vision-language-models
Apple researchers introduced FAE (Feature Auto-Encoder), a minimalist framework using a single attention layer and a double-decoder architecture to adapt high-dimensional self-supervised visual features into compact, generation-friendly latent spaces. FAE achieves competitive FID scores on ImageNet (1.29) and MS-COCO (6.90) for image generation while preserving semantic understanding capabilities of the original pre-trained encoders.
10 Dec 2025
The Astribot Team developed Lumo-1, a Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model that explicitly integrates structured reasoning with physical actions to achieve purposeful robotic control on their Astribot S1 bimanual mobile manipulator. This system exhibits superior generalization to novel objects and instructions, improves reasoning-action consistency through reinforcement learning, and outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in complex, long-horizon, and dexterous tasks.
UniUGP presents a unified framework for end-to-end autonomous driving, integrating scene understanding, future video generation, and trajectory planning through a hybrid expert architecture. This approach enhances interpretability with Chain-of-Thought reasoning and demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in challenging long-tail scenarios and multimodal capabilities across various benchmarks.
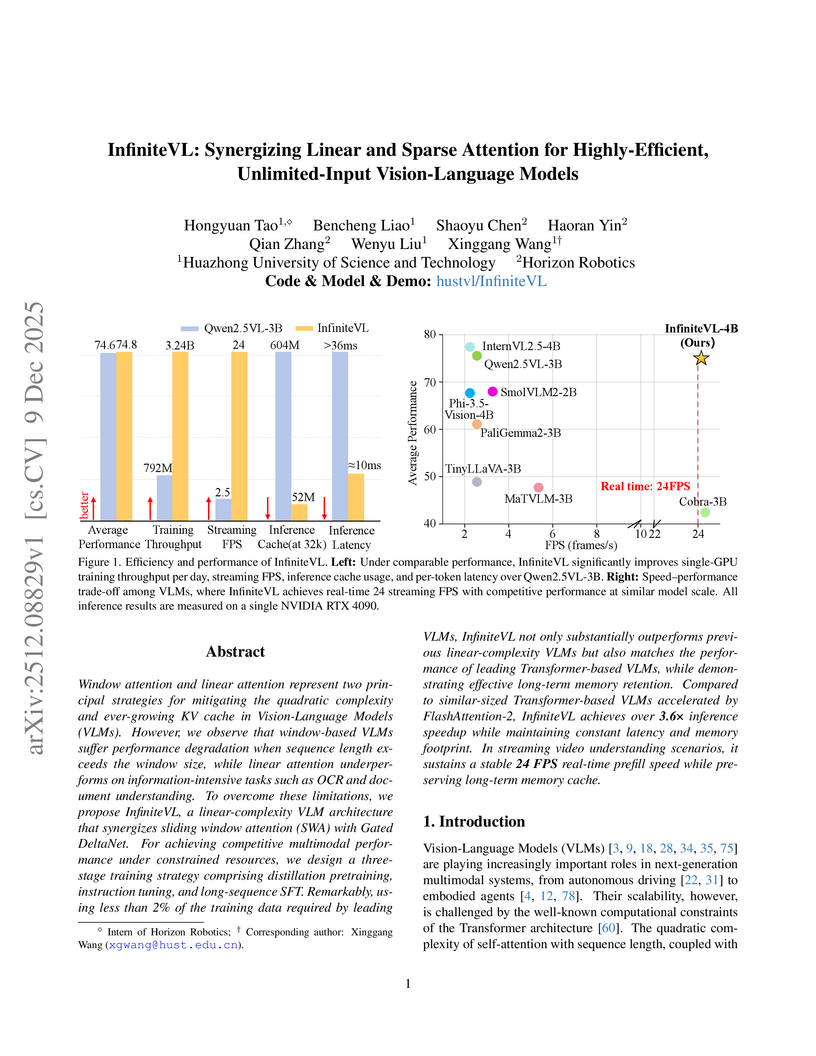
InfiniteVL, a collaboration between Huazhong University of Science and Technology and Horizon Robotics, introduces a hybrid Vision-Language Model that synergizes linear and sparse attention to enable unlimited multimodal input processing with constant latency and memory footprint. The model achieves performance competitive with Transformer-based VLMs on diverse benchmarks, including information-intensive tasks, while demonstrating significant inference speedups and robust real-time streaming capabilities.
Researchers from University of Wisconsin-Madison, UCLA, and Adobe Research introduce a computational framework for "relational visual similarity," which identifies image commonalities based on abstract logic rather than surface features. Their `relsim` model, trained on a novel dataset of images paired with anonymous group-derived captions, aligns significantly with human perception of relational similarity and outperforms existing attribute-based metrics in retrieval tasks.
Researchers at The Chinese University of Hong Kong and the University of Wisconsin-Madison developed an efficient framework for video multimodal large language models, significantly reducing computational overhead by employing concise reasoning and trainable visual token compression. This approach achieved state-of-the-art performance across video understanding benchmarks while eliminating the need for expensive Chain-of-Thought annotations and supervised fine-tuning.
