online-learning
TreeGRPO introduces a reinforcement learning framework that reinterprets diffusion model denoising as a sparse search tree, enabling both sample efficiency and precise credit assignment for post-training. This method achieves 2.4 times faster training convergence and enhances alignment quality with human preferences compared to prior approaches.
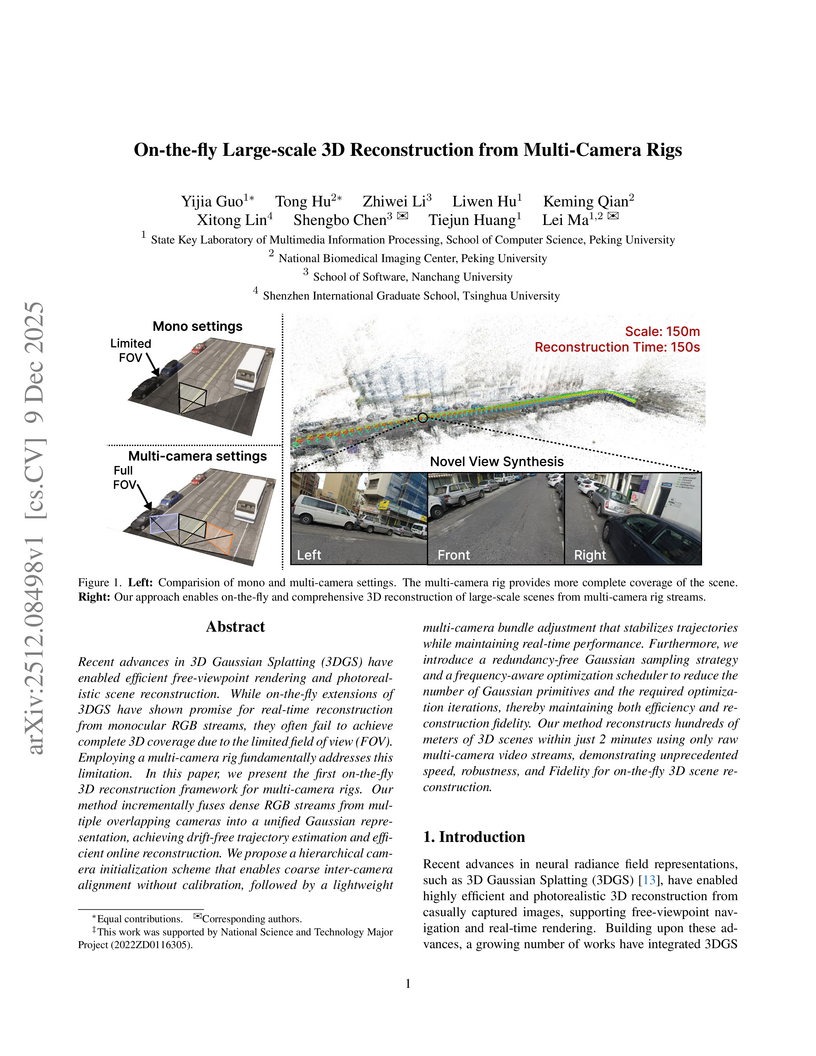
Researchers from Peking University, Nanchang University, and Tsinghua University developed the first on-the-fly 3D reconstruction framework for multi-camera rigs, enabling calibration-free, large-scale, and high-fidelity scene reconstruction. The system generates drift-free trajectories and photorealistic novel views, reconstructing 100 meters of road or 100,000 m² of aerial scenes in two minutes.
Researchers at ETH Zürich used a reinforcement learning agent to investigate how feedback influences skill acquisition in a complex physical fluid system. Their work demonstrated that learning high-performance skills, particularly those involving non-minimum phase dynamics, can require substantially richer sensory information during training than is necessary for their execution.
