self-supervised-learning
The Native Parallel Reasoner (NPR) framework allows Large Language Models to autonomously acquire and deploy genuine parallel reasoning capabilities, without relying on external teacher models. Experiments show NPR improves accuracy by up to 24.5% over baselines and delivers up to 4.6 times faster inference, maintaining 100% parallel execution across various benchmarks.
Apple researchers introduced FAE (Feature Auto-Encoder), a minimalist framework using a single attention layer and a double-decoder architecture to adapt high-dimensional self-supervised visual features into compact, generation-friendly latent spaces. FAE achieves competitive FID scores on ImageNet (1.29) and MS-COCO (6.90) for image generation while preserving semantic understanding capabilities of the original pre-trained encoders.
A new framework, Distribution Matching Variational AutoEncoder (DMVAE), explicitly aligns a VAE's aggregate latent distribution with a pre-defined reference distribution using score-based matching. The approach achieves a state-of-the-art gFID of 1.82 on ImageNet 256x256, demonstrating superior training efficiency for downstream generative models, particularly when utilizing Self-Supervised Learning features as the reference.
VALOR, developed at Caltech, presents an annotation-free framework that trains visual reasoners by employing multimodal verifiers to jointly tune an LLM for reasoning and specialized vision tools for visual grounding. This approach achieves superior performance on various visual reasoning benchmarks, including a 6.5% average improvement over direct-answer VLMs on OMNI3D-BENCH.
Meta AI developed Saber, a framework for zero-shot Reference-to-Video generation that leverages a masked training strategy on general video-text datasets, eliminating the need for specialized R2V data. It achieves superior identity consistency and overall performance on benchmarks like OpenS2V-Eval compared to methods trained on costly R2V datasets.
Researchers from Cornell University, Google, and UC Berkeley developed Selfi, a framework that refines pre-trained 3D Vision Foundation Model features through self-supervised geometric alignment. It achieves state-of-the-art pose-free novel view synthesis quality and robust camera pose estimation, often rivaling methods requiring ground-truth camera parameters.
Researchers at the University of Bonn and TU Delft developed a monocular visual SLAM system that accurately estimates camera poses and provides scale-consistent dense 3D reconstruction in dynamic settings. The method integrates a deep learning model for moving object segmentation and depth estimation with a geometric bundle adjustment framework, achieving superior tracking and depth accuracy on challenging datasets.
This research provides theoretical and empirical evidence that generative models are essential for achieving data-efficient compositional generalization in visual perception, demonstrating that enforcing necessary inductive biases is feasible for decoders but largely infeasible for encoders without knowledge of out-of-domain data. Generative methods, through techniques like replay and gradient-based search, significantly improve out-of-domain accuracy compared to non-generative counterparts.
Mimic2DM is a framework that learns to control physically simulated 3D characters from abundant 2D video data, bypassing explicit 3D reconstruction by formulating motion imitation as a physics-based 2D motion tracking problem. The system enables characters to perform complex human-object interactions and animal locomotion, outperforming two-stage methods and exhibiting implicit 3D understanding from diverse 2D viewpoints.
A two-stage self-supervised framework integrates the Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (JEPA) with Density Adaptive Attention Mechanisms (DAAM) to learn robust speech representations. This approach generates efficient, reversible discrete speech tokens at an ultra-low rate of 47.5 tokens/sec, designed for seamless integration with large language models.
