Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST)
In this paper, we re-explore a simple textbook Landau model describing improper ferroelectricity and show that in the limit where both proper and improper instabilities exist and compete, improper ferroelectrics can display switching between multiple polarisation states. Using first principles calculations we highlight how the hexagonal tungsten bronze materials may be an archetypal case, with the possibility to switch between improper and proper phases. The resulting functional characteristics are akin to "ferrielectrics", with switching behaviour in the form of a triple hysteresis loop. Such functionality could be ideal for creating non-volatile multistate systems for use in memory devices or as a backbone for neuromorphic computing.
Efficiently solving Optimal Power Flow (OPF) problems in power systems is crucial for operational planning and grid management. There is a growing need for scalable algorithms capable of handling the increasing variability, constraints, and uncertainties in modern power networks while providing accurate and fast solutions. To address this, machine learning techniques, particularly Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as promising approaches. This letter introduces SafePowerGraph-LLM, the first framework explicitly designed for solving OPF problems using Large Language Models (LLM)s. The proposed approach combines graph and tabular representations of power grids to effectively query LLMs, capturing the complex relationships and constraints in power systems. A new implementation of in-context learning and fine-tuning protocols for LLMs is introduced, tailored specifically for the OPF problem. SafePowerGraph-LLM demonstrates reliable performances using off-the-shelf LLM. Our study reveals the impact of LLM architecture, size, and fine-tuning and demonstrates our framework's ability to handle realistic grid components and constraints.
The ability to efficiently simulate a variety of interacting quantum systems on a single device is an overarching goal for digital and analog quantum simulators. In circuit quantum electrodynamical systems, strongly nonlinear superconducting oscillators are typically realized using transmon qubits, featuring a wide range of tunable couplings that are mainly achieved via flux-dependent inductive elements. Such controllability is highly desirable both for digital quantum information processing and for analog quantum simulations of various physical phenomena, such as arbitrary spin-spin interactions. Furthermore, broad tunability facilitates the study of driven-dissipative oscillator dynamics in previously unexplored parameter regimes. In this work, we demonstrate the ability to selectively activate different dynamical regimes between two strongly nonlinear oscillators using parametric modulation. In particular, our scheme enables access to regimes that are dominated by photon-hopping, two-mode squeezing, or cross-Kerr interactions. Finally, we observe level repulsion and attraction between Kerr-nonlinear oscillators in regimes where the nonlinearities exceed the coupling strengths and decay rates of the system. Our results could be used for realizing purely analog quantum simulators to study arbitrary spin systems as well as for exploring strongly nonlinear oscillator dynamics in previously unexplored interaction regimes.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities across various fields. However, their performance in technical domains such as telecommunications remains underexplored. This paper evaluates two open-source LLMs, Gemma 3 27B and DeepSeek R1 32B, on factual and reasoning-based questions derived from advanced wireless communications material. We construct a benchmark of 105 question-answer pairs and assess performance using lexical metrics, semantic similarity, and LLM-as-a-judge scoring. We also analyze consistency, judgment reliability, and hallucination through source attribution and score variance. Results show that Gemma excels in semantic fidelity and LLM-rated correctness, while DeepSeek demonstrates slightly higher lexical consistency. Additional findings highlight current limitations in telecom applications and the need for domain-adapted models to support trustworthy Artificial Intelligence (AI) assistants in engineering.
This paper presents a comprehensive cross-platform evaluation of reasoning capabilities in contemporary foundation models, establishing an infrastructure-agnostic benchmark across three computational paradigms: HPC supercomputing (MareNostrum 5), cloud platforms (Nebius AI Studio), and university clusters (a node with eight H200 GPUs).