08 Dec 2025
Despite impressive advances in agent systems, multi-turn tool-use scenarios remain challenging. It is mainly because intent is clarified progressively and the environment evolves with each tool call. While reusing past experience is natural, current LLM agents either treat entire trajectories or pre-defined subtasks as indivisible units, or solely exploit tool-to-tool dependencies, hindering adaptation as states and information evolve across turns. In this paper, we propose a State Integrated Tool Graph (SIT-Graph), which enhances multi-turn tool use by exploiting partially overlapping experience. Inspired by human decision-making that integrates episodic and procedural memory, SIT-Graph captures both compact state representations (episodic-like fragments) and tool-to-tool dependencies (procedural-like routines) from historical trajectories. Specifically, we first build a tool graph from accumulated tool-use sequences, and then augment each edge with a compact state summary of the dialog and tool history that may shape the next action. At inference time, SIT-Graph enables a human-like balance between episodic recall and procedural execution: when the next decision requires recalling prior context, the agent retrieves the state summaries stored on relevant edges and uses them to guide its next action; when the step is routine, it follows high-confidence tool dependencies without explicit recall. Experiments across multiple stateful multi-turn tool-use benchmarks show that SIT-Graph consistently outperforms strong memory- and graph-based baselines, delivering more robust tool selection and more effective experience transfer.
07 Dec 2025
MMDUET2, a Video MLLM developed by Peking University and Meituan, improves proactive interaction by using multi-turn reinforcement learning and a text-to-text chat template to autonomously determine when and what to respond during streaming video. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance on proactive interaction benchmarks, with a PAUC of 53.3 on the WEB dataset and significantly reduced reply duplication, while maintaining general video understanding capabilities.
In this paper, we examine the convergence landscape of multi-agent learning under uncertainty. Specifically, we analyze two stochastic models of regularized learning in continuous games -- one in continuous and one in discrete time with the aim of characterizing the long-run behavior of the induced sequence of play. In stark contrast to deterministic, full-information models of learning (or models with a vanishing learning rate), we show that the resulting dynamics do not converge in general. In lieu of this, we ask instead which actions are played more often in the long run, and by how much. We show that, in strongly monotone games, the dynamics of regularized learning may wander away from equilibrium infinitely often, but they always return to its vicinity in finite time (which we estimate), and their long-run distribution is sharply concentrated around a neighborhood thereof. We quantify the degree of this concentration, and we show that these favorable properties may all break down if the underlying game is not strongly monotone -- underscoring in this way the limits of regularized learning in the presence of persistent randomness and uncertainty.
