Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria
21 May 2024
A general mathematical framework is presented for establishing the existence and uniqueness of solutions to functional equations arising in behavioral modeling, utilizing Lipschitz spaces to ensure non-trivial solutions. The work specifically provides explicit conditions for unique solutions to a generalized paradise fish learning equation and proposes an efficient least-squares analytical approximation to overcome the exponential computational cost of standard iterative methods.
Facial expression recognition (FER) is a key research area in computer vision
and human-computer interaction. Despite recent advances in deep learning,
challenges persist, especially in generalizing to new scenarios. In fact,
zero-shot FER significantly reduces the performance of state-of-the-art FER
models. To address this problem, the community has recently started to explore
the integration of knowledge from Large Language Models for visual tasks. In
this work, we evaluate a broad collection of locally executed Visual Language
Models (VLMs), avoiding the lack of task-specific knowledge by adopting a
Visual Question Answering strategy. We compare the proposed pipeline with
state-of-the-art FER models, both integrating and excluding VLMs, evaluating
well-known FER benchmarks: AffectNet, FERPlus, and RAF-DB. The results show
excellent performance for some VLMs in zero-shot FER scenarios, indicating the
need for further exploration to improve FER generalization.
10 Sep 2024
Purpose: The teacher role in the classroom can explain important aspects of
the student's school experience. The teacher-student relationship, a central
dimension of social capital, influences students' engagement, and the teaching
style plays an important role in student outcomes. But there is scarce
literature that links teaching styles to teacher-student relationship. This
article aims to: 1) analyze whether there is a relationship between teaching
styles and the type of relationship perceived by students; 2) test whether this
relationship is equally strong for any teaching style; and 3) determine the
extent to which students' perceptions vary according to their profile.
Design/methodology/approach: A structural equation model with four latent
variables is estimated: two for the teacher-student relationship (emotional vs.
educational) and two for the teaching styles (directive vs. participative),
with information for 21126 sixth-grade primary-students in 2019 in Spain.
Findings: Teacher-student relationships and teaching styles are interconnected.
The participative style implies a better relationship. The perceptions of the
teacher are heterogeneous, depending on gender (girls perceive clearer than
boys) and with the educational background (children from lower educational
background perceive both types of teaching styles more clearly).
Originality/value: The analysis is based on the point of view of the addressee
of the teacher's work, i.e. the student. It provides a model that can be
replicated in any other education system. The latent variables, based on a
periodically administered questionnaire, could be estimated with data from
diagnostic assessments in other countries, which in turn would allow the
formulation of context-specific educational policy proposals that take into
account student feedback.
07 Oct 2025
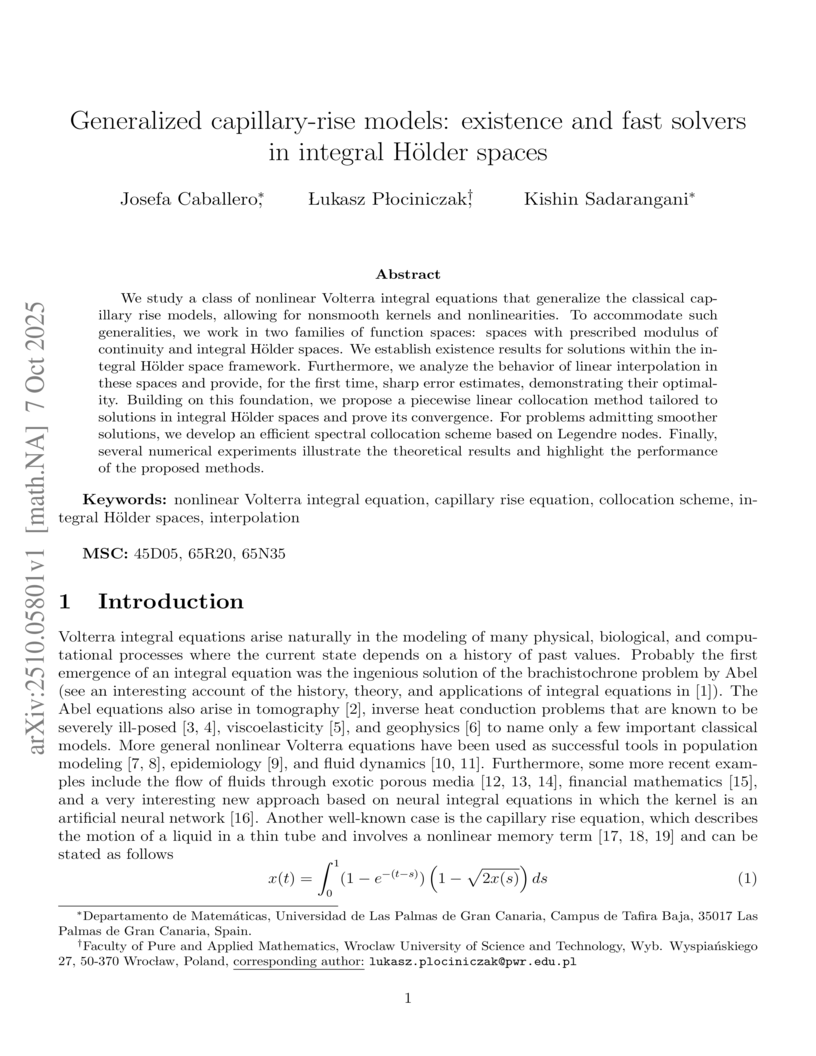
