CUHK
CUHKQuickLLaMA (Query-aware Inference for LLMs) introduces a training-free inference acceleration method that allows Large Language Models to efficiently process and accurately reason over arbitrarily long contexts, extending capabilities to up to 1 million tokens. The approach significantly improves performance on long-context benchmarks, outperforming prior state-of-the-art methods like InfLLM by over 7% on LLaMA3 while maintaining linear scaling of time and memory.
This paper identifies and characterizes a universal policy entropy collapse in reinforcement learning for large language models (LLMs), revealing an empirical law that links performance to entropy. It further provides a mechanistic understanding of this phenomenon through covariance analysis and proposes two covariance-aware regularization methods, Clip-Cov and KL-Cov, which successfully maintain higher entropy and improve LLM reasoning performance on math and coding tasks.
The PRIME framework enhances Large Language Model reasoning by efficiently integrating dense, token-level implicit rewards through online reinforcement learning. It achieves a 15.1% average improvement across key reasoning benchmarks and demonstrates 2.5x sample efficiency, outperforming larger models like Qwen2.5-Math-7B-Instruct with significantly less training data.
LLaVA-OneVision is an open Large Multimodal Model that achieves state-of-the-art performance among open LMMs across single-image, multi-image, and video tasks. This model narrows the performance gap with proprietary models like GPT-4V/o and demonstrates robust cross-modal task transfer, enabling diverse emergent visual understanding capabilities.
ReCamMaster introduces a framework for camera-controlled generative video re-rendering, enabling the synthesis of new videos from a single input video with novel camera trajectories. The method leverages a novel "Frame Dimension Conditioning" mechanism and a large-scale synthetic dataset, achieving improved visual quality, camera accuracy, and view synchronization over prior approaches.
Researchers at Nanyang Technological University, Stanford University, and ByteDance Seed developed the Mixture of Contexts (MoC) framework, enabling Diffusion Transformers to generate minute-long multi-shot videos with high coherence. This method achieved an 85% sparsity, a 7x reduction in FLOPs, and a 2.2x speedup compared to dense attention baselines, while maintaining or improving perceptual quality and consistency.
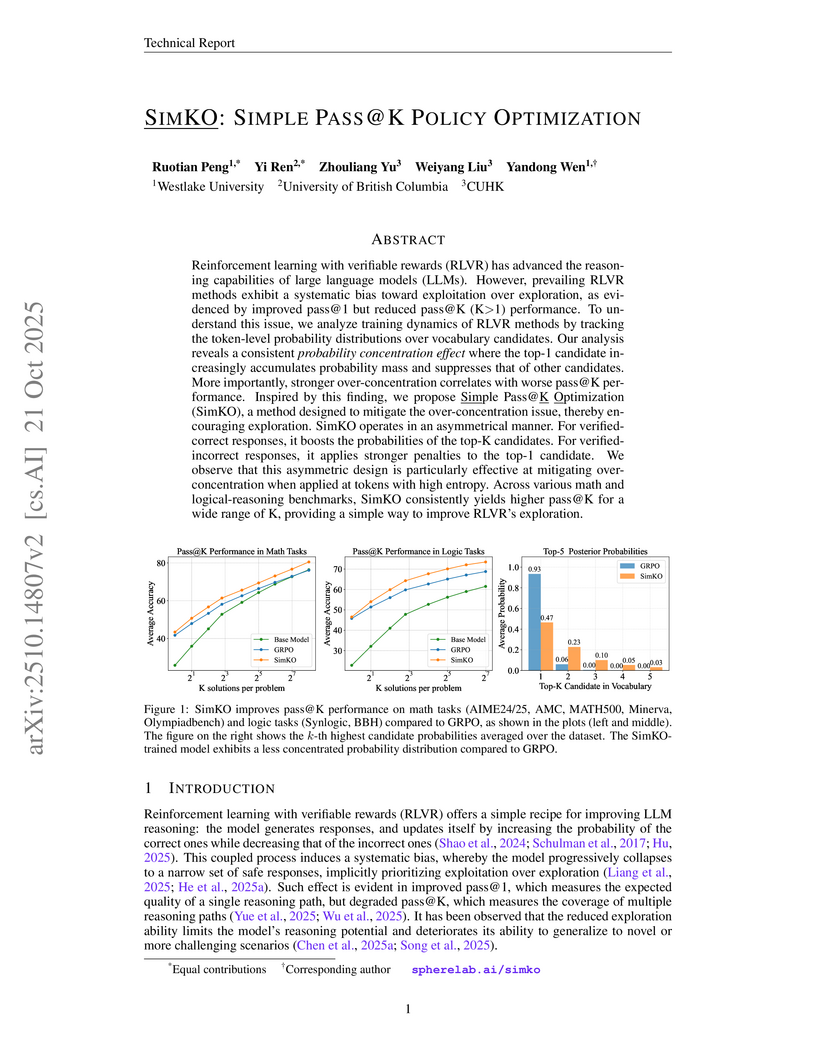
SimKO is a method that improves Large Language Models trained with Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards by mitigating a phenomenon called "probability over-concentration" during token generation. The approach employs asymmetric gradient redistribution to enhance `pass@K` performance while also improving `pass@1` on various math and logical reasoning tasks, consistently outperforming existing RLVR techniques.
