KULeuven
We reduce the study of perturbations of rotating black holes in higher-derivative extensions of general relativity to a system of decoupled radial equations that stem from a set of universal Teukolsky equations. We detail a complete computational strategy to obtain these decoupled equations in general higher-derivative theories. We apply this to six-derivative gravity to compute the shifts in the quasinormal mode frequencies with respect to those of Kerr black holes in general relativity. At linear order in the angular momentum we reproduce earlier results obtained with a metric perturbation approach. In contrast with this earlier work, however, the method given here applies also to post-merger black holes with significant spin, which are of particular observational interest.
Programming physical intelligence into mechanisms holds great promise for
machines that can accomplish tasks such as navigation of unstructured
environments while utilizing a minimal amount of computational resources and
electronic components. In this study, we introduce a novel design approach for
physically intelligent under-actuated mechanisms capable of autonomously
adjusting their motion in response to environmental interactions. Specifically,
multistability is harnessed to sequence the motion of different degrees of
freedom in a programmed order. A key aspect of this approach is that these
sequences can be passively reprogrammed through mechanical stimuli that arise
from interactions with the environment. To showcase our approach, we construct
a four degree of freedom robot capable of autonomously navigating mazes and
moving away from obstacles. Remarkably, this robot operates without relying on
traditional computational architectures and utilizes only a single linear
actuator.
Many machine learning techniques rely on minimizing the covariance between
output feature dimensions to extract minimally redundant representations from
data. However, these methods do not eliminate all dependencies/redundancies, as
linearly uncorrelated variables can still exhibit nonlinear relationships. This
work provides a differentiable and scalable algorithm for dependence
minimization that goes beyond linear pairwise decorrelation. Our method employs
an adversarial game where small networks identify dependencies among feature
dimensions, while the encoder exploits this information to reduce dependencies.
We provide empirical evidence of the algorithm's convergence and demonstrate
its utility in three applications: extending PCA to nonlinear decorrelation,
improving the generalization of image classification methods, and preventing
dimensional collapse in self-supervised representation learning.
12 Oct 2017
Post-asymptotic giant branch (post-AGB) stars are known to be chemically diverse. In this paper we present the first observational evidence of a star that has failed the third dredge-up (TDU). J005252.87-722842.9 is a A-type (Teff = 8250 ± 250K) luminous (8200 ± 700 L⊙), metal-poor ([Fe/H] = −1.18± 0.10), low-mass (Minitial ≈ 1.5 − 2.0 M⊙) post-AGB star in the Small Magellanic Cloud. Through a systematic abundance study, using high-resolution optical spectra from UVES, we found that this likely post-AGB object shows an intriguing photospheric composition with no confirmed carbon-enhancement (upper limit of [C/Fe] < 0.50) nor enrichment of s-process elements. We derived an oxygen abundance of [O/Fe] = 0.29 ± 0.1. For Fe and O, we took into account the effects of non-local thermodynamic equilibrium (NLTE). We could not derive an upper limit for the nitrogen abundance as there are no useful nitrogen lines within our spectral coverage. The chemical pattern displayed by this object has not been observed in single or binary post-AGBs. Based on its derived stellar parameters and inferred evolutionary state, single star nucleosynthesis models predict that this star should have undergone TDU episodes while on the AGB and be carbon-enriched. However, our observations are in contrast with these predictions. We identify two possible Galactic analogues which are likely to be post-AGB stars, but the lack of accurate distances (hence luminosities) to these objects does not allow us to confirm their post-AGB status. If they have low luminosities then they are likely to be dusty post-RGB stars. The discovery of J005252.87-722842.9 reveals a new stellar evolutionary channel whereby a star evolves without any third dredge-up episodes.
14 Apr 2011
We prove continuity of quantum conditional information S(ρ12∣ρ2)
with respect to the uniform convergence of states and obtain a bound which is
independent of the dimension of the second party. This can, e.g., be used to
prove the continuity of squashed entanglement.
