Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Beihang University
Beihang University The Hong Kong Polytechnic UniversityBeijing Academy of Artificial IntelligenceZhongguancun AcademyLuxiTechKey Laboratory of Brain Cognition and Brain-inspired Intelligence TechnologyBeijing Key Laboratory of Brain-Inspired General Intelligence Large ModelMetaX Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd.
The Hong Kong Polytechnic UniversityBeijing Academy of Artificial IntelligenceZhongguancun AcademyLuxiTechKey Laboratory of Brain Cognition and Brain-inspired Intelligence TechnologyBeijing Key Laboratory of Brain-Inspired General Intelligence Large ModelMetaX Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd.Mainstream Transformer-based large language models face major efficiency bottlenecks: training computation scales quadratically with sequence length, and inference memory grows linearly, limiting long-context processing. Building large models on non-NVIDIA platforms also poses challenges for stable and efficient training. To address this, we introduce SpikingBrain, a family of brain-inspired models designed for efficient long-context training and inference. SpikingBrain leverages the MetaX GPU cluster and focuses on three aspects: (1) Model Architecture: linear and hybrid-linear attention architectures with adaptive spiking neurons; (2) Algorithmic Optimizations: an efficient, conversion-based training pipeline and a dedicated spike coding framework; (3) System Engineering: customized training frameworks, operator libraries, and parallelism strategies tailored to MetaX hardware.
Using these techniques, we develop two models: SpikingBrain-7B, a linear LLM, and SpikingBrain-76B, a hybrid-linear MoE LLM. These models demonstrate the feasibility of large-scale LLM development on non-NVIDIA platforms, and training remains stable for weeks on hundreds of MetaX GPUs with Model FLOPs Utilization at expected levels. SpikingBrain achieves performance comparable to open-source Transformer baselines while using only about 150B tokens for continual pre-training. Our models also significantly improve long-context efficiency and deliver inference with (partially) constant memory and event-driven spiking behavior. For example, SpikingBrain-7B attains over 100x speedup in Time to First Token for 4M-token sequences. Furthermore, the proposed spiking scheme achieves 69.15 percent sparsity, enabling low-power operation. Overall, this work demonstrates the potential of brain-inspired mechanisms to drive the next generation of efficient and scalable large model design.
URSA presents a uniform discrete diffusion framework that incorporates a metric probability path for video generation, enabling iterative global refinement in discrete token space. This framework achieves performance competitive with state-of-the-art continuous diffusion models across text-to-video, image-to-video, and text-to-image benchmarks, while enhancing scalability and multi-task capabilities.
BAAI's OmniGen2 introduces an open-source unified multimodal generative model featuring a decoupled architecture, novel data pipelines, and a new benchmark for complex tasks. It achieves competitive performance on text-to-image (0.86 GenEval), image editing (state-of-the-art among open-source on ImgEdit-Bench with 3.44), and establishes a strong 7.18 baseline on the OmniContext benchmark for in-context generation.
RoboRefer introduces a 3D-aware Vision-Language Model that achieves precise spatial understanding and generalized multi-step spatial reasoning for robotics through a dedicated depth encoder and a sequential SFT-RFT training strategy. It outperforms state-of-the-art models on spatial referring benchmarks, improving average accuracy by 17.4% on RefSpatial-Bench, and successfully executes long-horizon tasks across diverse real-world robots.
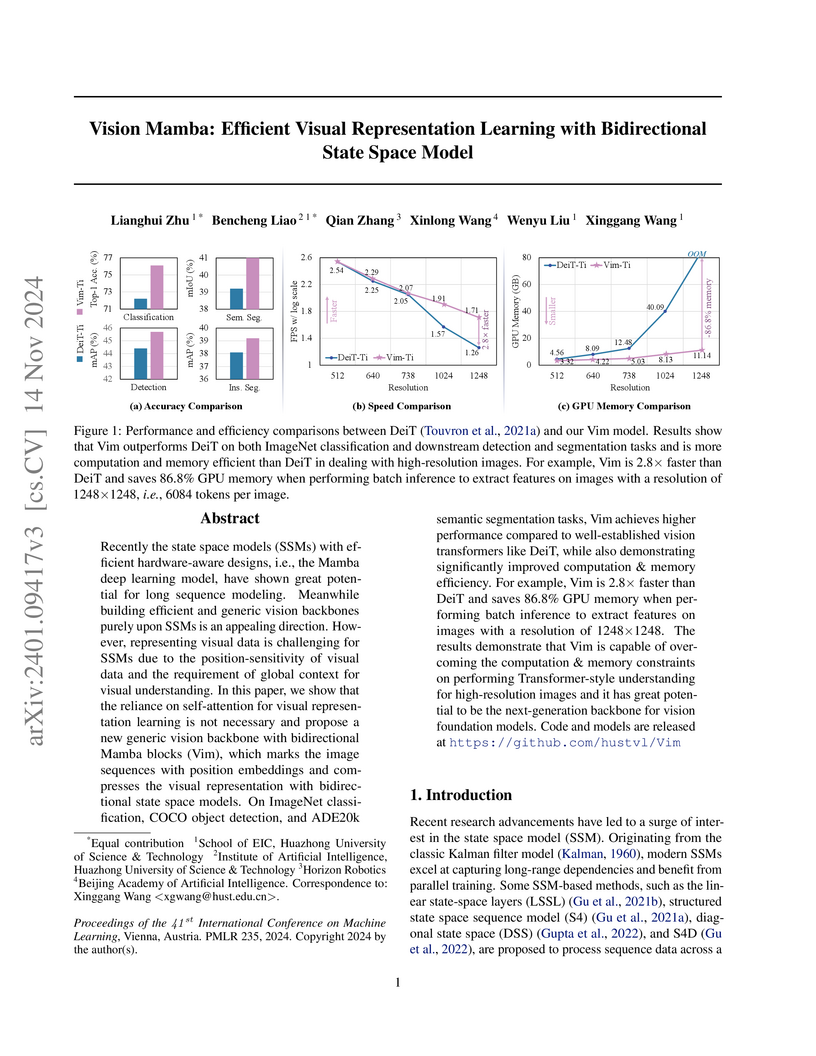
Vision Mamba (Vim) introduces the first purely State Space Model-based generic vision backbone, achieving competitive accuracy with Vision Transformers while offering significantly improved computational and memory efficiency for high-resolution images. The architecture adapts the Mamba model with a bidirectional processing scheme and hardware-aware optimizations.