We evaluate 15 foundation models across 79 problems spanning eight academic domains (Physics, Mathematics, Chemistry, Economics, Biology, Statistics, Calculus, and Optimization) through three experimental phases: (1) Baseline establishment: Six models (Mixtral-8x7B, Phi-3, LLaMA 3.1-8B, Gemma-2-9b, Mistral-7B, OLMo-7B) evaluated on 19 problems using MareNostrum 5, establishing methodology and reference performance; (2) Infrastructure validation: The 19-problem benchmark repeated on university cluster (seven models including Falcon-Mamba state-space architecture) and Nebius AI Studio (nine state-of-the-art models: Hermes-4 70B/405B, LLaMA 3.1-405B/3.3-70B, Qwen3 30B/235B, DeepSeek-R1, GPT-OSS 20B/120B) to confirm infrastructure-agnostic reproducibility; (3) Extended evaluation: Full 79-problem assessment on both university cluster and Nebius platforms, probing generalization at scale across architectural diversity.
The findings challenge conventional scaling assumptions, establish training data quality as more critical than model size, and provide actionable guidelines for model selection across educational, production, and research contexts. The tri-infrastructure methodology and 79-problem benchmark enable longitudinal tracking of reasoning capabilities as foundation models evolve.
20 Oct 2025
The growing negative impact of the visibility of satellites in the night sky is influencing the practice of astronomy and astrophotograph, both at the amateur and professional levels. The presence of these satellites has the effect of introducing streaks into the images captured during astronomical observation, requiring the application of additional post processing to mitigate the undesirable impact, whether for data loss or cosmetic reasons. In this paper, we show how we test and adapt various Deep Learning approaches to detect streaks in raw astronomical data captured between March 2022 and February 2023 with smart telescopes.
26 Mar 2025