CompressARC, developed by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, addresses the ARC-AGI benchmark by achieving 20% accuracy on evaluation puzzles without any pretraining, learning entirely at inference time from the target puzzle. It leverages a custom equivariant neural network and the Minimum Description Length principle to discover abstract reasoning patterns with extreme data efficiency.
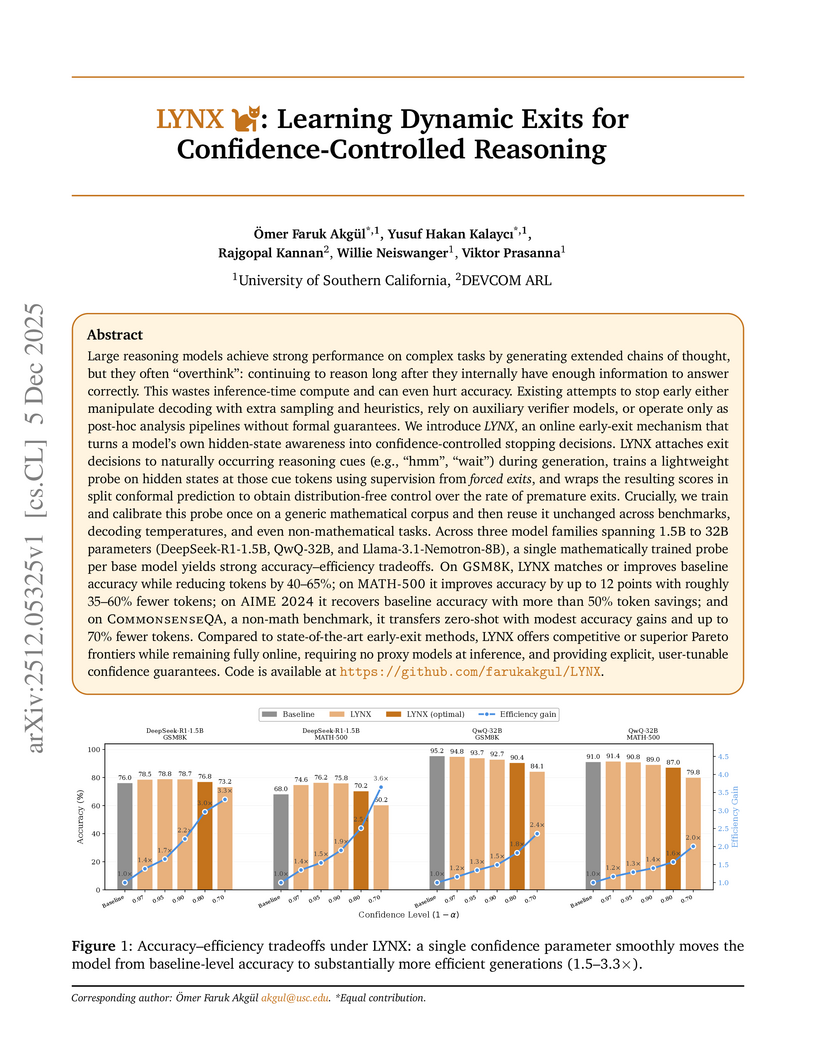
LYNX enables large language models to dynamically manage inference-time computation by making confidence-controlled early-exit decisions during reasoning. It combines internal model confidence signals with conformal prediction, leading to substantial token reductions (40-95%) while frequently maintaining or improving accuracy across various models and tasks.
VideoSSM, developed by researchers at The University of Hong Kong and PICO, ByteDance, introduces a hybrid state-space memory architecture to enable autoregressive long video generation. The model maintains temporal consistency and dynamism over minute-scale durations, achieving superior quality and preventing motion drift or content repetition while operating with linear computational complexity.
AutoSeg3D introduces a tracking-centric framework for online, real-time 3D instance segmentation, leveraging Long-Term Memory, Short-Term Memory, and Spatial Consistency Learning. This method achieves 45.5 AP on ScanNet200, a 2.8 AP improvement over the previous state-of-the-art ESAM, while operating at real-time speeds.
In this paper, we examine the robustness of Nash equilibria in continuous games, under both strategic and dynamic uncertainty. Starting with the former, we introduce the notion of a robust equilibrium as those equilibria that remain invariant to small -- but otherwise arbitrary -- perturbations to the game's payoff structure, and we provide a crisp geometric characterization thereof. Subsequently, we turn to the question of dynamic robustness, and we examine which equilibria may arise as stable limit points of the dynamics of "follow the regularized leader" (FTRL) in the presence of randomness and uncertainty. Despite their very distinct origins, we establish a structural correspondence between these two notions of robustness: strategic robustness implies dynamic robustness, and, conversely, the requirement of strategic robustness cannot be relaxed if dynamic robustness is to be maintained. Finally, we examine the rate of convergence to robust equilibria as a function of the underlying regularizer, and we show that entropically regularized learning converges at a geometric rate in games with affinely constrained action spaces.
Inspired by graph-based methodologies, we introduce a novel graph-spanning algorithm designed to identify changes in both offline and online data across low to high dimensions. This versatile approach is applicable to Euclidean and graph-structured data with unknown distributions, while maintaining control over error probabilities. Theoretically, we demonstrate that the algorithm achieves high detection power when the magnitude of the change surpasses the lower bound of the minimax separation rate, which scales on the order of nd. Our method outperforms other techniques in terms of accuracy for both Gaussian and non-Gaussian data. Notably, it maintains strong detection power even with small observation windows, making it particularly effective for online environments where timely and precise change detection is critical.