We study a class of nonlinear Volterra integral equations that generalize the classical capillary rise models, allowing for nonsmooth kernels and nonlinearities. To accommodate such generalities, we work in two families of function spaces: spaces with prescribed modulus of continuity and integral Hölder spaces. We establish existence results for solutions within the integral Hölder space framework. Furthermore, we analyze the behavior of linear interpolation in these spaces and provide, for the first time, sharp error estimates, demonstrating their optimality. Building on this foundation, we propose a piecewise linear collocation method tailored to solutions in integral Hölder spaces and prove its convergence. For problems admitting smoother solutions, we develop an efficient spectral collocation scheme based on Legendre nodes. Finally, several numerical experiments illustrate the theoretical results and highlight the performance of the proposed methods.
Action anticipation has become a prominent topic in Human Action Recognition (HAR). However, its application to real-world sports scenarios remains limited by the availability of suitable annotated datasets. This work presents a novel dataset of manually annotated soccer penalty kicks to predict shot direction based on pre-kick player movements. We propose a deep learning classifier to benchmark this dataset that integrates HAR-based feature embeddings with contextual metadata. We evaluate twenty-two backbone models across seven architecture families (MViTv2, MViTv1, SlowFast, Slow, X3D, I3D, C2D), achieving up to 63.9% accuracy in predicting shot direction (left or right), outperforming the real goalkeepers' decisions. These results demonstrate the dataset's value for anticipatory action recognition and validate our model's potential as a generalizable approach for sports-based predictive tasks.
This project explores the feasibility of remote patient monitoring based on the analysis of 3D movements captured with smartwatches. We base our analysis on the Kinematic Theory of Rapid Human Movement. We have validated our research in a real case scenario for stroke rehabilitation at the Guttmann Institute5 (neurorehabilitation hospital), showing promising results. Our work could have a great impact in remote healthcare applications, improving the medical efficiency and reducing the healthcare costs. Future steps include more clinical validation, developing multi-modal analysis architectures (analysing data from sensors, images, audio, etc.), and exploring the application of our technology to monitor other neurodegenerative diseases.
13 Oct 2025
We consider the initial-boundary value problem for a quasilinear time-fractional diffusion equation, and develop a fully discrete solver combining the parareal algorithm in time with a L1 finite-difference approximation of the Caputo derivative and a spectral Galerkin discretization in space. Our main contribution is the first rigorous convergence proof for the parareal-L1 scheme in this nonlinear subdiffusive setting. By constructing suitable energy norms and exploiting the orthogonality of the spectral basis, we establish that the parareal iterations converge exactly to the fully serial L1-spectral solution in a finite number of steps, with rates independent of the fractional exponent. The spectral spatial discretization yields exponential accuracy in space, while the parareal structure induces a clock speedup proportional to the number of processors, making the overall method highly efficient. Numerical experiments for both subdiffusive and classical diffusion problems confirm our theoretical estimates and demonstrate up to an order of magnitude reduction in computational time compared to the conventional sequential solver. We observe that the speedup of the parareal method increases linearly with the fine integrator degrees of freedom.
