Waymo LLC
Waymo developed EMMA, an End-to-End Multimodal Model for Autonomous Driving, which leverages a multimodal large language model (MLLM) foundation like Gemini to process raw camera data and generate diverse driving outputs as natural language text. This approach achieved state-of-the-art motion planning on nuScenes and competitive performance on Waymo datasets, demonstrating up to a 13.5% improvement with Chain-of-Thought reasoning.
Waymo LLC researchers developed WOD-E2E, a dataset of 4,021 segments explicitly featuring challenging long-tail scenarios, addressing the lack of diverse data for end-to-end autonomous driving systems. They also introduced the Rater Feedback Score (RFS), a human-aligned evaluation metric that effectively assesses model performance in multi-modal, safety-critical situations, demonstrating a mild correlation with traditional metrics like Average Distance Error (ADE).
S4-Driver introduces a scalable self-supervised multimodal large language model for end-to-end motion planning in autonomous vehicles. The model effectively transforms MLLM's 2D visual representations into 3D spatio-temporal features, achieving state-of-the-art performance on large-scale datasets like Waymo's internal benchmark without requiring human annotations for perception or prediction tasks.
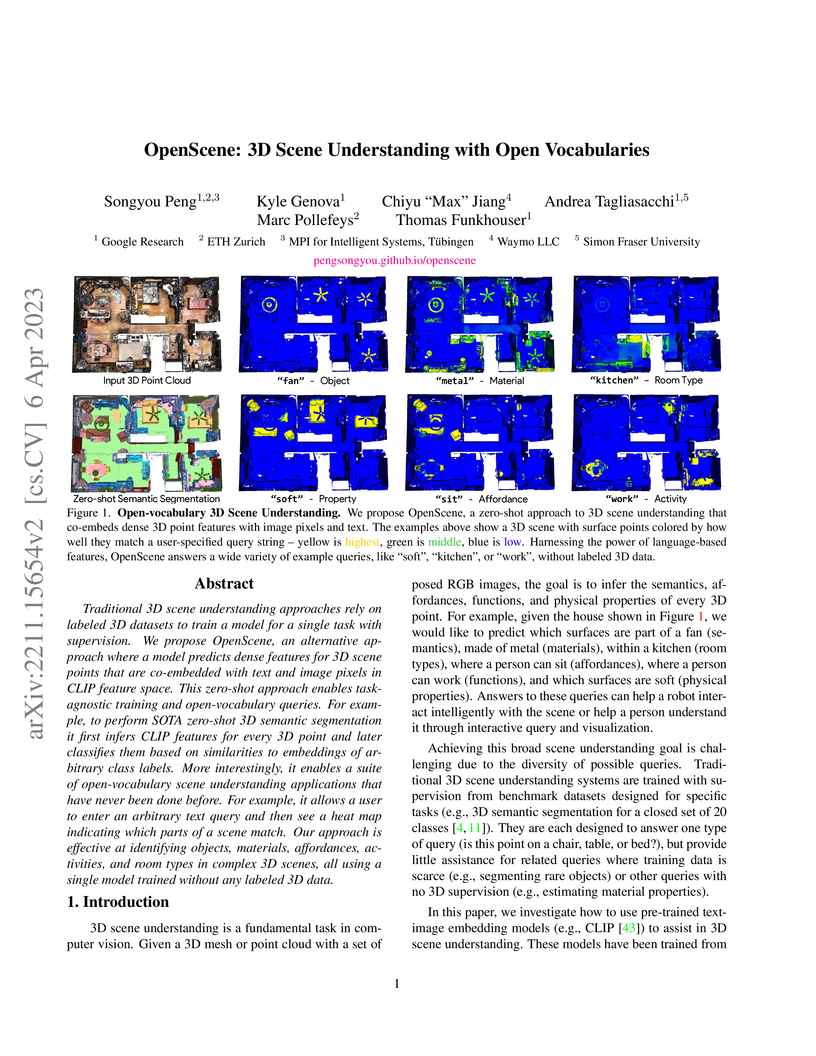
OpenScene introduces a zero-shot, open-vocabulary framework for 3D scene understanding, distilling knowledge from 2D vision-language models into 3D representations without requiring any 3D labeled data. This approach enables flexible querying of 3D scenes using arbitrary text and achieves competitive performance with older supervised methods while outperforming prior zero-shot approaches, for instance, securing 62.8% mIoU on 4 unseen ScanNet classes compared to 3DGenZ's 7.7%.