Structured output prediction problems are ubiquitous in machine learning. The
prominent approach leverages neural networks as powerful feature extractors,
otherwise assuming the independence of the outputs. These outputs, however,
jointly encode an object, e.g. a path in a graph, and are therefore related
through the structure underlying the output space. We discuss the semantic
loss, which injects knowledge about such structure, defined symbolically, into
training by minimizing the network's violation of such dependencies, steering
the network towards predicting distributions satisfying the underlying
structure. At the same time, it is agnostic to the arrangement of the symbols,
and depends only on the semantics expressed thereby, while also enabling
efficient end-to-end training and inference. We also discuss key improvements
and applications of the semantic loss. One limitations of the semantic loss is
that it does not exploit the association of every data point with certain
features certifying its membership in a target class. We should therefore
prefer minimum-entropy distributions over valid structures, which we obtain by
additionally minimizing the neuro-symbolic entropy. We empirically demonstrate
the benefits of this more refined formulation. Moreover, the semantic loss is
designed to be modular and can be combined with both discriminative and
generative neural models. This is illustrated by integrating it into generative
adversarial networks, yielding constrained adversarial networks, a novel class
of deep generative models able to efficiently synthesize complex objects
obeying the structure of the underlying domain.
29 Jul 2002
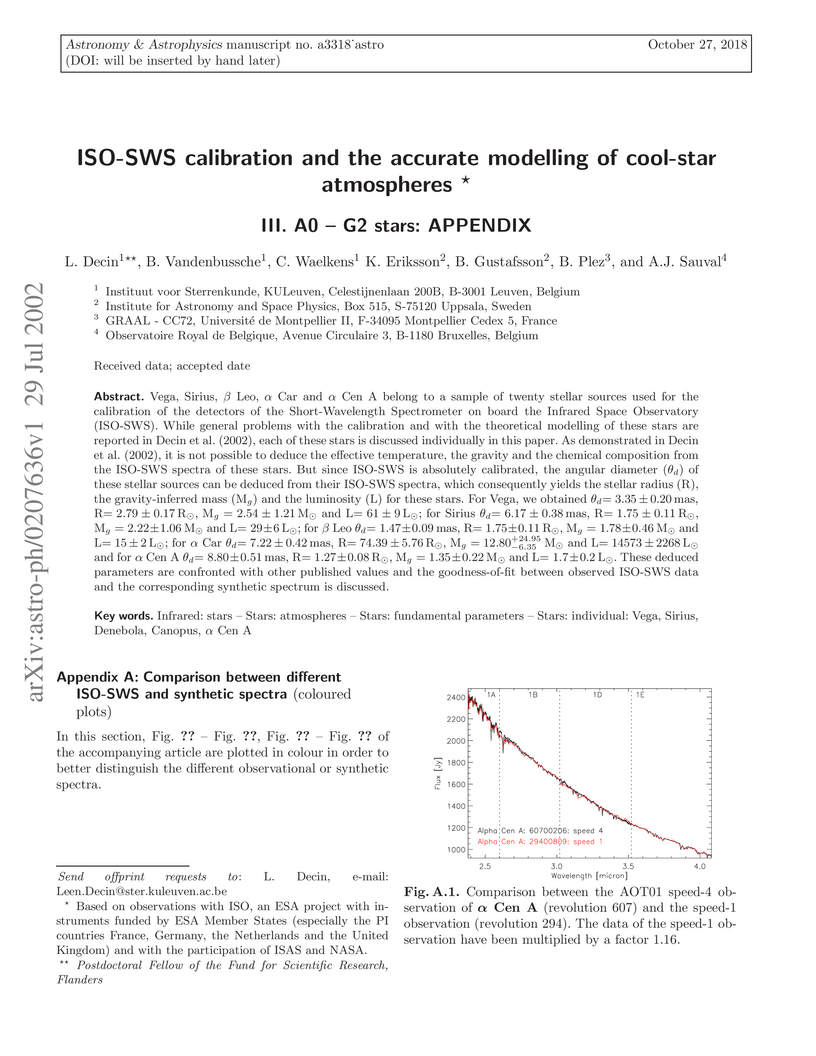
Vega, Sirius, Beta Leo, Alpha Car and Alpha Cen A belong to a sample of twenty stellar sources used for the calibration of the detectors of the Short-Wavelength Spectrometer on board the Infrared Space Observatory (ISO-SWS). While general problems with the calibration and with the theoretical modelling of these stars are reported in Decin et al. (2002), each of these stars is discussed individually in this paper. As demonstrated in Decin et al. (2002), it is not possible to deduce the effective temperature, the gravity and the chemical composition from the ISO-SWS spectra of these stars. But since ISO-SWS is absolutely calibrated, the angular diameter of these stellar sources can be deduced from their ISO-SWS spectra, which consequently yields the stellar radius (R), the gravity-inferred mass (M) and the luminosity (L) for these stars. These deduced parameters are confronted with other published values and the goodness-of-fit between observed ISO-SWS data and the corresponding synthetic spectrum is discussed.
