Valeo
A critical analysis of visual industrial anomaly detection highlights a disconnect between academic benchmarks and real-world performance, revealing that models achieving high scores on synthetic datasets often show significant degradation on actual production data and advocating for new evaluation standards and diverse industrial datasets. The study, a collaboration between Valeo and Intel, assesses state-of-the-art models on real production data, identifying best practices and areas for future research.
Researchers at Valeo.ai developed a new dataset, VAD, featuring complex real-world industrial images with diverse defects, including logical and unseen types. They also introduced SegAD, a supervised anomaly detection method that leverages existing anomaly detectors and segmentation-based local statistics to achieve 96.5% classification AUROC on VAD, detecting both known and previously unseen defects without requiring pixel-level annotations.
This survey paper provides a self-contained overview of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) for autonomous driving, systematically reviewing its applications across various tasks from control to high-level policy making. It highlights DRL's potential to address complex sequential decision-making while detailing significant challenges like the simulation-reality gap, sample efficiency, and the need for robust safety integration, guiding future research directions in this field.
Fisheye cameras are commonly employed for obtaining a large field of view in surveillance, augmented reality and in particular automotive applications. In spite of their prevalence, there are few public datasets for detailed evaluation of computer vision algorithms on fisheye images. We release the first extensive fisheye automotive dataset, WoodScape, named after Robert Wood who invented the fisheye camera in 1906. WoodScape comprises of four surround view cameras and nine tasks including segmentation, depth estimation, 3D bounding box detection and soiling detection. Semantic annotation of 40 classes at the instance level is provided for over 10,000 images and annotation for other tasks are provided for over 100,000 images. With WoodScape, we would like to encourage the community to adapt computer vision models for fisheye camera instead of using naive rectification.
Batch-Normalization (BN) layers have become fundamental components in the evermore complex deep neural network architectures. Such models require acceleration processes for deployment on edge devices. However, BN layers add computation bottlenecks due to the sequential operation processing: thus, a key, yet often overlooked component of the acceleration process is BN layers folding. In this paper, we demonstrate that the current BN folding approaches are suboptimal in terms of how many layers can be removed. We therefore provide a necessary and sufficient condition for BN folding and a corresponding optimal algorithm. The proposed approach systematically outperforms existing baselines and allows to dramatically reduce the inference time of deep neural networks.
Current parking area perception algorithms primarily focus on detecting vacant slots within a limited range, relying on error-prone homographic projection for both labeling and inference. However, recent advancements in Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) require interaction with end-users through comprehensive and intelligent Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs). These interfaces should present a complete perception of the parking area going from distinguishing vacant slots' entry lines to the orientation of other parked vehicles. This paper introduces Multi-Task Fisheye Cross View Transformers (MT F-CVT), which leverages features from a four-camera fisheye Surround-view Camera System (SVCS) with multihead attentions to create a detailed Bird-Eye View (BEV) grid feature map. Features are processed by both a segmentation decoder and a Polygon-Yolo based object detection decoder for parking slots and vehicles. Trained on data labeled using LiDAR, MT F-CVT positions objects within a 25m x 25m real open-road scenes with an average error of only 20 cm. Our larger model achieves an F-1 score of 0.89. Moreover the smaller model operates at 16 fps on an Nvidia Jetson Orin embedded board, with similar detection results to the larger one. MT F-CVT demonstrates robust generalization capability across different vehicles and camera rig configurations. A demo video from an unseen vehicle and camera rig is available at: this https URL.
