Central Michigan University
Accident detection and traffic analysis is a critical component of smart city
and autonomous transportation systems that can reduce accident frequency,
severity and improve overall traffic management. This paper presents a
comprehensive analysis of traffic accidents in different regions across the
United States using data from the National Highway Traffic Safety
Administration (NHTSA) Crash Report Sampling System (CRSS). To address the
challenges of accident detection and traffic analysis, this paper proposes a
framework that uses traffic surveillance cameras and action recognition systems
to detect and respond to traffic accidents spontaneously. Integrating the
proposed framework with emergency services will harness the power of traffic
cameras and machine learning algorithms to create an efficient solution for
responding to traffic accidents and reducing human errors. Advanced
intelligence technologies, such as the proposed accident detection systems in
smart cities, will improve traffic management and traffic accident severity.
Overall, this study provides valuable insights into traffic accidents in the US
and presents a practical solution to enhance the safety and efficiency of
transportation systems.
17 Oct 2025
Type I X-ray bursts (XRBs) are thermonuclear runaways on the surface of accreting neutron stars, powered by rapid proton-capture and alpha-capture processes on neutron-deficient nuclei. Uncertainties in the corresponding reaction rates remain a major limitation in modeling burst light curves and ashes. We present a systematic study of the sensitivity of XRB models to uncertainties in charged-particle-induced reaction rates across a broad parameter space of accretion rates and fuel compositions in low-mass X-ray binaries. The study proceeds in two stages: ignition conditions are first determined with a semi-analytic framework coupled to a full reaction network, followed by a sensitivity analysis using the ONEZONE model with individual rate variations. We identify 41 reactions that alter the burst light curve and 187 that significantly impact final abundances. Reactions on bottleneck isotopes in the alpha-p- and rp-process paths strongly affect both observables, while most (p, gamma) reactions on medium-mass (A > 32) and heavy-mass (A > 55) nuclei influence only the final composition. Medium-mass cases dominate in He-rich bursts, where the reaction flow terminates earlier, while heavy-mass cases appear in mixed H and He bursts with extended rp-process paths reaching A ~ 110. We identify a subset of reactions whose rate uncertainties exert influence on the final 12C yield in helium-rich bursts, which could have important consequences for the mechanism of ignition of carbon superbursts. Our results identify key targets for nuclear reaction experiments to reduce nuclear physics uncertainties in XRB models.
03 Sep 2025
We present a simple and efficient method to incorporate anharmonic effects in the vibrational frequency of molecules within density functional theory (DFT) calculations. This approach is closely related to the traditional vibrational complete interaction (VCI) technique, which uses the harmonic oscillator wavefunctions as the basis. In our implementation, we employ Gaussian-type orbitals (GTOs), with polynomial prefactors, as the basis set to evaluate the anharmonic Hamiltonian. Although these basis functions are non-orthogonal, the matrix elements such as overlap, kinetic energy terms, and position moments can be evaluated analytically. The terms in the Hamiltonian due to the anharmonic potentials are numerically calculated on a Hermite-Quadrature grid. The potentials can be evaluated using any electronic structure method. This framework enables us to accurately calculate the anharmonicity-corrected vibrational frequencies, the fundamental frequencies, and the corrections to bond lengths in diatomic molecules. This method is also generalized to handle coupled anharmonic oscillators, which is essential to model more complex phenomena such as nitrogen tunneling in the umbrella mode of ammonia (NH3) and Fermi resonances in carbon dioxide (CO2)
Non-Hermitian systems can have peculiar degeneracies of eigenstates called exceptional points (EPs). An EP of n degenerate states is said to have order n, and higher-order EPs (HEPs) with n≥3 exhibit rich intrinsic features potential for applications. However, traditional eigenvalue-based searches for HEPs are facing fundamental limitations in terms of complexity and implementation. Here, we propose a design paradigm for HEPs based on a simple property for matrices termed nilpotence and concise inductive procedure. The nilpotence always guarantees a HEP with designated order and helps divide the problem. Our inductive routine can repeatedly double EP order starting from known designs, such as a 2×2 parity-time-symmetric Hamiltonian. By applying our framework, we readily design reciprocal photonic cavity systems operating at HEPs with up to n=14 and find their unconventionally chiral, transparent, and enhanced responses. Our work opens up extensive possibilities for investigations and applications of HEPs in various physical systems.