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is a foundational component in robotics, AR/VR, and autonomous systems. With the rising focus on spatial AI in recent years, combining SLAM with semantic understanding has become increasingly important for enabling intelligent perception and interaction. Recent efforts have explored this integration, but they often rely on depth sensors or closed-set semantic models, limiting their scalability and adaptability in open-world environments. In this work, we present OpenMonoGS-SLAM, the first monocular SLAM framework that unifies 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with open-set semantic understanding. To achieve our goal, we leverage recent advances in Visual Foundation Models (VFMs), including MASt3R for visual geometry and SAM and CLIP for open-vocabulary semantics. These models provide robust generalization across diverse tasks, enabling accurate monocular camera tracking and mapping, as well as a rich understanding of semantics in open-world environments. Our method operates without any depth input or 3D semantic ground truth, relying solely on self-supervised learning objectives. Furthermore, we propose a memory mechanism specifically designed to manage high-dimensional semantic features, which effectively constructs Gaussian semantic feature maps, leading to strong overall performance. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves performance comparable to or surpassing existing baselines in both closed-set and open-set segmentation tasks, all without relying on supplementary sensors such as depth maps or semantic annotations.
Image fusion aims to blend complementary information from multiple sensing modalities, yet existing approaches remain limited in robustness, adaptability, and controllability. Most current fusion networks are tailored to specific tasks and lack the ability to flexibly incorporate user intent, especially in complex scenarios involving low-light degradation, color shifts, or exposure imbalance. Moreover, the absence of ground-truth fused images and the small scale of existing datasets make it difficult to train an end-to-end model that simultaneously understands high-level semantics and performs fine-grained multimodal alignment. We therefore present DiTFuse, instruction-driven Diffusion-Transformer (DiT) framework that performs end-to-end, semantics-aware fusion within a single model. By jointly encoding two images and natural-language instructions in a shared latent space, DiTFuse enables hierarchical and fine-grained control over fusion dynamics, overcoming the limitations of pre-fusion and post-fusion pipelines that struggle to inject high-level semantics. The training phase employs a multi-degradation masked-image modeling strategy, so the network jointly learns cross-modal alignment, modality-invariant restoration, and task-aware feature selection without relying on ground truth images. A curated, multi-granularity instruction dataset further equips the model with interactive fusion capabilities. DiTFuse unifies infrared-visible, multi-focus, and multi-exposure fusion-as well as text-controlled refinement and downstream tasks-within a single architecture. Experiments on public IVIF, MFF, and MEF benchmarks confirm superior quantitative and qualitative performance, sharper textures, and better semantic retention. The model also supports multi-level user control and zero-shot generalization to other multi-image fusion scenarios, including instruction-conditioned segmentation.
PRISM-WM introduces a world model that leverages a Mixture-of-Experts architecture with latent orthogonalization to accurately model hybrid dynamics in robotic systems. This approach significantly extends reliable planning horizons and achieves superior performance in high-dimensional continuous control tasks.
MIND-V introduces a hierarchical video generation framework for long-horizon robotic manipulation, autonomously synthesizing physically plausible and logically coherent operation videos. It employs a multi-stage architecture with reinforcement learning for physical alignment, providing a scalable method for generating robot training data.
CompressARC, developed by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, addresses the ARC-AGI benchmark by achieving 20% accuracy on evaluation puzzles without any pretraining, learning entirely at inference time from the target puzzle. It leverages a custom equivariant neural network and the Minimum Description Length principle to discover abstract reasoning patterns with extreme data efficiency.
The DoGe framework from Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory and collaborators introduces a context-first self-evolving learning approach that decouples cognitive processes for data-scarce vision-language reasoning. It achieves stable performance improvements of 5.7% for 3B-series models and 2.3% for 7B-series models across seven benchmarks, while enhancing policy exploration and mitigating reward hacking.
