performance
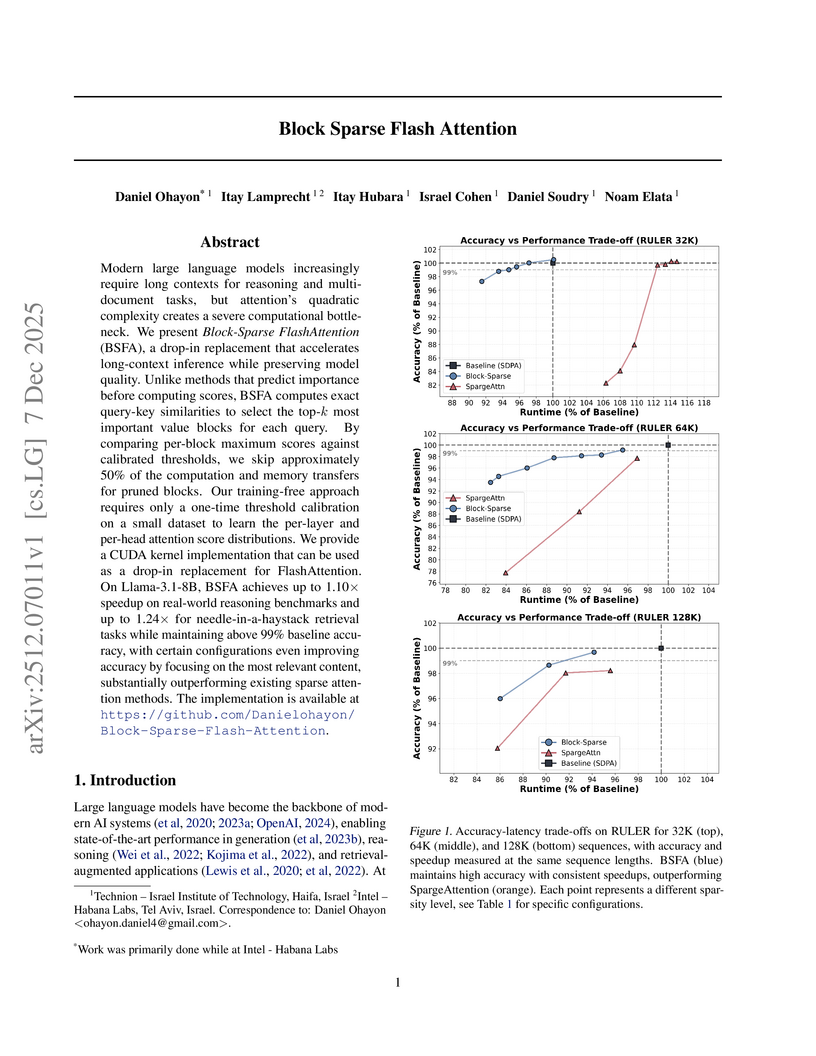
Block Sparse Flash Attention (BSFA) accelerates large language model inference for long input sequences by intelligently skipping computations for negligible value blocks based on exact attention scores. This training-free method maintains high accuracy while achieving speedups up to 1.24x on retrieval tasks and 1.10x for general reasoning.
10 Dec 2025
Always-on sensors are increasingly expected to embark a variety of tiny neural networks and to continuously perform inference on time-series of the data they sense. In order to fit lifetime and energy consumption requirements when operating on battery, such hardware uses microcontrollers (MCUs) with tiny memory budget e.g., 128kB of RAM. In this context, optimizing data flows across neural network layers becomes crucial. In this paper, we introduce TinyDéjàVu, a new framework and novel algorithms we designed to drastically reduce the RAM footprint required by inference using various tiny ML models for sensor data time-series on typical microcontroller hardware. We publish the implementation of TinyDéjàVu as open source, and we perform reproducible benchmarks on hardware. We show that TinyDéjàVu can save more than 60% of RAM usage and eliminate up to 90% of redundant compute on overlapping sliding window inputs.