18 Jul 2020
We present PyFLOSIC, an open-source, general-purpose Python implementation of the Fermi-Löwdin orbital self-interaction correction (FLO-SIC), which is based on the Python simulation of chemistry frame-work (PySCF) electronic structure and quantum chemistry code. Thanks to PySCF, PyFLOSIC can be used with any kind of Gaussian-type basis set, various kinds of radial and angular quadrature grids, and all exchange-correlation functionals within the local density approximation (LDA), generalized-gradient approximation (GGA), and meta-GGA provided in the Libxc and XCFun libraries. A central aspect of FLO-SIC are Fermi-orbital descriptors, which are used to estimate the self-interaction correction. Importantly, they can be initialized automatically within PyFLOSIC and optimized with an interface to the atomic simulation environment, a Python library which provides a variety of powerful gradient-based algorithms for geometry optimization. Although PyFLOSIC has already facilitated applications of FLO-SIC to chemical studies, it offers an excellent starting point for further developments in FLO-SIC approaches, thanks to its use of a high-level programming language and pronounced modularity.
Firms earning prediction plays a vital role in investment decisions, dividends expectation, and share price. It often involves multiple tensor-compatible datasets with non-linear multi-way relationships, spatiotemporal structures, and different levels of sparsity. Current non-linear tensor completion algorithms tend to learn noisy embedding and incur overfitting. This paper focuses on the embedding learning aspect of the tensor completion problem and proposes a new multi-layer neural network architecture for tensor factorization and completion (MLCTR). The network architecture entails multiple advantages: a series of low-rank matrix factorizations (MF) building blocks to minimize overfitting, interleaved transfer functions in each layer for non-linearity, and by-pass connections to reduce the gradient diminishing problem and increase the depths of neural networks. Furthermore, the model employs Stochastic Gradient Descent(SGD) based optimization for fast convergence in training. Our algorithm is highly efficient for imputing missing values in the EPS data. Experiments confirm that our strategy of incorporating non-linearity in factor matrices demonstrates impressive performance in embedding learning and end-to-end tensor models, and outperforms approaches with non-linearity in the phase of reconstructing tensors from factor matrices.
13 Oct 2025
The favorable energy configurations of nuclei at magic numbers of N neutrons and Z protons are fundamental for understanding the evolution of nuclear structure. The Z=50 (tin) isotopic chain is a frontier for such studies, with particular interest in nuclear binding at and around the doubly-magic \textsuperscript{100}Sn isotope. Precise mass measurements of neutron-deficient isotopes provide necessary anchor points for mass models to test extrapolations near the proton drip line, where experimental studies currently remain out of reach. In this work, we report the first Penning trap mass measurement of \textsuperscript{101}Sn. The determined mass excess of −59889.89(96)~keV for \textsuperscript{101}Sn represents a factor of 300 improvement over the current precision and indicates that \textsuperscript{101}Sn is less bound than previously thought. Mass predictions from a recently developed Bayesian model combination (BMC) framework employing statistical machine learning and nuclear masses computed within seven global models based on nuclear Density Functional Theory (DFT) agree within 1σ with experimental masses from the 48≤Z≤52 isotopic chains. This provides confidence in the extrapolation of tin masses down to N=46.
07 Aug 2018
Active learning is a proven pedagogical style that has demonstrated value by
improving students' performance and classroom experience. In spite of the
evidence, adoption of active learning in computer science remains relatively
low. To identify what barriers to adoption exist, an electronic survey was sent
to 369 computer science faculty in a state in the Upper Midwest and to 78
administrators and support staff. Analysis of the responses revealed that time
remained the most commonly reported barrier for faculty that desire to change
their teaching style, with 42.8% of faculty respondents disagreeing with the
statement that they have the time they need to change their teaching style.
Administrators and support staff also indicated that time was a concern but
that otherwise faculty were aware of active learning and had the resources they
need. Reported use of active learning pedagogy was much higher among faculty
that received pedagogical training during their undergraduate or graduate
studies. Given the time constraints of faculty, it is recommended that new
avenues be explored to provide future faculty with exposure to active learning
pedagogy in their undergraduate and graduate training.