Antiferroelectrics attract broad attention due to their unusual physical characteristics, chief among which is the double-hysteresis loop that separates their antipolar ground state from the voltage-induced polar phase, which is promising for applications in energy storage and electrocaloric cooling. However, their defining features (antipolar ground state and double-hysteresis loops) are increasingly challenged: materials with non-collinear and/or hybrid polar-antipolar order have been discovered, and double-hysteresis has been realized in materials without a conventional antipolar ground state. These developments add to the intensifying interest in fundamental and practical aspects of antiferroelectrics, and call for a fresh look at antiferroelectricity. In this Perspective, we provide an updated and all-encompassing definition of antiferroelectricity, discuss material systems with new antipolar orders and/or engineered double hysteresis, and reflect on emergent properties and theoretical approaches. This work casts a bird's eye view on the rapidly evolving trends that are shaping up the research on ferroics with antipolar order.
20 Oct 2025
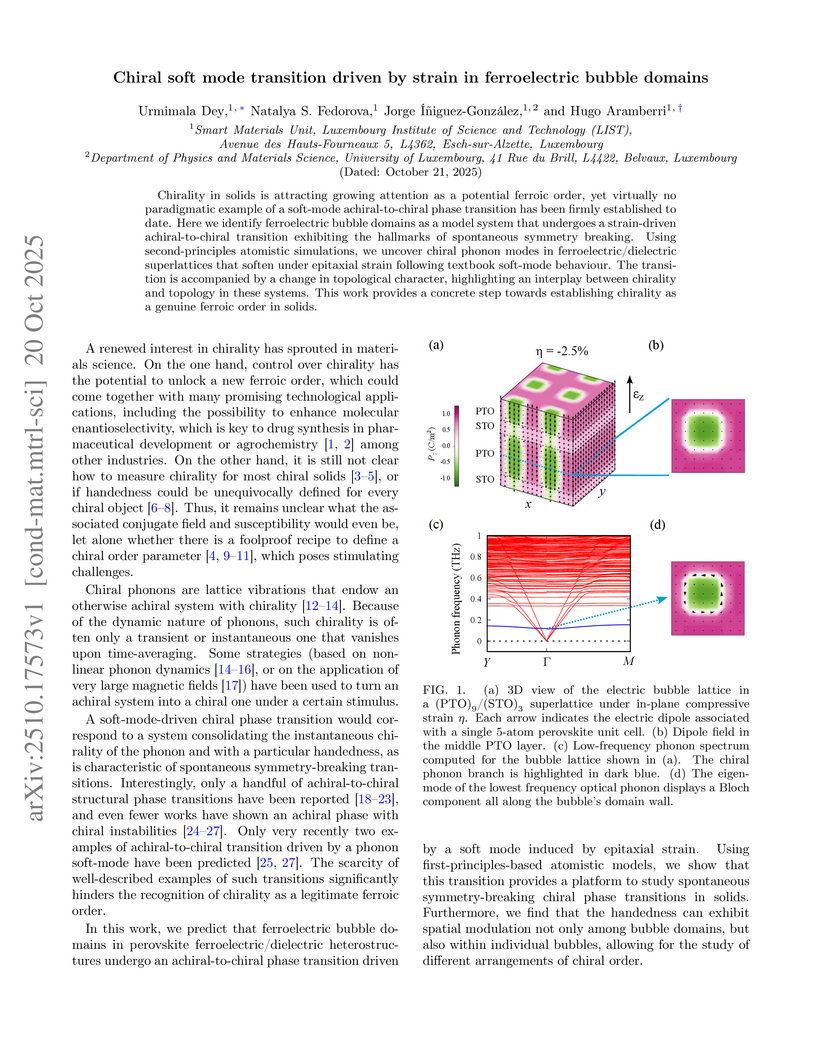
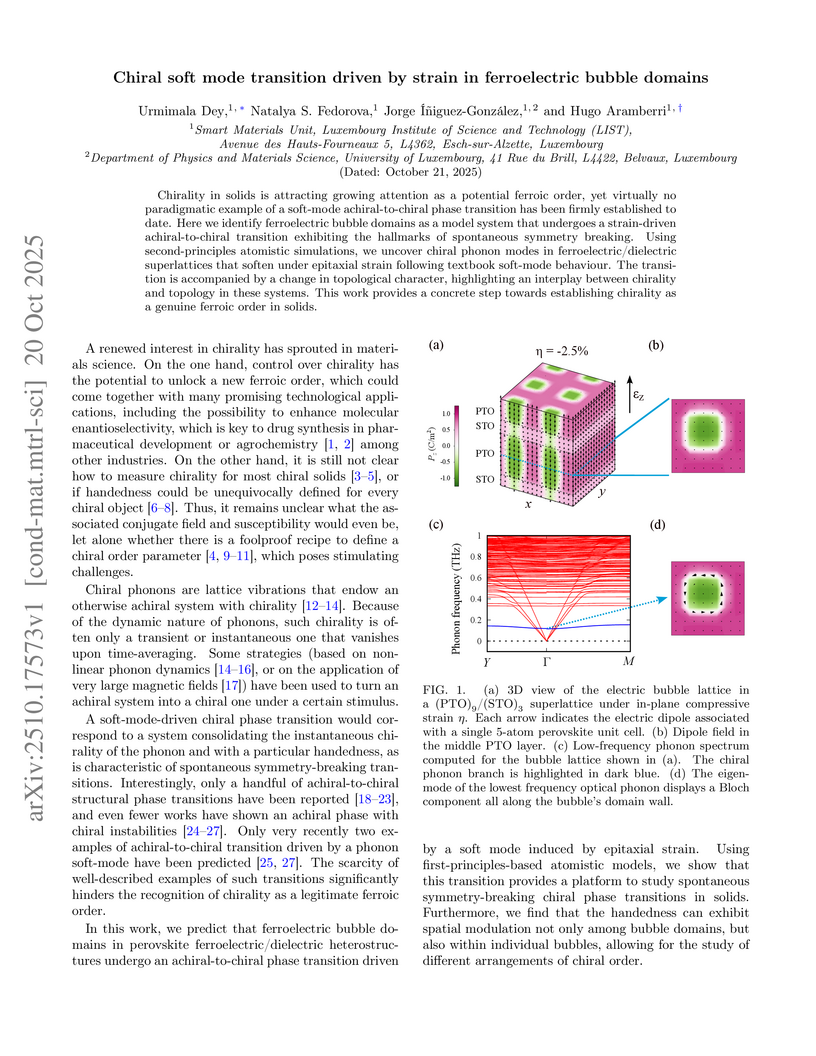
Chirality in solids is attracting growing attention as a potential ferroic order, yet virtually no paradigmatic example of a soft-mode achiral-to-chiral phase transition has been firmly established to date. Here we identify ferroelectric bubble domains as a model system that undergoes a strain-driven achiral-to-chiral transition exhibiting the hallmarks of spontaneous symmetry breaking. Using second-principles atomistic simulations, we uncover chiral phonon modes in ferroelectric/dielectric superlattices that soften under epitaxial strain following textbook soft-mode behaviour. The transition is accompanied by a change in topological character, highlighting an interplay between chirality and topology in these systems. This work provides a concrete step towards establishing chirality as a genuine ferroic order in solids.