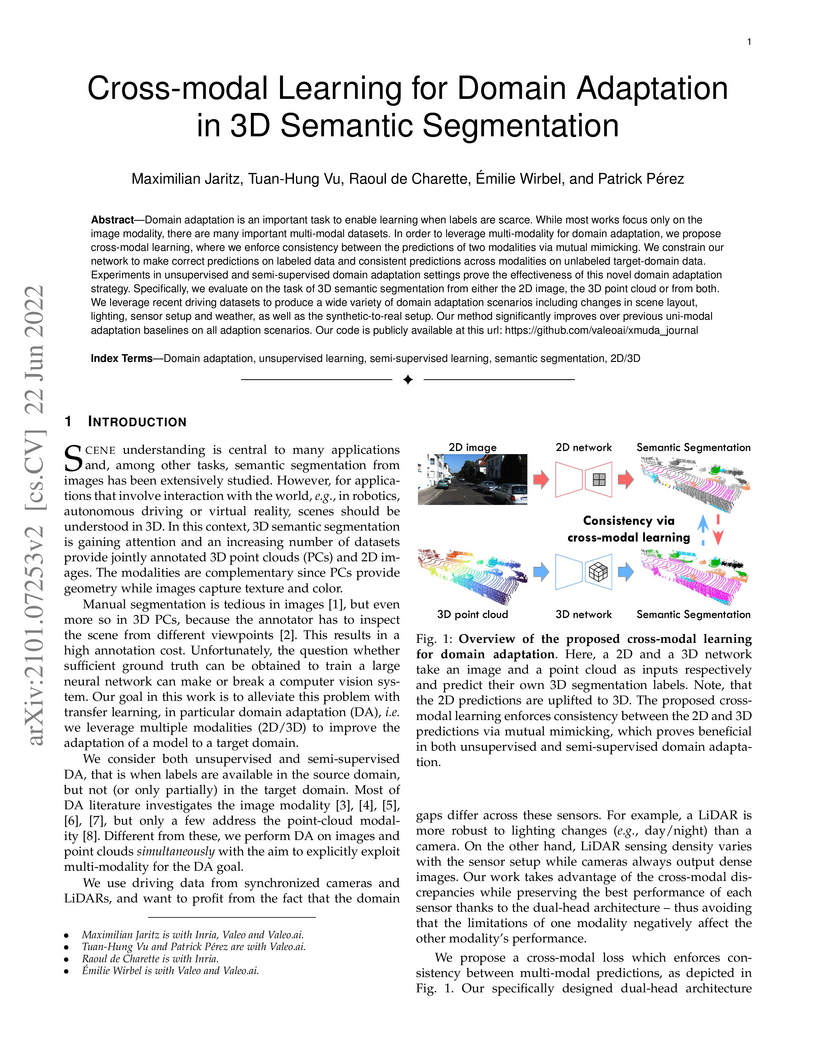
Domain adaptation is an important task to enable learning when labels are scarce. While most works focus only on the image modality, there are many important multi-modal datasets. In order to leverage multi-modality for domain adaptation, we propose cross-modal learning, where we enforce consistency between the predictions of two modalities via mutual mimicking. We constrain our network to make correct predictions on labeled data and consistent predictions across modalities on unlabeled target-domain data. Experiments in unsupervised and semi-supervised domain adaptation settings prove the effectiveness of this novel domain adaptation strategy. Specifically, we evaluate on the task of 3D semantic segmentation from either the 2D image, the 3D point cloud or from both. We leverage recent driving datasets to produce a wide variety of domain adaptation scenarios including changes in scene layout, lighting, sensor setup and weather, as well as the synthetic-to-real setup. Our method significantly improves over previous uni-modal adaptation baselines on all adaption scenarios. Our code is publicly available at this https URL
Researchers from Valeo and academic institutions developed ObsNet with Local Adversarial Attacks for accurate and fast Out-of-Distribution (OOD) detection in semantic segmentation, addressing the challenge of unknown objects in real-time safety-critical applications. This method significantly outperforms existing baselines in OOD detection metrics while being up to 21 times faster than ensemble methods.
Nighttime camera-based depth estimation is a highly challenging task, especially for autonomous driving applications, where accurate depth perception is essential for ensuring safe navigation. Models trained on daytime data often fail in the absence of precise but costly LiDAR. Even vision foundation models trained on large amounts of data are unreliable in low-light conditions. In this work, we aim to improve the reliability of perception systems at night time. To this end, we introduce Light Enhanced Depth (LED), a novel, cost-effective approach that significantly improves depth estimation in low-light environments by harnessing a pattern projected by high definition headlights available in modern vehicles. LED leads to significant performance boosts across multiple depth-estimation architectures (encoder-decoder, Adabins, DepthFormer, Depth Anything V2) both on synthetic and real datasets. Furthermore, increased performances beyond illuminated areas reveal a holistic enhancement in scene understanding. Finally, we release the Nighttime Synthetic Drive Dataset, a synthetic and photo-realistic nighttime dataset, which comprises 49,990 comprehensively annotated images.
