Civil Aviation University of China
Gaussian Difference, a method for instance-level change detection in 3D scenes, leverages 4D Gaussian Splatting combined with 2D instance segmentation and tracking to identify specific object alterations. This approach demonstrates enhanced robustness to lighting variations and achieves a total processing speed-up of approximately 7x compared to previous NeRF-based state-of-the-art methods.
28 Sep 2025
In this paper, a novel time domain sampling method based on the initial arrival time of waves is proposed to reconstruct acoustic sources, including point sources, curve sources, surface sources and block sources. The uniqueness of reconstructing sources whose spatial support is a convex region is proved. Theoretical analyses are provided to demonstrate the validity of the proposed sampling method in reconstructing various types of sound sources. The proposed algorithm does not involve the time integral, exhibits high computational efficiency, and demonstrates strong noise resistance. Numerical experiments are conducted to show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
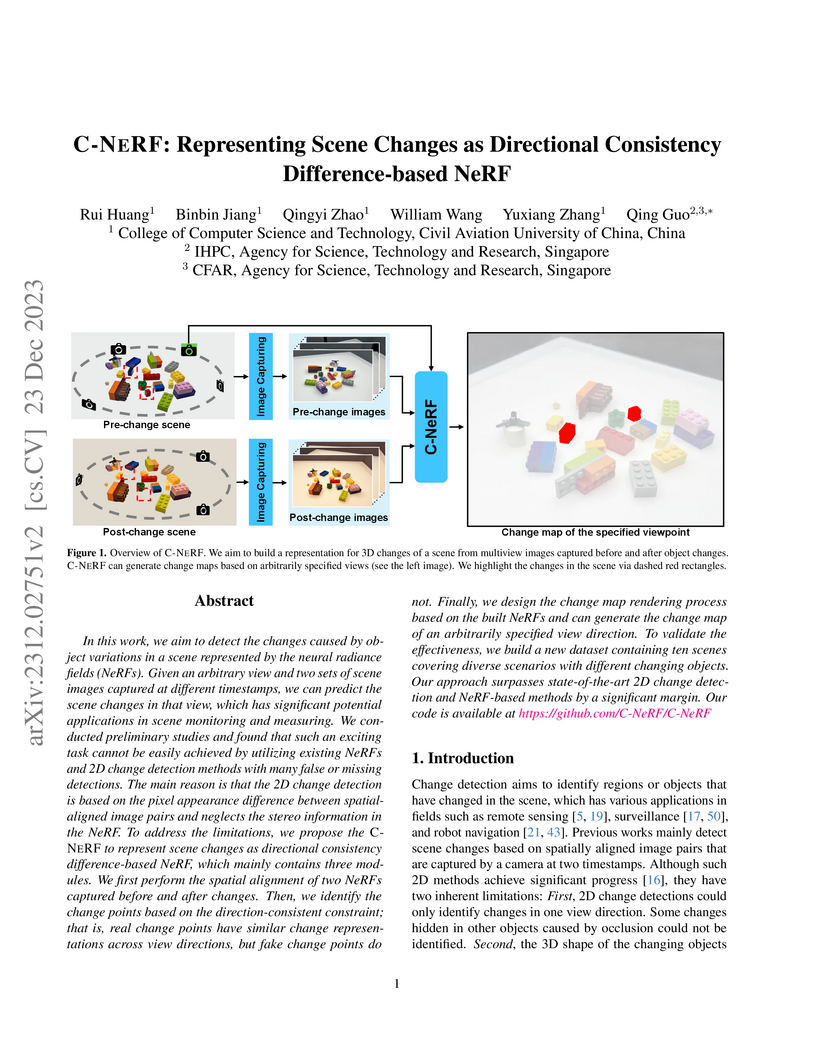
In this work, we aim to detect the changes caused by object variations in a scene represented by the neural radiance fields (NeRFs). Given an arbitrary view and two sets of scene images captured at different timestamps, we can predict the scene changes in that view, which has significant potential applications in scene monitoring and measuring. We conducted preliminary studies and found that such an exciting task cannot be easily achieved by utilizing existing NeRFs and 2D change detection methods with many false or missing detections. The main reason is that the 2D change detection is based on the pixel appearance difference between spatial-aligned image pairs and neglects the stereo information in the NeRF. To address the limitations, we propose the C-NERF to represent scene changes as directional consistency difference-based NeRF, which mainly contains three modules. We first perform the spatial alignment of two NeRFs captured before and after changes. Then, we identify the change points based on the direction-consistent constraint; that is, real change points have similar change representations across view directions, but fake change points do not. Finally, we design the change map rendering process based on the built NeRFs and can generate the change map of an arbitrarily specified view direction. To validate the effectiveness, we build a new dataset containing ten scenes covering diverse scenarios with different changing objects. Our approach surpasses state-of-the-art 2D change detection and NeRF-based methods by a significant margin.
