Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech)
11 Oct 2025
Robot person following (RPF) -- mobile robots that follow and assist a specific person -- has emerging applications in personal assistance, security patrols, eldercare, and logistics. To be effective, such robots must follow the target while ensuring safety and comfort for both the target and surrounding people. In this work, we present the first comprehensive study of RPF, which (i) surveys representative scenarios, motion-planning methods, and evaluation metrics with a focus on safety and comfort; (ii) introduces Follow-Bench, a unified benchmark simulating diverse scenarios, including various target trajectory patterns, crowd dynamics, and environmental layouts; and (iii) re-implements six representative RPF planners, ensuring that both safety and comfort are systematically considered. Moreover, we evaluate the two best-performing planners from our benchmark on a differential-drive robot to provide insights into the real-world deployment of RPF planners. Extensive simulation and real-world experiments provide a quantitative study of the safety-comfort trade-offs of existing planners, while revealing open challenges and future research directions.
The Log-Periodic Power Law Singularity (LPPLS) model offers a general
framework for capturing dynamics and predicting transition points in diverse
natural and social systems. In this work, we present two calibration techniques
for the LPPLS model using deep learning. First, we introduce the Mono-LPPLS-NN
(M-LNN) model; for any given empirical time series, a unique M-LNN model is
trained and shown to outperform state-of-the-art techniques in estimating the
nonlinear parameters (tc,m,ω) of the LPPLS model as evidenced by the
comprehensive distribution of parameter errors. Second, we extend the M-LNN
model to a more general model architecture, the Poly-LPPLS-NN (P-LNN), which is
able to quickly estimate the nonlinear parameters of the LPPLS model for any
given time-series of a fixed length, including previously unseen time-series
during training. The Poly class of models train on many synthetic LPPLS
time-series augmented with various noise structures in a supervised manner.
Given enough training examples, the P-LNN models also outperform
state-of-the-art techniques for estimating the parameters of the LPPLS model as
evidenced by the comprehensive distribution of parameter errors. Additionally,
this class of models is shown to substantially reduce the time to obtain
parameter estimates. Finally, we present applications to the diagnostic and
prediction of two financial bubble peaks (followed by their crash) and of a
famous rockslide. These contributions provide a bridge between deep learning
and the study of the prediction of transition times in complex time series.
Quantum metric, a probe to spacetime of the Hilbert space, has been found
measurable in the nonlinear electronic transport thus has attracted tremendous
interest. However, without comparing with mechanisms tied to disorder, it is
still unclear whether the quantum metric dominates in recent experiments. We
exhaust all possible mechanisms of nonlinear transport under the same symmetry
that the quantum metric emerges, by finding five more disorder-related
mechanisms and their nonlinear conductivity formulas. With the help of the
formulas, we derive the scaling law to identify distinct mechanisms in the
recent experiments [Gao, et al., Science 381, 181 (2023); Wang, et al., Nature
621, 487 (2023)], determine nonzero nonlinear conductivity elements for all 122
magnetic point groups to guide future experiments, and calculate the nonlinear
conductivity to explain the sophisticated features in the experiments of the
even-layered MnBi2Ti4 thin films. Our theory will facilitate future
experiments and applications of nonlinear transport.
The fundamental role of magnetic materials in modern science and technology has driven a rapid surge in research on unconventional magnetism in recent years. In particular, altermagnets, which simultaneously exhibit zero net magnetization in real space and anisotropic spin splitting in momentum space, have garnered significant interest for both fundamental physics and technological applications. Among these, RuO2 stands as the pioneering and most extensively studied altermagnet. While the intrinsic magnetic order of RuO2 is still a subject of active debate, numerous exotic phenomena characteristic of altermagnetism have been observed in RuO2 samples. In this review, we explore each facet of the altermagnetism through specific case studies in RuO2, systematically surveying its crystal and magnetic structures, electronic band properties, and transport phenomena. We critically assess the debate surrounding the intrinsic magnetism in RuO2, incorporating evidence from altermagnetic signatures in transport, as well as contrasting results from magnetic and spectroscopic measurements. Finally, possible future research directions in this field are discussed.