Researchers from Microsoft Research Asia, Xi'an Jiaotong University, and Fudan University developed VideoVLA, a robot manipulator that repurposes large pre-trained video generation models. This system jointly predicts future video states and corresponding actions, achieving enhanced generalization capabilities for novel objects and skills in both simulated and real-world environments.
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) exhibit substantial cross-modal inconsistency, producing different answers for semantically identical information presented across image, text, and mixed modalities. This problem persists even with perfect Optical Character Recognition (OCR), revealing an inherent reasoning challenge where text inputs generally achieve higher accuracy than image inputs.
ReViSE introduces a framework for reason-informed video editing that integrates self-reflective learning to overcome the limitations of current models in handling complex, reasoning-driven instructions. The approach establishes a new benchmark, RVE-Bench, and achieves improved performance, with a 38% gain in overall score for temporal reasoning compared to prior state-of-the-art methods.
09 Dec 2025
VALOR, developed at Caltech, presents an annotation-free framework that trains visual reasoners by employing multimodal verifiers to jointly tune an LLM for reasoning and specialized vision tools for visual grounding. This approach achieves superior performance on various visual reasoning benchmarks, including a 6.5% average improvement over direct-answer VLMs on OMNI3D-BENCH.
Researchers at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology developed BiCo, a one-shot method that precisely binds visual concepts from images and videos to text prompts, enabling flexible cross-modal composition. The approach achieved superior content generation quality, demonstrating a 54.67% improvement in overall quality over previous state-of-the-art methods in human evaluations.
Researchers from the University of Technology Sydney and Zhejiang University developed VideoCoF, a unified video editing framework that introduces a "Chain of Frames" approach for explicit visual reasoning. This method achieves mask-free, fine-grained edits, demonstrating a 15.14% improvement in instruction following and an 18.6% higher success ratio on their VideoCoF-Bench, while also providing robust length extrapolation.
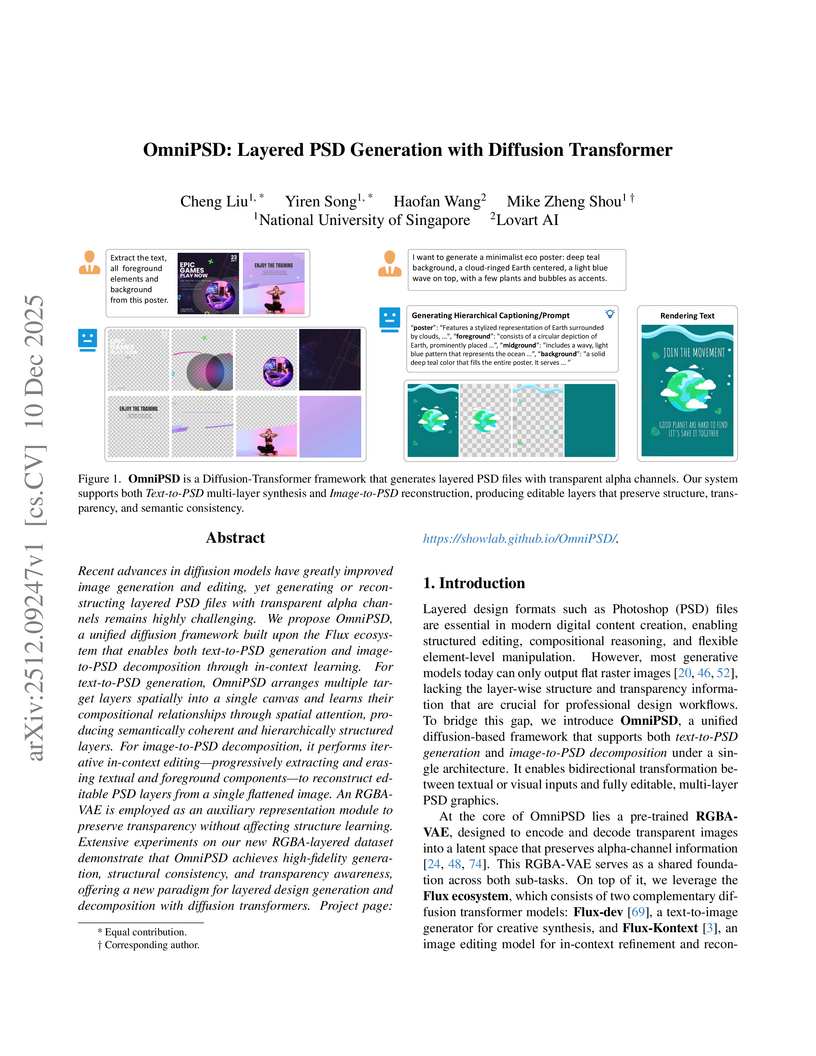
OmniPSD introduces a unified Diffusion Transformer framework capable of generating editable layered PSD files with transparent alpha channels from text descriptions and decomposing flattened images into constituent, editable layers. The system leverages a specialized RGBA-VAE and in-context layer reasoning to produce professional-grade assets that integrate directly into design software.
