2025
Crypto enthusiasts claim that buying and holding crypto assets yields high returns, often citing Bitcoin's past performance to promote other tokens and fuel fear of missing out. However, understanding the real risk-return trade-off and what factors affect future crypto returns is crucial as crypto becomes increasingly accessible to retail investors through major brokerages. We examine the HODL strategy through two independent analyses. First, we implement 480 million Monte Carlo simulations across 378 non-stablecoin crypto assets, net of trading fees and the opportunity cost of 1-month Treasury bills, and find strong evidence of survivorship bias and extreme downside concentration. At the 2-3 year horizon, the median excess return is -28.4 percent, the 1 percent conditional value at risk indicates that tail scenarios wipe out principal after all costs, and only the top quartile achieves very large gains, with a mean excess return of 1,326.7 percent. These results challenge the HODL narrative: across a broad set of assets, simple buy-and-hold loads extreme downside risk onto most investors, and the miracles mostly belong to the luckiest quarter. Second, using a Bayesian multi-horizon local projection framework, we find that endogenous predictors based on realized risk-return metrics have economically negligible and unstable effects, while macro-finance factors, especially the 24-week exponential moving average of the Fear and Greed Index, display persistent long-horizon impacts and high cross-basket stability. Where significant, a one-standard-deviation sentiment shock reduces forward top-quartile mean excess returns by 15-22 percentage points and median returns by 6-10 percentage points over 1-3 year horizons, suggesting that macro-sentiment conditions, rather than realized return histories, are the dominant indicators for future outcomes.
08 Dec 2025
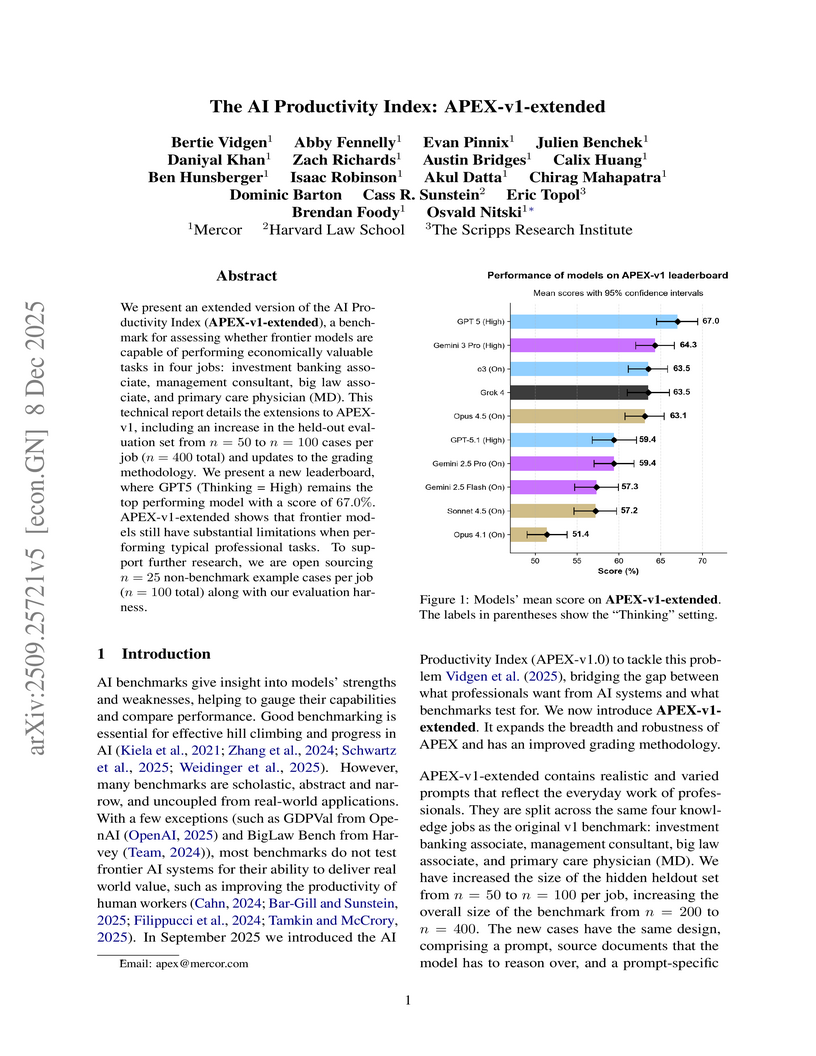
We present an extended version of the AI Productivity Index (APEX-v1-extended), a benchmark for assessing whether frontier models are capable of performing economically valuable tasks in four jobs: investment banking associate, management consultant, big law associate, and primary care physician (MD). This technical report details the extensions to APEX-v1, including an increase in the held-out evaluation set from n = 50 to n = 100 cases per job (n = 400 total) and updates to the grading methodology. We present a new leaderboard, where GPT5 (Thinking = High) remains the top performing model with a score of 67.0%. APEX-v1-extended shows that frontier models still have substantial limitations when performing typical professional tasks. To support further research, we are open sourcing n = 25 non-benchmark example cases per role (n = 100 total) along with our evaluation harness.