22 Dec 2024
This paper studies a novel algorithm for nonconvex composite minimization
which can be interpreted in terms of dual space nonlinear preconditioning for
the classical proximal gradient method. The proposed scheme can be applied to
additive composite minimization problems whose smooth part exhibits an
anisotropic descent inequality relative to a reference function. It is proved
that the anisotropic descent property is closed under pointwise average if the
Bregman distance generated by the conjugate reference function is jointly
convex. More specifically, for the exponential reference function we prove its
closedness under pointwise conic combinations. We analyze the method's
asymptotic convergence and prove its linear convergence under an anisotropic
proximal gradient dominance condition. Applications are discussed including
exponentially regularized LPs and logistic regression with nonsmooth
regularization. In numerical experiments we show significant improvements of
the proposed method over its Euclidean counterparts.
17 Oct 2001
Compile-time garbage collection (CTGC) is still a very uncommon feature within compilers. In previous work we have developed a compile-time structure reuse system for Mercury, a logic programming language. This system indicates which datastructures can safely be reused at run-time. As preliminary experiments were promising, we have continued this work and have now a working and well performing near-to-ship CTGC-system built into the Melbourne Mercury Compiler (MMC).
In this paper we present the multiple design decisions leading to this system, we report the results of using CTGC for a set of benchmarks, including a real-world program, and finally we discuss further possible improvements. Benchmarks show substantial memory savings and a noticeable reduction in execution time.
30 Jul 2002
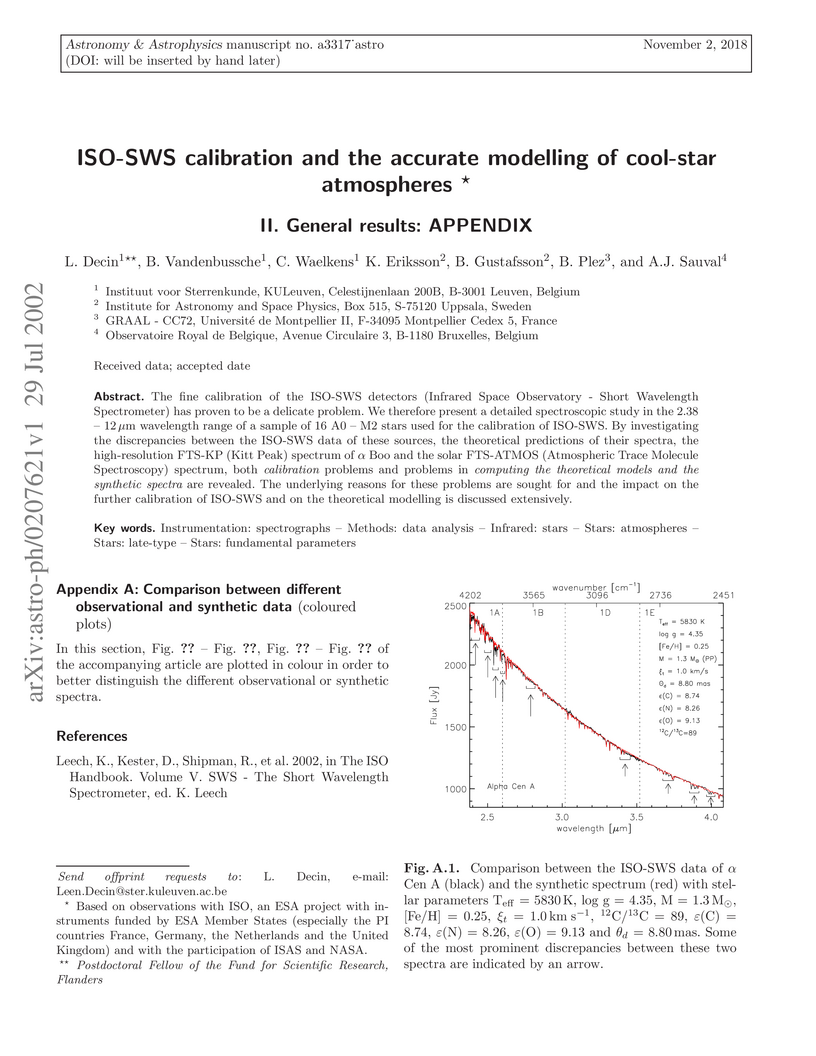
presented. The 2.38 -- 4.08 micron wavelength-range of band 1 of ISO-SWS (Short-Wavelength Spectrometers on board of the Infrared Space Observatory) in which many different molecules -- with their own dependence on each of the stellar parameters -- are absorbing, enables us to estimate the effective temperature, the gravity, the microturbulence, the metallicity, the CNO-abundances, the 12C/13C-ratio and the angular diameter from the ISO-SWS data. Using the Hipparcos' parallax, the radius, luminosity and gravity-inferred mass are derived. The stellar parameters obtained are in good agreement with other published values, though also some discrepancies with values deduced by other authors are noted. For a few stars (Delta Dra, Xi Dra, Alpha Tuc, H Sco and Alpha Cet) some parameters -- e.g. the CNO-abundances -- are derived for the first time. By examining the correspondence between different ISO-SWS observations of the same object and between the ISO-SWS data and the corresponding synthetic spectrum, it is shown that the relative accuracy of ISO-SWS in band 1 (2.38 -- 4.0 micron) is better than 2% for these high-flux sources. The high level of correspondence between observations and theoretical predictions, together with a confrontation of the estimated Teff(ISO) value with Teff-values derived from colours -- which demonstrates the consistency between V-K, BC(K), Teff and the angular diameter derived from optical or IR data -- proves that both the used MARCS models to derive the stellar quantities and the flux calibration of the ISO-SWS detectors have reached a high level of reliability.