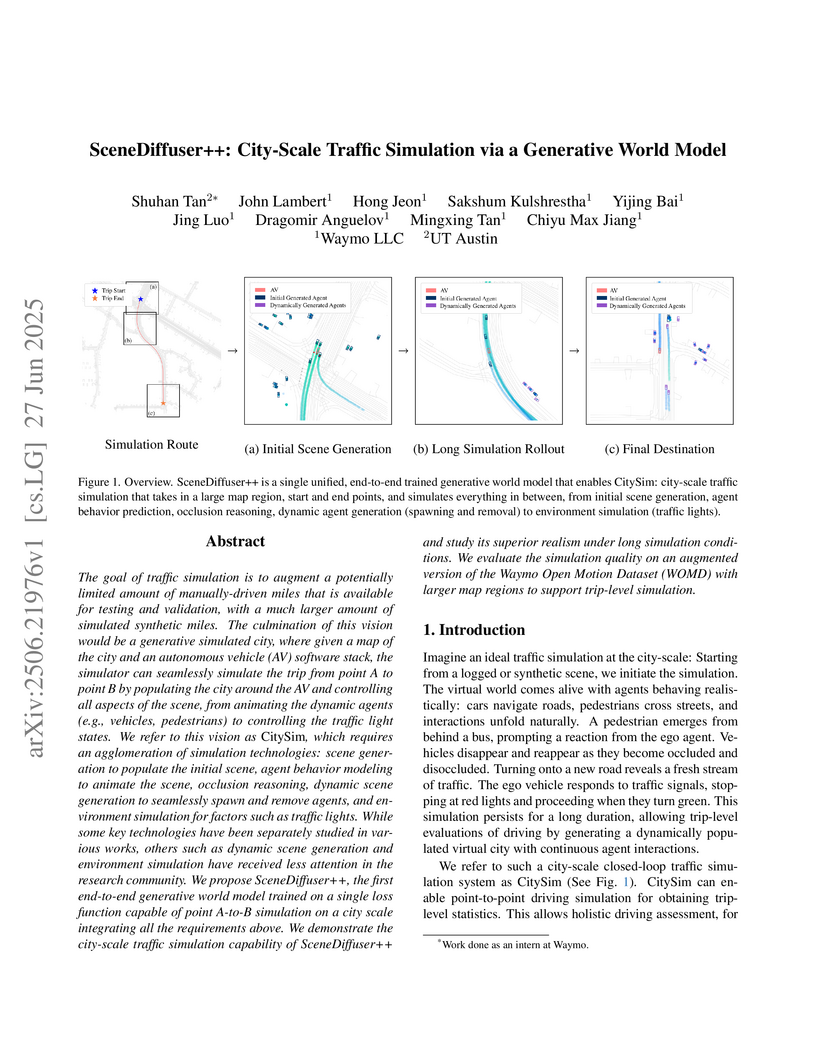
A generative world model named SceneDiffuser++ enables city-scale, trip-level traffic simulation by dynamically populating scenes with agents and realistically controlling traffic lights. This system generates diverse, long-duration synthetic driving miles, showing improved realism for agent insertion/removal and traffic light transitions compared to previous methods.
Researchers at Waymo empirically validate that neural scaling laws apply to joint motion forecasting and planning in autonomous driving, demonstrating that performance improves predictably with increased compute, data, and model size. The study quantifies optimal resource allocation, finding that optimal AV models are approximately 50 times smaller than large language models at equivalent compute and that improvements in open-loop supervised training strongly correlate with enhanced closed-loop safety in simulation.