Low-power microcontroller (MCU) hardware is currently evolving from single-core architectures to predominantly multi-core architectures. In parallel, new embedded software building blocks are more and more written in Rust, while C/C++ dominance fades in this domain. On the other hand, small artificial neural networks (ANN) of various kinds are increasingly deployed in edge AI use cases, thus deployed and executed directly on low-power MCUs. In this context, both incremental improvements and novel innovative services will have to be continuously retrofitted using ANNs execution in software embedded on sensing/actuating systems already deployed in the field. However, there was so far no Rust embedded software platform automating parallelization for inference computation on multi-core MCUs executing arbitrary TinyML models. This paper thus fills this gap by introducing Ariel-ML, a novel toolkit we designed combining a generic TinyML pipeline and an embedded Rust software platform which can take full advantage of multi-core capabilities of various 32bit microcontroller families (Arm Cortex-M, RISC-V, ESP-32). We published the full open source code of its implementation, which we used to benchmark its capabilities using a zoo of various TinyML models. We show that Ariel-ML outperforms prior art in terms of inference latency as expected, and we show that, compared to pre-existing toolkits using embedded C/C++, Ariel-ML achieves comparable memory footprints. Ariel-ML thus provides a useful basis for TinyML practitioners and resource-constrained embedded Rust developers.
29 Nov 2025
The increasing prevalence of thyroid cancer globally has led to the development of various computer-aided detection methods. Accurate segmentation of thyroid nodules is a critical first step in the development of AI-assisted clinical decision support systems. This study focuses on instance segmentation of thyroid nodules using YOLOv5 algorithms on ultrasound images. We evaluated multiple YOLOv5 variants (Nano, Small, Medium, Large, and XLarge) across two dataset versions, with and without doppler images. The YOLOv5-Large algorithm achieved the highest performance with a dice score of 91\% and mAP of 0.87 on the dataset including doppler images. Notably, our results demonstrate that doppler images, typically excluded by physicians, can significantly improve segmentation performance. The YOLOv5-Small model achieved 79\% dice score when doppler images were excluded, while including them improved performance across all model variants. These findings suggest that instance segmentation with YOLOv5 provides an effective real-time approach for thyroid nodule detection, with potential clinical applications in automated diagnostic systems.
Edge computing processes data where it is generated, enabling faster decisions, lower bandwidth usage, and improved privacy. However, edge devices typically operate under strict constraints on processing power, memory, and energy consumption, making them unsuitable for large language models (LLMs). Fortunately, Small Language Models (SLMs) offer lightweight alternatives that bring AI inference to resource-constrained environments by significantly reducing computational cost while remaining suitable for specialization and customization. In this scenario, selecting the hardware platform that best balances performance and efficiency for SLM inference is challenging due to strict resource limitations. To address this issue, this study evaluates the inference performance and energy efficiency of commercial CPUs (Intel and ARM), GPUs (NVIDIA), and NPUs (RaiderChip) for running SLMs. GPUs, the usual platform of choice, are compared against commercial NPUs and recent multi-core CPUs. While NPUs leverage custom hardware designs optimized for computation, modern CPUs increasingly incorporate dedicated features targeting language-model workloads. Using a common execution framework and a suite of state-of-the-art SLMs, we analyze both maximum achievable performance and processing and energy efficiency across commercial solutions available for each platform. The results indicate that specialized backends outperform general-purpose CPUs, with NPUs achieving the highest performance by a wide margin. Bandwidth normalization proves essential for fair cross-architecture comparisons. Although low-power ARM processors deliver competitive results when energy usage is considered, metrics that combine performance and power (such as EDP) again highlight NPUs as the dominant architecture. These findings show that designs optimized for both efficiency and performance offer a clear advantage for edge workloads.
Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models scale LLM capacity efficiently, but deployment on consumer GPUs is limited by the large memory footprint of inactive experts. Static post-training quantization reduces storage costs but cannot adapt to shifting activation patterns, causing accuracy loss under aggressive compression. So we present DynaExq, a runtime system that treats expert precision as a first-class, dynamically managed resource. DynaExq combines (1) a hotness-aware precision controller that continuously aligns expert bit-widths with long-term activation statistics, (2) a fully asynchronous precision-switching pipeline that overlaps promotion and demotion with MoE computation, and (3) a fragmentation-free memory pooling mechanism that supports hybrid-precision experts with deterministic allocation. Together, these components enable stable, non-blocking precision transitions under strict HBM budgets.
Across Qwen3-30B and Qwen3-80B MoE models and six representative benchmarks, DynaExq deploys large LLMs on single RTX 5090 and A6000 GPUs and improves accuracy by up to 4.03 points over static low-precision baselines. The results show that adaptive, workload-aware quantization is an effective strategy for memory-constrained MoE serving.
This research introduces Asymmetric Tile Buffering (ATB) to optimize General Matrix Multiplication (GEMM) on AI accelerators. The technique, which decouples input and output tile dimensions, significantly boosts arithmetic intensity and achieves record-breaking performance, demonstrating up to a 4.54x speedup on the AMD XDNA2
™ AI Engine for mixed-precision BFP16 operations.
20 Nov 2025
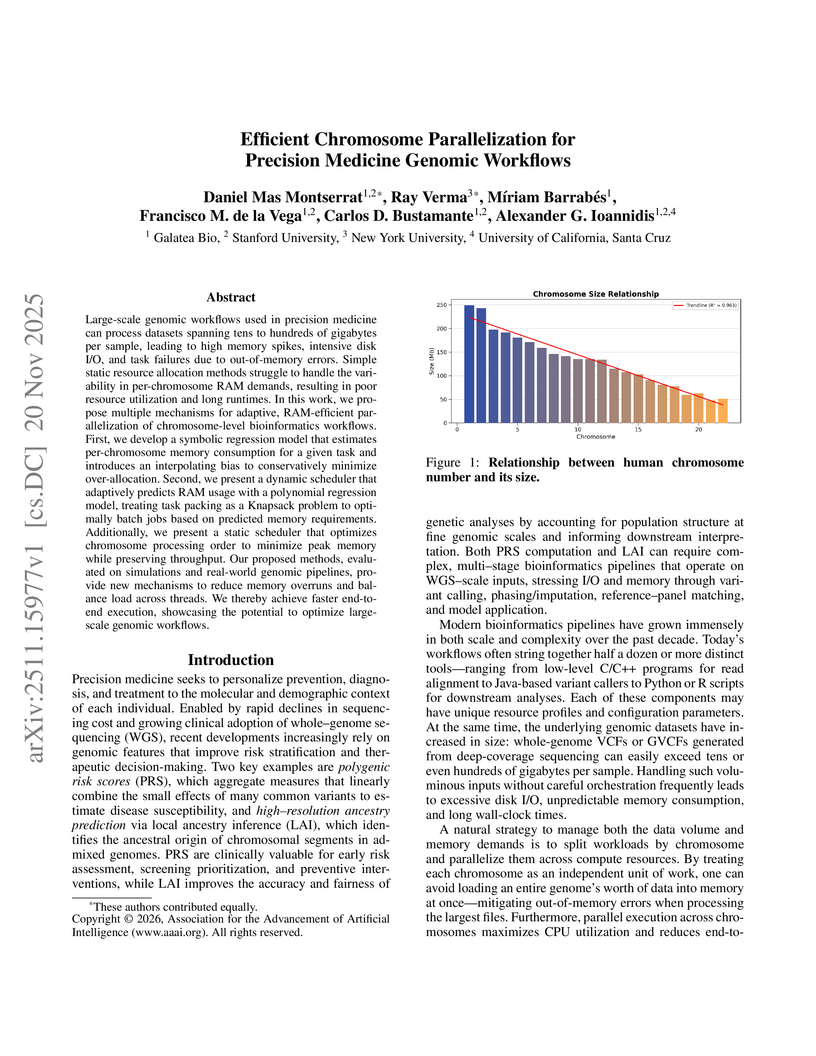
Large-scale genomic workflows used in precision medicine can process datasets spanning tens to hundreds of gigabytes per sample, leading to high memory spikes, intensive disk I/O, and task failures due to out-of-memory errors. Simple static resource allocation methods struggle to handle the variability in per-chromosome RAM demands, resulting in poor resource utilization and long runtimes. In this work, we propose multiple mechanisms for adaptive, RAM-efficient parallelization of chromosome-level bioinformatics workflows. First, we develop a symbolic regression model that estimates per-chromosome memory consumption for a given task and introduces an interpolating bias to conservatively minimize over-allocation. Second, we present a dynamic scheduler that adaptively predicts RAM usage with a polynomial regression model, treating task packing as a Knapsack problem to optimally batch jobs based on predicted memory requirements. Additionally, we present a static scheduler that optimizes chromosome processing order to minimize peak memory while preserving throughput. Our proposed methods, evaluated on simulations and real-world genomic pipelines, provide new mechanisms to reduce memory overruns and balance load across threads. We thereby achieve faster end-to-end execution, showcasing the potential to optimize large-scale genomic workflows.