Nighttime environments pose significant challenges for camera-based perception, as existing methods passively rely on the scene lighting. We introduce Lighting-driven Dynamic Active Sensing (LiDAS), a closed-loop active illumination system that combines off-the-shelf visual perception models with high-definition headlights. Rather than uniformly brightening the scene, LiDAS dynamically predicts an optimal illumination field that maximizes downstream perception performance, i.e., decreasing light on empty areas to reallocate it on object regions. LiDAS enables zero-shot nighttime generalization of daytime-trained models through adaptive illumination control. Trained on synthetic data and deployed zero-shot in real-world closed-loop driving scenarios, LiDAS enables +18.7% mAP50 and +5.0% mIoU over standard low-beam at equal power. It maintains performances while reducing energy use by 40%. LiDAS complements domain-generalization methods, further strengthening robustness without retraining. By turning readily available headlights into active vision actuators, LiDAS offers a cost-effective solution to robust nighttime perception.
Instance segmentation has gained recently huge attention in various computer vision applications. It aims at providing different IDs to different object of the scene, even if they belong to the same class. This is useful in various scenarios, especially in occlusions. Instance segmentation is usually performed as a two-stage pipeline. First, an object is detected, then semantic segmentation within the detected box area. This process involves costly up-sampling, especially for the segmentation part. Moreover, for some applications, such as LiDAR point clouds and aerial object detection, it is often required to predict oriented boxes, which add extra complexity to the two-stage pipeline. In this paper, we propose Insta-YOLO, a novel one-stage end-to-end deep learning model for real-time instance segmentation. The proposed model is inspired by the YOLO one-shot object detector, with the box regression loss is replaced with polynomial regression in the localization head. This modification enables us to skip the segmentation up-sampling decoder altogether and produces the instance segmentation contour from the polynomial output coefficients. In addition, this architecture is a natural fit for oriented objects. We evaluate our model on three datasets, namely, Carnva, Cityscapes and Airbus. The results show our model achieves competitive accuracy in terms of mAP with significant improvement in speed by 2x on GTX-1080 GPU.
Surround-View System (SVS) is an essential component in Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) and requires precise calibrations. However, conventional offline extrinsic calibration methods are cumbersome and time-consuming as they rely heavily on physical patterns. Additionally, these methods primarily focus on short-range areas surrounding the vehicle, resulting in lower calibration quality in more distant zones. To address these limitations, we propose Click-Calib, a pattern-free approach for offline SVS extrinsic calibration. Without requiring any special setup, the user only needs to click a few keypoints on the ground in natural scenes. Unlike other offline calibration approaches, Click-Calib optimizes camera poses over a wide range by minimizing reprojection distance errors of keypoints, thereby achieving accurate calibrations at both short and long distances. Furthermore, Click-Calib supports both single-frame and multiple-frame modes, with the latter offering even better results. Evaluations on our in-house dataset and the public WoodScape dataset demonstrate its superior accuracy and robustness compared to baseline methods. Code is available at this https URL.
Reinforcement Learning (RL) aims at learning an optimal behavior policy from its own experiments and not rule-based control methods. However, there is no RL algorithm yet capable of handling a task as difficult as urban driving. We present a novel technique, coined implicit affordances, to effectively leverage RL for urban driving thus including lane keeping, pedestrians and vehicles avoidance, and traffic light detection. To our knowledge we are the first to present a successful RL agent handling such a complex task especially regarding the traffic light detection. Furthermore, we have demonstrated the effectiveness of our method by winning the Camera Only track of the CARLA challenge.
