Borealis AI
This paper offers a comprehensive review of Normalizing Flows, a class of generative models allowing for efficient and exact computation of both sampling and probability density. It systematically categorizes diverse flow architectures, analyzes their mathematical properties and computational trade-offs, and benchmarks their empirical performance on standard datasets.
By leveraging the parallel scan algorithm for training, this work transforms classic LSTMs and GRUs into 'minLSTMs' and 'minGRUs,' demonstrating that these simplified, parallelizable models can achieve competitive performance with modern architectures like Mamba while being significantly more efficient and using fewer parameters. The study shows that foundational recurrent designs, when re-evaluated through a modern lens of parallel computation, remain highly effective.
FLORA introduces a new optimization technique for large neural networks, addressing the memory bottleneck of optimization states like gradients and momentum. By reinterpreting Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) as a gradient compression method and incorporating dynamic random projections, FLORA achieves sublinear memory complexity for these states while enabling high-rank weight updates, performing comparably to or better than full-memory baselines and significantly outperforming LoRA in full training scenarios.
Aaren (Attention as a recurrent neural network) exactly reformulates standard softmax attention as an RNN, delivering competitive performance across diverse sequential tasks while achieving constant memory and constant-time updates per token during inference, significantly improving efficiency over Transformers.
This research from the University of British Columbia and Borealis AI presents a method for autonomously generating Planning Domain Definition Language (PDDL) models using Large Language Models (LLMs) and environment interaction. It introduces the Exploration Walk (EW) metric to provide continuous feedback for LLM refinement, achieving a 66% average task solve rate across PDDL environments, which surpasses direct LLM planning.
A study on exposure bias in language generation formally defines how it causes super-linear error accumulation through an imitation learning perspective. It introduces new metrics to quantify this phenomenon, demonstrating its direct link to degenerate generation quality and explaining why perplexity fails to capture this issue.
A survey from Borealis AI comprehensively reviews Multiagent Deep Reinforcement Learning (MDRL), categorizing research into four areas and critically analyzing how concepts from traditional multiagent learning and reinforcement learning have been adapted to address challenges like non-stationarity and multiagent credit assignment.
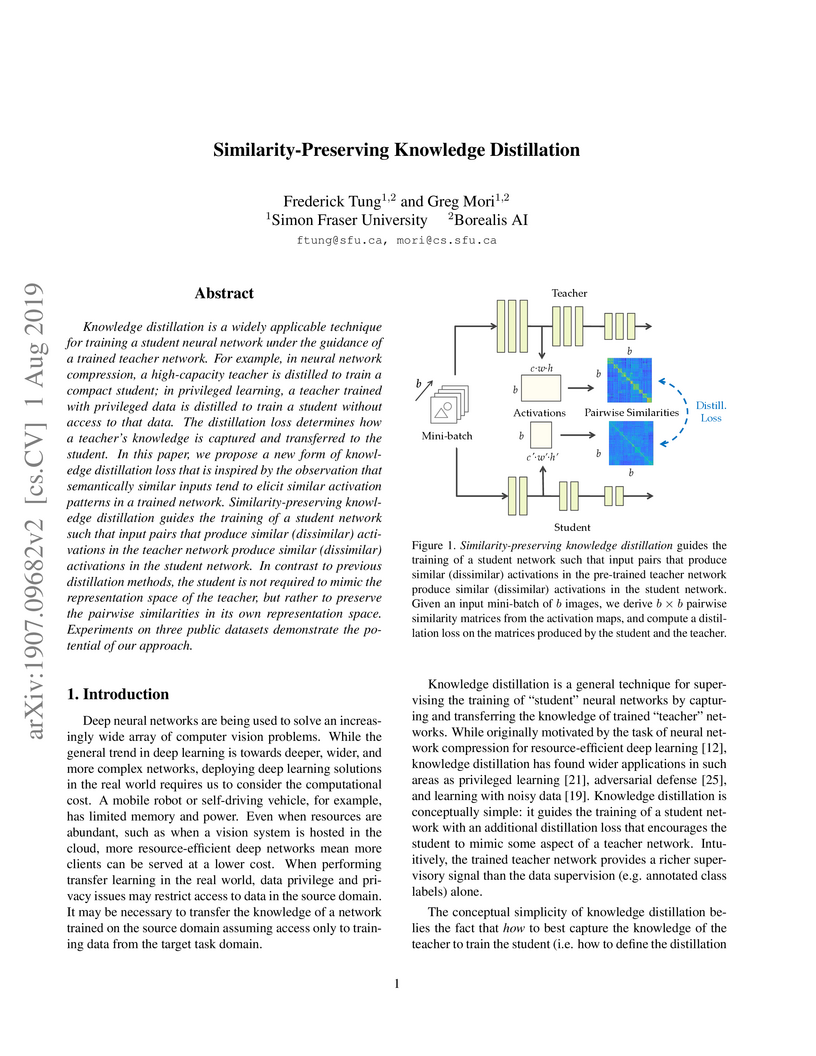
Researchers Frederick Tung and Greg Mori at Simon Fraser University and Borealis AI propose Similarity-Preserving Knowledge Distillation (SPKD), a method guiding a student network by preserving pairwise activation similarities from a teacher. SPKD consistently improved student network performance, enabling 5x model compression with only a 0.3% absolute accuracy loss on CIFAR-10 and facilitating effective transfer learning across disjoint domains.
