multi-task-learning
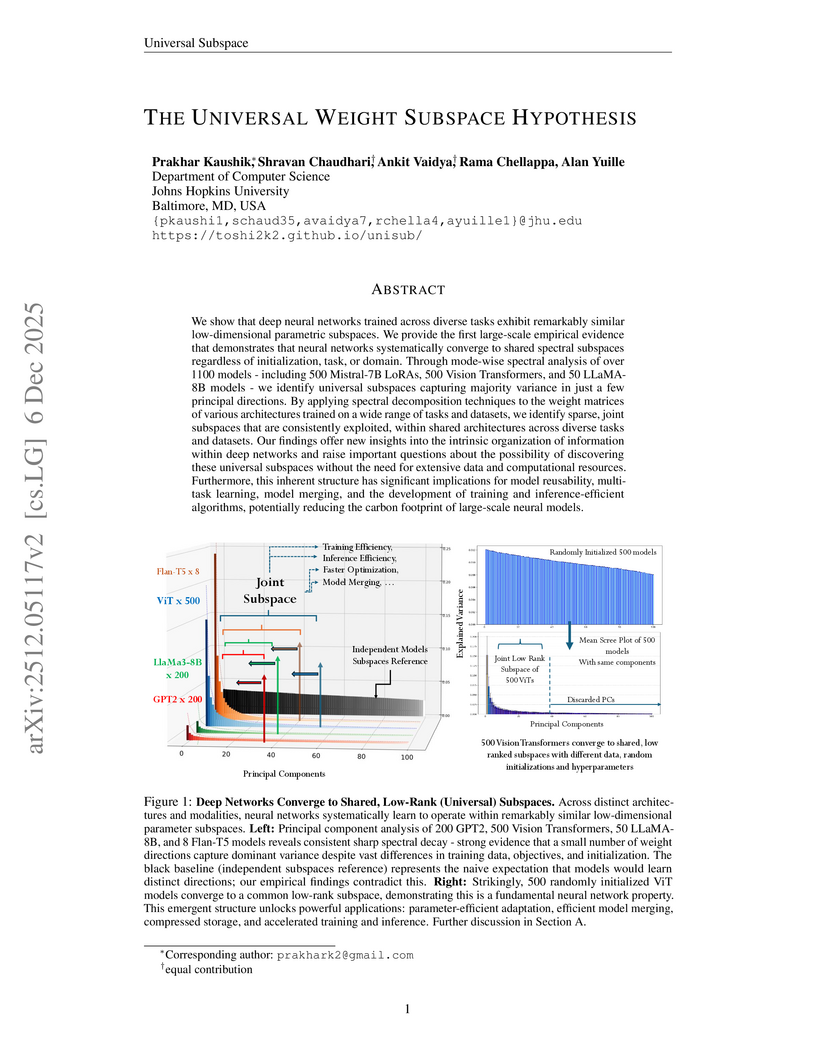
This paper presents the Universal Weight Subspace Hypothesis, demonstrating empirically that deep neural networks trained across diverse tasks and modalities converge to shared low-dimensional parametric subspaces. This convergence enables significant memory savings, such as up to 100x for Vision Transformers and LLaMA models, and 19x for LoRA adapters, while preserving model performance and enhancing efficiency in model merging and adaptation.
Researchers from Google DeepMind, University College London, and the University of Oxford developed D4RT, a unified feedforward model for reconstructing dynamic 4D scenes, encompassing depth, spatio-temporal correspondence, and camera parameters, from video using a single, flexible querying interface. The model achieved state-of-the-art accuracy across various 4D reconstruction and tracking benchmarks, with 3D tracking throughput 18-300 times faster and pose estimation over 100 times faster than prior methods.
09 Dec 2025
EcomBench introduces a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating foundation agents in e-commerce, drawing on genuine user demands and expert curation to assess real-world capabilities. The evaluation demonstrates that leading models achieve strong performance on basic tasks but struggle significantly with complex, multi-step e-commerce reasoning and integrating knowledge from various sources.
