University of G\"ottingen
Computer vision for animal behavior offers promising tools to aid research in ecology, cognition, and to support conservation efforts. Video camera traps allow for large-scale data collection, but high labeling costs remain a bottleneck to creating large-scale datasets. We thus need data-efficient learning approaches. In this work, we show that we can utilize self-supervised learning to considerably improve action recognition on primate behavior. On two datasets of great ape behavior (PanAf and ChimpACT), we outperform published state-of-the-art action recognition models by 6.1 %pt. accuracy and 6.3 %pt. mAP, respectively. We achieve this by utilizing a pretrained V-JEPA model and applying domain-adaptive pretraining (DAP), i.e. continuing the pretraining with in-domain data. We show that most of the performance gain stems from the DAP. Our method promises great potential for improving the recognition of animal behavior, as DAP does not require labeled samples. Code is available at this https URL
24 Sep 2025
Within the field of optimal experimental design, \emph{sensor placement} refers to the act of finding the optimal locations of data collecting sensors, with the aim to optimise reconstruction of an unknown parameter from finite data. In this work, we investigate sensor placement for the inverse problem of reconstructing a heat source given final time measurements. Employing forward and adjoint analysis of this PDE-driven model, we show how one can leverage the first author's recently invented \emph{redundant-dominant p-continuation} algorithm to obtain binary A-optimal sensor placements also for this time-dependent model.
To ensure animal welfare and effective management in pig farming, monitoring individual behavior is a crucial prerequisite. While monitoring tasks have traditionally been carried out manually, advances in machine learning have made it possible to collect individualized information in an increasingly automated way. Central to these methods is the localization of animals across space (object detection) and time (multi-object tracking). Despite extensive research of these two tasks in pig farming, a systematic benchmarking study has not yet been conducted. In this work, we address this gap by curating two datasets: PigDetect for object detection and PigTrack for multi-object tracking. The datasets are based on diverse image and video material from realistic barn conditions, and include challenging scenarios such as occlusions or bad visibility. For object detection, we show that challenging training images improve detection performance beyond what is achievable with randomly sampled images alone. Comparing different approaches, we found that state-of-the-art models offer substantial improvements in detection quality over real-time alternatives. For multi-object tracking, we observed that SORT-based methods achieve superior detection performance compared to end-to-end trainable models. However, end-to-end models show better association performance, suggesting they could become strong alternatives in the future. We also investigate characteristic failure cases of end-to-end models, providing guidance for future improvements. The detection and tracking models trained on our datasets perform well in unseen pens, suggesting good generalization capabilities. This highlights the importance of high-quality training data. The datasets and research code are made publicly available to facilitate reproducibility, re-use and further development.
Visual perception relies on inference of 3D scene properties such as shape, pose, and lighting. To understand how visual sensory neurons enable robust perception, it is crucial to characterize their selectivity to such physically interpretable factors. However, current approaches mainly operate on 2D pixels, making it difficult to isolate selectivity for physical scene properties. To address this limitation, we introduce a differentiable rendering pipeline that optimizes deformable meshes to obtain MEIs directly in 3D. The method parameterizes mesh deformations with radial basis functions and learns offsets and scales that maximize neuronal responses while enforcing geometric regularity. Applied to models of monkey area V4, our approach enables probing neuronal selectivity to interpretable 3D factors such as pose and lighting. This approach bridges inverse graphics with systems neuroscience, offering a way to probe neural selectivity with physically grounded, 3D stimuli beyond conventional pixel-based methods.
01 Apr 2023
We argue that the reported cases of Spontaneous Human Combustion (SHC) are
most likely due to the impact of the human body with an extremely high energy
particle like cosmic rays or Dark Matter. Normal and antimatter cosmic rays and
classical weakly-interacting massive particles (WIMPs) with energies of GeV to
ZeV can be easily ruled out due to their inability to dump enough energy into a
small region of human tissue, leaving as the single remaining candidate massive
Dark Matter particles. While primordial Black Holes would appear to be very
good candidates for inducing the SHC phenomenon, we show that the estimated
local Dark Matter density requires that the particles have masses of $\sim
10$\,kg, clearly ruling out this candidate. All of the other classic DM
candidates -- from scalar and pseudo-scalar spin 1/2 and spin 2 gauge singlets
to nuclearitic strange quark ``bowling balls'' -- can be ruled out. Axions
tailored to solve the CP-problem also cannot be invoked, no matter what mass is
considered. The only particles left are massive mega-axions (MaMAs), for which
there are an infinite number of possible string models.