23 Mar 2025
This paper offers the first comprehensive survey of Multimodal Chain-of-Thought (MCoT) reasoning, analyzing its evolution, diverse methodologies, and applications across various modalities. It consolidates scattered research, providing a systematic taxonomy, elucidating foundational concepts, and identifying future research directions to foster innovation in multimodal AI.
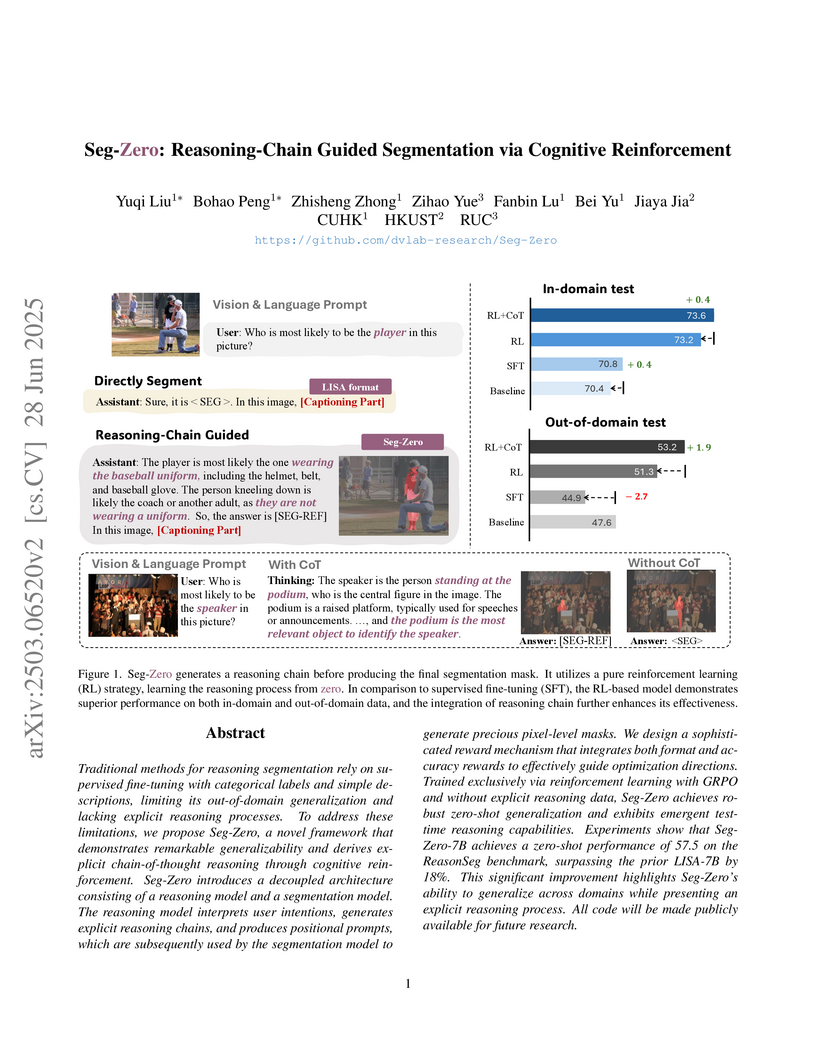
Seg-Zero introduces a pure reinforcement learning framework for reasoning segmentation, enabling emergent chain-of-thought capabilities without explicit reasoning data. The approach demonstrates superior zero-shot generalization and preserves general Visual Question Answering abilities, achieving 57.5 gIoU on ReasonSeg, an 18% improvement over the prior state-of-the-art LISA-7B.
DreamOmni2 introduces a multimodal instruction-based editing and generation framework that enables image manipulation using both text and multiple reference images for concrete objects and abstract attributes. The system, supported by a novel synthetic data pipeline and an enhanced Diffusion Transformer, achieves leading performance in human evaluations for image editing (e.g., 68.29% for abstract attribute editing) and competitive results in generation compared to commercial models.
