Razi University
The diagnosis of cancer is mainly performed by visual analysis of the
pathologists, through examining the morphology of the tissue slices and the
spatial arrangement of the cells. If the microscopic image of a specimen is not
stained, it will look colorless and textured. Therefore, chemical staining is
required to create contrast and help identify specific tissue components.
During tissue preparation due to differences in chemicals, scanners, cutting
thicknesses, and laboratory protocols, similar tissues are usually varied
significantly in appearance. This diversity in staining, in addition to
Interpretive disparity among pathologists more is one of the main challenges in
designing robust and flexible systems for automated analysis. To address the
staining color variations, several methods for normalizing stain have been
proposed. In our proposed method, a Stain-to-Stain Translation (STST) approach
is used to stain normalization for Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained
histopathology images, which learns not only the specific color distribution
but also the preserves corresponding histopathological pattern. We perform the
process of translation based on the pix2pix framework, which uses the
conditional generator adversarial networks (cGANs). Our approach showed
excellent results, both mathematically and experimentally against the state of
the art methods. We have made the source code publicly available.
07 Dec 2024
Collecting multiple longitudinal measurements and time-to-event outcomes is a common practice in clinical and epidemiological studies, often focusing on exploring associations between them. Joint modeling is the standard analytical tool for such data, with several R packages available. However, as the number of longitudinal markers increases, the computational burden and convergence challenges make joint modeling increasingly impractical.
This paper introduces a novel two-stage Bayesian approach to estimate joint models for multiple longitudinal measurements and time-to-event outcomes. The method builds on the standard two-stage framework but improves the initial stage by estimating a separate one-marker joint model for the event and each longitudinal marker, rather than relying on mixed models. These estimates are used to derive predictions of individual marker trajectories, avoiding biases from informative dropouts. In the second stage, a proportional hazards model is fitted, incorporating the predicted current values and slopes of the markers as time-dependent covariates. To address uncertainty in the first-stage predictions, a multiple imputation technique is employed when estimating the Cox model in the second stage.
This two-stage method allows for the analysis of numerous longitudinal markers, which is often infeasible with traditional multi-marker joint modeling. The paper evaluates the approach through simulation studies and applies it to the PBC2 dataset and a real-world dementia dataset containing 17 longitudinal markers. An R package, TSJM, implementing the method is freely available on GitHub: this https URL.
18 Sep 2024
The dynamics of a rain forest is extremely complex involving births, deaths
and growth of trees with complex interactions between trees, animals, climate,
and environment. We consider the patterns of recruits (new trees) and dead
trees between rain forest censuses. For a current census we specify regression
models for the conditional intensity of recruits and the conditional
probabilities of death given the current trees and spatial covariates. We
estimate regression parameters using conditional composite likelihood functions
that only involve the conditional first order properties of the data. When
constructing assumption lean estimators of covariance matrices of parameter
estimates we only need mild assumptions of decaying conditional correlations in
space while assumptions regarding correlations over time are avoided by
exploiting conditional centering of composite likelihood score functions. Time
series of point patterns from rain forest censuses are quite short while each
point pattern covers a fairly big spatial region. To obtain asymptotic results
we therefore use a central limit theorem for the fixed timespan - increasing
spatial domain asymptotic setting. This also allows us to handle the challenge
of using stochastic covariates constructed from past point patterns.
Conveniently, it suffices to impose weak dependence assumptions on the
innovations of the space-time process. We investigate the proposed methodology
by simulation studies and applications to rain forest data.
Recent studies in different fields of science caused emergence of needs for high performance computing systems like Cloud. A critical issue in design and implementation of such systems is resource allocation which is directly affected by internal and external factors like the number of nodes, geographical distance and communication latencies. Many optimizations took place in resource allocation methods in order to achieve better performance by concentrating on computing, network and energy resources. Communication latencies as a limitation of network resources have always been playing an important role in parallel processing (especially in fine-grained programs). In this paper, we are going to have a survey on the resource allocation issue in Cloud and then do an optimization on common resource allocation method based on the latencies of communications. Due to it, we added a table to Resource Agent (entity that allocates resources to the applicants) to hold the history of previous allocations. Then, a probability matrix was constructed for allocation of resources partially based on the history of latencies. Response time was considered as a metric for evaluation of proposed method. Results indicated the better response time, especially by increasing the number of tasks. Besides, the proposed method is inherently capable for detecting the unavailable resources through measuring the communication latencies. It assists other issues in cloud systems like migration, resource replication and fault tolerance.