15 Feb 2017
In this work, we have designed and implemented, based on traditional board
games such as the game of the Goose or Parchis, an educational software that
aim to reinforce the learning of children. The idea that we are going to
develop to do this is very simple: the children play with the same rules as in
the traditional game but we add the functionality that after throwing the dice
the system asks a question randomly chosen from a predefined database that can
be easily modified, and the game piece only moves in the case the question is
answered correctly.
Assessing the quality of movements for post-stroke patients during the rehabilitation phase is vital given that there is no standard stroke rehabilitation plan for all the patients. In fact, it depends basically on the patient's functional independence and its progress along the rehabilitation sessions. To tackle this challenge and make neurorehabilitation more agile, we propose an automatic assessment pipeline that starts by recognizing patients' movements by means of a shallow deep learning architecture, then measuring the movement quality using jerk measure and related measures. A particularity of this work is that the dataset used is clinically relevant, since it represents movements inspired from Fugl-Meyer a well common upper-limb clinical stroke assessment scale for stroke patients. We show that it is possible to detect the contrast between healthy and patients movements in terms of smoothness, besides achieving conclusions about the patients' progress during the rehabilitation sessions that correspond to the clinicians' findings about each case.
18 Apr 2013
Journal metrics are employed for the assessment of scientific scholar
journals from a general bibliometric perspective. In this context, the Thomson
Reuters journal impact factors (JIF) are the citation-based indicators most
used. The 2-year journal impact factor (2-JIF) counts citations to one and two
year old articles, while the 5-year journal impact factor (5-JIF) counts
citations from one to five year old articles. Nevertheless, these indicators
are not comparable among fields of science for two reasons: (i) each field has
a different impact maturity time, and (ii) because of systematic differences in
publication and citation behaviour across disciplines. In fact, the 5-JIF
firstly appeared in the Journal Citation Reports (JCR) in 2007 with the purpose
of making more comparable impacts in fields in which impact matures slowly.
However, there is not an optimal fixed impact maturity time valid for all the
fields. In some of them two years provides a good performance whereas in others
three or more years are necessary. Therefore, there is a problem when comparing
a journal from a field in which impact matures slowly with a journal from a
field in which impact matures rapidly. In this work, we propose the 2-year
maximum journal impact factor (2M-JIF), a new impact indicator that considers
the 2-year rolling citation time window of maximum impact instead of the
previous 2-year time window. Finally, an empirical application comparing 2-JIF,
5-JIF, and 2M-JIF shows that the maximum rolling target window reduces the
between-group variance with respect to the within-group variance in a random
sample of about six hundred journals from eight different fields.
Oceanographic forecasting impacts various sectors of society by supporting
environmental conservation and economic activities. Based on global circulation
models, traditional forecasting methods are computationally expensive and slow,
limiting their ability to provide rapid forecasts. Recent advances in deep
learning offer faster and more accurate predictions, although these data-driven
models are often trained with global data from numerical simulations, which may
not reflect reality. The emergence of such models presents great potential for
improving ocean prediction at a subregional domain. However, their ability to
predict fine-scale ocean processes, like mesoscale structures, remains largely
unknown. This work aims to adapt a graph neural network initially developed for
global weather forecasting to improve subregional ocean prediction,
specifically focusing on the Canary Current upwelling system. The model is
trained with satellite data and compared to state-of-the-art physical ocean
models to assess its performance in capturing ocean dynamics. Our results show
that the deep learning model surpasses traditional methods in precision despite
some challenges in upwelling areas. It demonstrated superior performance in
reducing RMSE errors compared to ConvLSTM and the GLORYS reanalysis,
particularly in regions with complex oceanic dynamics such as Cape Ghir, Cape
Bojador, and Cape Blanc. The model achieved improvements of up to 26.5%
relative to ConvLSTM and error reductions of up to 76% in 5-day forecasts
compared to the GLORYS reanalysis at these critical locations, highlighting its
enhanced capability to capture spatial variability and improve predictive
accuracy in complex areas. These findings suggest the viability of adapting
meteorological data-driven models for improving subregional medium-term ocean
forecasting.