Researchers from Nanjing University, CASIA, HKU, and other institutions introduced Video-MME, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) in video analysis, covering diverse domains, temporal lengths, and modalities. Evaluations on Video-MME revealed that commercial MLLMs, particularly Gemini 1.5 Pro, achieved higher accuracy than open-source models, and performance across all models declined with increasing video duration, despite gains from integrating subtitles and audio.
G-Designer introduces a framework using Graph Neural Networks to dynamically generate task-aware communication topologies for LLM-based multi-agent systems. This approach achieved superior performance on various benchmarks while significantly reducing token consumption by up to 95.33% and demonstrating high adversarial robustness.
This work comprehensively investigates applying Chain-of-Thought reasoning strategies to autoregressive image generation, demonstrating how verification and reinforcement mechanisms can significantly enhance image quality and text-to-image alignment. The proposed approach achieves a 24% improvement over the Show-o baseline on the GenEval benchmark, surpassing Stable Diffusion 3 by 15%.
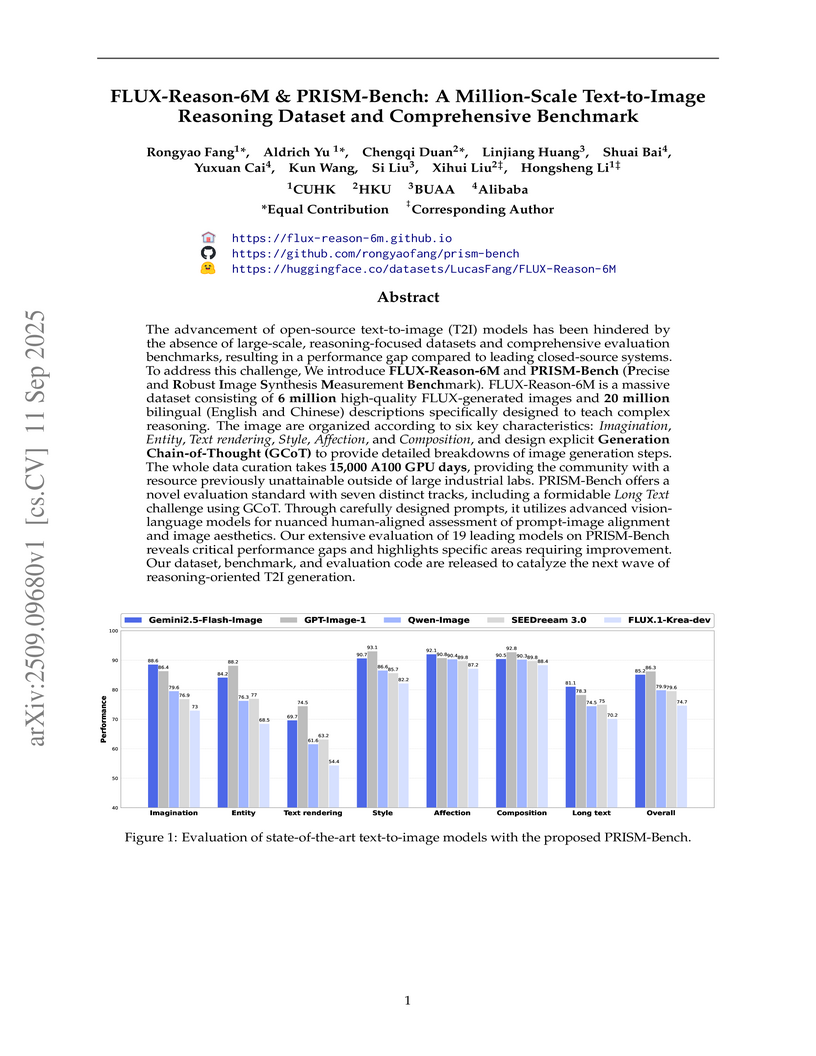
Researchers from CUHK, HKU, Beihang University, and Alibaba introduced FLUX-Reason-6M, a 6-million-image, reasoning-focused text-to-image dataset, and PRISM-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating T2I models. This work provides an open-source resource with 20 million bilingual captions, including Generation Chain-of-Thought prompts, aiming to advance T2I reasoning capabilities and offering a robust evaluation of 19 leading models, highlighting persistent challenges in text rendering and long instruction following.
Researchers from the Chinese University of Hong Kong and SmartMore developed VisionReasoner, a unified framework for visual perception that integrates a large vision-language model with reinforcement learning. This system handles diverse tasks including detection, segmentation, and counting through a shared reasoning process, demonstrating improved performance across these benchmarks and generating interpretable thought traces without explicit reasoning training.
