GREYC
This paper addresses the problem of exemplar-based texture synthesis. We introduce NIFTY, a hybrid framework that combines recent insights on diffusion models trained with convolutional neural networks, and classical patch-based texture optimization techniques. NIFTY is a non-parametric flow-matching model built on non-local patch matching, which avoids the need for neural network training while alleviating common shortcomings of patch-based methods, such as poor initialization or visual artifacts. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach compared to representative methods from the literature. Code is available at this https URL
Counterfactual explanations have shown promising results as a post-hoc framework to make image classifiers more explainable. In this paper, we propose DiME, a method allowing the generation of counterfactual images using the recent diffusion models. By leveraging the guided generative diffusion process, our proposed methodology shows how to use the gradients of the target classifier to generate counterfactual explanations of input instances. Further, we analyze current approaches to evaluate spurious correlations and extend the evaluation measurements by proposing a new metric: Correlation Difference. Our experimental validations show that the proposed algorithm surpasses previous State-of-the-Art results on 5 out of 6 metrics on CelebA.
Recent state-of-the-art algorithms in photometric stereo rely on neural networks and operate either through prior learning or inverse rendering optimization. Here, we revisit the problem of calibrated photometric stereo by leveraging recent advances in 3D inverse rendering using the Gaussian Splatting formalism. This allows us to parameterize the 3D scene to be reconstructed and optimize it in a more interpretable manner. Our approach incorporates a simplified model for light representation and demonstrates the potential of the Gaussian Splatting rendering engine for the photometric stereo problem.
Achieving high-fidelity 3D surface reconstruction while preserving fine details remains challenging, especially in the presence of materials with complex reflectance properties and without a dense-view setup. In this paper, we introduce a versatile framework that incorporates multi-view normal and optionally reflectance maps into radiance-based surface reconstruction. Our approach employs a pixel-wise joint re-parametrization of reflectance and surface normals, representing them as a vector of radiances under simulated, varying illumination. This formulation enables seamless incorporation into standard surface reconstruction pipelines, such as traditional multi-view stereo (MVS) frameworks or modern neural volume rendering (NVR) ones. Combined with the latter, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on multi-view photometric stereo (MVPS) benchmark datasets, including DiLiGenT-MV, LUCES-MV and Skoltech3D. In particular, our method excels in reconstructing fine-grained details and handling challenging visibility conditions. The present paper is an extended version of the earlier conference paper by Brument et al. (in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024), featuring an accelerated and more robust algorithm as well as a broader empirical evaluation. The code and data relative to this article is available at this https URL.
In recent years, Transformer-based auto-attention mechanisms have been
successfully applied to the analysis of a variety of context-reliant data
types, from texts to images and beyond, including data from non-Euclidean
geometries. In this paper, we present such a mechanism, designed to classify
sequences of Symmetric Positive Definite matrices while preserving their
Riemannian geometry throughout the analysis. We apply our method to automatic
sleep staging on timeseries of EEG-derived covariance matrices from a standard
dataset, obtaining high levels of stage-wise performance.
A multi-scale network (MS-PS) combined with a new comprehensive synthetic dataset enhances calibrated photometric stereo, achieving state-of-the-art 3D surface normal estimation for objects with complex non-Lambertian reflectance. The approach reduced mean angular error on the DiLiGenT benchmark to 5.84 degrees and on DiLiGenT10^2 to 11.33 degrees, outperforming previous methods.
In a real Hilbert space setting, we study the convergence properties of an inexact gradient algorithm featuring both viscous and Hessian driven damping for convex differentiable optimization. In this algorithm, the gradient evaluation can be subject to deterministic and stochastic perturbations. In the deterministic case, we show that under appropriate summability assumptions on the perturbation, our algorithm enjoys fast convergence of the objective values, of the gradients and weak convergence of the iterates toward a minimizer of the objective. In the stochastic case, assuming the perturbation is zero-mean, we can weaken our summability assumptions on the error variance and provide fast convergence of the values both in expectation and almost surely. We also improve the convergence rates from O(⋅) to o(⋅) in almost sure sense. We also prove almost sure summability property of the gradients, which implies the almost sure fast convergence of the gradients towards zero. We will highlight the trade-off between fast convergence and the applicable regime on the sequence of errors in the gradient computations. We finally report some numerical results to support our findings.