22 Apr 2025
This paper introduces COR-MCTS (Conservation of Resources - Monte Carlo Tree
Search), a novel tactical decision-making approach for automated driving
focusing on maneuver planning over extended horizons. Traditional
decision-making algorithms are often constrained by fixed planning horizons,
typically up to 6 seconds for classical approaches and 3 seconds for
learning-based methods limiting their adaptability in particular dynamic
driving scenarios. However, planning must be done well in advance in
environments such as highways, roundabouts, and exits to ensure safe and
efficient maneuvers. To address this challenge, we propose a hybrid method
integrating Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) with our prior utility-based
framework, COR-MP (Conservation of Resources Model for Maneuver Planning). This
combination enables long-term, real-time decision-making, significantly
enhancing the ability to plan a sequence of maneuvers over extended horizons.
Through simulations across diverse driving scenarios, we demonstrate that
COR-MCTS effectively improves planning robustness and decision efficiency over
extended horizons.
Automotive cameras, particularly surround-view cameras, tend to get soiled by
mud, water, snow, etc. For higher levels of autonomous driving, it is necessary
to have a soiling detection algorithm which will trigger an automatic cleaning
system. Localized detection of soiling in an image is necessary to control the
cleaning system. It is also necessary to enable partial functionality in
unsoiled areas while reducing confidence in soiled areas. Although this can be
solved using a semantic segmentation task, we explore a more efficient solution
targeting deployment in low power embedded system. We propose a novel method to
regress the area of each soiling type within a tile directly. We refer to this
as coverage. The proposed approach is better than learning the dominant class
in a tile as multiple soiling types occur within a tile commonly. It also has
the advantage of dealing with coarse polygon annotation, which will cause the
segmentation task. The proposed soiling coverage decoder is an order of
magnitude faster than an equivalent segmentation decoder. We also integrated it
into an object detection and semantic segmentation multi-task model using an
asynchronous back-propagation algorithm. A portion of the dataset used will be
released publicly as part of our WoodScape dataset to encourage further
research.
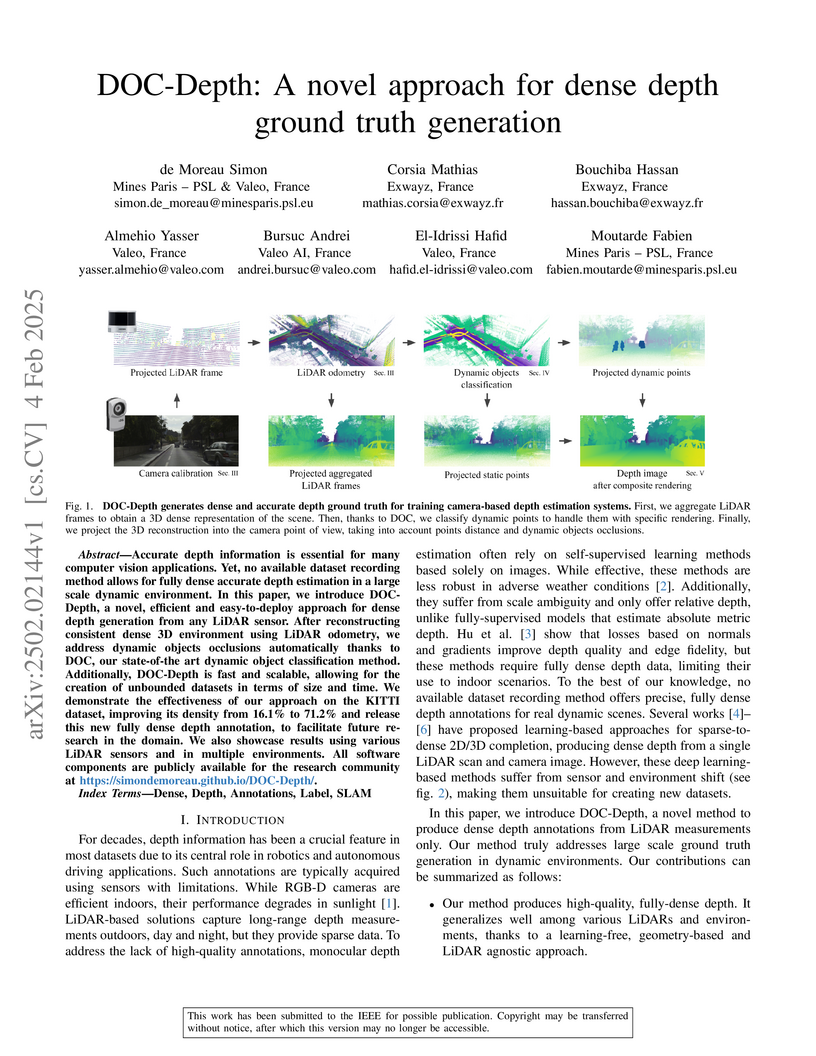
DOC-Depth, developed by researchers at Mines Paris - PSL, Valeo AI, and Exwayz, presents a learning-free, geometry-based pipeline for generating dense and accurate depth ground truth in dynamic outdoor environments from any LiDAR sensor. This method increases KITTI depth map density to 71.2% and robustly handles dynamic objects, enabling superior training data for autonomous driving.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) have gained a lot of popularity from
their introduction in 2014 till present. Research on GAN is rapidly growing and
there are many variants of the original GAN focusing on various aspects of deep
learning. GAN are perceived as the most impactful direction of machine learning
in the last decade. This paper focuses on the application of GAN in autonomous
driving including topics such as advanced data augmentation, loss function
learning, semi-supervised learning, etc. We formalize and review key
applications of adversarial techniques and discuss challenges and open problems
to be addressed.
