Military Institute of Science and Technology (MIST)
17 Apr 2024
This research focused on the development of a cost-effective IoT solution for energy and environment monitoring geared towards manufacturing industries. The proposed system is developed using open-source software that can be easily deployed in any manufacturing environment. The system collects real-time temperature, humidity, and energy data from different devices running on different communication such as TCP/IP, Modbus, etc., and the data is transferred wirelessly using an MQTT client to a database working as a cloud storage solution. The collected data is then visualized and analyzed using a website running on a host machine working as a web client.
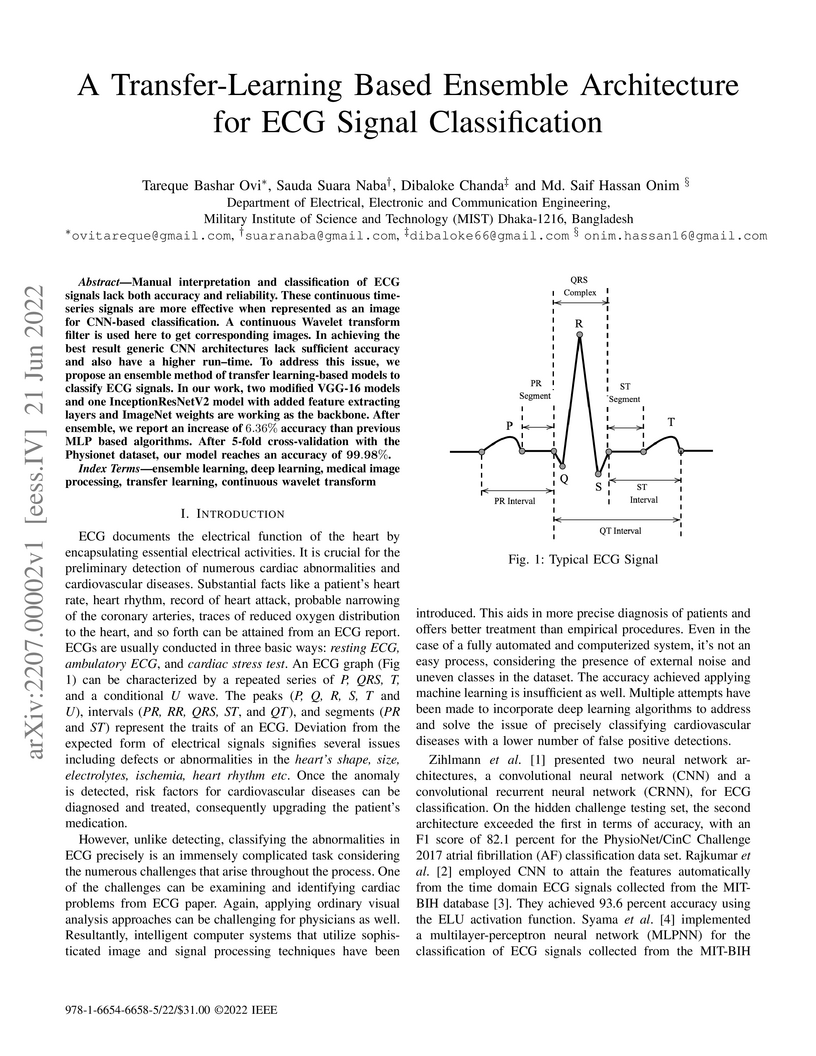
Manual interpretation and classification of ECG signals lack both accuracy and reliability. These continuous time-series signals are more effective when represented as an image for CNN-based classification. A continuous Wavelet transform filter is used here to get corresponding images. In achieving the best result generic CNN architectures lack sufficient accuracy and also have a higher run-time. To address this issue, we propose an ensemble method of transfer learning-based models to classify ECG signals. In our work, two modified VGG-16 models and one InceptionResNetV2 model with added feature extracting layers and ImageNet weights are working as the backbone. After ensemble, we report an increase of 6.36% accuracy than previous MLP-based algorithms. After 5-fold cross-validation with the Physionet dataset, our model reaches an accuracy of 99.98%.