SceneDiffuser presents a unified spatiotemporal diffusion model for autonomous driving, enabling both scene initialization and efficient closed-loop agent behavior rollout. It introduces an Amortized Autoregressive diffusion method that significantly reduces inference cost by 16x while maintaining high realism, and supports controllable scenario generation via generalized hard constraints and language-based prompting.
As autonomous driving systems mature, motion forecasting has received increasing attention as a critical requirement for planning. Of particular importance are interactive situations such as merges, unprotected turns, etc., where predicting individual object motion is not sufficient. Joint predictions of multiple objects are required for effective route planning. There has been a critical need for high-quality motion data that is rich in both interactions and annotation to develop motion planning models. In this work, we introduce the most diverse interactive motion dataset to our knowledge, and provide specific labels for interacting objects suitable for developing joint prediction models. With over 100,000 scenes, each 20 seconds long at 10 Hz, our new dataset contains more than 570 hours of unique data over 1750 km of roadways. It was collected by mining for interesting interactions between vehicles, pedestrians, and cyclists across six cities within the United States. We use a high-accuracy 3D auto-labeling system to generate high quality 3D bounding boxes for each road agent, and provide corresponding high definition 3D maps for each scene. Furthermore, we introduce a new set of metrics that provides a comprehensive evaluation of both single agent and joint agent interaction motion forecasting models. Finally, we provide strong baseline models for individual-agent prediction and joint-prediction. We hope that this new large-scale interactive motion dataset will provide new opportunities for advancing motion forecasting models.
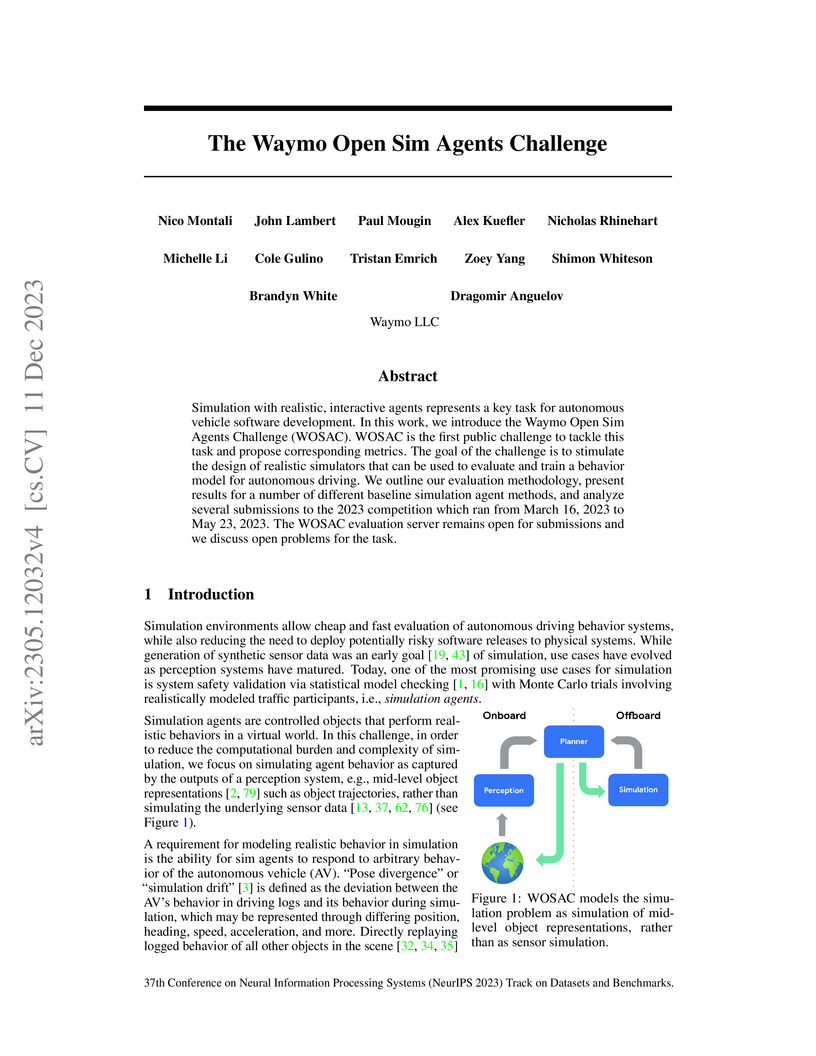
The Waymo Open Sim Agents Challenge (WOSAC) establishes a public benchmark for evaluating realistic and interactive simulation agents in autonomous driving. It defines traffic simulation as a conditional generative modeling problem and employs a novel approximate Negative Log Likelihood metric to quantify stochastic realism, finding that closed-loop trained, Transformer-based agents significantly outperform heuristic baselines.