Cheng et al. disentangle mathematical reasoning in large language models into abstract formulation and arithmetic computation, revealing that LLMs possess stronger abstract reasoning abilities but are bottlenecked by computational accuracy. Their findings demonstrate that Chain-of-Thought prompting primarily aids computation and that LLMs employ an 'abstract-then-compute' processing mechanism.
Time series~(TS) modeling is essential in dynamic systems like weather prediction and anomaly detection. Recent studies utilize Large Language Models (LLMs) for TS modeling, leveraging their powerful pattern recognition capabilities. These methods primarily position LLMs as the predictive backbone, often omitting the mathematical modeling within traditional TS models, such as periodicity. However, disregarding the potential of LLMs also overlooks their pattern recognition capabilities. To address this gap, we introduce \textit{LLM-TS Integrator}, a novel framework that effectively integrates the capabilities of LLMs into traditional TS modeling. Central to this integration is our \textit{mutual information} module. The core of this \textit{mutual information} module is a traditional TS model enhanced with LLM-derived insights for improved predictive abilities. This enhancement is achieved by maximizing the mutual information between traditional model's TS representations and LLM's textual representation counterparts, bridging the two modalities. Moreover, we recognize that samples vary in importance for two losses: traditional prediction and mutual information maximization. To address this variability, we introduce the \textit{sample reweighting} module to improve information utilization. This module assigns dual weights to each sample: one for prediction loss and another for mutual information loss, dynamically optimizing these weights via bi-level optimization. Our method achieves state-of-the-art or comparable performance across five mainstream TS tasks, including short-term and long-term forecasting, imputation, classification, and anomaly detection.
Graphs arise naturally in many real-world applications including social networks, recommender systems, ontologies, biology, and computational finance. Traditionally, machine learning models for graphs have been mostly designed for static graphs. However, many applications involve evolving graphs. This introduces important challenges for learning and inference since nodes, attributes, and edges change over time. In this survey, we review the recent advances in representation learning for dynamic graphs, including dynamic knowledge graphs. We describe existing models from an encoder-decoder perspective, categorize these encoders and decoders based on the techniques they employ, and analyze the approaches in each category. We also review several prominent applications and widely used datasets and highlight directions for future research.
Predicting multiple heterogeneous biological and medical targets is a challenge for traditional deep learning models. In contrast to single-task learning, in which a separate model is trained for each target, multi-task learning (MTL) optimizes a single model to predict multiple related targets simultaneously. To address this challenge, we propose the Multi-gate Mixture-of-Experts with Exclusivity (MMoEEx). Our work aims to tackle the heterogeneous MTL setting, in which the same model optimizes multiple tasks with different characteristics. Such a scenario can overwhelm current MTL approaches due to the challenges in balancing shared and task-specific representations and the need to optimize tasks with competing optimization paths. Our method makes two key contributions: first, we introduce an approach to induce more diversity among experts, thus creating representations more suitable for highly imbalanced and heterogenous MTL learning; second, we adopt a two-step optimization [6, 11] approach to balancing the tasks at the gradient level. We validate our method on three MTL benchmark datasets, including Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC-III) and PubChem BioAssay (PCBA).
30 Mar 2021
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has recently achieved significant advances
in various domains. However, explaining the policy of RL agents still remains
an open problem due to several factors, one being the complexity of explaining
neural networks decisions. Recently, a group of works have used
decision-tree-based models to learn explainable policies. Soft decision trees
(SDTs) and discretized differentiable decision trees (DDTs) have been
demonstrated to achieve both good performance and share the benefit of having
explainable policies. In this work, we further improve the results for
tree-based explainable RL in both performance and explainability. Our proposal,
Cascading Decision Trees (CDTs) apply representation learning on the decision
path to allow richer expressivity. Empirical results show that in both
situations, where CDTs are used as policy function approximators or as
imitation learners to explain black-box policies, CDTs can achieve better
performances with more succinct and explainable models than SDTs. As a second
contribution our study reveals limitations of explaining black-box policies via
imitation learning with tree-based explainable models, due to its inherent
instability.