06 May 2024
The pharmaceutical manufacturing faces critical challenges due to the global
threat of counterfeit drugs. This paper proposes a new approach of protected QR
codes to secure unique product information for safeguarding the pharmaceutical
supply chain. The proposed solution integrates secure QR code generation and
encrypted data transmission to establish a comprehensive anti-counterfeit
ecosystem. The protected QR codes encapsulate product information that cannot
be identified using traditional QR code scanners which protect the information
against replication and tampering. The system is developed with scalability in
mind, which can be easily implemented without introducing any additional
modification in the traditional supply chain.
27 Apr 2020
Blockchain is relatively a new area of research. However, a surge of research
studies on the blockchain has taken place in recent years. These research
studies have mostly focused on designing and developing conceptual frameworks
to build more reliable, transparent and efficient digital systems. While
blockchain brings a wide variety of benefits, it also imposes certain
challenges. Therefore, the objective of this research is to understand the
properties of blockchain, its current uses, observed benefits and pitfalls to
provide a balanced understanding of blockchain. A systematic literature review
approach was adopted in this paper in order to attain the objective. A total of
51 articles were selected and reviewed. As outcomes, this research provides a
summary of the state-of-the-art research studies conducted in the area of
blockchain. Furthermore, we develop a set of concept maps aiming to provide
in-depth knowledge on blockchain technology for its efficient and effective
usage in the development of future technological solutions.
The objective of this research is to explore the existing mobile applications developed for the COVID-19 pandemic. To obtain this research objective, firstly the related applications were selected through the systematic search technique in the popular application stores. Secondly, data related to the app objectives, functionalities provided by the app, user ratings, and user reviews were extracted. Thirdly, the extracted data were analyzed through the affinity diagram, noticing-collecting-thinking, and descriptive analysis. As outcomes, the review provides a state-of-the-art view of mobile apps developed for COVID-19 by revealing nine functionalities or features. It revealed ten factors related to information systems design characteristics that can guide future app design. The review outcome highlights the need for new development and further refinement of the existing applications considering not only the revealed objectives and their associated functionalities, but also revealed design characteristics such as reliability, performance, usefulness, supportive, security, privacy, flexibility, responsiveness, ease of use, and cultural sensitivity.
The segmentation of satellite images is crucial in remote sensing applications. Existing methods face challenges in recognizing small-scale objects in satellite images for semantic segmentation primarily due to ignoring the low-level characteristics of the underlying network and due to containing distinct amounts of information by different feature maps. Thus, in this research, a tri-level attention-based DeepLabv3+ architecture (DeepTriNet) is proposed for the semantic segmentation of satellite images. The proposed hybrid method combines squeeze-and-excitation networks (SENets) and tri-level attention units (TAUs) with the vanilla DeepLabv3+ architecture, where the TAUs are used to bridge the semantic feature gap among encoders output and the SENets used to put more weight on relevant features. The proposed DeepTriNet finds which features are the more relevant and more generalized way by its self-supervision rather we annotate them. The study showed that the proposed DeepTriNet performs better than many conventional techniques with an accuracy of 98% and 77%, IoU 80% and 58%, precision 88% and 68%, and recall of 79% and 55% on the 4-class this http URL dataset and the 15-class GID-2 dataset respectively. The proposed method will greatly contribute to natural resource management and change detection in rural and urban regions through efficient and semantic satellite image segmentation
Pixel Value Ordering (PVO) holds an impressive property for high fidelity
Reversible Data Hiding (RDH). In this paper, we introduce a dual-PVO (dPVO) for
Prediction Error Expansion(PEE), and thereby develop a new RDH scheme to offer
a better rate-distortion performance. Particularly, we propose to embed in two
phases: forward and backward. In the forward phase, PVO with classic PEE is
applied to every non-overlapping image block of size 1x3. In the backward
phase,minimum-set and maximum-set of pixels are determined from the pixels
predicted in the forward phase. The minimum set only contains the lowest
predicted pixels and the maximum set contains the largest predicted pixels of
each image block. Proposed dPVO withPEE is then applied to both sets, so that
the pixel values of the minimum set are increased and that of the maximum set
are decreased by a unit value. Thereby, the pixels predicted in the forward
embedding can partially be restored to their original values resulting in both
better-embedded image quality and a higher embedding rate. Experimental results
have recorded a promising rate-distortion performance of our scheme with a
significant improvement of embedded image quality at higher embedding rates
compared to the popular and state-of-the-art PVO-based RDHschemes.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.