Visual transformers have achieved remarkable performance in image
classification tasks, but this performance gain has come at the cost of
interpretability. One of the main obstacles to the interpretation of
transformers is the self-attention mechanism, which mixes visual information
across the whole image in a complex way. In this paper, we propose Hindered
Transformer (HiT), a novel interpretable by design architecture inspired by
visual transformers. Our proposed architecture rethinks the design of
transformers to better disentangle patch influences at the classification
stage. Ultimately, HiT can be interpreted as a linear combination of
patch-level information. We show that the advantages of our approach in terms
of explicability come with a reasonable trade-off in performance, making it an
attractive alternative for applications where interpretability is paramount.
In data-scarce scenarios, deep learning models often overfit to noise and irrelevant patterns, which limits their ability to generalize to unseen samples. To address these challenges in medical image segmentation, we introduce Diff-UMamba, a novel architecture that combines the UNet framework with the mamba mechanism to model long-range dependencies. At the heart of Diff-UMamba is a noise reduction module, which employs a signal differencing strategy to suppress noisy or irrelevant activations within the encoder. This encourages the model to filter out spurious features and enhance task-relevant representations, thereby improving its focus on clinically significant regions. As a result, the architecture achieves improved segmentation accuracy and robustness, particularly in low-data settings. Diff-UMamba is evaluated on multiple public datasets, including medical segmentation decathalon dataset (lung and pancreas) and AIIB23, demonstrating consistent performance gains of 1-3% over baseline methods in various segmentation tasks. To further assess performance under limited data conditions, additional experiments are conducted on the BraTS-21 dataset by varying the proportion of available training samples. The approach is also validated on a small internal non-small cell lung cancer dataset for the segmentation of gross tumor volume in cone beam CT, where it achieves a 4-5% improvement over baseline.
The use of optimal transport cost for learning generative models has become popular with Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Networks (WGAN). Training of WGAN relies on a theoretical background: the calculation of the gradient of the optimal transport cost with respect to the generative model parameters. We first demonstrate that such gradient may not be defined, which can result in numerical instabilities during gradient-based optimization. We address this issue by stating a valid differentiation theorem in the case of entropic regularized transport and specify conditions under which existence is ensured. By exploiting the discrete nature of empirical data, we formulate the gradient in a semi-discrete setting and propose an algorithm for the optimization of the generative model parameters. Finally, we illustrate numerically the advantage of the proposed framework.
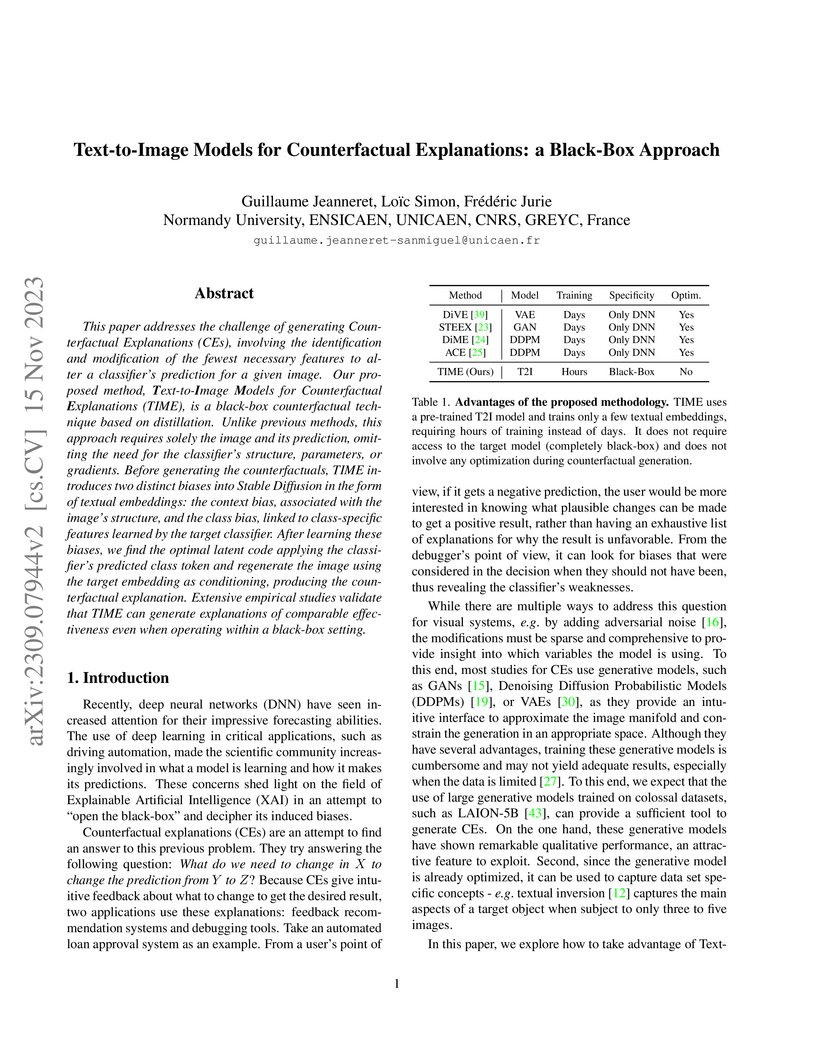
This paper addresses the challenge of generating Counterfactual Explanations (CEs), involving the identification and modification of the fewest necessary features to alter a classifier's prediction for a given image. Our proposed method, Text-to-Image Models for Counterfactual Explanations (TIME), is a black-box counterfactual technique based on distillation. Unlike previous methods, this approach requires solely the image and its prediction, omitting the need for the classifier's structure, parameters, or gradients. Before generating the counterfactuals, TIME introduces two distinct biases into Stable Diffusion in the form of textual embeddings: the context bias, associated with the image's structure, and the class bias, linked to class-specific features learned by the target classifier. After learning these biases, we find the optimal latent code applying the classifier's predicted class token and regenerate the image using the target embedding as conditioning, producing the counterfactual explanation. Extensive empirical studies validate that TIME can generate explanations of comparable effectiveness even when operating within a black-box setting.