12 Oct 2017
 Michigan State University
Michigan State University Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryFacility for Rare Isotope BeamsHope CollegeNational Superconducting Cyclotron LaboratoryReed CollegeCentral Michigan UniversityDavidson CollegeAugustana CollegeJoint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics - Center for the Evolution of the ElementsGettysburg College
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryFacility for Rare Isotope BeamsHope CollegeNational Superconducting Cyclotron LaboratoryReed CollegeCentral Michigan UniversityDavidson CollegeAugustana CollegeJoint Institute for Nuclear Astrophysics - Center for the Evolution of the ElementsGettysburg CollegeTheoretical calculations suggest the presence of low-lying excited states in
25O. Previous experimental searches by means of proton knockout on
26F produced no evidence for such excitations.
We search for excited states in 25O using the ${ {}^{24}\text{O} (d,p)
{}^{25}\text{O} }$ reaction. The theoretical analysis of excited states in
unbound 25,27O is based on the configuration interaction approach that
accounts for couplings to the scattering continuum.
We use invariant-mass spectroscopy to measure neutron-unbound states in
25O. For the theoretical approach, we use the complex-energy Gamow Shell
Model and Density Matrix Renormalization Group method with a finite-range
two-body interaction optimized to the bound states and resonances of
23−26O, assuming a core of 22O. We predict energies, decay widths,
and asymptotic normalization coefficients.
Our calculations in a large spdf space predict several low-lying excited
states in 25O of positive and negative parity, and we obtain an
experimental limit on the relative cross section of a possible ${ {J}^{\pi} =
{1/2}^{+} }statewithrespecttotheground−stateof^{25}$O at
σ1/2+/σg.s.=0.25−0.25+1.0. We also discuss how the
observation of negative parity states in 25O could guide the search for
the low-lying negative parity states in 27O.
Previous experiments based on the proton knockout of 26F suffered from
the low cross sections for the population of excited states in 25O because
of low spectroscopic factors. In this respect, neutron transfer reactions carry
more promise.
Action detection and public traffic safety are crucial aspects of a safe
community and a better society. Monitoring traffic flows in a smart city using
different surveillance cameras can play a significant role in recognizing
accidents and alerting first responders. The utilization of action recognition
(AR) in computer vision tasks has contributed towards high-precision
applications in video surveillance, medical imaging, and digital signal
processing. This paper presents an intensive review focusing on action
recognition in accident detection and autonomous transportation systems for a
smart city. In this paper, we focused on AR systems that used diverse sources
of traffic video capturing, such as static surveillance cameras on traffic
intersections, highway monitoring cameras, drone cameras, and dash-cams.
Through this review, we identified the primary techniques, taxonomies, and
algorithms used in AR for autonomous transportation and accident detection. We
also examined data sets utilized in the AR tasks, identifying the main sources
of datasets and features of the datasets. This paper provides potential
research direction to develop and integrate accident detection systems for
autonomous cars and public traffic safety systems by alerting emergency
personnel and law enforcement in the event of road accidents to minimize human
error in accident reporting and provide a spontaneous response to victims
24 Sep 2019
 Michigan State University
Michigan State University University of Notre Dame
University of Notre Dame University of British Columbia
University of British Columbia Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryUniversity of SurreySimon Fraser UniversityUniversity of ManitobaTRIUMFFacility for Rare Isotope Beams, Michigan State UniversityColorado School of MinesUniversity of YorkUniversity of GuelphSaint Mary’s UniversityCentral Michigan UniversityNational Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan State UniversityNiederrhein University of Applied Sciences
Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryUniversity of SurreySimon Fraser UniversityUniversity of ManitobaTRIUMFFacility for Rare Isotope Beams, Michigan State UniversityColorado School of MinesUniversity of YorkUniversity of GuelphSaint Mary’s UniversityCentral Michigan UniversityNational Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, Michigan State UniversityNiederrhein University of Applied SciencesThe elusive β−p+ decay was observed in 11Be by directly
measuring the emitted protons and their energy distribution for the first time
with the prototype Active Target Time Projection Chamber (pAT-TPC) in an
experiment performed at ISAC-TRIUMF. The measured β−p+ branching
ratio is orders of magnitude larger than any previous theoretical model
predicted. This can be explained by the presence of a narrow resonance in
11B above the proton separation energy.