21 Feb 2018
Ferroelectric materials are characterized by a spontaneous polar distortion. The behavior of such distortions in the presence of free charge is the key to the physics of metallized ferroelectrics in particular, and of structurally-polar metals more generally. Using first-principles simulations, here we show that a polar distortion resists metallization and the attendant suppression of long-range dipolar interactions in the vast majority of a sample of 11 representative ferroelectrics. We identify a meta-screening effect, occurring in the doped compounds as a consequence of the charge rearrangements associated to electrostatic screening, as the main factor determining the survival of a non-centrosymmetric phase. Our findings advance greatly our understanding of the essentials of structurally-polar metals, and offer guidelines on the behavior of ferroelectrics upon field-effect charge injection or proximity to conductive device elements.
Representing source code in a generic input format is crucial to automate software engineering tasks, e.g., applying machine learning algorithms to extract information. Visualizing code representations can further enable human experts to gain an intuitive insight into the code. Unfortunately, as of today, there is no universal tool that can simultaneously visualise different types of code representations. In this paper, we introduce a tool, CodeLens, which provides a visual interaction environment that supports various representation methods and helps developers understand and explore them. CodeLens is designed to support multiple programming languages, such as Java, Python, and JavaScript, and four types of code representations, including sequence of tokens, abstract syntax tree (AST), data flow graph (DFG), and control flow graph (CFG). By using CodeLens, developers can quickly visualize the specific code representation and also obtain the represented inputs for models of code. The Web-based interface of CodeLens is available at this http URL. The demonstration video can be found at this http URL.
In this paper, we re-explore a simple textbook Landau model describing improper ferroelectricity and show that in the limit where both proper and improper instabilities exist and compete, improper ferroelectrics can display switching between multiple polarisation states. Using first principles calculations we highlight how the hexagonal tungsten bronze materials may be an archetypal case, with the possibility to switch between improper and proper phases. The resulting functional characteristics are akin to "ferrielectrics", with switching behaviour in the form of a triple hysteresis loop. Such functionality could be ideal for creating non-volatile multistate systems for use in memory devices or as a backbone for neuromorphic computing.
20 Oct 2025
Chirality in solids is attracting growing attention as a potential ferroic order, yet virtually no paradigmatic example of a soft-mode achiral-to-chiral phase transition has been firmly established to date. Here we identify ferroelectric bubble domains as a model system that undergoes a strain-driven achiral-to-chiral transition exhibiting the hallmarks of spontaneous symmetry breaking. Using second-principles atomistic simulations, we uncover chiral phonon modes in ferroelectric/dielectric superlattices that soften under epitaxial strain following textbook soft-mode behaviour. The transition is accompanied by a change in topological character, highlighting an interplay between chirality and topology in these systems. This work provides a concrete step towards establishing chirality as a genuine ferroic order in solids.
The notion of Cyber-Physical-Social System (CPSS) is an emerging concept developed as a result of the need to understand the impact of Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) on humans and vice versa. This paradigm shift from CPS to CPSS was mainly attributed to the increasing use of sensor-enabled smart devices and the tight link with the users. The concept of CPSS has been around for over a decade and it has gained increasing attention over the past few years. The evolution to incorporate human aspects in the CPS research has unlocked a number of research challenges. Particularly human dynamics brings additional complexity that is yet to be explored. The exploration to conceptualise the notion of CPSS has been partially addressed in few scientific literatures. Although its conceptualisation has always been use-case dependent. Thus, there is a lack of generic view as most works focus on specific domains. Furthermore, the systemic core and design principles linking it with the theory of systems are loose. This work aims at addressing these issues by first exploring and analysing scientific literature to understand the complete spectrum of CPSS through a Systematic Literature Review (SLR). Thereby identifying the state-of-the-art perspectives on CPSS regarding definitions, underlining principles and application areas. Subsequently, based on the findings of the SLR, we propose a domain-independent definition and a meta-model for CPSS, grounded in the Theory of Systems. Finally, a discussion on feasible future research directions is presented based on the systemic notion and the proposed meta-models.