In this paper, a technology for massive data storage and computing named Hadoop is surveyed. Hadoop consists of heterogeneous computing devices like regular PCs abstracting away the details of parallel processing and developers can just concentrate on their computational problem. A Hadoop cluster is made of two parts: HDFs and Mapreduce. Hadoop cluster uses HDFS for data management. HDFS provides storage for input and output data in MapReduce jobs and is designed with abilities like high-fault tolerance, high-distribution capacity, and high throughput. It is also suitable for storing Terabyte data on clusters and it runs on flexible hardware like commodity devices.
The interaction between three photons is studied in de Sitter ambient space formalism. As a special case the half harmonic generator is considered, {\it i.e.} one photon decays to two same-energy photons. The scattering matrix elements are presented which define the indirect gravitational effect on quantum field theory. The null curvature limit of scattering matrix is obtained for comparing it with its Minkowskian counterpart. The Hamiltonian of this interaction, in Minkowski space-time, was presented by using the quantum vacuum fluctuation in the one-loop approximation.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming industries by connecting billions of devices to collect, process, and share data. However, the massive data volumes and real-time demands of IoT applications strain traditional cloud computing architectures. This paper explores the complementary roles of cloud, fog, and edge computing in enhancing IoT performance, focusing on their ability to reduce latency, improve scalability, and ensure data privacy. We propose a novel framework, the Hierarchical IoT Processing Architecture (HIPA), which dynamically allocates computational tasks across cloud, fog, and edge layers using machine learning. By synthesizing current research and introducing HIPA, this paper highlights how these paradigms can create efficient, secure, and scalable IoT ecosystems.
The imminent rise of autonomous vehicles (AVs) is revolutionizing the future of transport. The Vehicular Fog Computing (VFC) paradigm has emerged to alleviate the load of compute-intensive and delay-sensitive AV programs via task offloading to nearby vehicles. Effective VFC requires an intelligent and dynamic offloading algorithm. As a result, this paper adapts Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) for VFC offloading. First, a simulation environment utilizing realistic hardware and task specifications, in addition to a novel vehicular movement model based on grid-planned cities, is created. Afterward, a DRL-based algorithm is trained and tested on the environment with the goal of minimizing global task delay. The DRL model displays impressive results, outperforming other greedy and conventional methods. The findings further demonstrate the effectiveness of the DRL model in minimizing queue congestion, especially when compared to traditional cloud computing methods that struggle to handle the demands of a large fleet of vehicles. This is corroborated by queuing theory, highlighting the self-scalability of the VFC-based DRL approach.
Background: In clinical and epidemiological research, the integration of longitudinal measurements and time-to-event outcomes is vital for understanding relationships and improving risk prediction. However, as the number of longitudinal markers increases, joint model estimation becomes more complex, leading to long computation times and convergence issues. This study introduces a novel two-stage Bayesian approach for variable selection in joint models, illustrated through a practical application.
Methods: Our approach conceptualizes the analysis in two stages. In the first stage, we estimate one-marker joint models for each longitudinal marker related to the event, allowing for bias reduction from informative dropouts through individual marker trajectory predictions. The second stage employs a proportional hazard model that incorporates expected current values of all markers as time-dependent covariates. We explore continuous and Dirac spike-and-slab priors for variable selection, utilizing Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) techniques.
Results: The proposed method addresses the challenges of parameter estimation and risk prediction with numerous longitudinal markers, demonstrating robust performance through simulation studies. We further validate our approach by predicting dementia risk using the Three-City (3C) dataset, a longitudinal cohort study from France.
Conclusions: This two-stage Bayesian method offers an efficient process for variable selection in joint modeling, enhancing risk prediction capabilities in longitudinal studies. The accompanying R package VSJM, which is freely available at this https URL, facilitates implementation, making this approach accessible for diverse clinical applications.