Vision transformers have achieved encouraging progress in various computer vision tasks. A common belief is that this is attributed to the capability of self-attention in modeling the global dependencies among feature tokens. However, self-attention still faces several challenges in dense prediction tasks, including high computational complexity and absence of desirable inductive bias. To alleviate these issues, the potential advantages of combining vision transformers with Gabor filters are revisited, and a learnable Gabor filter (LGF) using convolution is proposed. The LGF does not rely on self-attention, and it is used to simulate the response of fundamental cells in the biological visual system to the input images. This encourages vision transformers to focus on discriminative feature representations of targets across different scales and orientations. In addition, a Bionic Focal Vision (BFV) block is designed based on the LGF. This block draws inspiration from neuroscience and introduces a Dual-Path Feed Forward Network (DPFFN) to emulate the parallel and cascaded information processing scheme of the biological visual cortex. Furthermore, a unified and efficient family of pyramid backbone networks called Focal Vision Transformers (FViTs) is developed by stacking BFV blocks. Experimental results indicate that FViTs demonstrate superior performance in various vision tasks. In terms of computational efficiency and scalability, FViTs show significant advantages compared with other counterparts.
In recent years, the remarkable success of deep neural networks (DNNs) in computer vision is largely due to large-scale, high-quality labeled datasets. Training directly on real-world datasets with label noise may result in overfitting. The traditional method is limited to deal with closed set label noise, where noisy training data has true class labels within the known label space. However, there are some real-world datasets containing open set label noise, which means that some samples belong to an unknown class outside the known label space. To address the open set label noise problem, we introduce a method based on Robust Sample Selection and Margin-Guided Module (RSS-MGM). Firstly, unlike the prior clean sample selection approach, which only select a limited number of clean samples, a robust sample selection module combines small loss selection or high-confidence sample selection to obtain more clean samples. Secondly, to efficiently distinguish open set label noise and closed set ones, margin functions are designed to filter open-set data and closed set data. Thirdly, different processing methods are selected for different types of samples in order to fully utilize the data's prior information and optimize the whole model. Furthermore, extensive experimental results with noisy labeled data from benchmark datasets and real-world datasets, such as CIFAR-100N-C, CIFAR80N-O, WebFG-469, and Food101N, indicate that our approach outperforms many state-of-the-art label noise learning methods. Especially, it can more accurately divide open set label noise samples and closed set ones.
16 May 2025
We propose an adaptive way to choose the anchoring parameters for the Halpern
iteration to find a fixed point of a nonexpansive mapping in a real Hilbert
space. We prove strong convergence of this adaptive Halpern iteration and
obtain the rate of asymptotic regularity at least O(1/k), where k is the number
of iterations. Numerical experiments are also provided to show advantages and
outperformance of our adaptive Halpern algorithm over the standard Halpern
algorithm.