03 Jan 2018
In this paper, we consider a class of Forward--Backward (FB) splitting methods that includes several variants (e.g. inertial schemes, FISTA) for minimizing the sum of two proper convex and lower semi-continuous functions, one of which has a Lipschitz continuous gradient, and the other is partly smooth relatively to a smooth active manifold M. We propose a unified framework, under which we show that, this class of FB-type algorithms (i) correctly identifies the active manifolds in a finite number of iterations (finite activity identification), and (ii) then enters a local linear convergence regime, which we characterize precisely in terms of the structure of the underlying active manifolds. For simpler problems involving polyhedral functions, we show finite termination. We also establish and explain why FISTA (with convergent sequences) locally oscillates and can be slower than FB. These results may have numerous applications including in signal/image processing, sparse recovery and machine learning. Indeed, the obtained results explain the typical behaviour that has been observed numerically for many problems in these fields such as the Lasso, the group Lasso, the fused Lasso and the nuclear norm regularization to name only a few.
In this paper, we propose a new hand gesture recognition method based on
skeletal data by learning SPD matrices with neural networks. We model the hand
skeleton as a graph and introduce a neural network for SPD matrix learning,
taking as input the 3D coordinates of hand joints. The proposed network is
based on two newly designed layers that transform a set of SPD matrices into a
SPD matrix. For gesture recognition, we train a linear SVM classifier using
features extracted from our network. Experimental results on a challenging
dataset (Dynamic Hand Gesture dataset from the SHREC 2017 3D Shape Retrieval
Contest) show that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
This paper explores the impact of incorporating sentiment, emotion, and
domain-specific lexicons into a transformer-based model for depression symptom
estimation. Lexicon information is added by marking the words in the input
transcripts of patient-therapist conversations as well as in social media
posts. Overall results show that the introduction of external knowledge within
pre-trained language models can be beneficial for prediction performance, while
different lexicons show distinct behaviours depending on the targeted task.
Additionally, new state-of-the-art results are obtained for the estimation of
depression level over patient-therapist interviews.
21 Nov 2024
In this paper, we propose two regularized proximal quasi-Newton methods with symmetric rank-1 update of the metric (SR1 quasi-Newton) to solve non-smooth convex additive composite problems. Both algorithms avoid using line search or other trust region strategies. For each of them, we prove a super-linear convergence rate that is independent of the initialization of the algorithm. The cubic regularized method achieves a rate of order (N1/2C)N/2, where N is the number of iterations and C is some constant, and the other gradient regularized method shows a rate of the order (N1/4C)N/2. To the best of our knowledge, these are the first global non-asymptotic super-linear convergence rates for regularized quasi-Newton methods and regularized proximal quasi-Newton methods. The theoretical properties are also demonstrated in two applications from machine learning.
