multi-modal-learning
Astra, a collaborative effort from Tsinghua University and Kuaishou Technology, introduces an interactive general world model using an autoregressive denoising framework to generate real-world futures with precise action interactions. The model achieves superior performance in instruction following and visual fidelity across diverse simulation scenarios while efficiently extending a pre-trained video diffusion backbone.
10 Dec 2025
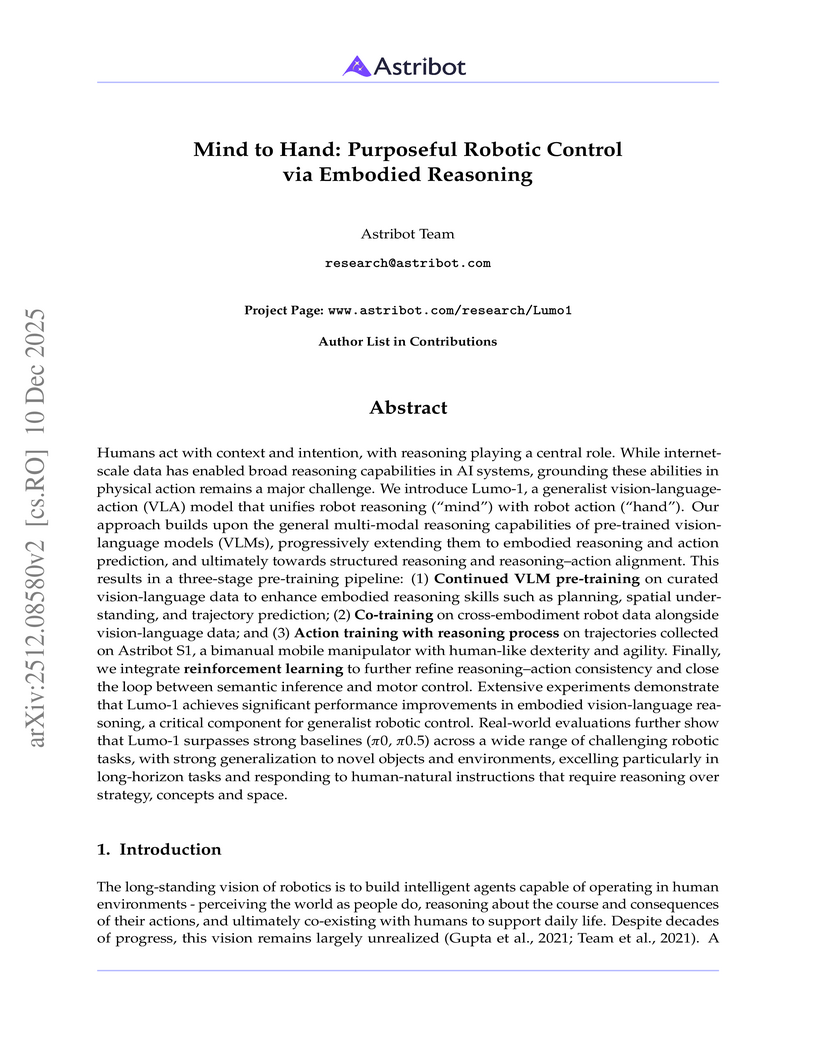
The Astribot Team developed Lumo-1, a Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model that explicitly integrates structured reasoning with physical actions to achieve purposeful robotic control on their Astribot S1 bimanual mobile manipulator. This system exhibits superior generalization to novel objects and instructions, improves reasoning-action consistency through reinforcement learning, and outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in complex, long-horizon, and dexterous tasks.