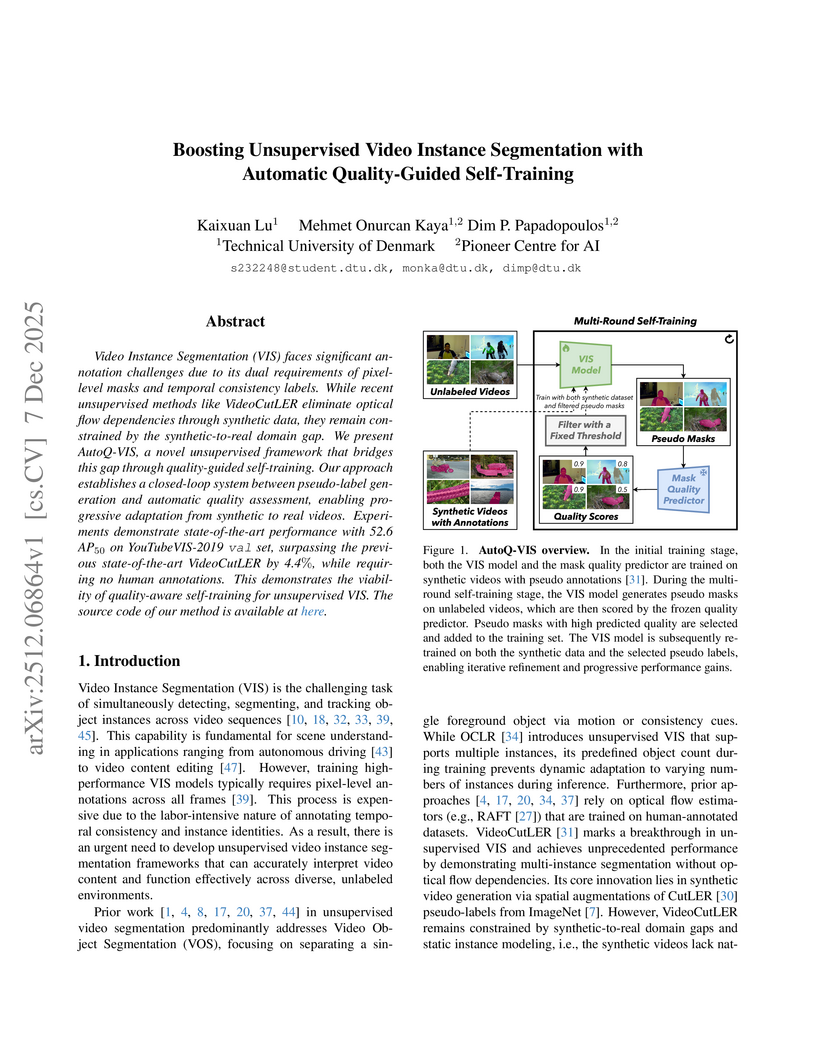
Video Instance Segmentation (VIS) faces significant annotation challenges due to its dual requirements of pixel-level masks and temporal consistency labels. While recent unsupervised methods like VideoCutLER eliminate optical flow dependencies through synthetic data, they remain constrained by the synthetic-to-real domain gap. We present AutoQ-VIS, a novel unsupervised framework that bridges this gap through quality-guided self-training. Our approach establishes a closed-loop system between pseudo-label generation and automatic quality assessment, enabling progressive adaptation from synthetic to real videos. Experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance with 52.6 AP50 on YouTubeVIS-2019 val set, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art VideoCutLER by 4.4%, while requiring no human annotations. This demonstrates the viability of quality-aware self-training for unsupervised VIS. We will release the code at this https URL.
OXTAL introduces an all-atom diffusion transformer model that generates organic crystal structures directly from a 2D molecular graph, learning both molecular conformations and periodic packing from over 600,000 experimental structures. The method demonstrates competitive accuracy against traditional DFT-based approaches in CCDC blind tests while offering significantly reduced computational inference costs.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in code intelligence tasks such as code generation, summarization, and translation. However, their reliance on linearized token sequences limits their ability to understand the structural semantics of programs. While prior studies have explored graphaugmented prompting and structure-aware pretraining, they either suffer from prompt length constraints or require task-specific architectural changes that are incompatible with large-scale instructionfollowing LLMs. To address these limitations, this paper proposes CGBridge, a novel plug-and-play method that enhances LLMs with Code Graph information through an external, trainable Bridge module. CGBridge first pre-trains a code graph encoder via selfsupervised learning on a large-scale dataset of 270K code graphs to learn structural code semantics. It then trains an external module to bridge the modality gap among code, graph, and text by aligning their semantics through cross-modal attention mechanisms. Finally, the bridge module generates structure-informed prompts, which are injected into a frozen LLM, and is fine-tuned for downstream code intelligence tasks. Experiments show that CGBridge achieves notable improvements over both the original model and the graphaugmented prompting method. Specifically, it yields a 16.19% and 9.12% relative gain in LLM-as-a-Judge on code summarization, and a 9.84% and 38.87% relative gain in Execution Accuracy on code translation. Moreover, CGBridge achieves over 4x faster inference than LoRA-tuned models, demonstrating both effectiveness and efficiency in structure-aware code understanding.
