embedding-methods
Researchers from Fudan University and Shanghai Innovation Institute introduced RoPE++, an extension of Rotary Position Embeddings that re-incorporates the previously discarded imaginary component of attention scores to improve long-context modeling in Large Language Models. This method consistently outperforms standard RoPE on various benchmarks and offers significant KV-cache and parameter efficiency.
07 Dec 2025
WisPaper introduces an AI-powered scholar search engine that unifies academic literature discovery, management, and continuous tracking within a single platform. Its core Deep Search component, powered by the WisModel agent, achieved 94.8% semantic similarity in query understanding and 93.70% overall accuracy in paper-criteria matching, demonstrating superior performance over leading commercial LLMs, especially in nuanced judgments.
Researchers from University of Wisconsin-Madison, UCLA, and Adobe Research introduce a computational framework for "relational visual similarity," which identifies image commonalities based on abstract logic rather than surface features. Their `relsim` model, trained on a novel dataset of images paired with anonymous group-derived captions, aligns significantly with human perception of relational similarity and outperforms existing attribute-based metrics in retrieval tasks.
The paper introduces Group Representational Position Encoding (GRAPE), a unified group-theoretic framework that re-conceptualizes and unifies existing positional encoding mechanisms like RoPE and ALiBi. It provides a principled design space for new encodings, demonstrating improved training stability and superior zero-shot performance in large language models.
A new framework, Distribution Matching Variational AutoEncoder (DMVAE), explicitly aligns a VAE's aggregate latent distribution with a pre-defined reference distribution using score-based matching. The approach achieves a state-of-the-art gFID of 1.82 on ImageNet 256x256, demonstrating superior training efficiency for downstream generative models, particularly when utilizing Self-Supervised Learning features as the reference.
Researchers from Alibaba Group and Wuhan University developed MUSE, a multimodal search-based framework for lifelong user interest modeling that integrates rich semantic information across both retrieval and fine-grained modeling stages. Deployed in Taobao's display advertising system, MUSE achieved a +12.6% CTR, +5.1% RPM, and +11.4% ROI in online A/B tests.
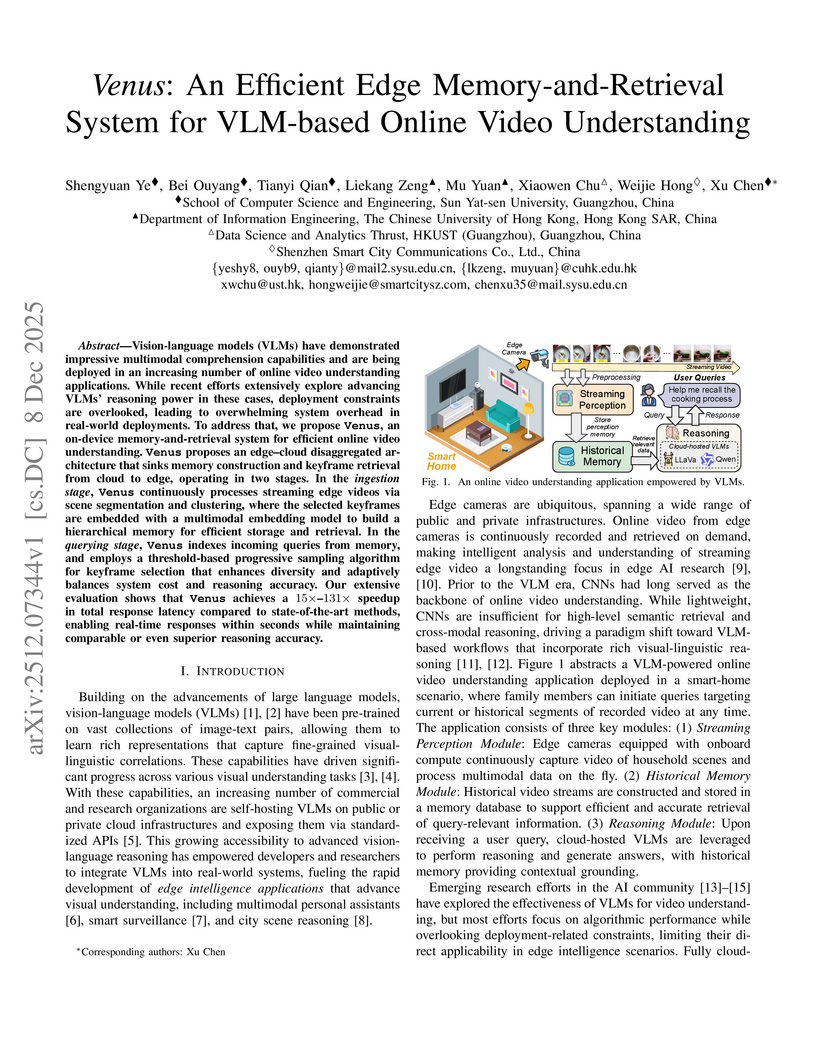
Vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive multimodal comprehension capabilities and are being deployed in an increasing number of online video understanding applications. While recent efforts extensively explore advancing VLMs' reasoning power in these cases, deployment constraints are overlooked, leading to overwhelming system overhead in real-world deployments. To address that, we propose Venus, an on-device memory-and-retrieval system for efficient online video understanding. Venus proposes an edge-cloud disaggregated architecture that sinks memory construction and keyframe retrieval from cloud to edge, operating in two stages. In the ingestion stage, Venus continuously processes streaming edge videos via scene segmentation and clustering, where the selected keyframes are embedded with a multimodal embedding model to build a hierarchical memory for efficient storage and retrieval. In the querying stage, Venus indexes incoming queries from memory, and employs a threshold-based progressive sampling algorithm for keyframe selection that enhances diversity and adaptively balances system cost and reasoning accuracy. Our extensive evaluation shows that Venus achieves a 15x-131x speedup in total response latency compared to state-of-the-art methods, enabling real-time responses within seconds while maintaining comparable or even superior reasoning accuracy.