04 Nov 2025
Recently, altermagnets have emerged as promising candidates in spintronics, uniquely combining large spin-polarized electronic states with zero net magnetization. A prominent example is α-MnTe, whose altermagnetic spin splitting, i.e., the degeneracy lift in momentum space induced by collinear magnetic order, has been experimentally observed. However, the direct evidence of its g-wave spin polarization, the key property for altermagnetic spintronics, is thus far lacking. By combining high-resolution spin- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (SARPES) with first-principles calculations, we reveal a kz-independent, Rashba-like spin texture in α-MnTe. Our results indicate that the observed spin polarization is primarily governed by spin-orbit coupling, whereas the magnetic order contributes to the splitting of energy bands but plays a much less dominant role in spin polarization due to the multi-domain nature. From this result, we further establish a way to prescreen altermagnet candidates that favor the formation of large antiferromagnetic domains based on symmetry analysis. Our work elucidates the interplay between magnetic order and spin-orbit coupling in governing spin polarization in altermagnet candidates, and thereby advances the materials design paradigm for spin-functional devices.
Localizing a person from a moving monocular camera is critical for
Human-Robot Interaction (HRI). To estimate the 3D human position from a 2D
image, existing methods either depend on the geometric assumption of a fixed
camera or use a position regression model trained on datasets containing little
camera ego-motion. These methods are vulnerable to fierce camera ego-motion,
resulting in inaccurate person localization. We consider person localization as
a part of a pose estimation problem. By representing a human with a four-point
model, our method jointly estimates the 2D camera attitude and the person's 3D
location through optimization. Evaluations on both public datasets and real
robot experiments demonstrate our method outperforms baselines in person
localization accuracy. Our method is further implemented into a
person-following system and deployed on an agile quadruped robot.
 Peking UniversitySouth China Normal University
Peking UniversitySouth China Normal University Huazhong University of Science and TechnologySouthern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech)China Three Gorges UniversityWuhan National High Magnetic Field CenterCollaborative Innovation Center of Quantum MatterSun Yet-Sen UniversityQuantum Science Center of Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area (Guangdong)International Center for Quantum Materials
Huazhong University of Science and TechnologySouthern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech)China Three Gorges UniversityWuhan National High Magnetic Field CenterCollaborative Innovation Center of Quantum MatterSun Yet-Sen UniversityQuantum Science Center of Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area (Guangdong)International Center for Quantum MaterialsThe realization of quantum transport effects at elevated temperatures has long intrigued researchers due to the implications for unveiling novel physics and developing quantum devices. In this work, we report remarkable quantum linear magnetoresistance (LMR) in the Weyl semiconductor tellurium at high temperatures of 40-300 K under strong magnetic fields up to 60 T. At high fields, the Weyl band features a large energy gap between the lowest and first Landau levels, which suppresses thermal excitation and preserves Landau quantization at high temperatures. The LMR is observed as long as majority carriers remain in the lowest Landau level without requiring monochromaticity, allowing it to persist up to room temperature. The inverse relationship between the LMR slope and temperature provides clear evidence that quantum LMR originates from high-temperature phonon scattering in the quantum limit, firstly demonstrating a theoretical prediction made nearly fifty years ago. This study highlights the key role of electron-phonon interaction and reveals an innovative quantum mechanism for achieving high-temperature LMR, fundamentally distinct from previous findings. Our results bridge a gap in the understanding of phonon-mediated quantum-limit physics and establish strong magnetic fields at high temperatures as a promising platform for exploring novel quantum phenomena.
11 Jul 2025
Autonomous robot person-following (RPF) systems are crucial for personal assistance and security but suffer from target loss due to occlusions in dynamic, unknown environments. Current methods rely on pre-built maps and assume static environments, limiting their effectiveness in real-world settings. There is a critical gap in re-finding targets under topographic (e.g., walls, corners) and dynamic (e.g., moving pedestrians) occlusions. In this paper, we propose a novel heuristic-guided search framework that dynamically builds environmental maps while following the target and explicitly addresses these two types of occlusions through distinct mechanisms. For topographic occlusions, a belief-guided search field estimates the likelihood of the target's presence and guides search toward promising frontiers. For dynamic occlusions, an observation-based search strategy adaptively switches between a fluid-following field and an overtaking potential field based on occluder motion patterns. Our results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms existing approaches in terms of search efficiency and success rates, both in simulations and real-world tests. Our target search method enhances the adaptability and reliability of RPF systems in unknown and dynamic environments, supporting their use in real-world applications.
Researchers theoretically established the concept of ferroelastic altermagnetism, demonstrating how mechanical strain can drive multistate nonvolatile switching of altermagnetic spin splitting and spin transport in 2D RuF4 and CuF2 monolayers. First-principles calculations predict robust ferroelasticity and altermagnetic properties in these materials, alongside low energy barriers for mechanical switching.