Cross-entropy loss and focal loss are the most common choices when training deep neural networks for classification problems. Generally speaking, however, a good loss function can take on much more flexible forms, and should be tailored for different tasks and datasets. Motivated by how functions can be approximated via Taylor expansion, we propose a simple framework, named PolyLoss, to view and design loss functions as a linear combination of polynomial functions. Our PolyLoss allows the importance of different polynomial bases to be easily adjusted depending on the targeting tasks and datasets, while naturally subsuming the aforementioned cross-entropy loss and focal loss as special cases. Extensive experimental results show that the optimal choice within the PolyLoss is indeed dependent on the task and dataset. Simply by introducing one extra hyperparameter and adding one line of code, our Poly-1 formulation outperforms the cross-entropy loss and focal loss on 2D image classification, instance segmentation, object detection, and 3D object detection tasks, sometimes by a large margin.
Monocular image-based 3D perception has become an active research area in recent years owing to its applications in autonomous driving. Approaches to monocular 3D perception including detection and tracking, however, often yield inferior performance when compared to LiDAR-based techniques. Through systematic analysis, we identified that per-object depth estimation accuracy is a major factor bounding the performance. Motivated by this observation, we propose a multi-level fusion method that combines different representations (RGB and pseudo-LiDAR) and temporal information across multiple frames for objects (tracklets) to enhance per-object depth estimation. Our proposed fusion method achieves the state-of-the-art performance of per-object depth estimation on the Waymo Open Dataset, the KITTI detection dataset, and the KITTI MOT dataset. We further demonstrate that by simply replacing estimated depth with fusion-enhanced depth, we can achieve significant improvements in monocular 3D perception tasks, including detection and tracking.
Panoptic image segmentation is the computer vision task of finding groups of pixels in an image and assigning semantic classes and object instance identifiers to them. Research in image segmentation has become increasingly popular due to its critical applications in robotics and autonomous driving. The research community thereby relies on publicly available benchmark dataset to advance the state-of-the-art in computer vision. Due to the high costs of densely labeling the images, however, there is a shortage of publicly available ground truth labels that are suitable for panoptic segmentation. The high labeling costs also make it challenging to extend existing datasets to the video domain and to multi-camera setups. We therefore present the Waymo Open Dataset: Panoramic Video Panoptic Segmentation Dataset, a large-scale dataset that offers high-quality panoptic segmentation labels for autonomous driving. We generate our dataset using the publicly available Waymo Open Dataset, leveraging the diverse set of camera images. Our labels are consistent over time for video processing and consistent across multiple cameras mounted on the vehicles for full panoramic scene understanding. Specifically, we offer labels for 28 semantic categories and 2,860 temporal sequences that were captured by five cameras mounted on autonomous vehicles driving in three different geographical locations, leading to a total of 100k labeled camera images. To the best of our knowledge, this makes our dataset an order of magnitude larger than existing datasets that offer video panoptic segmentation labels. We further propose a new benchmark for Panoramic Video Panoptic Segmentation and establish a number of strong baselines based on the DeepLab family of models. We will make the benchmark and the code publicly available. Find the dataset at this https URL.