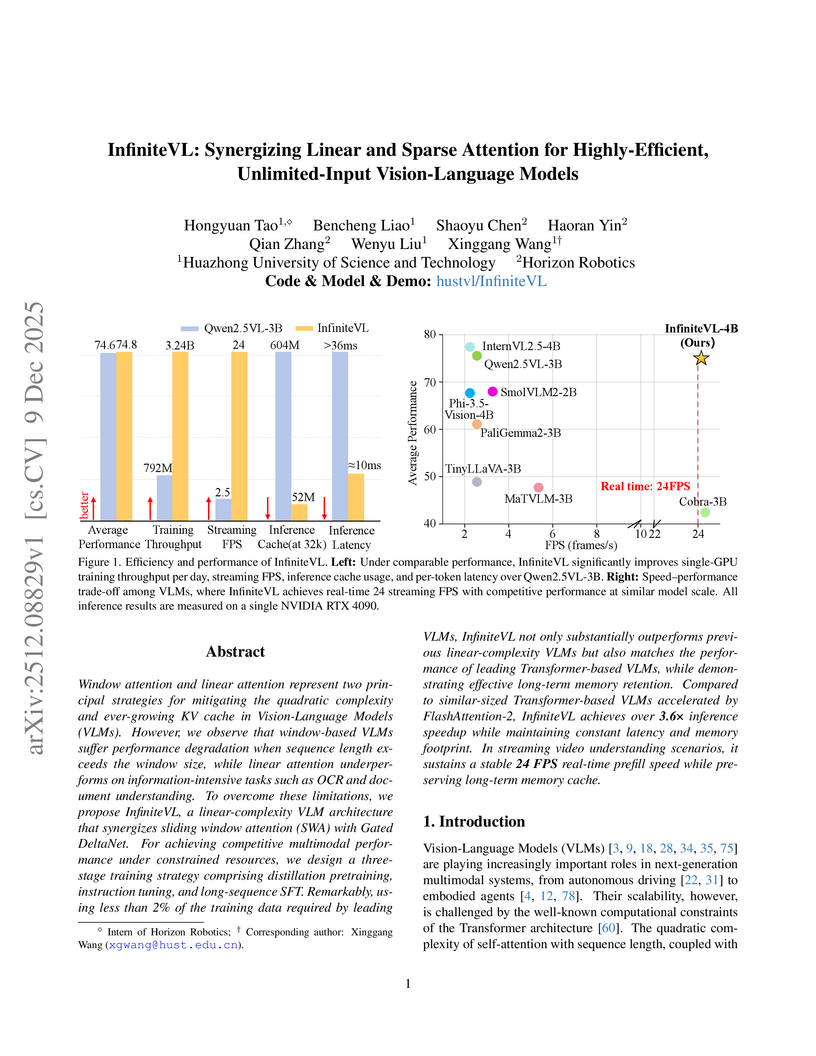
InfiniteVL, a collaboration between Huazhong University of Science and Technology and Horizon Robotics, introduces a hybrid Vision-Language Model that synergizes linear and sparse attention to enable unlimited multimodal input processing with constant latency and memory footprint. The model achieves performance competitive with Transformer-based VLMs on diverse benchmarks, including information-intensive tasks, while demonstrating significant inference speedups and robust real-time streaming capabilities.
Researchers from Microsoft Research Asia, Xi'an Jiaotong University, and Fudan University developed VideoVLA, a robot manipulator that repurposes large pre-trained video generation models. This system jointly predicts future video states and corresponding actions, achieving enhanced generalization capabilities for novel objects and skills in both simulated and real-world environments.
UniUGP presents a unified framework for end-to-end autonomous driving, integrating scene understanding, future video generation, and trajectory planning through a hybrid expert architecture. This approach enhances interpretability with Chain-of-Thought reasoning and demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in challenging long-tail scenarios and multimodal capabilities across various benchmarks.
SAM-Body4D introduces a training-free framework for 4D human body mesh recovery from videos, synergistically combining promptable video object segmentation and image-based human mesh recovery models with an occlusion-aware mask refinement module. The system produces temporally consistent and robust mesh trajectories, effectively handling occlusions and maintaining identity across frames.
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) exhibit substantial cross-modal inconsistency, producing different answers for semantically identical information presented across image, text, and mixed modalities. This problem persists even with perfect Optical Character Recognition (OCR), revealing an inherent reasoning challenge where text inputs generally achieve higher accuracy than image inputs.
07 Dec 2025
Large Language Model (LLM) agents are emerging to transform daily life. However, existing LLM agents primarily follow a reactive paradigm, relying on explicit user instructions to initiate services, which increases both physical and cognitive workload. In this paper, we propose ProAgent, the first end-to-end proactive agent system that harnesses massive sensory contexts and LLM reasoning to deliver proactive assistance. ProAgent first employs a proactive-oriented context extraction approach with on-demand tiered perception to continuously sense the environment and derive hierarchical contexts that incorporate both sensory and persona cues. ProAgent then adopts a context-aware proactive reasoner to map these contexts to user needs and tool calls, providing proactive assistance. We implement ProAgent on Augmented Reality (AR) glasses with an edge server and extensively evaluate it on a real-world testbed, a public dataset, and through a user study. Results show that ProAgent achieves up to 33.4% higher proactive prediction accuracy, 16.8% higher tool-calling F1 score, and notable improvements in user satisfaction over state-of-the-art baselines, marking a significant step toward proactive assistants. A video demonstration of ProAgent is available at this https URL.
Researchers from Meta AI and the University of Copenhagen developed OneStory, a framework for coherent multi-shot video generation that utilizes adaptive memory modules to model long-range cross-shot context. The method consistently outperforms existing baselines, achieving higher inter-shot coherence scores (e.g., 0.5813 average inter-shot coherence in text-to-multi-shot video tasks) and enhanced shot-level quality.