25 Jul 2025
Barenblatt solutions for the time-fractional porous medium equation: approach via integral equations
Barenblatt solutions for the time-fractional porous medium equation: approach via integral equations
This paper explores Barenblatt solutions of the time-fractional porous medium equation, characterized by a Caputo-type time derivative. Employing an integral equation approach, we rigorously prove the existence of these solutions and establish several fundamental properties, including upper and lower estimates, mass conservation, regularity, and monotonicity. To bridge theory and practice, we introduce a family of convergent numerical schemes specifically designed to compute the Barenblatt solutions, ensuring reliable and efficient approximations. The theoretical framework is enriched with various examples that illustrate the concepts and validate the effectiveness of the proposed numerical methods, enhancing the understanding and applicability of our results.
11 Oct 2013
These are the written discussions of the paper "Bayesian measures of model
complexity and fit" by D. Spiegelhalter et al. (2002), following the
discussions given at the Annual Meeting of the Royal Statistical Society in
Newcastle-upon-Tyne on September 3rd, 2013.
28 Sep 2020
PhD students report a higher prevalence of mental illness symptoms than highly educated individuals in the general population. This situation presents a serious problem for universities. Thus, the knowledge about this phenomenon is of great importance in decision-making. In this paper we use the Nature PhD survey 2019 and estimate several binomial logistic regression models to analyze the risk of interrupting doctoral studies. This risk is measured through the desire of change in either the supervisor or the area of expertise, or the wish of not pursue a PhD. Among the explanatory factors, we focus on the influence of anxiety/depression, discrimination, and bullying. As control variables we use demographic characteristics and others related with the doctoral program. Insufficient contact time with supervisors, and exceeding time spent studying -crossing the 50-h week barrier-, are risk factors of PhD studies interruption, but the most decisive risk factor is poor mental health. Universities should therefore foster an environment of well-being, which allows the development of autonomy and resilience of their PhD students or, when necessary, which fosters the development of conflict resolution skills.
This paper introduces IMASHRIMP, an adapted system for the automated morphological analysis of white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei}, aimed at optimizing genetic selection tasks in aquaculture. Existing deep learning and computer vision techniques were modified to address the specific challenges of shrimp morphology analysis from RGBD images. IMASHRIMP incorporates two discrimination modules, based on a modified ResNet-50 architecture, to classify images by the point of view and determine rostrum integrity. It is proposed a "two-factor authentication (human and IA)" system, it reduces human error in view classification from 0.97% to 0% and in rostrum detection from 12.46% to 3.64%. Additionally, a pose estimation module was adapted from VitPose to predict 23 key points on the shrimp's skeleton, with separate networks for lateral and dorsal views. A morphological regression module, using a Support Vector Machine (SVM) model, was integrated to convert pixel measurements to centimeter units. Experimental results show that the system effectively reduces human error, achieving a mean average precision (mAP) of 97.94% for pose estimation and a pixel-to-centimeter conversion error of 0.07 (+/- 0.1) cm. IMASHRIMP demonstrates the potential to automate and accelerate shrimp morphological analysis, enhancing the efficiency of genetic selection and contributing to more sustainable aquaculture this http URL code are available at this https URL
Advances in NERFs have allowed for 3D scene reconstructions and novel view
synthesis. Yet, efficiently editing these representations while retaining
photorealism is an emerging challenge. Recent methods face three primary
limitations: they're slow for interactive use, lack precision at object
boundaries, and struggle to ensure multi-view consistency. We introduce IReNe
to address these limitations, enabling swift, near real-time color editing in
NeRF. Leveraging a pre-trained NeRF model and a single training image with
user-applied color edits, IReNe swiftly adjusts network parameters in seconds.