08 Nov 2021
A globally convergent numerical method for a 3D coefficient inverse problem for a wave-like equation
A globally convergent numerical method for a 3D coefficient inverse problem for a wave-like equation
A version of the convexification globally convergent numerical method is constructed for a coefficient inverse problem for a wave-like partial differential equation. The presence of the Carleman Weight Function in the corresponding Tikhonov-like cost functional ensures the global strict convexity of this functional. Numerical results are presented to illustrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method.
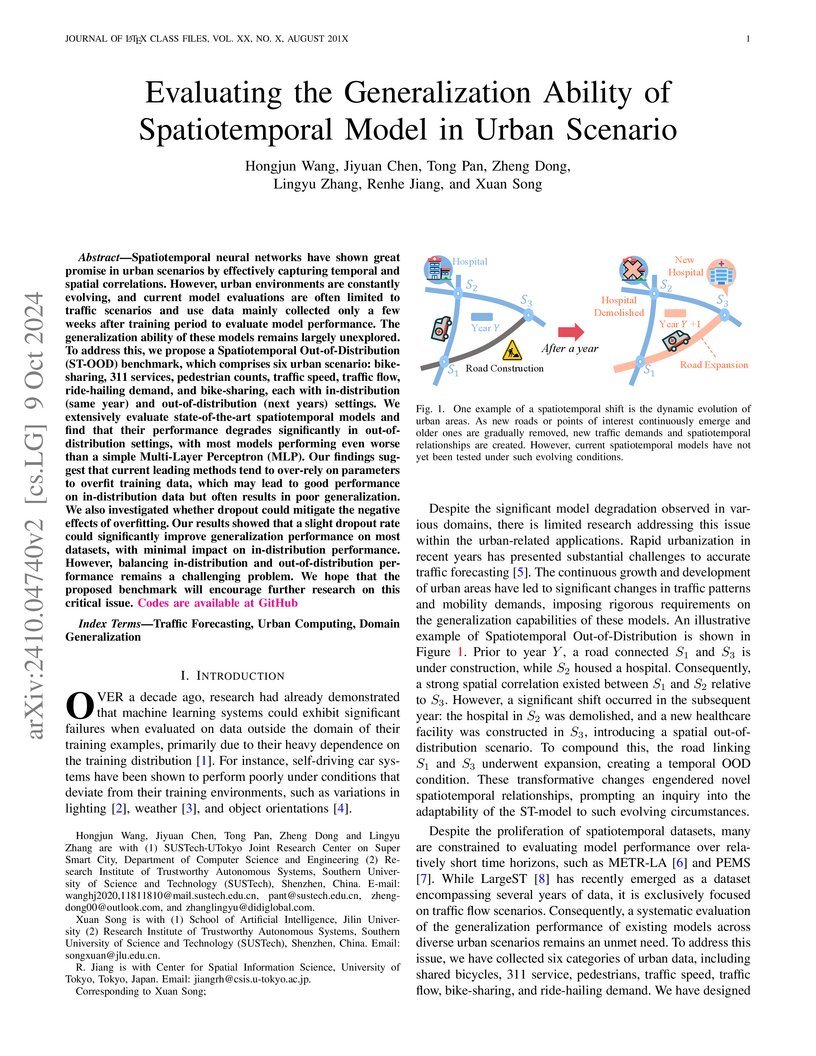
Spatiotemporal neural networks have shown great promise in urban scenarios by effectively capturing temporal and spatial correlations. However, urban environments are constantly evolving, and current model evaluations are often limited to traffic scenarios and use data mainly collected only a few weeks after training period to evaluate model performance. The generalization ability of these models remains largely unexplored. To address this, we propose a Spatiotemporal Out-of-Distribution (ST-OOD) benchmark, which comprises six urban scenario: bike-sharing, 311 services, pedestrian counts, traffic speed, traffic flow, ride-hailing demand, and bike-sharing, each with in-distribution (same year) and out-of-distribution (next years) settings. We extensively evaluate state-of-the-art spatiotemporal models and find that their performance degrades significantly in out-of-distribution settings, with most models performing even worse than a simple Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP). Our findings suggest that current leading methods tend to over-rely on parameters to overfit training data, which may lead to good performance on in-distribution data but often results in poor generalization. We also investigated whether dropout could mitigate the negative effects of overfitting. Our results showed that a slight dropout rate could significantly improve generalization performance on most datasets, with minimal impact on in-distribution performance. However, balancing in-distribution and out-of-distribution performance remains a challenging problem. We hope that the proposed benchmark will encourage further research on this critical issue.