14 Sep 2025
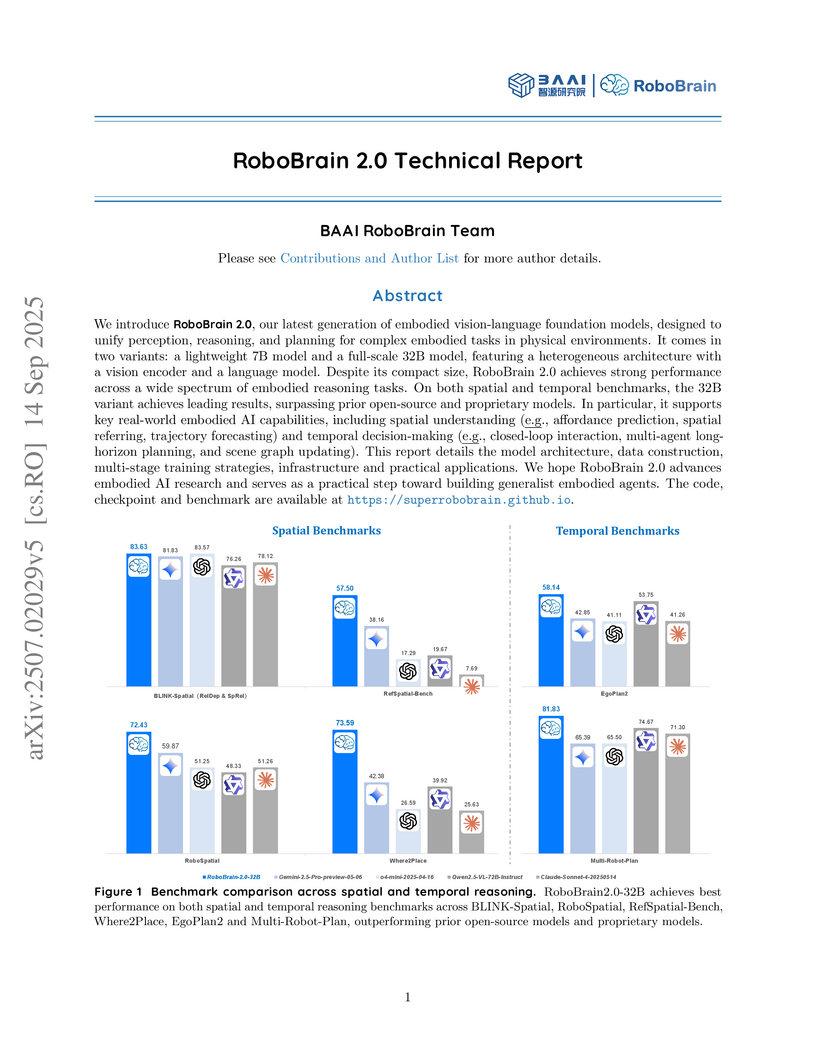
RoboBrain 2.0, an embodied vision-language foundation model from BAAI, integrates perception, reasoning, and planning to empower intelligent interaction in physical environments. It demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across numerous spatial and temporal reasoning benchmarks, including object placement prediction and multi-robot planning, establishing a new baseline for embodied AI capabilities.
Reason-RFT introduces a two-stage reinforcement fine-tuning framework to enhance the visual reasoning and generalization capabilities of Vision-Language Models. The method achieves state-of-the-art or highly competitive performance across various visual reasoning tasks, particularly demonstrating strong generalization under domain shifts while maintaining data efficiency.
MemoRAG is a retrieval-augmented generation framework that enhances long-context processing by incorporating a global memory module inspired by human cognition. The system processes entire long documents to form a high-level understanding, which then generates "answer clues" to guide precise retrieval, consistently outperforming existing RAG methods and long-context LLMs while efficiently managing GPU memory.