WorldReel develops a unified, feed-forward 4D generator that integrates geometry, motion, and appearance directly into a latent diffusion model, yielding videos with explicit 4D scene representations. The model achieves state-of-the-art photorealism and significantly improves geometric consistency and dynamic range, particularly for complex scenes with moving cameras.
RETAIN, developed at UC Berkeley, introduces a parameter merging strategy for generalist robot policies, interpolating pre-trained and finetuned weights to enable robust adaptation to new tasks. This approach enhances out-of-distribution generalization by approximately 40% on real-world robotic tasks while preserving the policy's existing broad capabilities in low-data scenarios.
Video unified models exhibit strong capabilities in understanding and generation, yet they struggle with reason-informed visual editing even when equipped with powerful internal vision-language models (VLMs). We attribute this gap to two factors: 1) existing datasets are inadequate for training and evaluating reasoning-aware video editing, and 2) an inherent disconnect between the models' reasoning and editing capabilities, which prevents the rich understanding from effectively instructing the editing process. Bridging this gap requires an integrated framework that connects reasoning with visual transformation. To address this gap, we introduce the Reason-Informed Video Editing (RVE) task, which requires reasoning about physical plausibility and causal dynamics during editing. To support systematic evaluation, we construct RVE-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark with two complementary subsets: Reasoning-Informed Video Editing and In-Context Video Generation. These subsets cover diverse reasoning dimensions and real-world editing scenarios. Building upon this foundation, we propose the ReViSE, a Self-Reflective Reasoning (SRF) framework that unifies generation and evaluation within a single architecture. The model's internal VLM provides intrinsic feedback by assessing whether the edited video logically satisfies the given instruction. The differential feedback that refines the generator's reasoning behavior during training. Extensive experiments on RVE-Bench demonstrate that ReViSE significantly enhances editing accuracy and visual fidelity, achieving a 32% improvement of the Overall score in the reasoning-informed video editing subset over state-of-the-art methods.
09 Dec 2025
VALOR, developed at Caltech, presents an annotation-free framework that trains visual reasoners by employing multimodal verifiers to jointly tune an LLM for reasoning and specialized vision tools for visual grounding. This approach achieves superior performance on various visual reasoning benchmarks, including a 6.5% average improvement over direct-answer VLMs on OMNI3D-BENCH.
Chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning has been highly successful in solving complex tasks in natural language processing, and recent multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have extended this paradigm to video reasoning. However, these models typically build on lengthy reasoning chains and large numbers of input visual tokens. Motivated by empirical observations from our benchmark study, we hypothesize that concise reasoning combined with a reduced set of visual tokens can be sufficient for effective video reasoning. To evaluate this hypothesis, we design and validate an efficient post-training and inference framework that enhances a video MLLM's reasoning capability. Our framework enables models to operate on compressed visual tokens and generate brief reasoning traces prior to answering. The resulting models achieve substantially improved inference efficiency, deliver competitive performance across diverse benchmarks, and avoid reliance on manual CoT annotations or supervised fine-tuning. Collectively, our results suggest that long, human-like CoT reasoning may not be necessary for general video reasoning, and that concise reasoning can be both effective and efficient. Our code will be released at this https URL.
Meta AI developed Saber, a framework for zero-shot Reference-to-Video generation that leverages a masked training strategy on general video-text datasets, eliminating the need for specialized R2V data. It achieves superior identity consistency and overall performance on benchmarks like OpenS2V-Eval compared to methods trained on costly R2V datasets.
05 Dec 2025
The EditThinker framework enhances instruction-following in any image editor by introducing an iterative reasoning process. It leverages a Multimodal Large Language Model to critique, reflect, and refine editing instructions, leading to consistent performance gains across diverse benchmarks and excelling in complex reasoning tasks.
We present WonderZoom, a novel approach to generating 3D scenes with contents across multiple spatial scales from a single image. Existing 3D world generation models remain limited to single-scale synthesis and cannot produce coherent scene contents at varying granularities. The fundamental challenge is the lack of a scale-aware 3D representation capable of generating and rendering content with largely different spatial sizes. WonderZoom addresses this through two key innovations: (1) scale-adaptive Gaussian surfels for generating and real-time rendering of multi-scale 3D scenes, and (2) a progressive detail synthesizer that iteratively generates finer-scale 3D contents. Our approach enables users to "zoom into" a 3D region and auto-regressively synthesize previously non-existent fine details from landscapes to microscopic features. Experiments demonstrate that WonderZoom significantly outperforms state-of-the-art video and 3D models in both quality and alignment, enabling multi-scale 3D world creation from a single image. We show video results and an interactive viewer of generated multi-scale 3D worlds in this https URL
Researchers introduce the novel UAV-Anti-UAV tracking task, where a pursuer drone tracks an adversarial one, and create the first million-scale benchmark dataset for this challenging air-to-air scenario. They also propose MambaSTS, a new baseline tracker that integrates spatial, temporal, and semantic learning using Mamba and Transformer architectures, achieving a Mean Accuracy (mACC) of 0.443, which is 6.6 percentage points higher than the next best method on the new benchmark.