20 Oct 2025
Arm-locking frequency stabilization is a key technique for suppressing laser frequency noise in space-based gravitational-wave detectors. The robustness of the arm-locking control loop is crucial for maintaining laser frequency stability, which directly impacts the accuracy of gravitational-wave measurements. In this work, a parametric stability analysis framework is developed by combining the D-subdivision theory with the Semi-Discretization method to map the stability regions of arm-locking systems in the parameter space and identify their critical stability boundaries. Based on the frequency-domain characteristics, a robust arm-locking controller is designed to enhance loop stability under parameter perturbations. Theoretical analysis and time-domain simulations confirm that the proposed controller maintains closed-loop stability and realize suppression of laser frequency noise against parameter perturbation.
Owing to advancements in deep learning technology, Vision Transformers (ViTs) have demonstrated impressive performance in various computer vision tasks. Nonetheless, ViTs still face some challenges, such as high computational complexity and the absence of desirable inductive biases. To alleviate these issues, {the potential advantages of combining eagle vision with ViTs are explored. We summarize a Bi-Fovea Visual Interaction (BFVI) structure inspired by the unique physiological and visual characteristics of eagle eyes. A novel Bi-Fovea Self-Attention (BFSA) mechanism and Bi-Fovea Feedforward Network (BFFN) are proposed based on this structural design approach, which can be used to mimic the hierarchical and parallel information processing scheme of the biological visual cortex, enabling networks to learn feature representations of targets in a coarse-to-fine manner. Furthermore, a Bionic Eagle Vision (BEV) block is designed as the basic building unit based on the BFSA mechanism and BFFN. By stacking BEV blocks, a unified and efficient family of pyramid backbone networks called Eagle Vision Transformers (EViTs) is developed. Experimental results show that EViTs exhibit highly competitive performance in various computer vision tasks, such as image classification, object detection and semantic segmentation. Compared with other approaches, EViTs have significant advantages, especially in terms of performance and computational efficiency. Code is available at this https URL
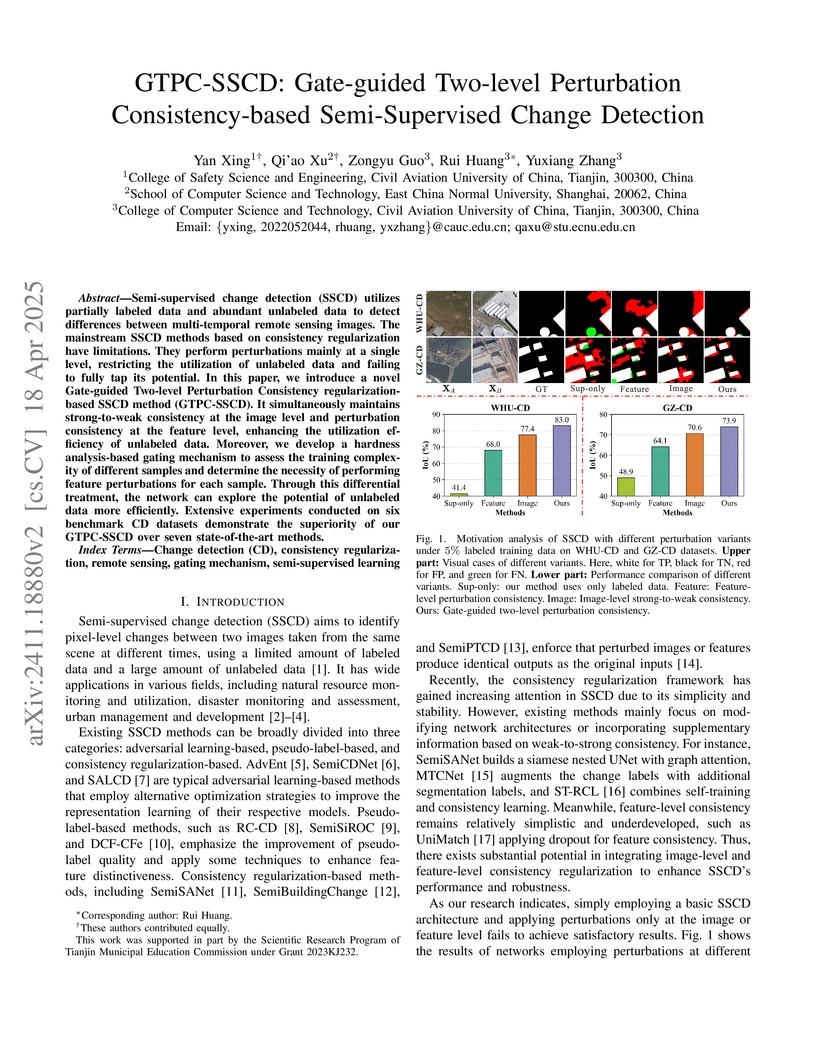
Semi-supervised change detection (SSCD) utilizes partially labeled data and
abundant unlabeled data to detect differences between multi-temporal remote
sensing images. The mainstream SSCD methods based on consistency regularization
have limitations. They perform perturbations mainly at a single level,
restricting the utilization of unlabeled data and failing to fully tap its
potential. In this paper, we introduce a novel Gate-guided Two-level
Perturbation Consistency regularization-based SSCD method (GTPC-SSCD). It
simultaneously maintains strong-to-weak consistency at the image level and
perturbation consistency at the feature level, enhancing the utilization
efficiency of unlabeled data. Moreover, we develop a hardness analysis-based