10 Dec 2025
Role-playing agents (RPAs) must simultaneously master many conflicting skills -- following multi-turn instructions, exhibiting domain knowledge, and adopting a consistent linguistic style. Existing work either relies on supervised fine-tuning (SFT) that over-fits surface cues and yields low diversity, or applies reinforcement learning (RL) that fails to learn multiple dimensions for comprehensive RPA optimization. We present MOA (Multi-Objective Alignment), a reinforcement-learning framework that enables multi-dimensional, fine-grained rubric optimization for general RPAs. MOA introduces a novel multi-objective optimization strategy that trains simultaneously on multiple fine-grained rubrics to boost optimization performance. Besides, to address the issues of model output diversity and quality, we have also employed thought-augmented rollout with off-policy guidance. Extensive experiments on challenging benchmarks such as PersonaGym and RoleMRC show that MOA enables an 8B model to match or even outperform strong baselines such as GPT-4o and Claude across numerous dimensions. This demonstrates the great potential of MOA in building RPAs that can simultaneously meet the demands of role knowledge, persona style, diverse scenarios, and complex multi-turn conversations.
PRISM-WM introduces a world model that leverages a Mixture-of-Experts architecture with latent orthogonalization to accurately model hybrid dynamics in robotic systems. This approach significantly extends reliable planning horizons and achieves superior performance in high-dimensional continuous control tasks.
Huawei Inc. developed EMMA (Efficient Multimodal Understanding, Generation, and Editing), a unified architecture that reduces visual tokens by 80% compared to previous models by employing a 32x compression autoencoder and channel-wise concatenation. EMMA-4B surpasses leading unified multimodal models and achieves competitive performance against specialized expert models across understanding, generation, and editing benchmarks.
Researchers from Fudan University developed a unified framework for Aerial Vision-Language Navigation, enabling UAVs to follow natural language instructions using only monocular RGB observations. This framework achieves state-of-the-art performance among RGB-only methods and demonstrates competitive capabilities compared to systems relying on additional sensors.
09 Dec 2025
Understanding human personality is crucial for web applications such as personalized recommendation and mental health assessment. Existing studies on personality detection predominantly adopt a "posts -> user vector -> labels" modeling paradigm, which encodes social media posts into user representations for predicting personality labels (e.g., MBTI labels). While recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have improved text encoding capacities, these approaches remain constrained by limited supervision signals due to label scarcity, and under-specified semantic mappings between user language and abstract psychological constructs. We address these challenges by proposing ROME, a novel framework that explicitly injects psychological knowledge into personality detection. Inspired by standardized self-assessment tests, ROME leverages LLMs' role-play capability to simulate user responses to validated psychometric questionnaires. These generated question-level answers transform free-form user posts into interpretable, questionnaire-grounded evidence linking linguistic cues to personality labels, thereby providing rich intermediate supervision to mitigate label scarcity while offering a semantic reasoning chain that guides and simplifies the text-to-personality mapping learning. A question-conditioned Mixture-of-Experts module then jointly routes over post and question representations, learning to answer questionnaire items under explicit supervision. The predicted answers are summarized into an interpretable answer vector and fused with the user representation for final prediction within a multi-task learning framework, where question answering serves as a powerful auxiliary task for personality detection. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets demonstrate that ROME consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving improvements (15.41% on Kaggle dataset).
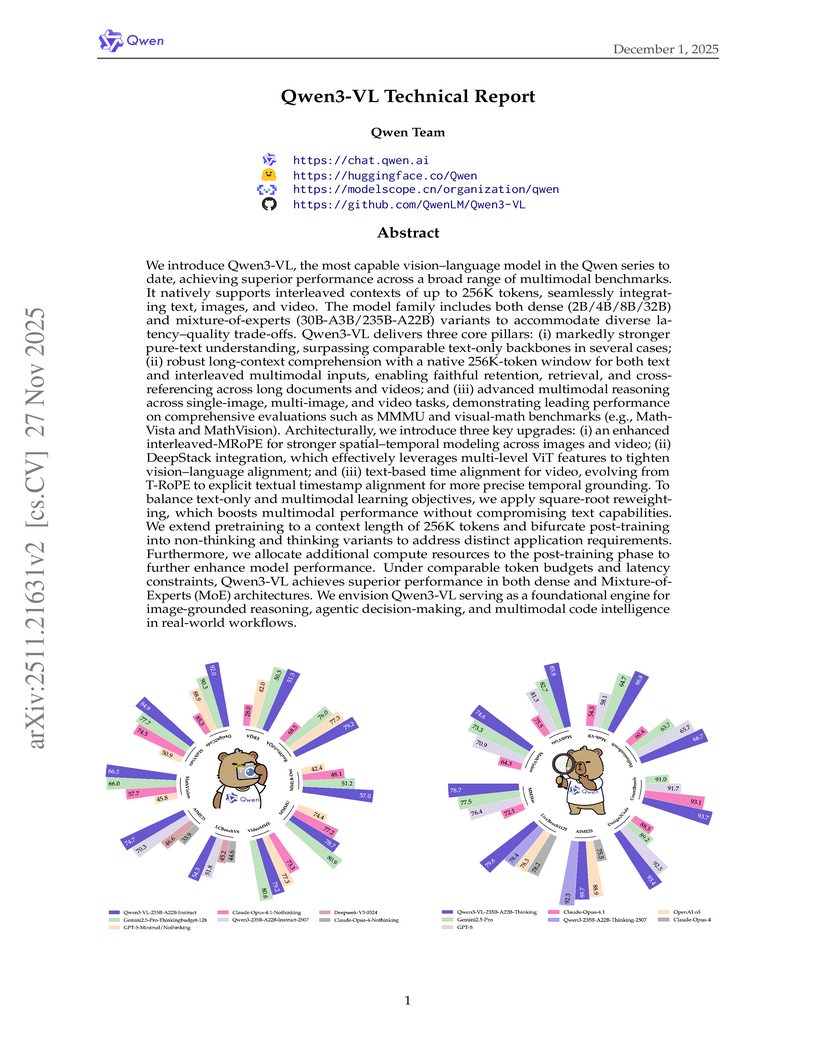