Closed-set 3D perception models trained on only a pre-defined set of object categories can be inadequate for safety critical applications such as autonomous driving where new object types can be encountered after deployment. In this paper, we present a multi-modal auto labeling pipeline capable of generating amodal 3D bounding boxes and tracklets for training models on open-set categories without 3D human labels. Our pipeline exploits motion cues inherent in point cloud sequences in combination with the freely available 2D image-text pairs to identify and track all traffic participants. Compared to the recent studies in this domain, which can only provide class-agnostic auto labels limited to moving objects, our method can handle both static and moving objects in the unsupervised manner and is able to output open-vocabulary semantic labels thanks to the proposed vision-language knowledge distillation. Experiments on the Waymo Open Dataset show that our approach outperforms the prior work by significant margins on various unsupervised 3D perception tasks.
26 Aug 2025
This paper presents crash rate benchmarks for evaluating US-based Automated Driving Systems (ADS) for multiple urban areas. The purpose of this study was to extend prior benchmarks focused only on surface streets to additionally capture freeway crash risk for future ADS safety performance assessments. Using publicly available police-reported crash and vehicle miles traveled (VMT) data, the methodology details the isolation of in-transport passenger vehicles, road type classification, and crash typology. Key findings revealed that freeway crash rates exhibit large geographic dependence variations with any-injury-reported crash rates being nearly 3.5 times higher in Atlanta (2.4 IPMM; the highest) when compared to Phoenix (0.7 IPMM; the lowest). The results show the critical need for location-specific benchmarks to avoid biased safety evaluations and provide insights into the vehicle miles traveled (VMT) required to achieve statistical significance for various safety impact levels. The distribution of crash types depended on the outcome severity level. Higher severity outcomes (e.g., fatal crashes) had a larger proportion of single-vehicle, vulnerable road users (VRU), and opposite-direction collisions compared to lower severity (police-reported) crashes. Given heterogeneity in crash types by severity, performance in low-severity scenarios may not be predictive of high-severity outcomes. These benchmarks are additionally used to quantify at the required mileage to show statistically significant deviations from human performance. This is the first paper to generate freeway-specific benchmarks for ADS evaluation and provides a foundational framework for future ADS benchmarking by evaluators and developers.
The Plug-and-Forecast (PnF) framework from Cornell, Waymo, and UC Berkeley enhances motion forecasting in autonomous driving by integrating multimodal large language models (MLLMs) in a plug-and-play, zero-shot manner. This approach yields consistent performance improvements on the Waymo Open Motion Dataset and nuScenes, achieving a 7.99% reduction in minADE on the top 10% hardest scenarios with a negligible increase in model parameters.
Semantic segmentation, which aims to classify every pixel in an image, is a key task in machine perception, with many applications across robotics and autonomous driving. Due to the high dimensionality of this task, most existing approaches use local operations, such as convolutions, to generate per-pixel features. However, these methods are typically unable to effectively leverage global context information due to the high computational costs of operating on a dense image. In this work, we propose a solution to this issue by leveraging the idea of superpixels, an over-segmentation of the image, and applying them with a modern transformer framework. In particular, our model learns to decompose the pixel space into a spatially low dimensional superpixel space via a series of local cross-attentions. We then apply multi-head self-attention to the superpixels to enrich the superpixel features with global context and then directly produce a class prediction for each superpixel. Finally, we directly project the superpixel class predictions back into the pixel space using the associations between the superpixels and the image pixel features. Reasoning in the superpixel space allows our method to be substantially more computationally efficient compared to convolution-based decoder methods. Yet, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in semantic segmentation due to the rich superpixel features generated by the global self-attention mechanism. Our experiments on Cityscapes and ADE20K demonstrate that our method matches the state of the art in terms of accuracy, while outperforming in terms of model parameters and latency.