12 Dec 2024
Dynamic event prediction, using joint modeling of survival time and longitudinal variables, is extremely useful in personalized medicine. However, the estimation of joint models including many longitudinal markers is still a computational challenge because of the high number of random effects and parameters to be estimated. In this paper, we propose a model averaging strategy to combine predictions from several joint models for the event, including one longitudinal marker only or pairwise longitudinal markers. The prediction is computed as the weighted mean of the predictions from the one-marker or two-marker models, with the time-dependent weights estimated by minimizing the time-dependent Brier score. This method enables us to combine a large number of predictions issued from joint models to achieve a reliable and accurate individual prediction. Advantages and limits of the proposed methods are highlighted in a simulation study by comparison with the predictions from well-specified and misspecified all-marker joint models as well as the one-marker and two-marker joint models. Using the PBC2 data set, the method is used to predict the risk of death in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. The method is also used to analyze a French cohort study called the 3C data. In our study, seventeen longitudinal markers are considered to predict the risk of death.
In this article, the new black hole solutions to the
Einstein-power-Maxwell-dilaton gravity theory have been investigated in a
four-dimensional space-time. The coupled scalar, electromagnetic and
gravitational field equations have been solved in a static and spherically
symmetric geometry. It has been shown that dilatonic potential, as the solution
to the scalar field equation, can be written in the form of a generalized
Liouville potential. Also, three classes of novel charged dilaton black hole
solutions, in the presence of power law nonlinear electrodynamics, have been
constructed out which are asymptotically non-flat and non-AdS. The conserved
and thermodynamic quantities have been calculated from geometrical and
thermodynamical approaches, separately. Since the results of these two
alternative approaches are identical one can argue that the first law of black
hole thermodynamics is valid for all of the new black hole solutions. The
thermodynamic stability or phase transition of the black holes have been
studied, making use of the canonical ensemble method. The points of type-1 and
type-2 phase transitions as well as the ranges at which the black holes are
stable have been indicated by considering the heat capacity of the new black
hole solutions. The global stability of the black holes have been studied
through the grand canonical ensemble method. Regarding the Gibbs free energy of
the black holes, the points of Hawking-Page phase transition and ranges of the
horizon radii at which the black holes are globally stable have been
determined.
23 Dec 2016
Recently, the Bayesian nonparametric approach in survival studies attracts
much more attentions. Because of multi modality in survival data, the mixture
models are very common in this field. One of the famous priors on Bayesian
nonparametric models is Dirichlet process prior. In this paper we introduce a
Bayesian nonparametric mixture model with Burr distribution(Burr type XII) as
the kernel of mixture model. Since the Burr distribution shares good properties
of common distributions on survival analysis, it has more flexibility than
other distributions. By applying this model to simulated and real failure time
data sets, we show the preference of this model and compare it with other
Dirichlet process mixture models with different kernels. And also we show that
this model can be applied for the right censored data. For calculating the
posterior of the parameters for inference and modeling, we used the MCMC
simulation methods, especially Gibbs sampling.
Researchers at Razi University analyzed the performance of Apache Spark's MLlib for scaling machine learning-based Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) on big data network traffic. The study demonstrated that Spark significantly reduces training times for several algorithms while maintaining high detection accuracy, with some models achieving up to 100% accuracy on botnet detection using the CSE-CIC-IDS2018 dataset.
This paper proposes a model based on gene expression programming for predicting the discharge coefficient of triangular labyrinth weirs. The parameters influencing discharge coefficient prediction were first examined and presented as crest height ratio to the head over the crest of the weir, a crest length of water to channel width, a crest length of water to the head over the crest of the weir, Froude number and vertex angle dimensionless parameters. Different models were then presented using sensitivity analysis in order to examine each of the dimensionless parameters presented in this study. In addition, an equation was presented through the use of nonlinear regression (NLR) for the purpose of comparison with GEP. The results of the studies conducted by using different statistical indexes indicated that GEP is more capable than NLR. This is to the extent that GEP predicts the discharge coefficient with an average relative error of approximately 2.5% in such a manner that the predicted values have less than 5% relative error in the worst model.