The sparse matrix-vector (SpMV) multiplication is an important computational
kernel, but it is notoriously difficult to execute efficiently. This paper
investigates algorithm performance for unstructured sparse matrices, which are
more common than ever because of the trend towards large-scale data collection.
The development of an SpMV multiplication algorithm for this type of data is
hard due to two factors. First, parallel load balancing issues arise because of
the unpredictable nonzero structure. Secondly, SpMV multiplication algorithms
are inevitably memory-bound because the sparsity causes a low arithmetic
intensity. Three state-of-the-art algorithms for parallel SpMV multiplication
on shared-memory systems are discussed. Six new hybrid algorithms are developed
which combine optimization techniques of the current algorithms. These
techniques include parallelization strategies, storage formats, and nonzero
orderings. A modern and high-performance implementation of all discussed
algorithms is provided as open-source software. Using this implementation the
algorithms are compared. Furthermore, SpMV multiplication algorithms require
the matrix to be stored in a specific storage format. Therefore, the conversion
time between these storage formats is also analyzed. Both tests are performed
for multiple unstructured sparse matrices on different machines: two multi-CPU
and two single-CPU architectures. We show that one of the newly developed
algorithms outperforms the current state-of-the-art by 19% on one of the
multi-CPU architectures. When taking conversion time into consideration, we
show that 472 SpMV multiplications are needed to cover the cost of converting
to a new storage format for one of the hybrid algorithms on a multi-CPU
machine.
29 Jul 2002
The fine calibration of the ISO-SWS detectors (Infrared Space Observatory - Short Wavelength Spectrometer) has proven to be a delicate problem. We therefore present a detailed spectroscopic study in the 2.38 -- 12 micron wavelength range of a sample of 16 A0 -- M2 stars used for the calibration of ISO-SWS. By investigating the discrepancies between the ISO-SWS data of these sources, the theoretical predictions of their spectra, the high-resolution FTS-KP (Kitt Peak) spectrum of Alpha Boo and the solar FTS-ATMOS (Atmospheric Trace Molecule Spectroscopy) spectrum, both calibration problems and problems in computing the theoretical models and the synthetic spectra are revealed. The underlying reasons for these problems are sought for and the impact on the further calibration of ISO-SWS and on the theoretical modelling is discussed extensively.