The study of emergent behaviors in large language model (LLM)-driven multi-agent systems is a critical research challenge, yet progress is limited by a lack of principled methodologies for controlled experimentation. To address this, we introduce Shachi, a formal methodology and modular framework that decomposes an agent's policy into core cognitive components: Configuration for intrinsic traits, Memory for contextual persistence, and Tools for expanded capabilities, all orchestrated by an LLM reasoning engine. This principled architecture moves beyond brittle, ad-hoc agent designs and enables the systematic analysis of how specific architectural choices influence collective behavior. We validate our methodology on a comprehensive 10-task benchmark and demonstrate its power through novel scientific inquiries. Critically, we establish the external validity of our approach by modeling a real-world U.S. tariff shock, showing that agent behaviors align with observed market reactions only when their cognitive architecture is appropriately configured with memory and tools. Our work provides a rigorous, open-source foundation for building and evaluating LLM agents, aimed at fostering more cumulative and scientifically grounded research.
We analyze 15,097 blocks proposed for inclusion in Ethereum's blockchain over an 8-minute window on December 3, 2024, during which 38 blocks were added to the chain. We classify transactions as exclusive -- present only in blocks from a single builder -- or private -- absent from the public mempool but included in blocks from multiple builders. We find that exclusive transactions account for 84% of the total fees paid by transactions in winning blocks. Furthermore, we show that exclusivity cannot be fully explained by exclusive relationships between senders and builders: about 7% of all exclusive transactions included on-chain, by value, come from senders who route exclusively to a single builder. Analyzing transaction logs shows that some exclusive transactions are duplicates or variations of the same strategy, but even accounting for that, the share of the total fees paid by transactions in winning blocks is at least 77.2%. Taken together, our findings highlight that exclusive transactions are the dominant source of builder revenues.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transitioned from a futuristic concept reserved for large corporations to a present-day, accessible, and essential growth lever for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs). For entrepreneurs and business leaders, strategic AI adoption is no longer an option but an imperative for competitiveness, operational efficiency, and long-term survival. This report provides a comprehensive framework for SME leaders to navigate this technological shift, offering the foundational knowledge, business case, practical applications, and strategic guidance necessary to harness the power of AI. The quantitative evidence supporting AI adoption is compelling; 91% of SMEs using AI report that it directly boosts their revenue. Beyond top-line growth, AI drives profound operational efficiencies, with studies showing it can reduce operational costs by up to 30% and save businesses more than 20 hours of valuable time each month. This transformation is occurring within the context of a seismic economic shift; the global AI market is projected to surge from 233.46Billionin2024toanastonishing1.77 Trillion by 2032. This paper demystifies the core concepts of AI, presents a business case based on market data, details practical applications, and lays out a phased, actionable adoption strategy.
Gillian K. Hadfield and Andrew Koh surveyed the emerging landscape of autonomous AI agents, arguing that economists must shift from viewing AI as a mere tool to recognizing its role as a distinct economic actor. Their work outlines critical, overlooked research questions concerning AI agents' impact on markets, organizations, and legal institutions, aiming to stimulate proactive economic inquiry into designing the future AI economy.
04 Aug 2025
Stablecoins have become a foundational component of the digital asset ecosystem, with their market capitalization exceeding 230 billion USD as of May 2025. As fiat-referenced and programmable assets, stablecoins provide low-latency, globally interoperable infrastructure for payments, decentralized finance, DeFi, and tokenized commerce. Their accelerated adoption has prompted extensive regulatory engagement, exemplified by the European Union's Markets in Crypto-assets Regulation, MiCA, the US Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for US Stablecoins Act, GENIUS Act, and Hong Kong's Stablecoins Bill. Despite this momentum, academic research remains fragmented across economics, law, and computer science, lacking a unified framework for design, evaluation, and application. This study addresses that gap through a multi-method research design. First, it synthesizes cross-disciplinary literature to construct a taxonomy of stablecoin systems based on custodial structure, stabilization mechanism, and governance. Second, it develops a performance evaluation framework tailored to diverse stakeholder needs, supported by an open-source benchmarking pipeline to ensure transparency and reproducibility. Third, a case study on Real World Asset tokenization illustrates how stablecoins operate as programmable monetary infrastructure in cross-border digital systems. By integrating conceptual theory with empirical tools, the paper contributes: a unified taxonomy for stablecoin design; a stakeholder-oriented performance evaluation framework; an empirical case linking stablecoins to sectoral transformation; and reproducible methods and datasets to inform future research. These contributions support the development of trusted, inclusive, and transparent digital monetary infrastructure.