14 Mar 2025
Multiferroic materials, characterized by the occurrence of two or more
ferroic properties, hold potential in future technological applications and
also exhibit intriguing phenomena caused by the interplay of multiple orders.
One such example is the formation of spin cycloid structures within
multiferroic materials, which we investigate in this work by focusing on their
magnon excitations and transport based on a general multiferroic Hamiltonian
with an antiferromagnetic order. More specifically, we identify the ground
state and explore the dynamics of magnon modes, revealing distinct in-plane and
out-of-plane modes with anisotropic dispersion relations.The magnon modes
include a massless excitation, known as the Goldstone boson, originating from
the spontaneous breaking of the translational symmetry by the formation of the
cycloid structures. By employing the Boltzmann transport formalism, the
magnonic thermal conductivity with spin cycloids and low-temperature
anisotropic behaviors is discussed. This work provides pathways to envision the
spin-textured multiferroics, which may serve as a fertile ground to look for
novel thermal and spin transport with the rich interplay of quasiparticles such
as magnons and phonons.
The molecular-to-atomic liquid-liquid transition (LLT) in high-pressure hydrogen is a fundamental topic touching domains from planetary science to materials modeling. Yet, the nature of the LLT is still under debate. To resolve it, numerical simulations must cover length and time scales spanning several orders of magnitude. We overcome these size and time limitations by constructing a fast and accurate machine-learning interatomic potential (MLIP) built on the MACE neural network architecture. The MLIP is trained on Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) density functional calculations and uses a modified loss function correcting for an energy bias in the molecular phase. Classical and path-integral molecular dynamics driven by this MLIP show that the LLT is always supercritical above the melting temperature. The position of the corresponding Widom line agrees with previous ab initio PBE calculations, which in contrast predicted a first-order LLT. According to our calculations, the crossover line becomes a first-order transition only inside the molecular crystal region. These results call for a reconsideration of the LLT picture previously drawn.
16 Feb 2024
The photoconversion of CO2 to hydrocarbons is a sustainable route to its
transformation into value-added compounds and, thereby, crucial to mitigating
the energy and climate crises. CuPt nanoparticles on TiO2 surfaces have been
reported to show promising photoconversion efficiency. For further progress, a
mechanistic understanding of the catalytic properties of these CuPt/TiO2
systems is vital. Here, we employ ab-initio calculations, machine
learning, and photocatalysis experiments to explore their configurational space
and examine their reactivity and find that the interface plays a key role in
stabilizing *CO2, *CO, and other CH-containing intermediates, facilitating
higher activity and selectivity for methane. A bias-corrected machine-learning
interatomic potential trained on density functional theory data enables
efficient exploration of the potential energy surfaces of numerous
CO2@CuPt/TiO2 configurations via basin-hopping Monte Carlo simulations,
greatly accelerating the study of these photocatalyst systems. Our simulations
show that CO2 preferentially adsorbs at the interface, with C atom bonded to
a Pt site and one O atom occupying an O-vacancy site. The interface also
promotes the formation of *CH and *CH2 intermediates. For confirmation, we
synthesize CuPt/TiO2 samples with a variety of compositions and analyze
their morphologies and compositions using scanning electron microscopy and
energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and measure their photocatalytic
activity. Our computational and experimental findings qualitatively agree and
highlight the importance of interface design for selective conversion of CO2
to hydrocarbons.
Microstructural evolution, particularly grain growth, plays a critical role
in shaping the physical, optical, and electronic properties of materials.