The Qwen Team at Alibaba Group introduced Qwen3-VL, an open-source family of vision-language models that integrates text, image, and video understanding with native ultra-long context support up to 256K tokens. It achieved state-of-the-art results across a wide range of multimodal benchmarks, including VQA, multimodal reasoning, grounding, and video understanding, demonstrating over 70% accuracy for 32 out of 39 supported OCR languages.
This research introduces a method that uses semantically grounded linguistic "motion tokens" to abstract continuous robot actions, enabling a two-stage pretraining and fine-tuning strategy to bridge numerical scale discrepancies across diverse robotic datasets. The approach achieves up to 14.1% higher average success rates on benchmarks like SimplerEnv compared to baselines and reduces the modality gap between action and language representations.
FreeGen introduces a feed-forward reconstruction-generation co-training framework that integrates 3D Gaussian Splatting with geometry-aware diffusion models for free-viewpoint driving scene synthesis. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes dataset, with an FID of 11.34 and FVD of 44.98 at a 12m lateral shift, outperforming previous methods without requiring auxiliary LiDAR or 3D bounding box annotations.
Recent studies have shown the success of deep learning in solving forward and inverse problems in engineering and scientific computing domains, such as physics-informed neural networks (PINNs). In the fields of atmospheric science and environmental monitoring, estimating emission source locations is a central task that further relies on multiple model parameters that dictate velocity profiles and diffusion parameters. Estimating these parameters at the same time as emission sources from scarce data is a difficult task. In this work, we achieve this by leveraging the flexibility and generality of PINNs. We use a weighted adaptive method based on the neural tangent kernels to solve a source inversion problem with parameter estimation on the 2D and 3D advection-diffusion equations with unknown velocity and diffusion coefficients that may vary in space and time. Our proposed weighted adaptive method is presented as an extension of PINNs for forward PDE problems to a highly ill-posed source inversion and parameter estimation problem. The key idea behind our methodology is to attempt the joint recovery of the solution, the sources along with the unknown parameters, thereby using the underlying partial differential equation as a constraint that couples multiple unknown functional parameters, leading to more efficient use of the limited information in the measurements. We present various numerical experiments, using different types of measurements that model practical engineering systems, to show that our proposed method is indeed successful and robust to additional noise in the measurements.
Machine learning (ML) offers a powerful path toward discovering sustainable polymer materials, but progress has been limited by the lack of large, high-quality, and openly accessible polymer datasets. The Open Polymer Challenge (OPC) addresses this gap by releasing the first community-developed benchmark for polymer informatics, featuring a dataset with 10K polymers and 5 properties: thermal conductivity, radius of gyration, density, fractional free volume, and glass transition temperature. The challenge centers on multi-task polymer property prediction, a core step in virtual screening pipelines for materials discovery. Participants developed models under realistic constraints that include small data, label imbalance, and heterogeneous simulation sources, using techniques such as feature-based augmentation, transfer learning, self-supervised pretraining, and targeted ensemble strategies. The competition also revealed important lessons about data preparation, distribution shifts, and cross-group simulation consistency, informing best practices for future large-scale polymer datasets. The resulting models, analysis, and released data create a new foundation for molecular AI in polymer science and are expected to accelerate the development of sustainable and energy-efficient materials. Along with the competition, we release the test dataset at this https URL. We also release the data generation pipeline at this https URL, which simulates more than 25 properties, including thermal conductivity, radius of gyration, and density.