The ReTreever architecture introduces Tree Cross Attention (TCA), a dynamic, tree-based retrieval module that reduces the computational complexity of attention-based model inference from linear O(N) to logarithmic O(log N). This method achieved comparable performance to standard cross-attention using substantially fewer tokens (e.g., 50 times fewer on a memory retrieval task) and outperformed fixed-capacity models like Perceiver IO.
Most neural networks are trained using first-order optimization methods, which are sensitive to the parameterization of the model. Natural gradient descent is invariant to smooth reparameterizations because it is defined in a coordinate-free way, but tractable approximations are typically defined in terms of coordinate systems, and hence may lose the invariance properties. We analyze the invariance properties of the Kronecker-Factored Approximate Curvature (K-FAC) algorithm by constructing the algorithm in a coordinate-free way. We explicitly construct a Riemannian metric under which the natural gradient matches the K-FAC update; invariance to affine transformations of the activations follows immediately. We extend our framework to analyze the invariance properties of K-FAC applied to convolutional networks and recurrent neural networks, as well as metrics other than the usual Fisher metric.
Neural Processes (NPs) are popular methods in meta-learning that can estimate
predictive uncertainty on target datapoints by conditioning on a context
dataset. Previous state-of-the-art method Transformer Neural Processes (TNPs)
achieve strong performance but require quadratic computation with respect to
the number of context datapoints, significantly limiting its scalability.
Conversely, existing sub-quadratic NP variants perform significantly worse than
that of TNPs. Tackling this issue, we propose Latent Bottlenecked Attentive
Neural Processes (LBANPs), a new computationally efficient sub-quadratic NP
variant, that has a querying computational complexity independent of the number
of context datapoints. The model encodes the context dataset into a constant
number of latent vectors on which self-attention is performed. When making
predictions, the model retrieves higher-order information from the context
dataset via multiple cross-attention mechanisms on the latent vectors. We
empirically show that LBANPs achieve results competitive with the
state-of-the-art on meta-regression, image completion, and contextual
multi-armed bandits. We demonstrate that LBANPs can trade-off the computational
cost and performance according to the number of latent vectors. Finally, we
show LBANPs can scale beyond existing attention-based NP variants to larger
dataset settings.
RankSim introduces a regularization technique that explicitly aligns the ranking of neighbors in label space with their learned feature space representations, addressing deep imbalanced regression. The method achieves new state-of-the-art performance on age estimation and sentence similarity benchmarks, notably improving generalization on few-shot and zero-shot data and reducing Mean Absolute Error to 6.91 on the AgeDB-DIR dataset.
The performance of neural networks improves when more parameters are used. However, the model sizes are constrained by the available on-device memory during training and inference. Although applying techniques like quantization can alleviate the constraint, they suffer from performance degradation. In this work, we introduce NeuZip, a new weight compression scheme based on the entropy of floating-point numbers in neural networks. With NeuZip, we are able to achieve memory-efficient training and inference without sacrificing performance. Notably, we significantly reduce the memory footprint of training a Llama-3 8B model from 31GB to less than 16GB, while keeping the training dynamics fully unchanged. In inference, our method can reduce memory usage by more than half while maintaining near-lossless performance. Our code is publicly available.
CONR (Contrastive Regularizer) adapts contrastive learning to deep imbalanced regression by explicitly modeling local and global label relationships in continuous label spaces. It boosts state-of-the-art baselines on four datasets (age, depth, gaze estimation), particularly for minority samples, and learns more effective feature representations.
19 Apr 2024
Machine-based prediction of real-world events is garnering attention due to
its potential for informed decision-making. Whereas traditional forecasting
predominantly hinges on structured data like time-series, recent breakthroughs
in language models enable predictions using unstructured text. In particular,
(Zou et al., 2022) unveils AutoCast, a new benchmark that employs news articles
for answering forecasting queries. Nevertheless, existing methods still trail
behind human performance. The cornerstone of accurate forecasting, we argue,
lies in identifying a concise, yet rich subset of news snippets from a vast
corpus. With this motivation, we introduce AutoCast++, a zero-shot
ranking-based context retrieval system, tailored to sift through expansive news
document collections for event forecasting. Our approach first re-ranks
articles based on zero-shot question-passage relevance, honing in on
semantically pertinent news. Following this, the chosen articles are subjected
to zero-shot summarization to attain succinct context. Leveraging a pre-trained
language model, we conduct both the relevance evaluation and article
summarization without needing domain-specific training. Notably, recent
articles can sometimes be at odds with preceding ones due to new facts or
unanticipated incidents, leading to fluctuating temporal dynamics. To tackle
this, our re-ranking mechanism gives preference to more recent articles, and we
further regularize the multi-passage representation learning to align with
human forecaster responses made on different dates. Empirical results
underscore marked improvements across multiple metrics, improving the
performance for multiple-choice questions (MCQ) by 48% and true/false (TF)
questions by up to 8%. Code is available at
this https URL
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.