Frontier language model quality increasingly hinges on our ability to organize web-scale text corpora for training. Today's dominant tools trade off speed and flexibility: lexical classifiers (e.g., FastText) are fast but limited to producing classification output scores, while the vector-valued outputs of transformer text embedding models flexibly support numerous workflows (e.g., clustering, classification, and retrieval) but are computationally expensive to produce. We introduce Luxical, a library for high-speed "lexical-dense" text embeddings that aims to recover the best properties of both approaches for web-scale text organization. Luxical combines sparse TF--IDF features, a small ReLU network, and a knowledge distillation training regimen to approximate large transformer embedding models at a fraction of their operational cost. In this technical report, we describe the Luxical architecture and training objective and evaluate a concrete Luxical model in two disparate applications: a targeted webcrawl document retrieval test and an end-to-end language model data curation task grounded in text classification. In these tasks we demonstrate speedups ranging from 3x to 100x over varying-sized neural baselines, and comparable to FastText model inference during the data curation task. On these evaluations, the tested Luxical model illustrates favorable compute/quality trade-offs for large-scale text organization, matching the quality of neural baselines. Luxical is available as open-source software at this https URL.
Pre-training decoder-only language models relies on vast amounts of high-quality data, yet the availability of such data is increasingly reaching its limits. While metadata is commonly used to create and curate these datasets, its potential as a direct training signal remains under-explored. We challenge this status quo and propose LIME (Linguistic Metadata Embeddings), a method that enriches token embeddings with metadata capturing syntax, semantics, and contextual properties. LIME substantially improves pre-training efficiency. Specifically, it adapts up to 56% faster to the training data distribution, while introducing only 0.01% additional parameters at negligible compute overhead. Beyond efficiency, LIME improves tokenization, leading to remarkably stronger language modeling capabilities and generative task performance. These benefits persist across model scales (500M to 2B). In addition, we develop a variant with shifted metadata, LIME+1, that can guide token generation. Given prior metadata for the next token, LIME+1 improves reasoning performance by up to 38% and arithmetic accuracy by up to 35%.
Background: The deployment of personalized Large Language Models (LLMs) is currently constrained by the stability-plasticity dilemma. Prevailing alignment methods, such as Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), rely on stochastic weight updates that often incur an "alignment tax" -- degrading general reasoning capabilities.
Methods: We propose the Soul Engine, a framework based on the Linear Representation Hypothesis, which posits that personality traits exist as orthogonal linear subspaces. We introduce SoulBench, a dataset constructed via dynamic contextual sampling. Using a dual-head architecture on a frozen Qwen-2.5 base, we extract disentangled personality vectors without modifying the backbone weights.
Results: Our experiments demonstrate three breakthroughs. First, High-Precision Profiling: The model achieves a Mean Squared Error (MSE) of 0.011 against psychological ground truth. Second, Geometric Orthogonality: T-SNE visualization confirms that personality manifolds are distinct and continuous, allowing for "Zero-Shot Personality Injection" that maintains original model intelligence. Third, Deterministic Steering: We achieve robust control over behavior via vector arithmetic, validated through extensive ablation studies.
Conclusion: This work challenges the necessity of fine-tuning for personalization. By transitioning from probabilistic prompting to deterministic latent intervention, we provide a mathematically rigorous foundation for safe, controllable AI personalization.