A major challenge in reconstructing buildings from LiDAR point clouds lies in accurately capturing building surfaces under varying point densities and noise interference. To flexibly gather high-quality 3D profiles of the building in diverse resolution, we propose OCCDiff applying latent diffusion in the occupancy function space. Our OCCDiff combines a latent diffusion process with a function autoencoder architecture to generate continuous occupancy functions evaluable at arbitrary locations. Moreover, a point encoder is proposed to provide condition features to diffusion learning, constraint the final occupancy prediction for occupancy decoder, and insert multi-modal features for latent generation to latent encoder. To further enhance the model performance, a multi-task training strategy is employed, ensuring that the point encoder learns diverse and robust feature representations. Empirical results show that our method generates physically consistent samples with high fidelity to the target distribution and exhibits robustness to noisy data.
05 Dec 2025
Researchers at Fudan University and Microsoft Research Asia developed HiMoE-VLA, a generalist vision-language-action model, which employs a Hierarchical Mixture-of-Experts architecture to effectively manage the inherent heterogeneity in large-scale robotic datasets. This model achieved state-of-the-art performance, including 3.967 consecutively completed tasks on CALVIN and 97.8% average success on LIBERO, alongside robust generalization in real-world single and dual-arm manipulation.
Speech Enhancement (SE) and Speech Separation (SS) have traditionally been treated as distinct tasks in speech processing. However, real-world audio often involves both background noise and overlapping speakers, motivating the need for a unified solution. While recent approaches have attempted to integrate SE and SS within multi-stage architectures, these approaches typically involve complex, parameter-heavy models and rely on supervised training, limiting scalability and generalization. In this work, we propose UniVoiceLite, a lightweight and unsupervised audio-visual framework that unifies SE and SS within a single model. UniVoiceLite leverages lip motion and facial identity cues to guide speech extraction and employs Wasserstein distance regularization to stabilize the latent space without requiring paired noisy-clean data. Experimental results demonstrate that UniVoiceLite achieves strong performance in both noisy and multi-speaker scenarios, combining efficiency with robust generalization. The source code is available at this https URL.
Researchers from Sorbonne Université and Criteo AI Lab introduce ECHO, a framework for efficient generative transformer operators that addresses the scalability and long-horizon error accumulation issues in neural operators for PDEs. ECHO achieves high spatio-temporal compression and accurate, multi-task solutions for million-point PDE trajectories, notably enabling super-resolution forecasting on a 1024x1024 Vorticity grid without out-of-memory errors where other models failed.
03 Dec 2025
Researchers from MMLab, CUHK and Meituan developed OneThinker, a unified multimodal large language model capable of diverse visual understanding tasks across images and videos. This model utilizes an EMA-GRPO algorithm to achieve robust performance across 31 benchmarks, setting new state-of-the-art results for many tasks.
Researchers from the University of Hong Kong, Beijing Institute of Technology, and the University of Delaware developed UniTS, a unified time series generative model based on flow matching, capable of performing four distinct remote sensing tasks: reconstruction, cloud removal, semantic change detection, and forecasting. UniTS demonstrated superior performance across these tasks, achieving over 1.88 dB PSNR improvement for cloud removal on a new challenging dataset with 84.02% average cloud coverage, and the best mIoU scores for semantic change detection.
Recent studies have witnessed significant advances in image restoration foundation models driven by improvements in the scale and quality of pre-training data. In this work, we find that the data mixture proportions from different restoration tasks are also a critical factor directly determining the overall performance of all-in-one image restoration models. To this end, we propose a high-capacity diffusion-based image restoration foundation model, FoundIR-v2, which adopts a data equilibrium scheduling paradigm to dynamically optimize the proportions of mixed training datasets from different tasks. By leveraging the data mixing law, our method ensures a balanced dataset composition, enabling the model to achieve consistent generalization and comprehensive performance across diverse tasks. Furthermore, we introduce an effective Mixture-of-Experts (MoE)-driven scheduler into generative pre-training to flexibly allocate task-adaptive diffusion priors for each restoration task, accounting for the distinct degradation forms and levels exhibited by different tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method can address over 50 sub-tasks across a broader scope of real-world scenarios and achieves favorable performance against state-of-the-art approaches.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.