Vehicular fog computing (VFC) can be considered as an important alternative to address the existing challenges in intelligent transportation systems (ITS). The main purpose of VFC is to perform computational tasks through various vehicles. At present, VFCs include powerful computing resources that bring the computational resources nearer to the requesting devices. This paper presents a new algorithm based on meta-heuristic optimization method for task scheduling problem in VFC. The task scheduling in VFC is formulated as a multi-objective optimization problem, which aims to reduce makespan and monetary cost. The proposed method utilizes the grey wolf optimization (GWO) and assigns the different priorities to static and dynamic fog nodes. Dynamic fog nodes represent the parked or moving vehicles and static fog nodes show the stationary servers. Afterwards, the tasks that require the most processing resources are chosen and allocated to fog nodes. The GWO-based method is extensively evaluated in more details. Furthermore, the effectiveness of various parameters in GWO algorithm is analyzed. We also assess the proposed algorithm on real application and random data. The outcomes of our experiments confirm that, in comparison to previous works, our algorithm is capable of offering the lowest monetary cost.
26 May 2019
The statistical rank tests play important roles in univariate non-parametric
data analysis. If one attempts to generalize the rank tests to a multivariate
case, the problem of defining a multivariate order will occur. It is not clear
how to define a multivariate order or statistical rank in a meaningful way. One
approach to overcome this problem is to use the notion of data depth which
measures the centrality of a point with respect to a given data set. In other
words, a data depth can be applied to indicate how deep a point is located with
respect to a given data set. Using data depth, a multivariate order can be
defined by ordering the data points according to their depth values. Various
notions of data depth have been introduced over the last decades. In this
thesis, we discuss three depth functions: two well-known depth functions
halfspace depth and simplicial depth, and one recently defined depth function
named as β-skeleton depth, β≥1. The β-skeleton depth is
equivalent to the previously defined spherical depth and lens depth when
β=1 and β=2, respectively. Our main focus in this thesis is to
explore the geometric and algorithmic aspects of β-skeleton depth.
The Internet of Things has affected all aspects of daily life, and the number of IoT devices is increasing day by day. According to forecasts, the number of Internet of Things devices will reach one trillion devices by 2035. The increase in the number of devices connected to the Internet will cause various concerns. One of the most important concerns is the energy and power consumption of these devices. Although Internet of Things modules are low in energy consumption, their widespread and large-scale use has made the issue of power consumption become the most important challenge in this field. For this reason, it is necessary to use communication protocols that, in addition to establishing efficient communication, impose minimal power consumption on the network. In this paper, application layer protocols such as MQTT, MQTT-SN, CoAP, and HTTP are simulated using the tools available in the Contiki operating system, including COOJA and Powertrace, and they { are evaluated} and compared with each other in terms of power consumption. According to the simulations performed by the mentioned tools, the MQTT-SN protocol was the least consuming protocol in terms of power consumption. After that, the CoAP protocol is placed, and with a slight difference, the MQTT protocol, which consumes more than MQTT-SN. Finally, the HTTP protocol consumes the most power, which makes it unsuitable for communication in the Internet of Things
22 Sep 2021
Recent years have seen growing interest in the diagnosis of Coronary Artery
Disease (CAD) with machine learning methods to reduce the cost and health
implications of conventional diagnosis. This paper introduces a CAD diagnosis
method with a novel feature extraction technique called the Profile-Based
Binary Feature Extraction (PBBFE). In this method, after partitioning numerical
features, frequent itemsets are extracted by the Apriori algorithm and then
used as features to increase the CAD diagnosis accuracy. The proposed method
consists of two main phases. In the first phase, each patient is assigned a
profile based on age, gender, and medical condition, and then all numerical
features are discretized based on assigned profiles. All features then undergo
a binarization process to become ready for feature extraction by Apriori. In
the last step of this phase, frequent itemsets are extracted from the dataset
by Apriori and used to build a new dataset. In the second phase, the Genetic
Algorithm and the Support Vector Machine are used to identify the best subset
of extracted features for classification. The proposed method was tested on the
Z-Alizadeh Sani dataset, which is one the richest databases in the field of
CAD. Performance comparisons conducted on this dataset showed that the proposed
method outperforms all major alternative methods with 98.35% accuracy, 100%
sensitivity, and 94.25% specificity. The proposed method also achieved the
highest accuracy on several other datasets.