This adjustment allows the model to generate new scene views, accurately
representing the color changes from the training image while also controlling
object boundaries and view-specific effects. Object boundary control is
achieved by integrating a trainable segmentation module into the model. The
process gains efficiency by retraining only the weights of the last network
layer. We observed that neurons in this layer can be classified into those
responsible for view-dependent appearance and those contributing to diffuse
appearance. We introduce an automated classification approach to identify these
neuron types and exclusively fine-tune the weights of the diffuse neurons. This
further accelerates training and ensures consistent color edits across
different views. A thorough validation on a new dataset, with edited object
colors, shows significant quantitative and qualitative advancements over
competitors, accelerating speeds by 5x to 500x.
Researchers developed an algorithm to accurately track electron capture processes in classical molecular dynamics simulations of plasmas. This method combines energetic, temporal, and average energy criteria to reliably distinguish between bound and free electrons, which was validated through independent energy distribution analysis showing deviations typically less than 1%.
The Kinematic Theory of rapid movements, and its associated Sigma-Lognormal, model 2D spatiotemporal trajectories. It is constructed mainly as a temporal overlap of curves between virtual target points. Specifically, it uses an arc and a lognormal as primitives for the representation of the trajectory and velocity, respectively. This paper proposes developing this model, in what we call the Kinematic Theory Transform, which establishes a mathematical framework that allows further primitives to be used. Mainly, we evaluate Euler curves to link virtual target points and Gaussian, Beta, Gamma, Double-bounded lognormal, and Generalized Extreme Value functions to model the bell-shaped velocity profile. Using these primitives, we report reconstruction results with spatiotemporal trajectories executed by human beings, animals, and anthropomorphic robots.
Biomedical decision making involves multiple signal processing, either from
different sensors or from different channels. In both cases, information fusion
plays a significant role. A deep learning based electroencephalogram channels'
feature level fusion is carried out in this work for the electroencephalogram
cyclic alternating pattern A phase classification. Channel selection, fusion,
and classification procedures were optimized by two optimization algorithms,
namely, Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Optimization. The developed
methodologies were evaluated by fusing the information from multiple
electroencephalogram channels for patients with nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy
and patients without any neurological disorder, which was significantly more
challenging when compared to other state of the art works. Results showed that
both optimization algorithms selected a comparable structure with similar
feature level fusion, consisting of three electroencephalogram channels, which
is in line with the CAP protocol to ensure multiple channels' arousals for CAP
detection. Moreover, the two optimized models reached an area under the
receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.82, with average accuracy ranging
from 77% to 79%, a result which is in the upper range of the specialist
agreement. The proposed approach is still in the upper range of the best state
of the art works despite a difficult dataset, and has the advantage of
providing a fully automatic analysis without requiring any manual procedure.
Ultimately, the models revealed to be noise resistant and resilient to multiple
channel loss.
08 Oct 2014
The citation potential is a measure of the probability of being cited. Obviously, it is different among fields of science, social science, and humanities because of systematic differences in publication and citation behaviour across disciplines. In the past, the citation potential was studied at journal level considering the average number of references in established groups of journals (for example, the crown indicator is based on the journal subject categories in the Web of Science database). In this paper, some characterizations of the author's scientific research through three different research dimensions are proposed: production (journal papers), impact (journal citations), and reference (bibliographical sources). Then, we propose different measures of the citation potential for authors based on a proportion of these dimensions. An empirical application, in a set of 120 randomly selected highly productive authors from the CSIC Research Centre (Spain) in four subject areas, shows that the ratio between production and impact dimensions is a normalized measure of the citation potential at the level of individual authors. Moreover, this ratio reduces the between-group variance in relation to the within-group variance in a higher proportion than the rest of the indicators analysed. Furthermore, it is consistent with the type of journal impact indicator used. A possible application of this result is in the selection and promotion process within interdisciplinary institutions, since it allows comparisons of authors based on their particular scientific research.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.