12 Mar 2024
Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) for advanced logic
transistor technologies are deposited by various modifications of the chemical
vapor deposition (CVD) method using a wide variety of precursors. Being a major
electrical performance limiter, the TMD crystal grain size strongly differs
between the various CVD precursor chemistries from nano- to millimeter-sized
crystals. However, it remains unclear how the CVD precursor chemistry affects
the nucleation density and resulting TMD crystal grain size. This work
postulates guiding principles to design a CVD process for highly crystalline
TMD deposition using a quantitative analytical model benchmarked against
literature. The TMD nucleation density reduces favorably under low
supersaturation conditions, where the metal precursor sorption on the starting
surface is reversible and the corresponding metal precursor desorption rate
exceeds the overall deposition rate. Such reversible precursor adsorption
guarantees efficient long-range gas-phase lateral diffusion of precursor
species in addition to short-range surface diffusion, which vitally increases
crystal grain size. As such, the proposed model explains the large spread in
experimentally observed TMD nucleation densities and crystal grain sizes for
state-of-the-art CVD chemistries. Ultimately, it empowers the reader to
interpret and modulate precursor adsorption and diffusion reactions through
designing CVD precursor chemistries compatible with temperature sensitive
application schemes.
The integration of learning and reasoning is high on the research agenda in AI. Nevertheless, there is only a little attention to use existing background knowledge for reasoning about partially observed scenes to answer questions about the scene. Yet, we as humans use such knowledge frequently to infer plausible answers to visual questions (by eliminating all inconsistent ones). Such knowledge often comes in the form of constraints about objects and it tends to be highly domain or environment-specific. We contribute a novel benchmark called CLEVR-POC for reasoning-intensive visual question answering (VQA) in partially observable environments under constraints. In CLEVR-POC, knowledge in the form of logical constraints needs to be leveraged to generate plausible answers to questions about a hidden object in a given partial scene. For instance, if one has the knowledge that all cups are colored either red, green or blue and that there is only one green cup, it becomes possible to deduce the color of an occluded cup as either red or blue, provided that all other cups, including the green one, are observed. Through experiments, we observe that the low performance of pre-trained vision language models like CLIP (~ 22%) and a large language model (LLM) like GPT-4 (~ 46%) on CLEVR-POC ascertains the necessity for frameworks that can handle reasoning-intensive tasks where environment-specific background knowledge is available and crucial. Furthermore, our demonstration illustrates that a neuro-symbolic model, which integrates an LLM like GPT-4 with a visual perception network and a formal logical reasoner, exhibits exceptional performance on CLEVR-POC.
02 Jul 2011
We consider 3D active plane rotators, where the interaction between the spins is of XY-type and where each spin is driven to rotate. For the clock-model, when the spins take N\gg1 possible values, we conjecture that there are two low-temperature regimes. At very low temperatures and for small enough drift the phase diagram is a small perturbation of the equilibrium case. At larger temperatures the massless modes appear and the spins start to rotate synchronously for arbitrary small drift. For the driven XY-model we prove that there is essentially a unique translation-invariant and stationary distribution despite the fact that the dynamics is not ergodic.
06 Sep 2016
DDEBIFTOOL is a collection of Matlab routines for numerical bifurcation
analysis of systems of delay differential equations with discrete constant and
state-dependent delays. The package supports continuation and stability
analysis of steady state solutions and periodic solutions. Further one can
compute and continue several local and global bifurcations: fold and Hopf
bifurcations of steady states; folds, period doublings and torus bifurcations
of periodic orbits; and connecting orbits between equilibria. To analyse the
stability of steady state solutions, approximations are computed to the
rightmost, stability-determining roots of the characteristic equation which can
subsequently be used as starting values in a Newton procedure. For periodic
solutions, approximations to the Floquet multipliers are computed. The manual
describes the structure of the package, its routines, and its data and method
parameter structures.
07 Sep 2007
This paper and the results therein are geared towards building a basic toolbox for calculations in quantum information theory of quasi-free fermionic systems. Various entropy and relative entropy measures are discussed and the calculation of these reduced to evaluating functions on the one-particle component of quasi-free states.