This article presents the first-ever blockchain which can simultaneously
handle device and data security, which is important for the emerging
Internet-of-Everything (IoE). This article presents a unique concept of
blockchain that integrates hardware security primitives called Physical
Unclonable Functions (PUFs) to solve scalability, latency, and energy
requirement challenges and is called PUFchain. Data management and security
(and privacy) of data, devices, and individuals, are some of the issues in the
IoE architectures that need to be resolved. Integrating the blockchain into the
IoE environment can help solve these issues and helps in the aspects of data
storage and security. This article introduces a new blockchain architecture
called PUFchain and introduces a new consensus algorithm called "Proof of
PUF-Enabled Authentication" (PoP) for deployment in PUFchain. The proposed PoP
is the PUF integration into our previously proposed Proof-of-Authentication
(PoAh) consensus algorithm and can be called "Hardware-Assisted
Proof-of-Authentication (HA-PoAh)". However, PUF integration is possible in the
existing and new consensus algorithms. PoP utilizes PUFs which are responsible
for generating a unique key that cannot be cloned and hence provide the highest
level of security. A PUF uses the nanoelectronic manufacturing variations that
are introduced during the fabrication of an integrated circuit to generate the
keys. Hence, once generated from a PUF module, the keys cannot be cloned or
generated from any other module. PUFchain uses a PUF and Hashing module which
performs the necessary cryptographic functions. Hence the mining process is
offloaded to the hardware module which reduces the processing times. PoP is
approximately 1,000X faster than the well-established Proof-of-Work (PoW) and
5X faster than Proof-of-Authentication (PoAh).
The chiral Fe3O(NC5H5)3(O2CC6H5)6 molecular cation, with C3
symmetry, is composed of three six-fold coordinated spin-carrying Fe3+
cations that form a perfect equilateral triangle. Experimental reports
demonstrating the spin-electric effect in this system also identify the
presence of a magnetic uni-axis and suggest that this molecule may be a good
candidate for an externally controllable molecular qubit. Here we demonstrate,
using standard density-functional methods, that the spin-electric behavior of
this molecule could be even more interesting as there are energetically
competitive reference states associated with both high and low local spins
(S=5/2 vs. S=1/2) on the Fe3+ ions. Each of these structures allow for
spin-electric ground states. We find that qualitative differences in the
broadening of the Fe(2s) and O(1s) core levels and the single-spin anisotropy
Hamiltonian may be used to confirm whether the high-spin manifold is lower in
energy than the low-spin manifold.
While 5G mobile communication systems are currently in deployment,
researchers around the world have already started to discuss 6G technology and
funding agencies started their first programs with a 6G label. Although it may
seem like a good idea from a historical point of view with returning
generations every decade, this contribution will show that there is a great
risk of introducing 6G labels at this time. While the reasons to not talk about
6G yet are manifold, some of the more dominant ones are i.) there exists a lack
of real technology advancements introduced by a potential 6G system; ii.) the
flexibility of the 5G communication system introduced by softwarization
concepts, such as in the Internet community, allows for daily updates; and
iii.) introducing widespread 6G discussions can have a negative impact on the
deployment and evolution of 5G with completely new business cases and customer
ecosystems compared to its predecessors. Finally, as we do not believe that 5G
is the end of our journey, we will provide an outlook on the future of mobile
communication systems, independent of the current mainstream discussion.