15 Jul 2025
This study develops a capacity expansion model for a fully decarbonized European electricity system using an Adaptive Robust Optimization (ARO) framework. The model endogenously identifies the worst regional Dunkelflaute events, prolonged periods of low wind and solar availability, and incorporates multiple extreme weather realizations within a single optimization run. Results show that system costs rise nonlinearly with the geographic extent of these events: a single worst-case regional disruption increases costs by 9%, but broader disruptions across multiple regions lead to much sharper increases, up to 51%. As Dunkelflaute conditions extend across most of Europe, additional cost impacts level off, with a maximum increase of 71%. The optimal technology mix evolves with the severity of weather stress: while renewables, batteries, and interregional transmission are sufficient to manage localized events, large-scale disruptions require long-term hydrogen storage and load shedding to maintain system resilience. Central European regions, especially Germany and France, emerge as systemic bottlenecks, while peripheral regions bear the cost of compensatory overbuilding. These findings underscore the need for a coordinated European policy strategy that goes beyond national planning to support cross-border infrastructure investment, scale up flexible technologies such as long-duration storage, and promote a geographically balanced deployment of renewables to mitigate systemic risks associated with Dunkelflaute events.
17 Oct 2025
An analysis of real-world interactions with Microsoft Bing Copilot provides an empirical understanding of generative AI's applicability to occupations. The study reveals AI's concentration in knowledge-based activities, offering validation for existing predictive models of its labor market impact.
We derive the first closed-form condition under which artificial intelligence (AI) capital profits could sustainably finance a universal basic income (UBI) without additional taxes or new job creation. In a Solow-Zeira economy characterized by a continuum of automatable tasks, a constant net saving rate s, and task-elasticity \sigma < 1, we analyze how the AI capability threshold--defined as the productivity level of AI relative to pre-AI automation--varies under different economic scenarios. At present economic parameters, we find that AI systems must achieve only approximately 5-6 times existing automation productivity to finance an 11%-of-GDP UBI, in the worst case situation where *no* new jobs or tasks are created.
Our analysis also reveals some specific policy levers: raising public revenue share (e.g. profit taxation) of AI capital from the current 15% to about 33% halves the required AI capability threshold to attain UBI to 3 times existing automotion productivity, but gains diminish beyond 50% public revenue share, especially if regulatory costs increase. Market structure also strongly affects outcomes: monopolistic or concentrated oligopolistic markets reduce the threshold by increasing economic rents, whereas heightened competition significantly raises it.
Overall, these results suggest a couple policy recommendations: maximizing public revenue share up to a point so that operating costs are minimized, and strategically managing market competition can ensure AI's growing capabilities translate into meaningful social benefits within realistic technological progress scenarios.
15 Apr 2025
This research explores the capabilities of large language models as trading agents in simulated financial markets. It demonstrates that LLMs can effectively execute diverse trading strategies and influence market dynamics, exhibiting behaviors such as price convergence and liquidity provision, though with an observed asymmetry in correcting undervaluation versus overvaluation.
14 Apr 2025
Using complete-count register data spanning three generations, we compare
inter- and multigenerational transmission processes across municipalities in
Sweden. We first document spatial patterns in intergenerational (parent-child)
mobility, and study whether those patterns are robust to the choice of mobility
statistic and the quality of the underlying microdata. We then ask whether
there exists similar geographic variation in multigenerational mobility.
Interpreting those patterns through the lens of a latent factor model, we
identify which features of the transmission process vary across places.
09 Apr 2025
We propose a supervised method to detect causal attribution in political
texts, distinguishing between expressions of merit and blame. Analyzing four
million tweets shared by U.S. Congress members from 2012 to 2023, we document a
pronounced shift toward causal attribution following the 2016 presidential
election. The shift reflects changes in rhetorical strategy rather than
compositional variation in the actors or topics of the political debate. Within
causal communication, a trade-off emerges between positive and negative tone,
with power status as the key determinant: government emphasizes merit, while
opposition casts blame. This pattern distinguishes causal from purely affective
communication. Additionally, we find that blame is associated with lower trust
in politicians, perceived government effectiveness, and spreads more virally
than merit.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.