We present a standard form of master equations (ME) for general one-dimensional non-Markovian (history-dependent) jump processes, complemented by an asymptotic solution derived from an expanded system-size approach. The ME is obtained by developing a general Markovian embedding using a suitable set of auxiliary field variables. This Markovian embedding uses a Laplace-convolution operation applied to the velocity trajectory. We introduce an asymptotic method tailored for this ME standard, generalising the system-size expansion for these jump processes. Under specific stability conditions tied to a single noise source, upon coarse-graining, the Generalized Langevin Equation (GLE) emerges as a universal approximate model for point processes in the weak-coupling limit. This methodology offers a unified analytical toolset for general non-Markovian processes, reinforcing the universal applicability of the GLE founded in microdynamics and the principles of statistical physics.
Quantifying the perceptual similarity of two images is a long-standing problem in low-level computer vision. The natural image domain commonly relies on supervised learning, e.g., a pre-trained VGG, to obtain a latent representation. However, due to domain shift, pre-trained models from the natural image domain might not apply to other image domains, such as medical imaging. Notably, in medical imaging, evaluating the perceptual similarity is exclusively performed by specialists trained extensively in diverse medical fields. Thus, medical imaging remains devoid of task-specific, objective perceptual measures. This work answers the question: Is it necessary to rely on supervised learning to obtain an effective representation that could measure perceptual similarity, or is self-supervision sufficient? To understand whether recent contrastive self-supervised representation (CSR) may come to the rescue, we start with natural images and systematically evaluate CSR as a metric across numerous contemporary architectures and tasks and compare them with existing methods. We find that in the natural image domain, CSR behaves on par with the supervised one on several perceptual tests as a metric, and in the medical domain, CSR better quantifies perceptual similarity concerning the experts' ratings. We also demonstrate that CSR can significantly improve image quality in two image synthesis tasks. Finally, our extensive results suggest that perceptuality is an emergent property of CSR, which can be adapted to many image domains without requiring annotations.
27 Sep 2021
Quantum confinement is a restriction on the motion of electrons in a material
to specific region, resulting in discrete energy levels rather than continuous
energy bands. In certain materials quantum confinement could dramatically
reshape the electronic structure and properties of the surface with respect to
the bulk. Here, in the recently discovered kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5
(A=K, Rb, Cs) family of materials, we unveil the dominant role of quantum
confinement in determining their surface electronic structure. Combining
angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) measurement and
density-functional theory simulation, we report the observations of
two-dimensional quantum well states due to the confinement of bulk electron
pocket and Dirac cone to the nearly isolated surface layer. The theoretical
calculations on the slab model also suggest that the ARPES observed spectra are
almost entirely contributed by the top two layers. Our results not only explain
the disagreement of band structures between the recent experiments and
calculations, but also suggest an equally important role played by quantum
confinement, together with strong correlation and band topology, in shaping the
electronic properties of this family of materials.
15 Oct 2024
 University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China Nanjing UniversityAnhui UniversityInternational Quantum AcademyQuantum Science Center of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (Guangdong)Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech)High Magnetic Field Laboratory, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Nanjing UniversityAnhui UniversityInternational Quantum AcademyQuantum Science Center of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (Guangdong)Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech)High Magnetic Field Laboratory, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of SciencesThe search for a giant Nernst effect beyond conventional mechanisms offers advantages for developing advanced thermoelectric devices and understanding charge-entropy conversion. Here, we study the Seebeck and Nernst effects of HfTe5 over a wide range of magnetic fields. By tracking the unusual magneto-thermoelectric responses, we reveal two magnetic-field-driven phase transitions proposed for weak topological insulators: the gap-closing transition of the zeroth Landau bands and the topological Lifshitz transition. After the magnetic fields exceed approximately ten times the quantum limit, we observe that the Nernst signal no longer varies with the fields, forming a plateau with a remarkably large value, reaching up to 50 {\mu}V/K at 2 K. We theoretically explain the giant Nernst plateau as a unique signature of the ideal 1D Weyl phase formed in such high fields. Our findings expand the understanding of ideal Weyl physics and open new avenues for realizing novel thermoelectric effects without fundamental constraints.
29 Mar 2024
Using a pure electric current to control kagome noncollinear antiferromagnets
is promising in information storage and processing, but a full description is
still lacking, in particular, on intrinsic (i.e., no external magnetic fields
or external spin currents) spin-orbit torques. In this work, we
self-consistently describe the relations among the electronic structure,
magnetic structure, spin accumulations, and intrinsic spin-orbit torques, in
the magnetic dynamics of a noncollinear antiferromagnet driven by a pure
electric current. Our calculation can yield a critical current density
comparable with those in the experiments, when considering the boost from the
out-of-plane magnetic dynamics induced by the current-driven spin accumulation
on individual magnetic moments. We stress the parity symmetry breaking in
deterministic switching among magnetic structures. This work will be helpful
for future applications of noncollinear antiferromagnets.