03 Dec 2018
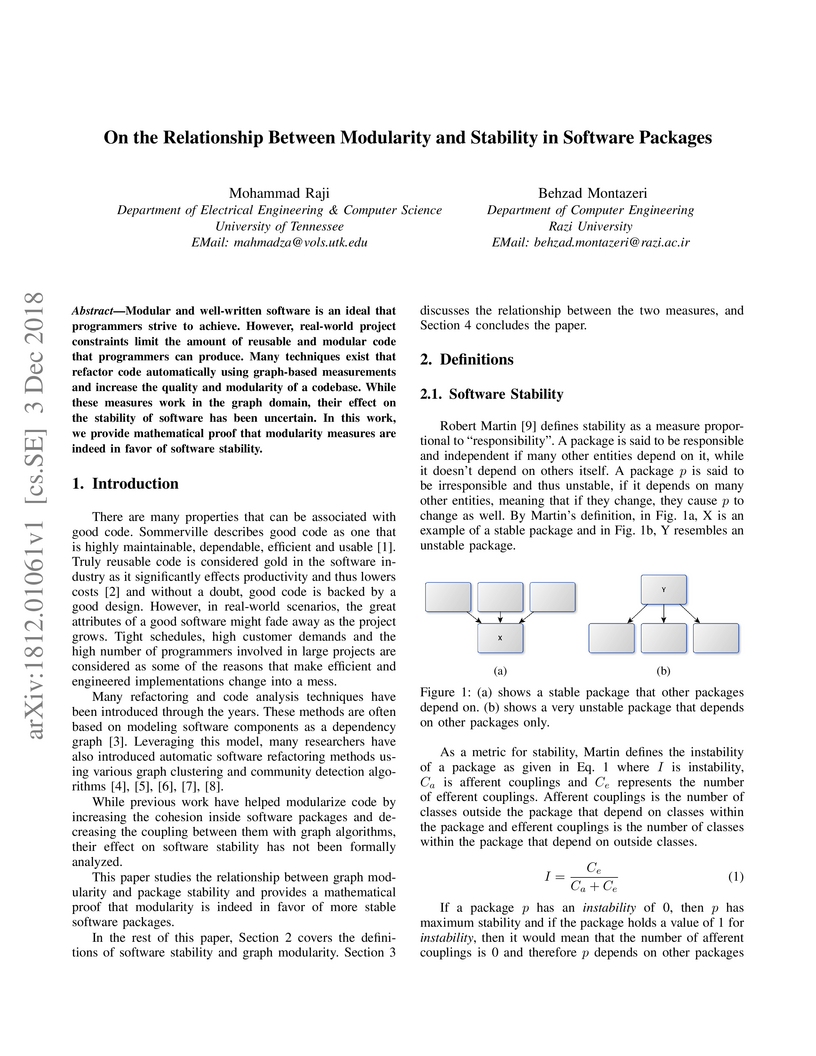
Modular and well-written software is an ideal that programmers strive to
achieve. However, real-world project constraints limit the amount of reusable
and modular code that programmers can produce. Many techniques exist that
refactor code automatically using graph-based measurements and increase the
quality and modularity of a codebase. While these measures work in the graph
domain, their effect on the stability of software has been uncertain. In this
work, we provide mathematical proof that modularity measures are indeed in
favor of software stability.
Active Queue Management (AQM), a network-layer congestion control technique endorsed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), encourages routers to discard packets before the occurrence of buffer overflow. Traditional AQM techniques often employ heuristic approaches that require meticulous parameter adjustments, limiting their real-world applicability. In contrast, Machine Learning (ML) approaches offer highly adaptive, data-driven solutions custom to dynamic network conditions. Consequently, many researchers have adapted ML for AQM throughout the years, resulting in a wide variety of algorithms ranging from predicting congestion via supervised learning to discovering optimal packet-dropping policies with reinforcement learning. Despite these remarkable advancements, no previous work has compiled these methods in the form of a survey article. This paper presents the first thorough documentation and analysis of ML-based algorithms for AQM, in which the strengths and limitations of each proposed method are evaluated and compared. In addition, a novel taxonomy of ML approaches based on methodology is also established. The review is concluded by discussing unexplored research gaps and potential new directions for more robust ML-AQM methods.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.