gating mechanism to assess the training complexity of different samples and
determine the necessity of performing feature perturbations for each sample.
Through this differential treatment, the network can explore the potential of
unlabeled data more efficiently. Extensive experiments conducted on six
benchmark CD datasets demonstrate the superiority of our GTPC-SSCD over seven
state-of-the-art methods.
25 Jan 2018
There are increasing real-time live applications in virtual reality, where it
plays an important role in capturing and retargetting 3D human pose. But it is
still challenging to estimate accurate 3D pose from consumer imaging devices
such as depth camera. This paper presents a novel cascaded 3D full-body pose
regression method to estimate accurate pose from a single depth image at 100
fps. The key idea is to train cascaded regressors based on Gradient Boosting
algorithm from pre-recorded human motion capture database. By incorporating
hierarchical kinematics model of human pose into the learning procedure, we can
directly estimate accurate 3D joint angles instead of joint positions. The
biggest advantage of this model is that the bone length can be preserved during
the whole 3D pose estimation procedure, which leads to more effective features
and higher pose estimation accuracy. Our method can be used as an
initialization procedure when combining with tracking methods. We demonstrate
the power of our method on a wide range of synthesized human motion data from
CMU mocap database, Human3.6M dataset and real human movements data captured in
real time. In our comparison against previous 3D pose estimation methods and
commercial system such as Kinect 2017, we achieve the state-of-the-art
accuracy.
Existing video captioning methods merely provide shallow or simplistic
representations of object behaviors, resulting in superficial and ambiguous
descriptions. However, object behavior is dynamic and complex. To
comprehensively capture the essence of object behavior, we propose a dynamic
action semantic-aware graph transformer. Firstly, a multi-scale temporal
modeling module is designed to flexibly learn long and short-term latent action
features. It not only acquires latent action features across time scales, but
also considers local latent action details, enhancing the coherence and
sensitiveness of latent action representations. Secondly, a visual-action
semantic aware module is proposed to adaptively capture semantic
representations related to object behavior, enhancing the richness and
accurateness of action representations. By harnessing the collaborative efforts
of these two modules,we can acquire rich behavior representations to generate
human-like natural descriptions. Finally, this rich behavior representations
and object representations are used to construct a temporal objects-action
graph, which is fed into the graph transformer to model the complex temporal
dependencies between objects and actions. To avoid adding complexity in the
inference phase, the behavioral knowledge of the objects will be distilled into
a simple network through knowledge distillation. The experimental results on
MSVD and MSR-VTT datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves
significant performance improvements across multiple metrics.