Traditional phase-field modeling accurately simulates these phenomena but is
computationally intensive, especially for large systems and fine spatial
resolutions. While machine learning approaches have been employed to accelerate
simulations, they often struggle with resolution dependence and generalization
across different grain scales. This study introduces a novel approach utilizing
Fourier Neural Operator (FNO) to achieve resolution-invariant modeling of
microstructure evolution in multi-grain systems. FNO operates in the Fourier
space and can inherently handle varying resolutions by learning mappings
between function spaces. By integrating FNO with the phase field method, we
developed a surrogate model that significantly reduces computational costs
while maintaining high accuracy across different spatial scales. We generated a
comprehensive dataset from phase-field simulations using the Fan Chen model,
capturing grain evolution over time. Data preparation involved creating
input-output pairs with a time shift, allowing the model to predict future
microstructures based on current and past states. The FNO-based neural network
was trained using sequences of microstructures and demonstrated remarkable
accuracy in predicting long-term evolution, even for unseen configurations and
higher-resolution grids not encountered during training.
In NLP, Zero-Shot Classification (ZSC) has become essential for enabling models to classify text into categories unseen during training, particularly in low-resource languages and domains where labeled data is scarce. While pretrained language models (PLMs) have shown promise in ZSC, they often rely on large training datasets or external knowledge, limiting their applicability in multilingual and low-resource scenarios. Recent approaches leveraging natural language prompts reduce the dependence on large training datasets but struggle to effectively incorporate available labeled data from related classification tasks, especially when these datasets originate from different languages or distributions. Moreover, existing prompt-based methods typically rely on manually crafted prompts in a specific language, limiting their adaptability and effectiveness in cross-lingual settings. To address these challenges, we introduce RoSPrompt, a lightweight and data-efficient approach for training soft prompts that enhance cross-lingual ZSC while ensuring robust generalization across data distribution shifts. RoSPrompt is designed for small multilingual PLMs, enabling them to leverage high-resource languages to improve performance in low-resource settings without requiring extensive fine-tuning or high computational costs. We evaluate our approach on multiple multilingual PLMs across datasets covering 106 languages, demonstrating strong cross-lingual transfer performance and robust generalization capabilities over unseen classes.
The high-pressure behaviour of Na2CuF4 is explored by powder neutron
diffraction and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. A first-order
phase transition is observed to take place between 2.4 - 2.9 GPa, involving a
reorientation of the Jahn-Teller (JT) long axes of the (CuF6) octahedra (and
therefore the dz2 Cu orbitals), in agreement with our DFT calculations
which suggest a transition at 2.8 GPa. The transition can be described as being
between a state of ferro-orbital order and one of A-type antiferro-orbital
order, reflecting a shift in the associated electronic instability from being
in the zone-center to zone boundary of the first Brillouin zone of the parent
structure, with pressure. This change results in a decoupling of magnitude of
the associated Jahn-Teller distortion of the Cu-F bond lengths from the lattice
strain. This scenario is supported by our observations that the compressibility
of the pre-transition phase is highly anisotropic, whilst in the
post-transition phase it becomes almost isotropic, and that we observed no
further decrease of the magnitude the JT distortion up to 5 GPa, or melting of
the OO in our DFT calculations up to at least 5 GPa.
02 Jul 2025
Antiferroelectrics are emerging as advanced functional materials and are fertile ground for unusual electric effects. For example, they enhance the recoverable energy density in energy storage applications and give rise to large electromechanical responses. Here, we demonstrate noncollinearity in dipolar order as an additional degree of freedom, unlocking physical properties that are symmetry-forbidden in classical antiferroelectrics. We show that noncollinear order of electric dipole moments in K3[Nb3O6|(BO3)2] leads to a coexistence of antiferroelectric and ferroelectric behaviors. Besides the double-hysteresis loop observed in antiferroelectrics, a pronounced piezoresponse and electrically switchable domains are observed, separated by atomically sharp and micrometer-long charged domain walls. Hybrid antiferroelectric-ferroelectric responses are expected in a wide range of noncollinear systems, giving a new dimension to the research on antiferroelectrics and multifunctional oxides in general.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.