Full waveform inversion (FWI) has become a widely adopted technique for high-resolution subsurface imaging. However, its inherent strong nonlinearity often results in convergence toward local minima. Recently, deep image prior-based reparameterized FWI (DIP-FWI) has been proposed to alleviate the dependence on massive training data. By exploiting the spectral bias and implicit regularization in the neural network architecture, DIP-FWI can effectively avoid local minima and reconstruct more geologically plausible velocity models. Nevertheless, existing DIP-FWI typically use a fixed random input throughout the inversion process, which fails to utilize the mapping and correlation between the input and output of the network. Moreover, under complex geological conditions, the lack of informative prior in the input can exacerbate the ill-posedness of the inverse problem, leading to artifacts and unstable reconstructions. To address these limitations, we propose a self-reinforced DIP-FWI (SRDIP-FWI) framework, in which a steering algorithm alternately updates both the network parameters and the input at each iteration using feedback from the current network output. This design allows adaptive structural enhancement and improved regularization, thereby effectively mitigating the ill-posedness in FWI. Additionally, we analyze the spectral bias of the network in SRDIP-FWI and quantify its role in multiscale velocity model building. Synthetic tests and field land data application demonstrate that SRDIP-FWI achieves superior resolution, improved accuracy and greater depth penetration compared to multiscale FWI. More importantly, SRDIP-FWI eliminates the need for manual frequency-band selection and time-window picking, substantially simplifying the inversion workflow. Overall, the proposed method provides a novel, adaptive and robust framework for accurate subsurface velocity model reconstruction.
Pruning has emerged as a promising direction for accelerating large language model (LLM) inference, yet existing approaches often suffer from instability because they rely on offline calibration data that may not generalize across inputs. In this work, we introduce Token Filtering, a lightweight online structured pruning technique that makes pruning decisions directly during inference without any calibration data. The key idea is to measure token redundancy via joint key-value similarity and skip redundant attention computations, thereby reducing inference cost while preserving critical information. To further enhance stability, we design a variance-aware fusion strategy that adaptively weights key and value similarity across heads, ensuring that informative tokens are retained even under high pruning ratios. This design introduces no additional memory overhead and provides a more reliable criterion for token importance. Extensive experiments on LLaMA-2 (7B/13B), LLaMA-3 (8B), and Mistral (7B) demonstrate that Token Filtering consistently outperforms prior structured pruning methods, preserving accuracy on commonsense reasoning benchmarks and maintaining strong performance on challenging tasks such as MMLU, even with 50% pruning.
07 Dec 2025
Adam is a widely used optimizer in neural network training due to its adaptive learning rate. However, because different data samples influence model updates to varying degrees, treating them equally can lead to inefficient convergence. To address this, a prior work proposed adapting the sampling distribution using a bandit framework to select samples adaptively. While promising, the bandit-based variant of Adam suffers from limited theoretical guarantees. In this paper, we introduce Adam with Combinatorial Bandit Sampling (AdamCB), which integrates combinatorial bandit techniques into Adam to resolve these issues. AdamCB is able to fully utilize feedback from multiple samples at once, enhancing both theoretical guarantees and practical performance. Our regret analysis shows that AdamCB achieves faster convergence than Adam-based methods including the previous bandit-based variant. Numerical experiments demonstrate that AdamCB consistently outperforms existing methods.
Distribution shifts at test time degrade image classifiers. Recent continual test-time adaptation (CTTA) methods use masking to regulate learning, but often depend on calibrated uncertainty or stable attention scores and introduce added complexity. We ask: do we need custom-made masking designs, or can a simple random masking schedule suffice under strong corruption? We introduce Mask to Adapt (M2A), a simple CTTA approach that generates a short sequence of masked views (spatial or frequency) and adapts with two objectives: a mask consistency loss that aligns predictions across different views and an entropy minimization loss that encourages confident outputs. Motivated by masked image modeling, we study two common masking families -- spatial masking and frequency masking -- and further compare subtypes within each (spatial: patch vs.\ pixel; frequency: all vs.\ low vs.\ high). On CIFAR10C/CIFAR100C/ImageNetC (severity~5), M2A (Spatial) attains 8.3\%/19.8\%/39.2\% mean error, outperforming or matching strong CTTA baselines, while M2A (Frequency) lags behind. Ablations further show that simple random masking is effective and robust. These results indicate that a simple random masking schedule, coupled with consistency and entropy objectives, is sufficient to drive effective test-time adaptation without relying on uncertainty or attention signals.