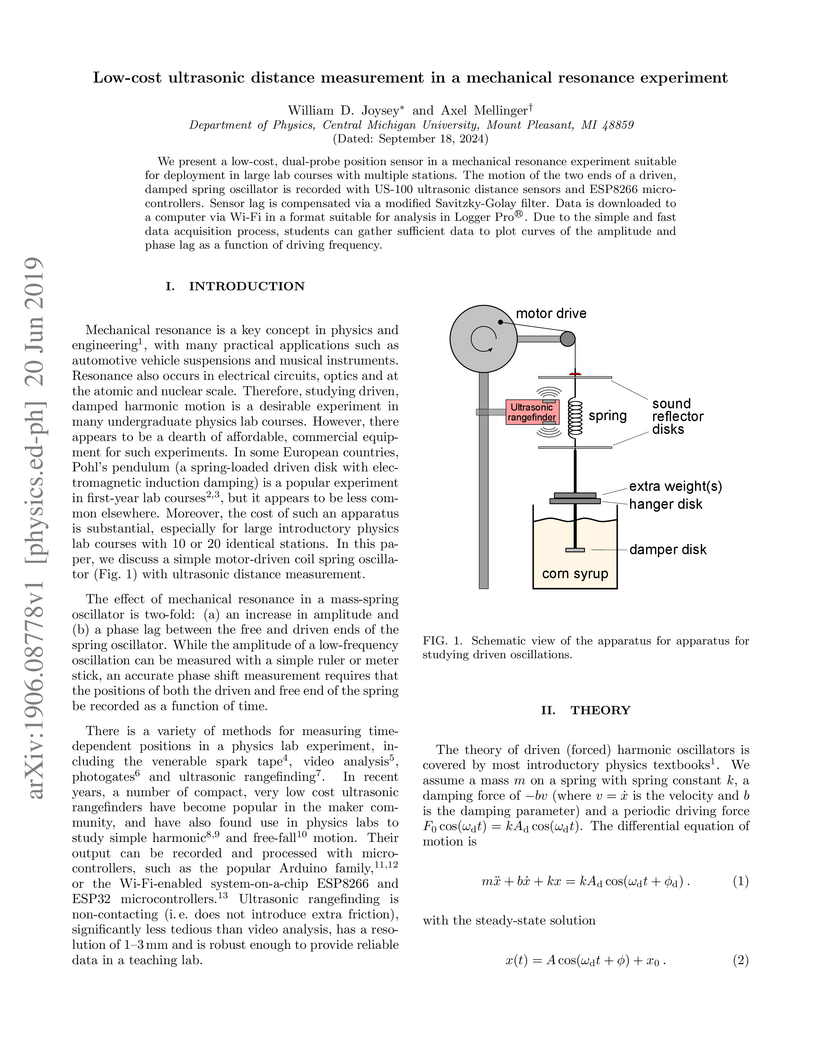
We present a low-cost, dual-probe position sensor in a mechanical resonance
experiment suitable for deployment in large lab courses with multiple stations.
The motion of the two ends of a driven, damped spring oscillator is recorded
with US-100 ultrasonic distance sensors and ESP8266 microcontrollers. Sensor
lag is compensated via a modified Savitzky-Golay filter. Data is downloaded to
a computer via Wi-Fi in a format suitable for analysis in Logger Pro. Due to
the simple and fast data acquisition process, students can gather sufficient
data to plot curves of the amplitude and phase lag as a function of driving
frequency.
19 Apr 2021
Two-dimensional materials on metallic surfaces or stacked one on top of the
other can form a variety of moir\'e superstructures depending on the possible
parameter and symmetry mismatch and misorientation angle. In most cases, such
as incommensurate lattices or identical lattices but with a small twist angle,
the common periodicity may be very large, thus making numerical simulations
prohibitive. We propose here a general procedure to determine the minimal
simulation cell which approximates, within a certain tolerance and a certain
size, the primitive cell of the common superlattice, given the two interfacing
lattices and the relative orientation angle. As case studies to validate our
procedure, we report two applications of particular interest: the case of
misaligned hexagonal/hexagonal identical lattices, describing a twisted
graphene bilayer or a graphene monolayer grown on Ni(111), and the case of
hexagonal/square lattices, describing for instance a graphene monolayer grown
on Ni(100) surface. The first one, which has also analytic solutions,
constitutes a solid benchmark for the algorithm; the second one shows that a
very nice description of the experimental observations can be obtained also
using the resulting relatively small coincidence cells.
13 Oct 2020
Background: In the "island of inversion", ground states of neutron-rich sd-shell nuclei exhibit strong admixtures of intruder configurations from the fp shell. The nucleus 30Mg, located at the boundary of the island of inversion, serves as a cornerstone to track the structural evolution as one approaches this region. Purpose: Spin-parity assignments for excited states in 30Mg, especially negative-parity levels, have yet to be established. In the present work, the nuclear structure of 30Mg was investigated by in-beam γ-ray spectroscopy mainly focusing on firm spin-parity determinations. Method: High-intensity rare-isotope beams of 31Mg, 32Mg, 34Si, and 35P bombarded a Be target to induce nucleon removal reactions populating states in 30Mg. γ rays were detected by the state-of-the-art γ-ray tracking array GRETINA. For the direct one-neutron removal reaction, final-state exclusive cross sections and parallel momentum distributions were deduced. Multi-nucleon removal reactions from different projectiles were exploited to gain complementary information. Results: With the aid of the parallel momentum distributions, an updated level scheme with revised spin-parity assignments was constructed. Spectroscopic factors associated with each state were also deduced. Conclusions: Results were confronted with large-scale shell-model calculations using two different effective interactions, showing excellent agreement with the present level scheme. However, a marked difference in the spectroscopic factors indicates that the full delineation of the transition into the island of inversion remains a challenge for theoretical models.