Controlling the size of droplets, for example in biological cells, is challenging because large droplets typically outcompete smaller droplets due to surface tension. This coarsening is generally accelerated by hydrodynamic effects, but active chemical reactions can suppress it. We show that the interplay of these processes leads to three different dynamical regimes: (i) Advection dominates the coalescence of small droplets, (ii) diffusion leads to Ostwald ripening for intermediate sizes, and (iii) reactions finally suppress coarsening. Interestingly, a range of final droplet sizes is stable, of which one is selected depending on initial conditions. Our analysis demonstrates that hydrodynamic effects control initial droplet sizes, but they do not affect the later dynamics, in contrast to passive emulsions.
Fingerprint recognition plays an important role in many commercial applications and is used by millions of people every day, e.g. for unlocking mobile phones. Fingerprint image segmentation is typically the first processing step of most fingerprint algorithms and it divides an image into foreground, the region of interest, and background. Two types of error can occur during this step which both have a negative impact on the recognition performance: 'true' foreground can be labeled as background and features like minutiae can be lost, or conversely 'true' background can be misclassified as foreground and spurious features can be introduced. The contribution of this paper is threefold: firstly, we propose a novel factorized directional bandpass (FDB) segmentation method for texture extraction based on the directional Hilbert transform of a Butterworth bandpass (DHBB) filter interwoven with soft-thresholding. Secondly, we provide a manually marked ground truth segmentation for 10560 images as an evaluation benchmark. Thirdly, we conduct a systematic performance comparison between the FDB method and four of the most often cited fingerprint segmentation algorithms showing that the FDB segmentation method clearly outperforms these four widely used methods. The benchmark and the implementation of the FDB method are made publicly available.
15 Jan 2018
We consider the problem of minimizing a convex, separable, nonsmooth function subject to linear constraints. The numerical method we propose is a block-coordinate extension of the Chambolle-Pock primal-dual algorithm. We prove convergence of the method without resorting to assumptions like smoothness or strong convexity of the objective, full-rank condition on the matrix, strong duality or even consistency of the linear system. Freedom from imposing the latter assumption permits convergence guarantees for misspecified or noisy systems.
27 Jul 2023
Traditional AI-planning methods for task planning in robotics require a symbolically encoded domain description. While powerful in well-defined scenarios, as well as human-interpretable, setting this up requires substantial effort. Different from this, most everyday planning tasks are solved by humans intuitively, using mental imagery of the different planning steps. Here we suggest that the same approach can be used for robots, too, in cases which require only limited execution accuracy. In the current study, we propose a novel sub-symbolic method called Simulated Mental Imagery for Planning (SiMIP), which consists of perception, simulated action, success-checking and re-planning performed on 'imagined' images. We show that it is possible to implement mental imagery-based planning in an algorithmically sound way by combining regular convolutional neural networks and generative adversarial networks. With this method, the robot acquires the capability to use the initially existing scene to generate action plans without symbolic domain descriptions, while at the same time plans remain human-interpretable, different from deep reinforcement learning, which is an alternative sub-symbolic approach. We create a dataset from real scenes for a packing problem of having to correctly place different objects into different target slots. This way efficiency and success rate of this algorithm could be quantified.
16 Oct 2025
Reservoir computers can be used to predict time series generated by spatio-temporal chaotic systems. Using multiple reservoirs in parallel has shown improved performances for these predictions, by effectively reducing the input dimensionality of each reservoir. Similarly, one may further reduce the dimensionality of the input data by transforming to a lower-dimensional latent space. Combining both approaches, we show that using dimensionality-reduced latent space predictions for parallel reservoir computing not only reduces computational costs, but also leads to better prediction results for small to medium reservoir sizes. In the combined approach we further demonstrate that dimensionality reduction improves small-reservoir predictions regardless of noise contaminating the training data. The benefit of dimensionality-reduced parallel reservoir computing is illustrated and evaluated on the basis of the prediction of the one-dimensional Kuramoto-Sivashinsky equation.
Developing a unified theory describing both ductile and brittle yielding constitutes a fundamental challenge of non-equilibrium statistical physics. Recently, it has been proposed that the nature of the yielding transition is controlled by physics akin to that of the quasistatically driven Random field Ising model (RFIM), which has served as the paradigm for understanding the effect of quenched disorder in slowly driven systems with short-ranged interactions. However, this theoretical picture neglects both the dynamics of, and the elasticity-induced long-ranged interactions between, the mesoscopic material constituents. Here, we address these two aspects and provide a unified theory building on the Hébraud-Lequeux elastoplastic description. The first aspect is crucial to understanding the competition between the imposed deformation rate and the finite timescale of plastic rearrangements: we provide a dynamical description of the macroscopic stress drop and predictions for the divergence of the peak susceptibility with inverse shear rate. The second is essential in order to capture properly the behaviour in the limit of quasistatic driving, where avalanches of plasticity diverge with system size at any value of the strain. We fully characterise the avalanche behaviour, which is radically different to that of the RFIM. In the quasistatic, infinite size limit, we find that both models have mean-field Landau exponents, obscuring the effect of the interactions. We show, however, that the latter profoundly affect the behaviour of finite systems approaching the spinodal-like brittle yield point, where we recover qualitatively the finite-size trends found in particle simulations, and modify the nature of the random critical point separating ductile and brittle yielding, where we predict critical behaviour on top of the marginality present at any value of the strain.