Uni-NaVid presents a unified Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model capable of addressing four distinct embodied navigation tasks by processing ego-centric video and natural language instructions. The model employs a novel online visual token merging mechanism to achieve a 5 Hz inference speed, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance in simulation and strong real-world generalization.
01 Nov 2025
Long-video understanding~(LVU) is a challenging problem in computer vision. Existing methods either downsample frames for single-pass reasoning, sacrificing fine-grained details, or depend on textual reasoning over task-agnostic representations, hindering task-specific perception and exploration. In this paper, we propose VideoExplorer, a framework grounded in the principle of ``thinking with video'', which naturally intertwines planning, temporal grounding, and scalable perception into a coherent reasoning process. Rather than reasoning over a static context, VideoExplorer iteratively formulates sub-questions, locates relevant moments, and performs task-oriented, temporally scalable video understanding until reaching the final answer, enabling faithful, efficient, and interpretable reasoning. To address the lack of LVU training resources, we construct a long-video reasoning dataset using difficulty-adaptive sampling to ensure high-quality trajectories on complex tasks. Building on this dataset, we design a two-stage training pipeline: supervised trajectory initialization followed by trajectory-level preference optimization, encouraging adaptive temporal grounding and iterative information integration guided by downstream rewards. Extensive evaluations on popular long-video understanding and reasoning benchmarks demonstrate VideoExplorer's significant advantage over existing baselines, highlighting its robustness, adaptability, and efficiency. Our code is made publicly available in this repository(this https URL).
27 Aug 2025
GraspVLA, a grasping foundation model from Galbot and Peking University, demonstrates robust zero-shot sim-to-real transfer and open-vocabulary grasping by pre-training exclusively on SynGrasp-1B, a billion-scale synthetic action dataset, achieving around 90% success rates on diverse real-world object categories.
Researchers from Tsinghua University and Xiaomi EV developed DGGT, a feedforward, pose-free framework for 4D reconstruction of dynamic driving scenes. The method achieves 27.41 dB PSNR and 0.846 SSIM on the Waymo Open Dataset for novel view synthesis, outperforming prior work while processing scenes in 0.39 seconds and demonstrating strong zero-shot generalization across diverse datasets.
Researchers from NUS, HKUST, and EPFL propose a systematic black-box framework for evaluating how large language models express confidence. Their empirical study reveals pervasive overconfidence in LLMs, but shows that combining sampling with aggregation strategies can significantly improve failure prediction, for example, boosting AUROC from 54.8% to 92.7% in arithmetic reasoning tasks.
Researchers from Peking University, BAAI, and CAS present RoboBrain, an MLLM-based model designed to bridge the gap between high-level human instructions and concrete robotic actions. Leveraging the new ShareRobot dataset, RoboBrain integrates planning, affordance perception, and trajectory prediction, achieving improved performance on established robotic benchmarks.
Researchers introduce EditScore, a series of high-fidelity, open-source reward models, and a new benchmark, EditReward-Bench, to enable stable online Reinforcement Learning for instruction-guided image editing. These specialized reward models, ranging from 7B to 72B parameters, significantly enhance the performance of leading image editing models like OmniGen2, achieving up to a +0.40 increase in overall score on GEdit-Bench-EN.
OmniGen, developed by the Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence (BAAI), introduces a unified diffusion model capable of performing diverse image generation tasks like text-to-image, image editing, and subject-driven generation within a single framework. The model achieves competitive performance with 3.8 billion parameters, demonstrating parameter efficiency compared to much larger specialized models while streamlining complex multi-step workflows into end-to-end instructions.
Researchers from BAAI and several top Chinese universities introduce MLVU, a multi-task long video understanding benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by utilizing videos from 3 minutes to over 2 hours and featuring 9 diverse tasks. The benchmark reveals that even leading MLLMs like GPT-4o achieve only moderate performance (54.5% average on multiple-choice tasks), indicating significant room for improvement in handling extended temporal reasoning.
JudgeLM, developed by researchers from Huazhong University of Science & Technology and BAAI, is a framework for fine-tuning open-source Large Language Models to serve as scalable and efficient evaluators. It achieves up to 89.32% agreement with GPT-4 and a 133.3x speedup in evaluation time, demonstrating superior alignment with human judgments than its GPT-4 teacher on specific benchmarks.
Emu2, a 37-billion-parameter generative multimodal model developed by the Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence (BAAI), demonstrates robust in-context learning capabilities by predicting the next multimodal element in a sequence. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot settings across a wide range of multimodal understanding and generation tasks, including visual question answering, referring expression comprehension, text-to-image generation, and subject-driven image editing.
20 Oct 2025
RoboBench introduces a comprehensive evaluation benchmark for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) acting as embodied brains, assessing five cognitive dimensions through real-world robotic data and a novel MLLM-as-world-simulator for planning. The benchmark reveals that current MLLMs still lag behind human performance across all evaluated cognitive abilities, particularly in complex planning and execution failure analysis.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.