3D object detection in point clouds is a core component for modern robotics and autonomous driving systems. A key challenge in 3D object detection comes from the inherent sparse nature of point occupancy within the 3D scene. In this paper, we propose Sparse Window Transformer (SWFormer ), a scalable and accurate model for 3D object detection, which can take full advantage of the sparsity of point clouds. Built upon the idea of window-based Transformers, SWFormer converts 3D points into sparse voxels and windows, and then processes these variable-length sparse windows efficiently using a bucketing scheme. In addition to self-attention within each spatial window, our SWFormer also captures cross-window correlation with multi-scale feature fusion and window shifting operations. To further address the unique challenge of detecting 3D objects accurately from sparse features, we propose a new voxel diffusion technique. Experimental results on the Waymo Open Dataset show our SWFormer achieves state-of-the-art 73.36 L2 mAPH on vehicle and pedestrian for 3D object detection on the official test set, outperforming all previous single-stage and two-stage models, while being much more efficient.
24 Oct 2024
Waymo researchers quantified the safety performance of their Waymo Driver in rider-only operations over 7.1 million miles, demonstrating an 80% reduction in any-injury-reported crashes and a 55% reduction in police-reported crashes compared to robust human driving benchmarks. This analysis utilized a rigorous methodology to address biases inherent in comparing autonomous and human crash data.
Continued improvements in deep learning architectures have steadily advanced
the overall performance of 3D object detectors to levels on par with humans for
certain tasks and datasets, where the overall performance is mostly driven by
common examples. However, even the best performing models suffer from the most
naive mistakes when it comes to rare examples that do not appear frequently in
the training data, such as vehicles with irregular geometries. Most studies in
the long-tail literature focus on class-imbalanced classification problems with
known imbalanced label counts per class, but they are not directly applicable
to the intra-class long-tail examples in problems with large intra-class
variations such as 3D object detection, where instances with the same class
label can have drastically varied properties such as shapes and sizes. Other
works propose to mitigate this problem using active learning based on the
criteria of uncertainty, difficulty, or diversity. In this study, we identify a
new conceptual dimension - rareness - to mine new data for improving the
long-tail performance of models. We show that rareness, as opposed to
difficulty, is the key to data-centric improvements for 3D detectors, since
rareness is the result of a lack in data support while difficulty is related to
the fundamental ambiguity in the problem. We propose a general and effective
method to identify the rareness of objects based on density estimation in the
feature space using flow models, and propose a principled cost-aware
formulation for mining rare object tracks, which improves overall model
performance, but more importantly - significantly improves the performance for
rare objects (by 30.97\%
30 Oct 2020
Waymo's mission to reduce traffic injuries and fatalities and improve
mobility for all has led us to expand deployment of automated vehicles on
public roads without a human driver behind the wheel. As part of this process,
Waymo is committed to providing the public with informative and relevant data
regarding the demonstrated safety of Waymo's automated driving system, which we
call the Waymo Driver. The data presented in this paper represents more than
6.1 million miles of automated driving in the Phoenix, Arizona metropolitan
area, including operations with a trained operator behind the steering wheel
from calendar year 2019 and 65,000 miles of driverless operation without a
human behind the steering wheel from 2019 and the first nine months of 2020.
The paper includes every collision and minor contact experienced during these
operations as well as every predicted contact identified using Waymo's
counterfactual, what if, simulation of events had the vehicle's trained
operator not disengaged automated driving. There were 47 contact events that
occurred over this time period, consisting of 18 actual and 29 simulated
contact events, none of which would be expected to result in severe or life
threatening injuries. This paper presents the collision typology and severity
for each actual and simulated event, along with diagrams depicting each of the
most significant events. Nearly all the events involved one or more road rule
violations or other errors by a human driver or road user, including all eight
of the most severe events, which we define as involving actual or expected
airbag deployment in any involved vehicle. When compared to national collision
statistics, the Waymo Driver completely avoided certain collision modes that
human driven vehicles are frequently involved in, including road departure and
collisions with fixed objects.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.