11 Aug 2025
We describe the 31-derivations and transposed Poisson structures of the Nambu 3-Lie algebras Aωδ and Af,k. Specifically, we first present that Aωδ is finitely generated and graded. Then we find that Aωδ has non-trivial 31-derivations and admits only trivial transposed Poisson structures. The 3-Lie algebra Af,k admits non-trivial transposed Poisson structures.
Existing Mamba-based approaches in remote sensing change detection have enhanced scanning models, yet remain limited by their inability to capture long-range dependencies between image channels effectively, which restricts their feature representation capabilities. To address this limitation, we propose a 3D selective scan module (3D-SSM) that captures global information from both the spatial plane and channel perspectives, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of the this http URL on the 3D-SSM, we present two key components: a spatiotemporal interaction module (SIM) and a multi-branch feature extraction module (MBFEM). The SIM facilitates bi-temporal feature integration by enabling interactions between global and local features across images from different time points, thereby enhancing the detection of subtle changes. Meanwhile, the MBFEM combines features from the frequency domain, spatial domain, and 3D-SSM to provide a rich representation of contextual information within the image. Our proposed method demonstrates favourable performance compared to state-of-the-art change detection methods on five benchmark datasets through extensive experiments. Code is available at this https URL
Semi-supervised change detection (SSCD) utilizes partially labeled data and a
large amount of unlabeled data to detect changes. However, the
transformer-based SSCD network does not perform as well as the
convolution-based SSCD network due to the lack of labeled data. To overcome
this limitation, we introduce a new decoder called Cross Branch Feature Fusion
CBFF, which combines the strengths of both local convolutional branch and
global transformer branch. The convolutional branch is easy to learn and can
produce high-quality features with a small amount of labeled data. The
transformer branch, on the other hand, can extract global context features but
is hard to learn without a lot of labeled data. Using CBFF, we build our SSCD
model based on a strong-to-weak consistency strategy. Through comprehensive
experiments on WHU-CD and LEVIR-CD datasets, we have demonstrated the
superiority of our method over seven state-of-the-art SSCD methods.
24 Mar 2025
Localization of robots using subsurface features observed by
ground-penetrating radar (GPR) enhances and adds robustness to common sensor
modalities, as subsurface features are less affected by weather, seasons, and
surface changes. We introduce an innovative multimodal odometry approach using
inputs from GPR, an inertial measurement unit (IMU), and a wheel encoder. To
efficiently address GPR signal noise, we introduce an advanced feature
representation called the subsurface feature matrix (SFM). The SFM leverages
frequency domain data and identifies peaks within radar scans. Additionally, we
propose a novel feature matching method that estimates GPR displacement by
aligning SFMs. The integrations from these three input sources are consolidated
using a factor graph approach to achieve multimodal robot odometry. Our method
has been developed and evaluated with the CMU-GPR public dataset, demonstrating
improvements in accuracy and robustness with real-time performance in robotic
odometry tasks.
It is a challenging problem that solving the \textit{multivariate linear
model} (MLM) Ax=b with the ℓ1-norm
approximation method such that ∣∣Ax−b∣∣1, the
ℓ1-norm of the \textit{residual error vector} (REV), is minimized. In
this work, our contributions lie in two aspects: firstly, the equivalence
theorem for the structure of the ℓ1-norm optimal solution to the MLM is
proposed and proved; secondly, a unified algorithmic framework for solving the
MLM with ℓ1-norm optimization is proposed and six novel algorithms
(L1-GPRS, L1-TNIPM, L1-HP, L1-IST, L1-ADM, L1-POB) are designed. There are
three significant characteristics in the algorithms discussed: they are
implemented with simple matrix operations which do not depend on specific
optimization solvers; they are described with algorithmic pseudo-codes and
implemented with Python and Octave/MATLAB which means easy usage; and the high
accuracy and efficiency of our six new algorithms can be achieved successfully
in the scenarios with different levels of data redundancy. We hope that the
unified theoretic and algorithmic framework with source code released on GitHub
could motivate the applications of the ℓ1-norm optimization for parameter
estimation of MLM arising in science, technology, engineering, mathematics,
economics, and so on.