We present a mutually aligned diffusion framework for cross-modal
biomechanical motion generation, guided by a dynamical systems perspective. By
treating each modality, e.g., observed joint angles (X) and ground reaction
forces (Y), as complementary observations of a shared underlying locomotor
dynamical system, our method aligns latent representations at each diffusion
step, so that one modality can help denoise and disambiguate the other. Our
alignment approach is motivated by the fact that local time windows of X and
Y represent the same phase of an underlying dynamical system, thereby
benefiting from a shared latent manifold. We introduce a simple local latent
manifold alignment (LLMA) strategy that incorporates first-order and
second-order alignment within the latent space for robust cross-modal
biomechanical generation without bells and whistles. Through experiments on
multimodal human biomechanics data, we show that aligning local latent dynamics
across modalities improves generation fidelity and yields better
representations.
15 Mar 2018
We consider multivariate copula-based stationary time-series under Gaussian
subordination. Observed time series are subordinated to long-range dependent
Gaussian processes and characterized by arbitrary marginal copula
distributions. First of all, we establish limit theorems for the marginal and
quantile marginal empirical processes of multivariate stationary long-range
dependent sequences under Gaussian subordination. Furthermore, we establish the
asymptotic behavior of sequential empirical copula processes under
non-restrictive smoothness assumptions. The limiting processes in the case of
long-memory sequences are quite different from the cases of of i.i.d. and
weakly dependent observations.
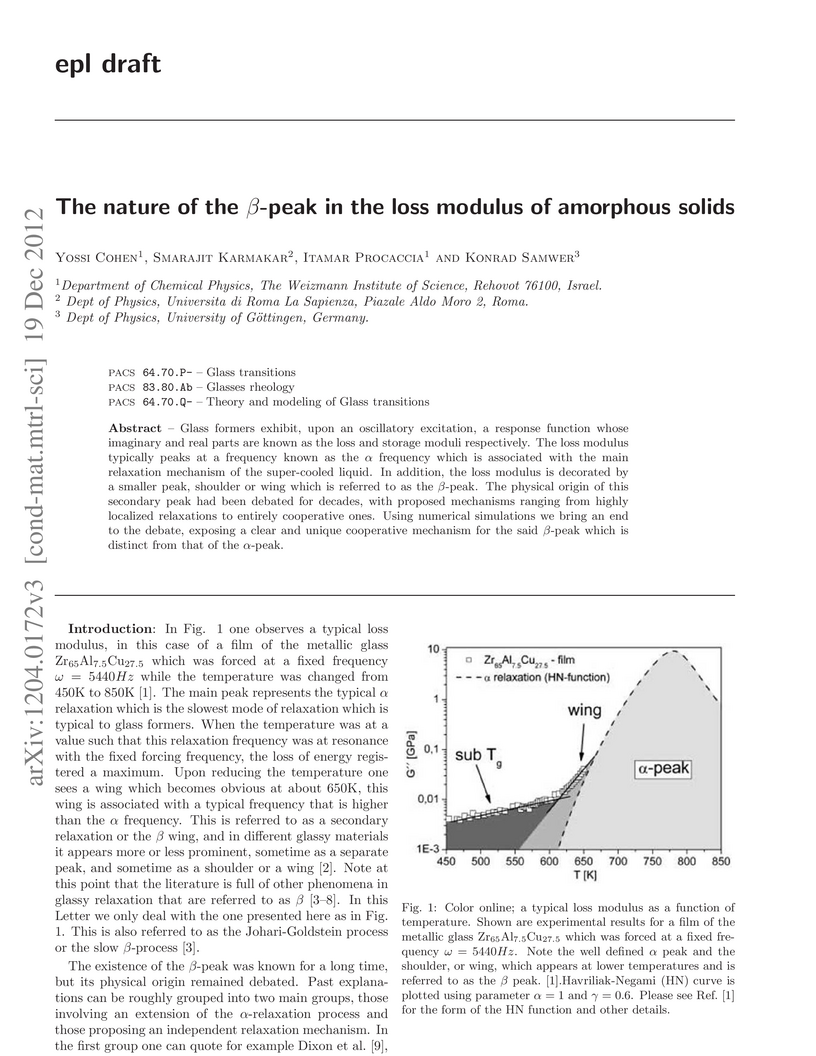
Glass formers exhibit, upon an oscillatory excitation, a response function whose imaginary and real parts are known as the loss and storage moduli respectively. The loss modulus typically peaks at a frequency known as the \alpha frequency which is associated with the main relaxation mechanism of the super-cooled liquid. In addition, the loss modulus is decorated by a smaller peak, shoulder or wing which is referred to as the \beta-peak. The physical origin of this secondary peak had been debated for decades, with proposed mechanisms ranging from highly localized relaxations to entirely cooperative ones. Using numerical simulations we bring an end to the debate, exposing a clear and unique cooperative mechanism for the said \beta-peak which is distinct from that of the α-peak.