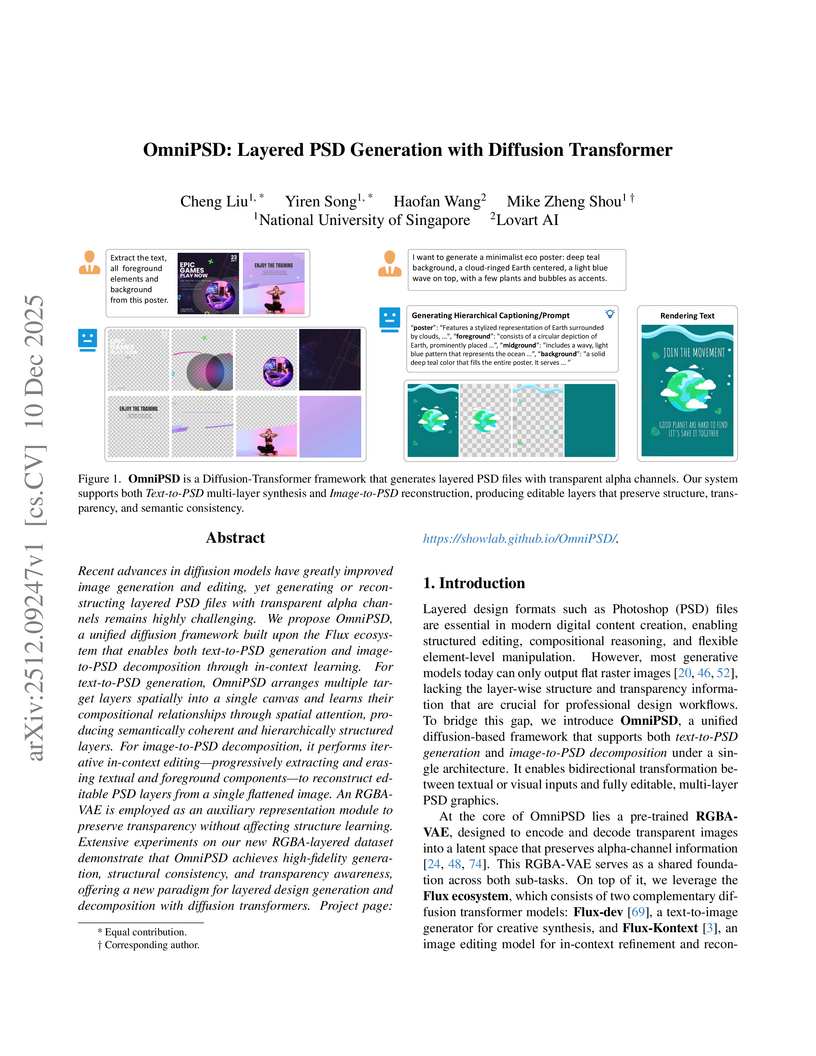
Recent advances in diffusion models have greatly improved image generation and editing, yet generating or reconstructing layered PSD files with transparent alpha channels remains highly challenging. We propose OmniPSD, a unified diffusion framework built upon the Flux ecosystem that enables both text-to-PSD generation and image-to-PSD decomposition through in-context learning. For text-to-PSD generation, OmniPSD arranges multiple target layers spatially into a single canvas and learns their compositional relationships through spatial attention, producing semantically coherent and hierarchically structured layers. For image-to-PSD decomposition, it performs iterative in-context editing, progressively extracting and erasing textual and foreground components to reconstruct editable PSD layers from a single flattened image. An RGBA-VAE is employed as an auxiliary representation module to preserve transparency without affecting structure learning. Extensive experiments on our new RGBA-layered dataset demonstrate that OmniPSD achieves high-fidelity generation, structural consistency, and transparency awareness, offering a new paradigm for layered design generation and decomposition with diffusion transformers.
An independent research team secured 1st place in the 2025 BEHAVIOR Challenge, achieving a 26% q-score by enhancing a Vision-Language-Action model (Pi0.5) with innovations like correlated noise for flow matching, "System 2" stage tracking, and practical inference-time heuristics. The approach demonstrated emergent recovery behaviors and addressed challenges in long-horizon, complex manipulation tasks.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.