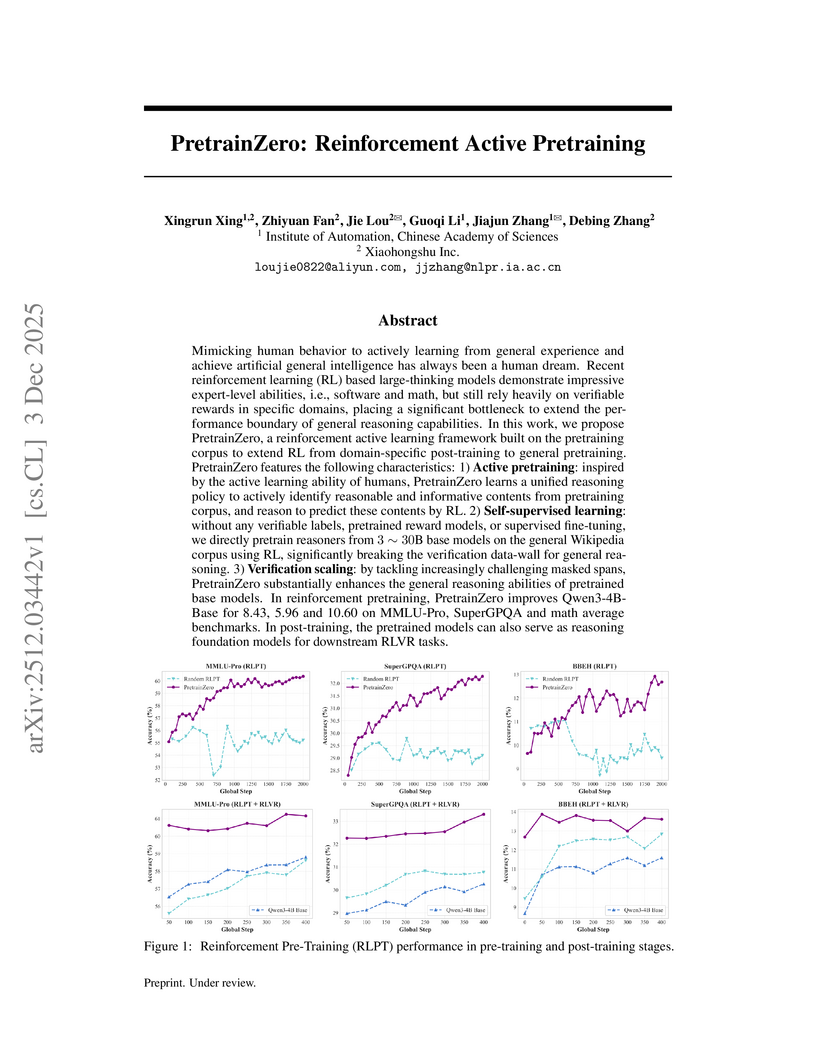
PretrainZero introduces a self-supervised reinforcement active pretraining framework that enables large language models to acquire general reasoning capabilities directly from real-world, noisy data like Wikipedia. This method achieved substantial performance improvements across diverse reasoning benchmarks, including MMLU-Pro and various math tasks, by allowing models to actively learn from self-generated, verifiable challenges.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.