Predictive modeling of stellarator plasmas is crucial for advancing nuclear fusion energy, yet it faces unique computational difficulties. One of the main challenges is accurately simulating the dynamics of specific particle species that are not well captured by fluid models, which necessitates the use of hybrid fluid-kinetic models. The non-axisymmetric geometry of stellarators fundamentally couples the toroidal Fourier modes, in contrast to what happens in tokamaks, requiring different numerical and computational treatment.
This work presents a novel, globally coupled projection scheme inside the JOREK finite element framework. The approach ensures a self-consistent and physically accurate transfer of kinetic markers to the fluid grid, effectively handling the complex 3D mesh by constructing and solving a unified linear system that encompasses all toroidal harmonics simultaneously. To manage the computational complexity of this coupling, the construction of the system's matrix is significantly accelerated using the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). The efficient localization of millions of particles is made possible by implementing a 3D R-Tree spatial index, which supports this projection and ensures computational tractability at scale.
On realistic Wendelstein 7-X stellarator geometries, the fidelity of the framework is rigorously shown. In sharp contrast to the uncoupled approaches' poor performance, quantitative convergence tests verify that the coupled scheme attains the theoretically anticipated spectral convergence.
This study offers a crucial capability for the predictive analysis and optimization of next-generation stellarator designs by developing a validated, high-fidelity computational tool.
Sparse GNN aggregations (CSR SpMM/SDDMM) vary widely in performance with degree skew, feature width, and GPU micro-architecture. We present AutoSAGE, an input-aware CUDA scheduler that chooses tiling and mapping per input using a lightweight estimate refined by on-device micro-probes, with a guardrail that safely falls back to vendor kernels and a persistent cache for deterministic replay. AutoSAGE covers SpMM and SDDMM and composes into a CSR attention pipeline (SDDMM -> row-softmax -> SpMM). On Reddit and OGBN-Products, it matches vendor baselines at bandwidth-bound feature widths and finds gains at small widths; on synthetic sparsity and skew stress tests it achieves up to 4.7x kernel-level speedups. We release CUDA sources, Python bindings, a reproducible harness, and replayable cache logs.
The deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) in production environments requires efficient inference serving systems that balance throughput, latency, and resource utilization. This paper presents a comprehensive empirical evaluation of two prominent open-source LLM serving frameworks: vLLM and HuggingFace Text Generation Inference (TGI). We benchmark these systems across multiple dimensions including throughput performance, end-to-end latency, GPU memory utilization, and scalability characteristics using LLaMA-2 models ranging from 7B to 70B parameters. Our experiments reveal that vLLM achieves up to 24x higher throughput than TGI under high-concurrency workloads through its novel PagedAttention mechanism, while TGI demonstrates lower tail latencies for interactive single-user scenarios. We provide detailed performance profiles for different deployment scenarios and offer practical recommendations for system selection based on workload characteristics. Our findings indicate that the choice between these frameworks should be guided by specific use-case requirements: vLLM excels in high-throughput batch processing scenarios, while TGI is better suited for latency-sensitive interactive applications with moderate concurrency.