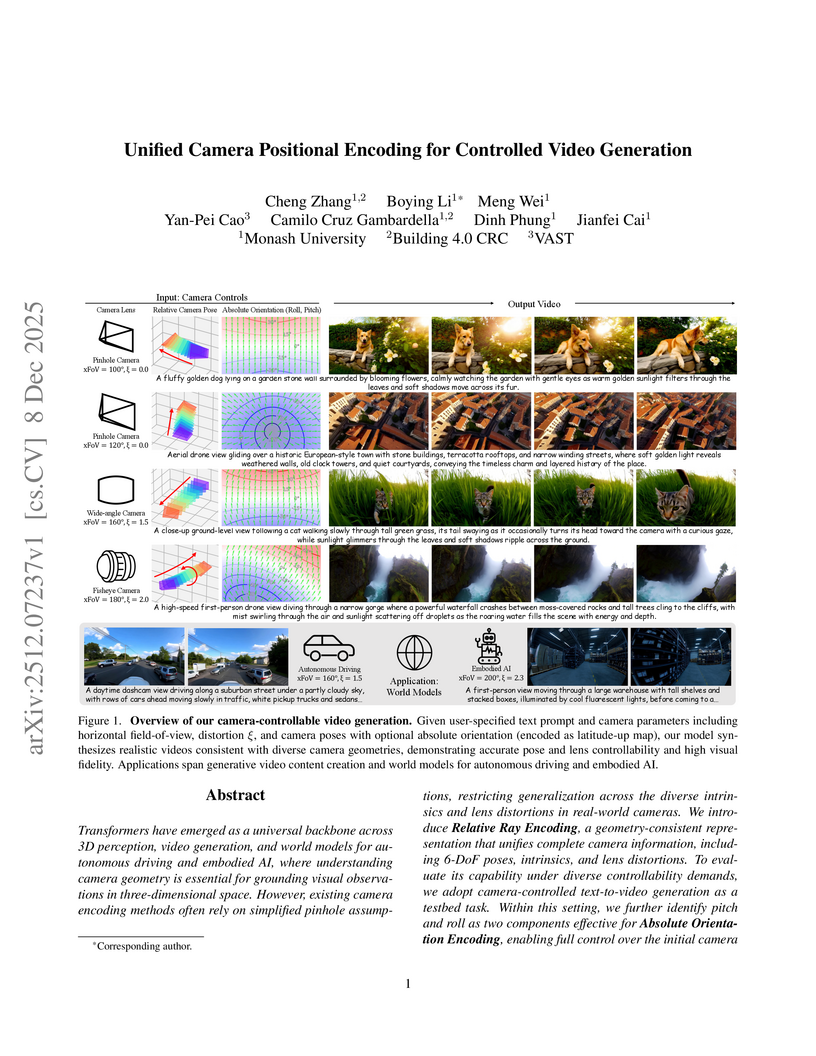
This work from Monash University introduces Unified Camera Positional Encoding (UCPE), a framework that enables fine-grained control over diverse camera geometries, including 6-DoF poses, intrinsics, and lens distortions, in video generation. UCPE integrates into Diffusion Transformers using a lightweight adapter, leading to superior control accuracy in lens, absolute orientation, and relative pose, while maintaining high visual fidelity.
KAIST researchers developed TabPFN-GN, a method that reformulates graph node classification as a tabular learning problem, enabling a pre-trained tabular foundation model to achieve competitive or superior performance compared to Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) without graph-specific training. The method outperforms baseline GNNs on 5 out of 6 heterophilous datasets and ranks first on 3 homophilous datasets.
New York University researchers investigated whether state-of-the-art self-supervised video models, including V-JEPA, could acquire intuitive physics by training on developmentally realistic egocentric visual data from the SAYCam dataset. They found that all models, regardless of training data volume or distribution, achieved only slightly above chance performance (0.50-0.54 accuracy) on the IntPhys2 benchmark, failing to bridge the substantial gap with human understanding.
Enzymes are crucial catalysts that enable a wide range of biochemical reactions. Efficiently identifying specific enzymes from vast protein libraries is essential for advancing biocatalysis. Traditional computational methods for enzyme screening and retrieval are time-consuming and resource-intensive. Recently, deep learning approaches have shown promise. However, these methods focus solely on the interaction between enzymes and reactions, overlooking the inherent hierarchical relationships within each domain. To address these limitations, we introduce FGW-CLIP, a novel contrastive learning framework based on optimizing the fused Gromov-Wasserstein distance. FGW-CLIP incorporates multiple alignments, including inter-domain alignment between reactions and enzymes and intra-domain alignment within enzymes and reactions. By introducing a tailored regularization term, our method minimizes the Gromov-Wasserstein distance between enzyme and reaction spaces, which enhances information integration across these domains. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the superiority of FGW-CLIP in challenging enzyme-reaction tasks. On the widely-used EnzymeMap benchmark, FGW-CLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance in enzyme virtual screening, as measured by BEDROC and EF metrics. Moreover, FGW-CLIP consistently outperforms across all three splits of ReactZyme, the largest enzyme-reaction benchmark, demonstrating robust generalization to novel enzymes and reactions. These results position FGW-CLIP as a promising framework for enzyme discovery in complex biochemical settings, with strong adaptability across diverse screening scenarios.