VisionZip introduces a method to reduce visual token redundancy in Vision Language Models (VLMs) by intelligently selecting dominant tokens and merging contextual ones. The approach achieves up to an 8x reduction in prefilling time while maintaining high model performance across image and video understanding tasks.
G
G
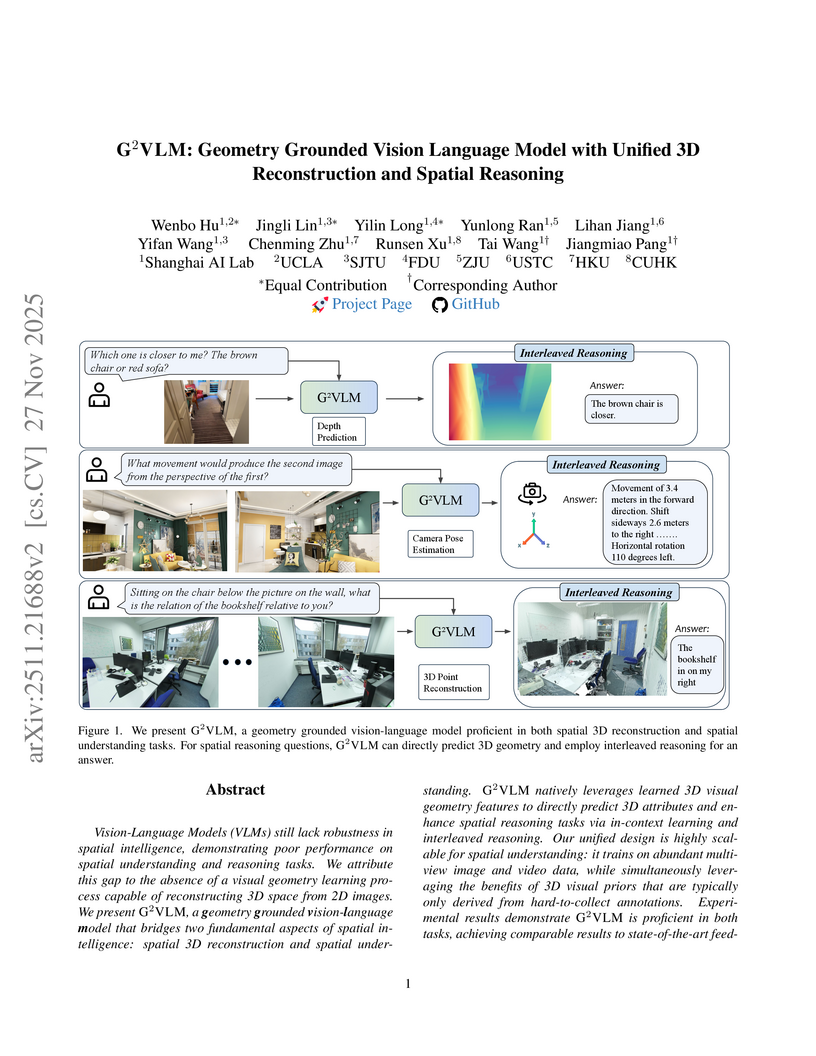
²VLM integrates 3D reconstruction and spatial reasoning within a single Vision-Language Model, addressing the spatial intelligence limitations of current VLMs. It learns explicit visual geometry from 2D data using a Mixture-of-Transformer-Experts architecture, leading to robust spatial understanding and strong performance on both 3D reconstruction and complex spatial reasoning benchmarks.
18 Oct 2025
Geometric-Mean Policy Optimization (GMPO) stabilizes reinforcement learning for large language models (LLMs) by employing a geometric mean for token-level reward aggregation. This approach yielded an average 4.1% improvement in Pass@1 accuracy over GRPO on mathematical reasoning benchmarks and showed gains in multimodal and Mixture-of-Experts settings, demonstrating more stable training and enhanced policy exploration.
CodePlot-CoT introduces a code-driven Chain-of-Thought paradigm, enabling Vision Language Models (VLMs) to generate precise visual aids by producing executable plotting code that is then rendered and re-integrated into the reasoning process. This method, along with the new Math-VR dataset, allowed CodePlot-CoT to achieve up to a 21% performance increase on mathematical visual reasoning tasks, surpassing larger models and those using direct image generation.
HybridVLA introduces a unified Vision-Language-Action model that integrates both diffusion-based continuous action prediction and autoregressive reasoning within a shared Large Language Model backbone. This approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in robotic manipulation, demonstrating up to 19% higher success rates over prior methods in real-world tasks and strong generalization to unseen conditions.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.