Researchers from Tsinghua University developed Think-at-Hard (TaH), a framework that improves reasoning in large language models by selectively applying deeper latent iterations only to tokens identified as challenging. This approach prevents 'latent overthinking,' achieving accuracy gains of 4.0-5.4% over single-iteration baselines while maintaining computational efficiency.
Transformers have become the backbone of modern AI, yet their high computational demands pose critical system challenges. While sparse training offers efficiency gains, existing methods fail to preserve critical structural relationships between weight matrices that interact multiplicatively in attention and feed-forward layers. This oversight leads to performance degradation at high sparsity levels. We introduce EcoSpa, an efficient structured sparse training method that jointly evaluates and sparsifies coupled weight matrix pairs, preserving their interaction patterns through aligned row/column removal. EcoSpa introduces a new granularity for calibrating structural component importance and performs coupled estimation and sparsification across both pre-training and fine-tuning scenarios. Evaluations demonstrate substantial improvements: EcoSpa enables efficient training of LLaMA-1B with 50\% memory reduction and 21\% faster training, achieves 2.2× model compression on GPT-2-Medium with 2.4 lower perplexity, and delivers 1.6× inference speedup. The approach uses standard PyTorch operations, requiring no custom hardware or kernels, making efficient transformer training accessible on commodity hardware.
ProfilingAgent automates deep neural network optimization by employing an LLM-guided multi-agent system to interpret static and dynamic profiling data, generating adaptive layer-wise pruning and quantization strategies. This approach yields superior accuracy-efficiency trade-offs, achieving up to 1.66x inference speedups and 74.7% memory reduction on models like ViT-B/16 and Swin-B while largely preserving accuracy.
15 Aug 2025
Research introduces the SAFE-AI framework and an AI behavior taxonomy to prevent failures in AI-driven software engineering. An empirical evaluation demonstrates that current state-of-the-art large language models universally fall short of defined safety thresholds when generating code.
16 Jul 2025
Writing GPU kernels is a challenging task and critical for AI systems' efficiency. It is also highly iterative: domain experts write code and improve performance through execution feedback. Moreover, it presents verifiable rewards like correctness and speedup, making it a natural environment to apply Reinforcement Learning (RL). To explicitly incorporate the iterative nature of this process into training, we develop a flexible multi-turn RL recipe that addresses unique challenges encountered in real-world settings, such as learning from long trajectories and effective reward attribution across turns. We present Kevin - K(ernel D)evin, the first model trained with multi-turn RL for CUDA kernel generation and optimization. In our evaluation setup, Kevin shows significant gains over its base model (QwQ-32B), improving correctness of generated kernels (in pure CUDA) from 56% to 82% and mean speedup from 0.53x to 1.10x of baseline (PyTorch Eager), and surpassing frontier models like o4-mini (0.78x). Finally, we study its behavior across test-time scaling axes: we found scaling serial refinement more beneficial than parallel sampling. In particular, when given more refinement turns, Kevin shows a higher rate of improvement.
17 Jun 2025
This work introduces agentic plan caching to reduce LLM serving costs for multi-step agentic applications by caching and adapting structured plan templates from prior executions. The system achieved a 46.62% average reduction in LLM serving costs while maintaining 96.67% of optimal application-level performance.
Researchers at UCLA developed Adaptive Parallel Decoding (APD), an algorithm that enables diffusion large language models (dLLMs) to generate text with substantially higher throughput by dynamically sampling multiple tokens in parallel. This method achieves Pareto-optimal performance against leading autoregressive models, with minimal impact on generation quality.