LiDAR is crucial for robust 3D scene perception in autonomous driving. LiDAR
perception has the largest body of literature after camera perception. However,
multi-task learning across tasks like detection, segmentation, and motion
estimation using LiDAR remains relatively unexplored, especially on
automotive-grade embedded platforms. We present a real-time multi-task
convolutional neural network for LiDAR-based object detection, semantics, and
motion segmentation. The unified architecture comprises a shared encoder and
task-specific decoders, enabling joint representation learning. We propose a
novel Semantic Weighting and Guidance (SWAG) module to transfer semantic
features for improved object detection selectively. Our heterogeneous training
scheme combines diverse datasets and exploits complementary cues between tasks.
The work provides the first embedded implementation unifying these key
perception tasks from LiDAR point clouds achieving 3ms latency on the embedded
NVIDIA Xavier platform. We achieve state-of-the-art results for two tasks,
semantic and motion segmentation, and close to state-of-the-art performance for
3D object detection. By maximizing hardware efficiency and leveraging
multi-task synergies, our method delivers an accurate and efficient solution
tailored for real-world automated driving deployment. Qualitative results can
be seen at this https URL
Surround-view fisheye cameras are commonly used for near-field sensing in
automated driving scenarios, including urban driving and auto valet parking.
Four fisheye cameras, one on each side, are sufficient to cover 360{\deg}
around the vehicle capturing the entire near-field region. Based on surround
view cameras, there has been much research on parking slot detection with main
focus on the occupancy status in recent years, but little work on whether the
free slot is compatible with the mission of the ego vehicle or not. For
instance, some spots are handicap or electric vehicles accessible only. In this
paper, we tackle parking spot classification based on the surround view camera
system. We adapt the object detection neural network YOLOv4 with a novel
polygon bounding box model that is well-suited for various shaped parking
spaces, such as slanted parking slots. To the best of our knowledge, we present
the first detailed study on parking spot detection and classification on
fisheye cameras for auto valet parking scenarios. The results prove that our
proposed classification approach is effective to distinguish between regular,
electric vehicle, and handicap parking spots.
Surround-view fisheye cameras are commonly used for near-field sensing in automated driving. Four fisheye cameras on four sides of the vehicle are sufficient to cover 360° around the vehicle capturing the entire near-field region. Some primary use cases are automated parking, traffic jam assist, and urban driving. There are limited datasets and very little work on near-field perception tasks as the focus in automotive perception is on far-field perception. In contrast to far-field, surround-view perception poses additional challenges due to high precision object detection requirements of 10cm and partial visibility of objects. Due to the large radial distortion of fisheye cameras, standard algorithms cannot be extended easily to the surround-view use case. Thus, we are motivated to provide a self-contained reference for automotive fisheye camera perception for researchers and practitioners. Firstly, we provide a unified and taxonomic treatment of commonly used fisheye camera models. Secondly, we discuss various perception tasks and existing literature. Finally, we discuss the challenges and future direction.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.