27 Oct 2016
In this paper, we propose a multi-step inertial Forward--Backward splitting
algorithm for minimizing the sum of two non-necessarily convex functions, one
of which is proper lower semi-continuous while the other is differentiable with
a Lipschitz continuous gradient. We first prove global convergence of the
scheme with the help of the Kurdyka-{\L}ojasiewicz property. Then, when the
non-smooth part is also partly smooth relative to a smooth submanifold, we
establish finite identification of the latter and provide sharp local linear
convergence analysis. The proposed method is illustrated on a few problems
arising from statistics and machine learning.
05 Jun 2025
Our approach is part of the close link between continuous dissipative dynamical systems and optimization algorithms. We aim to solve convex minimization problems by means of stochastic inertial differential equations which are driven by the gradient of the objective function. This will provide a general mathematical framework for analyzing fast optimization algorithms with stochastic gradient input. Our study is a natural extension of our previous work devoted to the first-order in time stochastic steepest descent. Our goal is to develop these results further by considering second-order stochastic differential equations in time, incorporating a viscous time-dependent damping and a Hessian-driven damping. To develop this program, we rely on stochastic Lyapunov analysis. Assuming a square-integrability condition on the diffusion term times a function dependant on the viscous damping, and that the Hessian-driven damping is a positive constant, our first main result shows that almost surely, there is convergence of the values, and states fast convergence of the values in expectation. Besides, in the case where the Hessian-driven damping is zero, we conclude with the fast convergence of the values in expectation and in almost sure sense, we also managed to prove almost sure weak convergence of the trajectory. We provide a comprehensive complexity analysis by establishing several new pointwise and ergodic convergence rates in expectation for the convex and strongly convex case.
This paper studies least-square regression penalized with partly smooth
convex regularizers. This class of functions is very large and versatile
allowing to promote solutions conforming to some notion of low-complexity.
Indeed, they force solutions of variational problems to belong to a
low-dimensional manifold (the so-called model) which is stable under small
perturbations of the function. This property is crucial to make the underlying
low-complexity model robust to small noise. We show that a generalized
"irrepresentable condition" implies stable model selection under small noise
perturbations in the observations and the design matrix, when the
regularization parameter is tuned proportionally to the noise level. This
condition is shown to be almost a necessary condition. We then show that this
condition implies model consistency of the regularized estimator. That is, with
a probability tending to one as the number of measurements increases, the
regularized estimator belongs to the correct low-dimensional model manifold.
This work unifies and generalizes several previous ones, where model
consistency is known to hold for sparse, group sparse, total variation and
low-rank regularizations.
03 Sep 2024
The balance game is played on a graph G by two players, Admirable (A) and
Impish (I), who take turns selecting unlabeled vertices of G. Admirable
labels the selected vertices by 0 and Impish by 1, and the resulting label
on any edge is the sum modulo 2 of the labels of the vertices incident to
that edge. Let e0 and e1 denote the number of edges labeled by 0 and
1 after all the vertices are labeled. The discrepancy in the balance game is
defined as d=e1−e0. The two players have opposite goals: Admirable
attempts to minimize the discrepancy d while Impish attempts to maximize d.
When (A) makes the first move in the game, the (A)-start game balance number,
bgA(G), is the value of d when both players play optimally, and when (I)
makes the first move in the game, the (I)-start game balance number,
bgI(G), is the value of d when both players play optimally. Among other
results, we show that if G has order n, then $-\log_2(n) \le b^A_g(G) \le
\frac{n}{2}ifnisevenand0 \le b^A_g(G) \le \frac{n}{2} + \log_2(n)$ if
n is odd. Moreover we show that $b^A_g(G) + b^I_g(\overline{G}) = \lfloor n/2
\rfloor$.
This paper proposes a new neural network based on SPD manifold learning for
skeleton-based hand gesture recognition. Given the stream of hand's joint
positions, our approach combines two aggregation processes on respectively
spatial and temporal domains. The pipeline of our network architecture consists
in three main stages. The first stage is based on a convolutional layer to
increase the discriminative power of learned features. The second stage relies
on different architectures for spatial and temporal Gaussian aggregation of
joint features. The third stage learns a final SPD matrix from skeletal data. A
new type of layer is proposed for the third stage, based on a variant of
stochastic gradient descent on Stiefel manifolds. The proposed network is
validated on two challenging datasets and shows state-of-the-art accuracies on
both datasets.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.