Accurate prediction of protein-protein binding affinity is vital for understanding molecular interactions and designing therapeutics. We adapt Boltz-2, a state-of-the-art structure-based protein-ligand affinity predictor, for protein-protein affinity regression and evaluate it on two datasets, TCR3d and PPB-affinity. Despite high structural accuracy, Boltz-2-PPI underperforms relative to sequence-based alternatives in both small- and larger-scale data regimes. Combining embeddings from Boltz-2-PPI with sequence-based embeddings yields complementary improvements, particularly for weaker sequence models, suggesting different signals are learned by sequence- and structure-based models. Our results echo known biases associated with training with structural data and suggest that current structure-based representations are not primed for performant affinity prediction.
This research provides a systematic investigation into masking designs for self-supervised learning on molecular graphs, formalizing the pretraining pipeline and employing information-theoretic measures. The study reveals that the semantic richness of the prediction target is crucial for downstream performance, particularly when paired with expressive encoder architectures.
Environmental variables are increasingly affecting agricultural decision-making, yet accessible and scalable tools for soil assessment remain limited. This study presents a robust and scalable modeling system for estimating soil properties in croplands, including soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (N), available phosphorus (P), exchangeable potassium (K), and pH, using remote sensing data and environmental covariates. The system employs a hybrid modeling approach, combining the indirect methods of modeling soil through proxies and drivers with direct spectral modeling. We extend current approaches by using interpretable physics-informed covariates derived from radiative transfer models (RTMs) and complex, nonlinear embeddings from a foundation model. We validate the system on a harmonized dataset that covers Europes cropland soils across diverse pedoclimatic zones. Evaluation is conducted under a robust validation framework that enforces strict spatial blocking, stratified splits, and statistically distinct train-test sets, which deliberately make the evaluation harder and produce more realistic error estimates for unseen regions. The models achieved their highest accuracy for SOC and N. This performance held across unseen locations, under both spatial cross-validation and an independent test set. SOC obtained a MAE of 5.12 g/kg and a CCC of 0.77, and N obtained a MAE of 0.44 g/kg and a CCC of 0.77. We also assess uncertainty through conformal calibration, achieving 90 percent coverage at the target confidence level. This study contributes to the digital advancement of agriculture through the application of scalable, data-driven soil analysis frameworks that can be extended to related domains requiring quantitative soil evaluation, such as carbon markets.
Rotary Position Embeddings (RoPE) have become a standard for encoding sequence order in Large Language Models (LLMs) by applying rotations to query and key vectors in the complex plane. Standard implementations, however, utilize only the real component of the complex-valued dot product for attention score calculation. This simplification discards the imaginary component, which contains valuable phase information, leading to a potential loss of relational details crucial for modeling long-context dependencies. In this paper, we propose an extension that re-incorporates this discarded imaginary component. Our method leverages the full complex-valued representation to create a dual-component attention score. We theoretically and empirically demonstrate that this approach enhances the modeling of long-context dependencies by preserving more positional information. Furthermore, evaluations on a suite of long-context language modeling benchmarks show that our method consistently improves performance over the standard RoPE, with the benefits becoming more significant as context length increases. The code is available at this https URL.
Existing fine-grained image retrieval (FGIR) methods learn discriminative embeddings by adopting semantically sparse one-hot labels derived from category names as supervision. While effective on seen classes, such supervision overlooks the rich semantics encoded in category names, hindering the modeling of comparability among cross-category details and, in turn, limiting generalization to unseen categories. To tackle this, we introduce LaFG, a Language-driven framework for Fine-Grained Retrieval that converts class names into attribute-level supervision using large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs). Treating each name as a semantic anchor, LaFG prompts an LLM to generate detailed, attribute-oriented descriptions. To mitigate attribute omission in these descriptions, it leverages a frozen VLM to project them into a vision-aligned space, clustering them into a dataset-wide attribute vocabulary while harvesting complementary attributes from related categories. Leveraging this vocabulary, a global prompt template selects category-relevant attributes, which are aggregated into category-specific linguistic prototypes. These prototypes supervise the retrieval model to steer
Rohit Goswami, affiliated with EPFL and TurtleTech ehf., introduced a two-dimensional RMSD projection method for visualizing and validating reaction pathways in computational chemistry. This method maps high-dimensional reaction trajectories onto a 2D surface based on intrinsic geometric distances, allowing for robust convergence diagnosis, clear landscape topology visualization, and nuanced comparison of different potential energy surfaces.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.