25 Aug 2022
The purpose of this paper is to provide a systematic discussion of a generalized barycenter based on a variant of unbalanced optimal transport (UOT) that defines a distance between general non-negative, finitely supported measures by allowing for mass creation and destruction modeled by some cost parameter. They are denoted as Kantorovich-Rubinstein (KR) barycenter and distance. In particular, we detail the influence of the cost parameter to structural properties of the KR barycenter and the KR distance. For the latter we highlight a closed form solution on ultra-metric trees. The support of such KR barycenters of finitely supported measures turns out to be finite in general and its structure to be explicitly specified by the support of the input measures. Additionally, we prove the existence of sparse KR barycenters and discuss potential computational approaches. The performance of the KR barycenter is compared to the OT barycenter on a multitude of synthetic datasets. We also consider barycenters based on the recently introduced Gaussian Hellinger-Kantorovich and Wasserstein-Fisher-Rao distances.
09 Jan 2015
Tail dependence models for distributions attracted to a max-stable law are fitted using observations above a high threshold. To cope with spatial, high-dimensional data, a rank-based M-estimator is proposed relying on bivariate margins only. A data-driven weight matrix is used to minimize the asymptotic variance. Empirical process arguments show that the estimator is consistent and asymptotically normal. Its finite-sample performance is assessed in simulation experiments involving popular max-stable processes perturbed with additive noise. An analysis of wind speed data from the Netherlands illustrates the method.
In weakly perturbed systems that are close to integrability, thermalization can be delayed by the formation of prethermalization plateaus. We study the build-up of density-density correlations after a weak interaction quench in the Hubbard model in d>1 dimensions using unitary perturbation theory. Starting from a pre-quench state at temperature T, we show that the prethermalization values of the post-quench correlations are equal to the equilibrium values of the interacting model at the same temperature T. This is explained by the local character of density-density correlations.
We give a precise formulation of T-duality for Ramond-Ramond fields. This gives a canonical isomorphism between the "geometrically invariant" subgroups of the twisted differential K-theory of certain principal torus bundles. Our result combines topological T-duality with the Buscher rules found in physics.
03 Dec 2024
The discovery of the kagome metal CsV3Sb5 sparked broad interest, due to the coexistence of a charge density wave (CDW) phase and possible unconventional superconductivity in the material. In this study, we use low-energy electron diffraction (LEED) with a μm-sized electron beam to explore the periodic lattice distortion at the antimony-terminated surface in the CDW phase. We recorded high-quality backscattering diffraction patterns in ultrahigh vacuum from multiple cleaved samples. Unexpectedly, we did not find superstructure reflexes at intensity levels predicted from dynamical LEED calculations for the reported 2×2×2 bulk structure. Our results suggest that in CsV3Sb5 the periodic lattice distortion accompanying the CDW is less pronounced at Sb-terminated surfaces than in the bulk.
Phase balanced states are a highly under-explored class of solutions of the
Kuramoto model and other coupled oscillator models on networks. So far, coupled
oscillator research focused on phase synchronized solutions. Yet, global
constraints on oscillators may forbid synchronized state, rendering phase
balanced states as the relevant stable state. If for example oscillators are
driving the contractions of a fluid filled volume, conservation of fluid volume
constraints oscillators to balanced states as characterized by a vanishing
Kuramoto order parameter. It has previously been shown that stable, balanced
patterns in the Kuramoto model exist on circulant graphs. However, which
non-circulant graphs first of all allow for balanced states and what
characterizes the balanced states is unknown. Here, we derive rules of how to
build non-circulant, planar graphs allowing for balanced states from the simple
cycle graph by adding loops or edges to it. We thereby identify different
classes of small planar networks allowing for balanced states. Investigating
the balanced states' characteristics, we find that the variance in basin
stability scales linearly with the size of the graph for these networks. We
introduce the balancing ratio as a new order parameter based on the basin
stability approach to classify balanced states on networks and evaluate it
analytically for a subset of the network classes. Our results offer an
analytical description of non-circulant graphs supporting stable, balanced
states and may thereby help to understand the topological requirements on
oscillator networks under global constraints.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.