The set of quasi-free affine maps on the state space is determined and fully characterized in terms of operations on one-particle subspaces. For a subclass of trace preserving completely positive maps and for their duals, Choi matrices and Jamiolkowski states are discussed.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using learning-based approaches for solving combinatorial problems, either in an end-to-end manner or in conjunction with traditional optimization algorithms. In both scenarios, the challenge lies in encoding the targeted combinatorial problems into a structure compatible with the learning algorithm. Many existing works have proposed problem-specific representations, often in the form of a graph, to leverage the advantages of \textit{graph neural networks}. However, these approaches lack generality, as the representation cannot be easily transferred from one combinatorial problem to another one. While some attempts have been made to bridge this gap, they still offer a partial generality only. In response to this challenge, this paper advocates for progress toward a fully generic representation of combinatorial problems for learning-based approaches. The approach we propose involves constructing a graph by breaking down any constraint of a combinatorial problem into an abstract syntax tree and expressing relationships (e.g., a variable involved in a constraint) through the edges. Furthermore, we introduce a graph neural network architecture capable of efficiently learning from this representation. The tool provided operates on combinatorial problems expressed in the XCSP3 format, handling all the constraints available in the 2023 mini-track competition. Experimental results on four combinatorial problems demonstrate that our architecture achieves performance comparable to dedicated architectures while maintaining generality. Our code and trained models are publicly available at \url{this https URL}.
Second-generation circumbinary discs around evolved binary stars, such as post-Asymptotic Giant Branch (post-AGB) binaries, provide insights into poorly understood mechanisms of dust processing and disc evolution across diverse stellar environments. We present a multi-wavelength polarimetric survey of five evolved binary systems - AR Pup, HR 4049, HR 4226, U Mon, and V709 Car - using the Very Large Telescope SPHERE/ZIMPOL instrument. Post-AGB discs show significant polarimetric brightness at optical and near-IR wavelengths, often exceeding 1% of the system's total intensity. We also measured a maximum fractional polarisation of the scattered light for AR Pup of ~0.7 in the V-band and ~0.55 in the I-band. To investigate wavelength-dependent polarisation, we combine the SPHERE/ZIMPOL dataset with results from previous SPHERE/IRDIS studies. This analysis reveals that post-AGB discs exhibit a grey to blue polarimetric colour in the optical and near-IR. Along with high fractional polarisation of the scattered light and polarised intensity distribution, these findings are consistent with a surface dust composition dominated by porous aggregates, reinforcing independent observational evidence for such grains in post-AGB circumbinary discs. We also find evidence of diverse disc geometries within the post-AGB sample, including arcs, asymmetries and significant variations in disc size across optical and near-IR wavelengths for some systems (U Mon, V709 Car). On comparing post-AGB discs to circumstellar environments around AGB stars and YSOs, we found that post-AGB systems exhibit a higher degree of polarisation than single AGB stars and are comparable to the brightest protoplanetary discs around YSOs.
The goal of this study is to reconstruct the evolution and the dust formation
processes during the final AGB phases of a sample of carbon-rich, post-AGB
Galactic stars, with particular attention to the determination of the past
mass-loss history. We study the IR excess of sources classified as single stars
by means of dust formation modelling where dust grains form and grow in a
static wind and expand from the surface of the star. The method is applied to
various evolutionary stages of the final AGB phase of stars with different
masses and metallicities. The detailed analysis of the SED of the sources
investigated, which included the derivation of the luminosities and the dust
properties, is used to infer information on mass loss, efficiency of dust
formation, and wind dynamics. We confirm previous results that most of the
investigated sources descend from low-mass(M<1.5Msun) progenitors that reached
the C-star stage. Metal-poor carbon stars are characterised by higher IR
excesses with respect to their more metal-rich counterparts of similar
luminosity due to a higher surface carbon-to-oxygen excess. This work confirms
previous conclusions that more luminous stars descending from higher-mass
progenitors are generally more opaque due to shorter evolutionary timescales
that place the dust shell closer to the central object. We also find that the
mass-loss rate at the tip of the AGB phase of metal-rich low-mass carbon stars
is approximately 1-1.5x10^-5Msun/yr, whereas in the metal-poor domain
M~4-5x10^-5Msun/yr is required. These results indicate the need for an upwards
revision of the theoretical mass-loss rates of low-mass carbon stars in the
available literature, which in turn require a revised determination of carbon
dust yields by AGB stars.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.