Researchers from Meta AI and the University of Copenhagen developed OneStory, a framework for coherent multi-shot video generation that utilizes adaptive memory modules to model long-range cross-shot context. The method consistently outperforms existing baselines, achieving higher inter-shot coherence scores (e.g., 0.5813 average inter-shot coherence in text-to-multi-shot video tasks) and enhanced shot-level quality.
Researchers at Zhejiang University developed Video-QTR, a query-driven temporal reasoning framework for video understanding that dynamically allocates perceptual resources based on query intent. This system achieved state-of-the-art accuracy on long-video benchmarks while reducing input frame consumption by up to 73%.
NoisyCLIP offers a method for assessing language-to-latent alignment during the reverse diffusion process in conditional diffusion models, facilitating early detection of misalignments. This approach reduces computational costs in image generation by up to 50% while maintaining high semantic fidelity.
07 Dec 2025
ProAgent introduces an end-to-end proactive LLM agent system leveraging on-demand multi-modal sensory contexts from AR glasses to anticipate user needs without explicit commands. It achieved a 33.4% higher proactive accuracy and 16.8% higher F1-score for tool calling compared to existing baselines, while operating efficiently on edge devices.
Researchers from Peking University and collaborators developed VABench, a comprehensive, multi-dimensional benchmark for synchronous audio-video generation, which employs 15 fine-grained metrics and 7 content categories to evaluate models like Sora2 and Veo3. This framework provides an objective assessment of multimodal outputs, identifying challenges in areas like human sounds and stereo audio while aligning strongly with human perceptual judgments.
RETAIN, developed at UC Berkeley, introduces a parameter merging strategy for generalist robot policies, interpolating pre-trained and finetuned weights to enable robust adaptation to new tasks. This approach enhances out-of-distribution generalization by approximately 40% on real-world robotic tasks while preserving the policy's existing broad capabilities in low-data scenarios.
04 Dec 2025
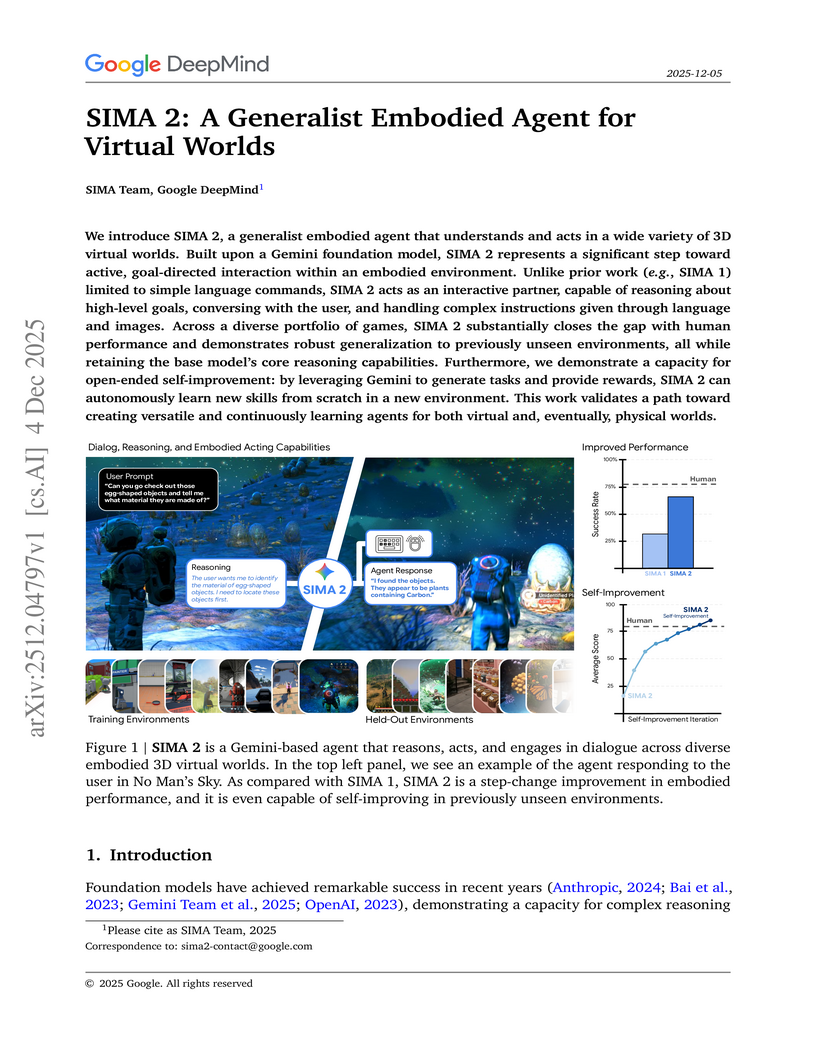
Google DeepMind developed SIMA 2, a generalist embodied agent powered by a Gemini Flash-Lite model, capable of understanding and acting in diverse 3D virtual worlds. It substantially doubles the task success rate of its predecessor SIMA 1, generalizes to unseen commercial games and photorealistic environments, and demonstrates autonomous skill acquisition through a Gemini-based self-improvement mechanism.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.