05 Nov 2025
Large Language Models (LLMs) achieve impressive reasoning capabilities at the cost of substantial inference overhead, posing substantial deployment challenges. Although distilled Small Language Models (SLMs) significantly enhance efficiency, their performance suffers as they fail to follow LLMs' reasoning paths. Luckily, we reveal that only a small fraction of tokens genuinely diverge reasoning paths between LLMs and SLMs. Most generated tokens are either identical or exhibit neutral differences, such as minor variations in abbreviations or expressions. Leveraging this insight, we introduce **Roads to Rome (R2R)**, a neural token routing method that selectively utilizes LLMs only for these critical, path-divergent tokens, while leaving the majority of token generation to the SLM. We also develop an automatic data generation pipeline that identifies divergent tokens and generates token-level routing labels to train the lightweight router. We apply R2R to combine R1-1.5B and R1-32B models from the DeepSeek family, and evaluate on challenging math, coding, and QA benchmarks. With an average activated parameter size of 5.6B, R2R surpasses the average accuracy of R1-7B by 1.6x, outperforming even the R1-14B model. Compared to R1-32B, it delivers a 2.8x wall-clock speedup with comparable performance, advancing the Pareto frontier of test-time scaling efficiency. Our code is available at this https URL.
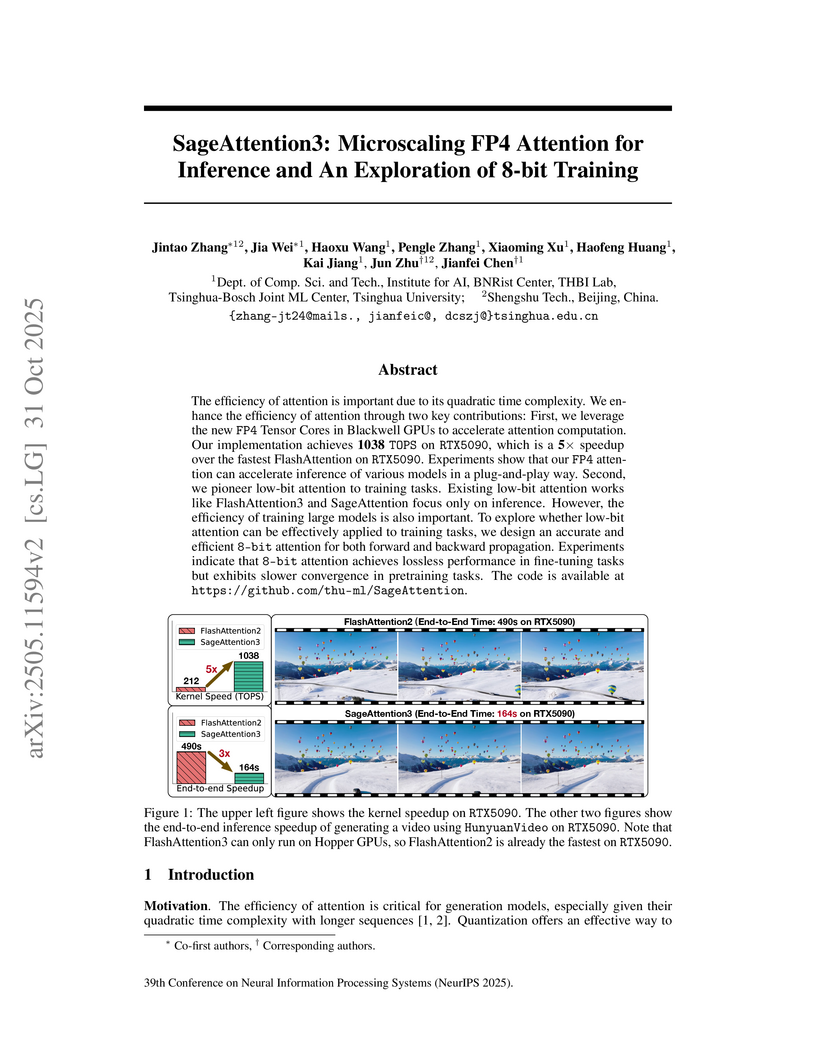
Tsinghua University researchers developed SageAttention3, the first FP4 attention for inference, achieving over 1000 TOPS and up to 5x speedup on Blackwell GPUs with maintained accuracy. They also introduced SageBwd, an 8-bit attention mechanism enabling lossless fine-tuning with up to 1.67x training speedup.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.