TD(λ) with function approximation has proved empirically successful for some complex reinforcement learning problems. For linear approximation, TD(λ) has been shown to minimise the squared error between the approximate value of each state and the true value. However, as far as policy is concerned, it is error in the relative ordering of states that is critical, rather than error in the state values. We illustrate this point, both in simple two-state and three-state systems in which TD(λ)--starting from an optimal policy--converges to a sub-optimal policy, and also in backgammon. We then present a modified form of TD(λ), called STD(λ), in which function approximators are trained with respect to relative state values on binary decision problems. A theoretical analysis, including a proof of monotonic policy improvement for STD(λ) in the context of the two-state system, is presented, along with a comparison with Bertsekas' differential training method [1]. This is followed by successful demonstrations of STD(λ) on the two-state system and a variation on the well known acrobot problem.
Camera-based temporal 3D object detection has shown impressive results in autonomous driving, with offline models improving accuracy by using future frames. Knowledge distillation (KD) can be an appealing framework for transferring rich information from offline models to online models. However, existing KD methods overlook future frames, as they mainly focus on spatial feature distillation under strict frame alignment or on temporal relational distillation, thereby making it challenging for online models to effectively learn future knowledge. To this end, we propose a sparse query-based approach, Future Temporal Knowledge Distillation (FTKD), which effectively transfers future frame knowledge from an offline teacher model to an online student model. Specifically, we present a future-aware feature reconstruction strategy to encourage the student model to capture future features without strict frame alignment. In addition, we further introduce future-guided logit distillation to leverage the teacher's stable foreground and background context. FTKD is applied to two high-performing 3D object detection baselines, achieving up to 1.3 mAP and 1.3 NDS gains on the nuScenes dataset, as well as the most accurate velocity estimation, without increasing inference cost.
We reveal a critical yet underexplored flaw in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs): even when these models know the correct answer, they frequently arrive there through incorrect reasoning paths. The core issue is not a lack of knowledge, but a path selection bias within the vast reasoning search space. Although LVLMs are often capable of sampling correct solution trajectories, they disproportionately favor unstable or logically inconsistent ones, leading to erratic and unreliable outcomes. The substantial disparity between Pass@K (with large K) and Pass@1 across numerous models provides compelling evidence that such failures primarily stem from misreasoning rather than ignorance. To systematically investigate and address this issue, we propose PSO (Path-Select Optimization), a two-stage post-training framework designed to enhance both the reasoning performance and stability of existing LVLMs. In the first stage, we employ Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with template and answer-based rewards to cultivate structured, step-by-step reasoning. In the second stage, we conduct online preference optimization, where the model samples reasoning paths from GRPO-generated data, self-evaluates them, and aligns itself toward the preferred trajectories. Incorrect or suboptimal paths are concurrently stored in a Negative Replay Memory (NRM) as hard negatives, which are periodically revisited to prevent the model from repeating prior mistakes and to facilitate continual reasoning refinement. Extensive experiments show that PSO effectively prunes invalid reasoning paths, substantially enhances reasoning accuracy (with 7.4% improvements on average), and yields more stable and consistent chains of thought. Our code will be available at this https URL.
Conformal prediction provides a pivotal and flexible technique for uncertainty quantification by constructing prediction sets with a predefined coverage rate. Many online conformal prediction methods have been developed to address data distribution shifts in fully adversarial environments, resulting in overly conservative prediction sets. We propose Conformal Optimistic Prediction (COP), an online conformal prediction algorithm incorporating underlying data pattern into the update rule. Through estimated cumulative distribution function of non-conformity scores, COP produces tighter prediction sets when predictable pattern exists, while retaining valid coverage guarantees even when estimates are inaccurate. We establish a joint bound on coverage and regret, which further confirms the validity of our approach. We also prove that COP achieves distribution-free, finite-sample coverage under arbitrary learning rates and can converge when scores are i.i.d.. The experimental results also show that COP can achieve valid coverage and construct shorter prediction intervals than other baselines.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.