Ask or search anything...
Researchers at Emory University and Mayo Clinic developed Res-SRDiff, an efficient diffusion model, that reconstructs high-resolution MRI from low-resolution inputs by integrating a residual error-shifting mechanism. This approach enables high-fidelity super-resolution in just four sampling steps, achieving reconstruction speeds of 0.46 seconds per brain slice and 0.95 seconds per prostate slice, while preserving fine anatomical details.
View blogBiomedGPT introduces the first open-source, lightweight generalist vision-language foundation model for biomedicine, successfully addressing diverse tasks by unifying text and image data within a transformer architecture. The model achieved state-of-the-art results in 16 out of 25 experiments and demonstrated strong zero-shot capabilities, often outperforming larger proprietary models despite its smaller parameter count.
View blogResearchers from Microsoft and leading medical institutions developed COLIPRI, a 3D vision-language pre-training framework that integrates contrastive learning, radiology report generation, and masked autoencoding to enhance understanding of 3D medical images. The framework significantly improved the clinical accuracy of generated radiology reports and achieved strong performance in global classification and retrieval tasks.
View blogThis survey critically evaluates the progress in deep learning-based medical image segmentation from 2015 to 2024, concluding that while performance has improved significantly, the problem remains unsolved, especially concerning clinical viability and generalization. It identifies persistent challenges across various segmentation paradigms and outlines future research directions, including the development of intelligent segmentation agents and the need for new evaluation metrics that quantify human-in-the-loop efficiency.
View blogA deep learning framework, EAGLE, was developed to efficiently analyze whole slide pathology images, achieving an average AUROC of 0.742 across 31 tasks while processing images over 99% faster than previous methods by selectively focusing on critical regions.
View blogEViT-UNet presents an efficient U-shaped deep learning architecture for medical image segmentation that balances high accuracy with low computational cost. This approach strategically integrates convolutional operations and vision transformer blocks, achieving an average DSC of 80.9% on the Synapse dataset with only 5.4 GMac, making it suitable for deployment on resource-constrained mobile and edge devices.
View blogMedAlign introduces a clinician-generated dataset for evaluating Large Language Models on complex instruction-following tasks using comprehensive Electronic Health Records. It reveals that state-of-the-art LLMs achieve a maximum of 65% correctness on these tasks, highlighting the critical role of context length and a misalignment in current medical LLM fine-tuning approaches, while identifying automated metrics that correlate with clinician judgment.
View blogThis survey critically evaluates current conversational agents for mental health, highlighting their limitations in explainability, safety, and clinical grounding. It proposes a framework for building knowledge-infused, trustworthy virtual mental health assistants and advocates for new evaluation metrics for responsible development.
View blog UCLA
UCLA
 University College London
University College London University of Oxford
University of Oxford
 Emory University
Emory University

 University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge Microsoft
Microsoft
 ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich Stanford University
Stanford University
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 University of Pennsylvania
University of Pennsylvania
 University of Washington
University of Washington Imperial College London
Imperial College London
 Arizona State University
Arizona State University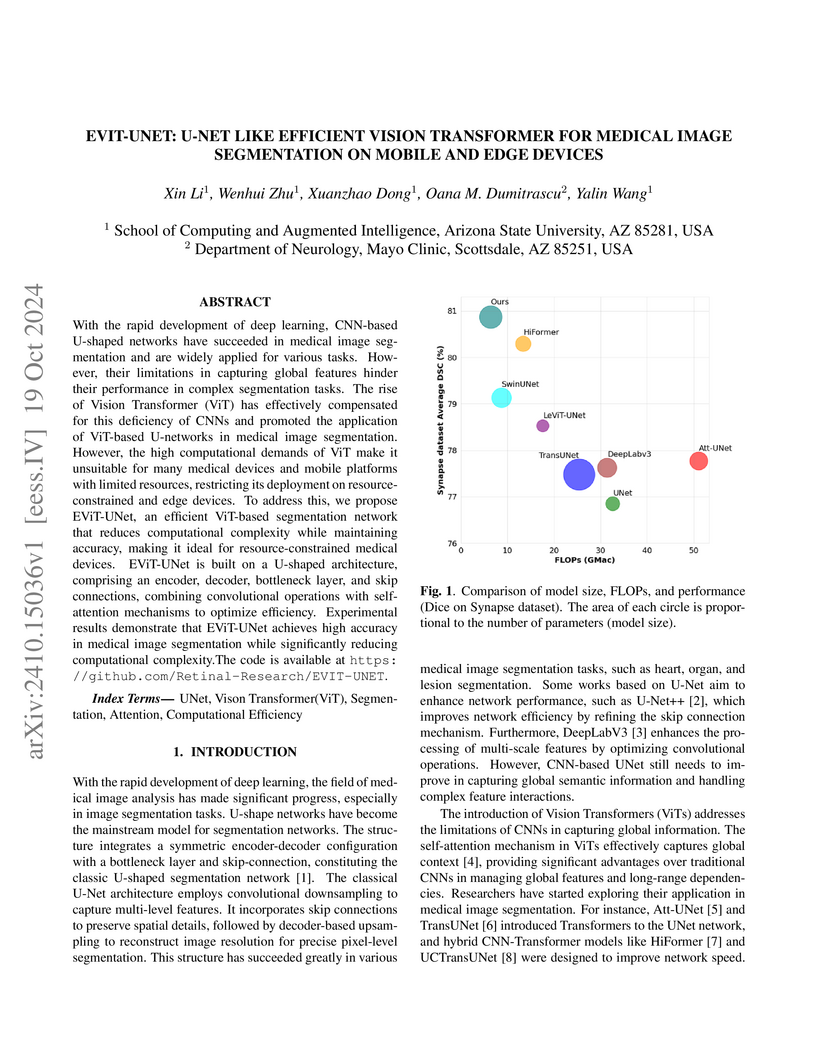

 Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University