Multimessenger observations of the neutron star merger event GW170817 have
re-energized the debate over the astrophysical origins of the most massive
elements via the r-process nucleosynthesis. A key aspect of such studies is
comparing astronomical observations to theoretical nucleosynthesis yields in a
meaningful way. To perform realistic nucleosynthesis calculations,
understanding the uncertainty in microphysics details such as nuclear reaction
rates is as essential as understanding uncertainties in modeling the
astrophysical environment. We present an investigation of neutron capture rate
calculations' uncertainty away from stability using the Hauser-Feshbach model.
We provide a quantitative measure of the calculations' dependability when we
extrapolate models of statistical properties to nuclei in an r-process network.
We select several level density and gamma-ray strength models appropriate for
neutron-capture and use them to calculate the reaction rate for each nucleus in
the network. We observe how statistical properties affect the theoretical
reaction rates. The rates are then sampled with the Monte Carlo technique and
used in network calculations to map the range of possible r-process abundances.
The results show that neutron capture rates can vary by a couple of orders of
magnitude between calculations. Phenomenological models provide smoother
results than semi-microscopic. They cannot, however, reproduce nuclear
structure changes such as shell closures. While semi-microscopic models predict
nuclear structure effects away from stability, it is not clear that these
results are quantitatively accurate. The effect of the uncertainty on r-process
yields is large enough to impede comparisons between observation and
calculations. Progress in developing better microscopic models of gamma
strengths and level densities is urgently needed to improve the fidelity of
r-process models.
 Stanford UniversityBoston CollegeUniversity of OuluSouthwest Research InstituteAmerican Association of Variable Star ObserversMontana State UniversityCentral Michigan UniversityU.S. Naval ObservatoryRoyal Observatory of BelgiumNRC Herzberg Astronomy and Astrophysics Research CentreNational Solar ObservatoryHigh Altitude ObservatoryHarvard College Observatory
Stanford UniversityBoston CollegeUniversity of OuluSouthwest Research InstituteAmerican Association of Variable Star ObserversMontana State UniversityCentral Michigan UniversityU.S. Naval ObservatoryRoyal Observatory of BelgiumNRC Herzberg Astronomy and Astrophysics Research CentreNational Solar ObservatoryHigh Altitude ObservatoryHarvard College ObservatoryOver the past decades and even centuries, the astronomical community has
accumulated a signif-icant heritage of recorded observations of a great many
astronomical objects. Those records con-tain irreplaceable information about
long-term evolutionary and non-evolutionary changes in our Universe, and their
preservation and digitization is vital. Unfortunately, most of those data risk
becoming degraded and thence totally lost. We hereby call upon the astronomical
community and US funding agencies to recognize the gravity of the situation,
and to commit to an interna-tional preservation and digitization efforts
through comprehensive long-term planning supported by adequate resources,
prioritizing where the expected scientific gains, vulnerability of the
origi-nals and availability of relevant infrastructure so dictates. The
importance and urgency of this issue has been recognized recently by General
Assembly XXX of the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in its Resolution
B3: "on preservation, digitization and scientific exploration of his-torical
astronomical data". We outline the rationale of this promotion, provide
examples of new science through successful recovery efforts, and review the
potential losses to science if nothing it done.
05 Oct 2020
The recent availability of quantum annealers has fueled a new area of
information technology where such devices are applied to address practically
motivated and computationally difficult problems with hardware that exploits
quantum mechanical phenomena. D-Wave annealers are promising platforms to solve
these problems in the form of quadratic unconstrained binary optimization. Here
we provide a formulation of the Chinese postman problem that can be used as a
tool for probing the local connectivity of graphs and networks. We treat the
problem classically with a tabu algorithm and using a D-Wave device. We
systematically analyze computational parameters associated with the specific
hardware. Our results clarify how the interplay between the embedding due to
limited connectivity of the Chimera graph, the definition of logical qubits,
and the role of spin-reversal controls the probability of reaching the expected
solution.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.