16 May 2025
The difference-of-convex algorithm (DCA) and its variants are the most
popular methods to solve the difference-of-convex optimization problem. Each
iteration of them is reduced to a convex optimization problem, which generally
needs to be solved by iterative methods such as proximal gradient algorithm.
However, these algorithms essentially belong to some iterative methods of fixed
point problems of averaged mappings, and their convergence speed is generally
slow. Furthermore, there is seldom research on the termination rule of these
iterative algorithms solving the subproblem of DCA. To overcome these defects,
we ffrstly show that the subproblem of the linearized proximal method (LPM) in
each iteration is equal to the ffxed point problem of a contraction. Secondly,
by using Picard iteration to approximately solve the subproblem of LPM in each
iteration, we propose a contractive difference-ofconvex algorithm (cDCA) where
an adaptive termination rule is presented. Both global subsequential
convergence and global convergence of the whole sequence of cDCA are
established. Finally, preliminary results from numerical experiments are
promising.
Change detection, a critical task in remote sensing and computer vision, aims
to identify pixel-level differences between image pairs captured at the same
geographic area but different times. It faces numerous challenges such as
illumination variation, seasonal changes, background interference, and shooting
angles, especially with a large time gap between images. While current methods
have advanced, they often overlook temporal dependencies and overemphasize
prominent changes while ignoring subtle but equally important changes. To
address these limitations, we introduce \textbf{CEBSNet}, a novel
change-excited and background-suppressed network with temporal dependency
modeling for change detection. During the feature extraction, we utilize a
simple Channel Swap Module (CSM) to model temporal dependency, reducing
differences and noise. The Feature Excitation and Suppression Module (FESM) is
developed to capture both obvious and subtle changes, maintaining the integrity
of change regions. Additionally, we design a Pyramid-Aware Spatial-Channel
Attention module (PASCA) to enhance the ability to detect change regions at
different sizes and focus on critical regions. We conduct extensive experiments
on three common street view datasets and two remote sensing datasets, and our
method achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
18 Jun 2025
Flag codes are a class of multishot network codes comprising sequences of nested subspaces (flags) within the vector space Fqn, where q is a prime power. In this paper, we propose a family of constructions for full flag codes based on partial spreads. The distances of this family include maximum distance (optimum distance flag codes), second-maximum distance (quasi-optimum distance flag codes), as well as other feasible values. The structure of these flag codes resembles that of a \textquotedblleft sandwich", consisting of one layer of companion matrix and two layers of partial spreads. Furthermore, we present an efficient decoding algorithm for these codes.
22 Jul 2025
Sum-rank metric codes, as a generalization of Hamming codes and rank metric codes, have important applications in fields such as multi-shot linear network coding, space-time coding and distributed storage systems. The purpose of this study is to construct sum-rank metric codes based on orthogonal spaces over finite fields, and calculate the list sizes outputted by different decoding algorithms. The following achievements have been obtained.
In this study, we construct a cyclic orthogonal group of order qn−1 and an Abelian non-cyclic orthogonal group of order (qn−1)2 based on the companion matrices of primitive polynomials over finite fields. By selecting different subspace generating matrices, maximum rank distance (MRD) codes with parameters (n×2n,q2n,n)q and (n×4n,q4n,n)q are constructed respectively. Two methods for constructing sum-rank metric codes are proposed for the constructed MRD codes, and the list sizes outputted under the list decoding algorithm are calculated. Subsequently, the [n,k,d]qn/q-system is used to relate sum-rank metric codes to subspace designs. The list size of sum-rank metric codes under the list decoding algorithm is calculated based on subspace designs. This calculation method improves the decoding success rate compared with traditional methods.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.