04 Jan 2024
Spatial, momentum and energy separation of electronic spins in condensed
matter systems guides the development of novel devices where spin-polarized
current is generated and manipulated. Recent attention on a set of previously
overlooked symmetry operations in magnetic materials leads to the emergence of
a new type of spin splitting, enabling giant and momentum-dependent spin
polarization of energy bands on selected antiferromagnets. Despite the
ever-growing theoretical predictions, the direct spectroscopic proof of such
spin splitting is still lacking. Here, we provide solid spectroscopic and
computational evidence for the existence of such materials. In the noncoplanar
antiferromagnet MnTe2, the in-plane components of spin are found to be
antisymmetric about the high-symmetry planes of the Brillouin zone, comprising
a plaid-like spin texture in the antiferromagnetic (AFM) ground state. Such an
unconventional spin pattern, further found to diminish at the high-temperature
paramagnetic state, stems from the intrinsic AFM order instead of spin-orbit
coupling (SOC). Our finding demonstrates a new type of quadratic spin texture
induced by time-reversal breaking, placing AFM spintronics on a firm basis and
paving the way for studying exotic quantum phenomena in related materials.
20 Nov 2019
The performance of a neural network for a given task is largely determined by
the initial calibration of the network parameters. Yet, it has been shown that
the calibration, also referred to as training, is generally NP-complete. This
includes networks with binary weights, an important class of networks due to
their practical hardware implementations. We therefore suggest an alternative
approach to training binary neural networks. It utilizes a quantum
superposition of weight configurations. We show that the quantum training
guarantees with high probability convergence towards the globally optimal set
of network parameters. This resolves two prominent issues of classical
training: (1) the vanishing gradient problem and (2) common convergence to
suboptimal network parameters. Moreover we achieve a provable
polynomial---sometimes exponential---speedup over classical training for
certain classes of tasks. We design an explicit training algorithm and
implement it in numerical simulations.
20 Apr 2020
We simulate a simplified version of the price process including bubbles and crashes proposed in Kreuser and Sornette (2018). The price process is defined as a geometric random walk combined with jumps modelled by separate, discrete distributions associated with positive (and negative) bubbles. The key ingredient of the model is to assume that the sizes of the jumps are proportional to the bubble size. Thus, the jumps tend to efficiently bring back excess bubble prices close to a normal or fundamental value (efficient crashes). This is different from existing processes studied that assume jumps that are independent of the mispricing. The present model is simplified compared to Kreuser and Sornette (2018) in that we ignore the possibility of a change of the probability of a crash as the price accelerates above the normal price. We study the behaviour of investment strategies that maximize the expected log of wealth (Kelly criterion) for the risky asset and a risk-free asset. We show that the method behaves similarly to Kelly on Geometric Brownian Motion in that it outperforms other methods in the long-term and it beats classical Kelly. As a primary source of outperformance, we determine knowledge about the presence of crashes, but interestingly find that knowledge of only the size, and not the time of occurrence, already provides a significant and robust edge. We then perform an error analysis to show that the method is robust with respect to variations in the parameters. The method is most sensitive to errors in the expected return.
30 Nov 2020
Space-time is one of the most essential, yet most mysterious concepts in physics. In quantum mechanics it is common to understand time as a marker of instances of evolution and define states around all the space but at one time; while in general relativity space-time is taken as a combinator, curved around mass. Here we present a unified approach on both space and time in quantum theory, and build quantum states across spacetime instead of only on spatial slices. We no longer distinguish measurements on the same system at different times with measurements on different systems at one time and construct spacetime states upon these measurement statistics. As a first step towards non-relativistic quantum field theory, we consider how to approach this in the continuous-variable multi-mode regime. We propose six possible definitions for spacetime states in continuous variables, based on four different measurement processes: quadratures, displaced parity operators, position measurements and weak measurements. The basic idea is to treat different instances of time as different quantum modes. They are motivated by the pseudo-density matrix formulation among indefinite causal structures and the path integral formalism. We show that these definitions lead to desirable properties, and raise the differences and similarities between spatial and temporal correlations. An experimental proposal for tomography is presented, construing the operational meaning of the spacetime states.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.